MI SYS API
REVISION HISTORY¶
| Revision No. | Description |
Date |
|---|---|---|
| 3.0 | 12/05/2020 | |
| 3.1 | 01/06/2021 | |
| 3.2 | 04/21/2021 | |
| 3.3 | 04/27/2021 | |
| 3.4 | 06/02/2021 | |
| 3.5 | 06/29/2021 | |
| 3.6 | 07/22/2021 | |
| 08/25/2021 | ||
| 3.7 | 11/05/2021 | |
| 3.8 | 11/26/2021 | |
| 3.9 | 11/30/2021 | |
| 12/08/2021 | ||
| 3.10 | 03/30/2022 | |
| 3.11 | 05/16/2022 | |
| 05/19/2022 | ||
| 07/27/2022 | ||
| 3.12 | 09/21/2022 | |
| 10/28/2022 | ||
| 12/01/2022 | ||
| 3.13 | 03/16/2023 | |
| 3.14 | 11/10/2023 | |
| 3.15 | 12/05/2023 | |
| 02/19/2024 | ||
| 04/26/2024 | ||
| 3.16 | 06/05/2024 | |
| 3.17 | 08/19/2024 | |
| 3.18 | 08/27/2024 | |
| 3.19 | 09/02/2024 | |
| 3.20 | 09/05/2024 | |
| 3.21 | 10/17/2024 | |
| 3.22 | 01/10/2025 | |
| 3.23 | 04/24/2025 |
1. OVERVIEW¶
1.1. Module Description¶
MI_SYS is the fundamental module of the entire MI system, providing basic functions such as driver registration, multimedia memory management, implementation of worker threads, multimedia data stream management, power management, etc. for the operation of other MI modules. The user interface provided by MI_SYS allows applications to control the binding relationships, input/output frame rates, and read/write data of MI modules. As shown in Figure 1-1.
Figure 1-1 : MI_SYS System Framework
The ko file corresponding to MI_SYS is mi_sys.ko, the library files are libmi_sys.so and libmi_sys.a, and the header files are mi_sys.h, mi_sys_sideband_datatype.h and mi_sys_datatype.h. Please refer to the API interface description.
Keyword Description
-
ID: Identity, which means unique encoding.
-
MI: SStar SDK Middle Interface, in this article, a similar structure of "MI_SYS" represents the MI SYS module, a simple "MI" refers to the entire SDK.
-
MMA: MMA refers to a physical memory pool managed by MI_SYS, specifically used for data input and output in MI modules.
-
Hex: Hexadecimal.
-
Kernel Mode: Kernel Mode refers to code that works in Kernel environments and has control over the hardware that operates directly, such as functions and threads in ko.
-
User Mode: User Mode refers to code that works in User environment, such as customer applications, system calls, and so on.
-
APP: Application, which refers primarily to an application that calls the MI API.
-
API: Application Programming Interface.
-
NVR: Network Video Recorder.
-
DVR: Digital Video Recorder.
-
XVR: A Video Recorder with any one or more functions combinations. Currently Sstar XVR consists of DVR and NVR.
-
IPC: IP Camera.
-
HW: Hardware.
-
Dev: Device, represents for MI module device in this article.
-
Chn: Channel, represents a channel of MI module device.
-
Port: Port, represents a port in the MI module device channel.
-
STR: Suspend to RAM, it is a power management mode in the Linux system. The principle is to save the current running state of the system to the memory, while turning off or reducing the power consumption of hardware.
-
DMABUF: The Linux dma-buf subsystem is used for sharing physical memory among multiple device drivers and subsystems, as well as synchronizing asynchronous hardware access.
-
Soc: System on Chip.
-
SocId: SocId, represents for specific Soc serial number, some platform use PCIE for multi-chip cascading, so SocId needs to be used to distinguish. Some interfaces support cross-Soc settings in MI_SYS, which have SocId parameters. As shown in Figure 1-2, bridging Soc1 and Soc2 by PCIE. Take Soc1 as Master to run Linux environment, MI SDK and customer service program. Take Soc as Slave to run Linux environment and MI SDK. You can choose to operate on Soc1 or Soc2 by calling the API carrying the SocId parameter.
Figure 1-2: PCIE cascaded Soc model
Additional notes:
-
Without separate instructions, the MI_SYS in this article have the same meaning as SYS, and the remaining modules have similar names.
-
All module names that appear in this article can be found in MI_ModuleId_e.
1.2. Basic structure¶
A typical MI module will have a Dev/Chn/Port three-stage structure as shown in the Figure 1-3 below.
-
Dev: An MI module will have one or more Devs, and in general different Devs indicate that the module device needs to invoke different HW resources or work in different working patterns. For example, VENC needs to invoke different HW resources when encoding H264/H265 and Jpeg, and Dev has to separate.
-
Chn: A Dev will have one or more Chns, which generally mean that the channel is different, and that the channel, although it shares HW resources with other Chns under Dev, is different from the data source or working pattern. For example, the source of the code flow is different, Chn is generally not the same.
-
Port: A Chn will have one or more ports, including Input Port (for data inflow) and Output Port (for data outflow). Different Ports indicate that the channel shares HW resources and data sources with other Ports under Dev and Chn, but the parameters that need to be set are different, such as different resolutions. In general, port is the smallest independent unit for the customer to operate the MI module because it identifies all the information: HW resources, data sources and parameter properties.
Tips:
InputPort and OutputPort are not necessary in a chn, it depends on the behaviours of module.
Figure 1-3: Three-level structure of the MI module
Figure 1‑3 lists the different scenarios of Port arrangement under a single Chn in MI_SYS:
-
InputPort only, which is required for data inflow, but no need for output module. Such as Disp, which display the results on the Panel directly.
-
Output only, which does not need for data input, or input data without modules in MI_SYS. Such as VDEC, in which the data can be sent to Vdec RingPool directly by calling the VDEC interface.
-
One InputPort and one OutputPort, which are used by modules for single data input and output. Such as LDC, data input first, and then hardware process to output result.
-
One InputPort and more than one OutputPort, which are used for single data input and diffrent output process to output different data. Such as SCL, share a data source but output various results according diffrent OutputPort parameters.
Tips:
The boundaries between Chn and Port are not always clear, if there is a difference between the interpretation of a module's API documentation and the explanation above, call the module to its API documentation.
1.3. Function Introduction¶
The main functions of MI_SYS are summarized as follows:
-
Implement MI system initialization, provide each module with a registered device node, and establish a general interface for the proc system.
-
Provides interfaces for each module to establish working threads, and manages the creation, operation, and destruction of threads in each module.
-
Provides interfaces for each module to apply for MMA continuous physical memory, manage memory allocation, map virtual addresses, and memory recycling.
-
Provides interfaces for establishing binding relationships between modules and manages data flow between modules.
-
Provides a user-mode interface for accessing MMA physical memory and supports reading and writing the input and output images of the MI module.
-
Provides MI_SYS DMA_HEAP and DMA_BUF interfaces to support user programs to apply for MI_SYS dmabuf and input and output dmabuf to MI module.
-
Provides STR callback function interface for each module to ensure that the STR process module is suspended and resumed correctly.
1.4. Application Scenario¶
MI SYS can be applied to the following scenarios:
-
Pure linux
In the Linux environment, development can be carried out based on the API interface provided by MI_SYS, and Linux features such as STR and dmabuf are also supported.
-
Pure rtos
In the RTOS environment, applications can be developed based on the API interface provided by MI_SYS, and features such as STR and dmabuf are not supported.
-
Dualos
In the Dualos environment, applications can be developed based on the API interface provided by MI_SYS, and features such as STR and dmabuf are not supported.
1.5. Chip Differences¶
The functions of MI_SYS are similar across all platforms and do not affect usage.
1.6. How it works¶
1.6.1. Data flow control¶
The following figure is a typical DISPCAM data flow model with the following flow procedures:
-
Establish a binding relationship with Vif->Isp->Scl->Venc & Disp;
-
Sensor feeds the data into vif processing;
-
Vif sends the processed data to the memory requested by Output Port and sends it to the Isp;
-
Isp receives and processes the data, and writes the result into the memory requested by the output port and send it to the Scl;
-
Scl receives and processes the data, and writes the result into the memory requested by the output port and send it to the Venc and Disp;
-
Venc receives the data, feeds the encoder for coding processing, and writes the encoded data to the RingPool memory area;
-
The user calls Venc's interface to retrieve the stream and feeds it into the user's business layer app.
-
Disp receives data and displays the input data when the next vsync arrives.
Figure 1-4: A typical IPC data stream model
1.6.2 Frame Rate Control¶
Frame rate control refers to controlling the input and output image frame rate of each level of module through software to meet the user's scene requirements and reduce system bandwidth.
Frame rate control is applied to the input/output port of the MI module. Its basic principle is:
-
Calculate the real-time frame rate of the port.
-
Calculate the difference between the real-time frame rate and the expected frame rate, and decide whether to drop frames.
Tips:
To ensure the ease of use of the interface, MI_SYS will automatically calibrate the frame rate of the previous output.
If there is a difference between the u32SrcFrmrate set by user and the internal calculation value of MI_SYS, the calculated value will replace u32SrcFrmrate for frame rate control. But the calculation takes time, when the frame rate changes greatly, there will be 1-2 seconds of jitter.
In summary, when using the MI_SYS_BindXXX interface, please ensure that the two frame rates are set accurately. When the frame rate changes, please call MI_SYS_BindXXX actively.
The following assumes that the u32SrcFrmrate set by the user is the accurate previous frame rate, and u32DstFrmrate is the required next frame rate.
1.6.2.1. One-to-One Binding
As shown in Figure 1-5, one-to-one binding frame rate control
-
Assume that ISP Output Port0 is bound to SCL Input Port0, and the frame rate is controlled to 60:30. That is, the output frame rate of ISP Output Port is 60fps, and the user expects the input frame rate of SCL Input Port to be 30fps.
-
MI_SYS will calculate the actual frame rate of the ISP and SCL ports respectively, assuming that the actual frame rate is consistent with the frame rate set by the user.
-
At the ISP Output Port, since the ISP real frame rate of 60fps is greater than the expected frame rate of 30fps, MI_SYS will actively drop frames, reducing the frame rate from 60fps to 30fps. (The green part indicates frame drop)
-
At SCL Input Port0, the frame rate output by the previous ISP is the real frame rate of SCL Input Port0, that is, 30fps, which is consistent with the expected frame rate of SCL Input Port0, so MI_SYS will not drop frames.
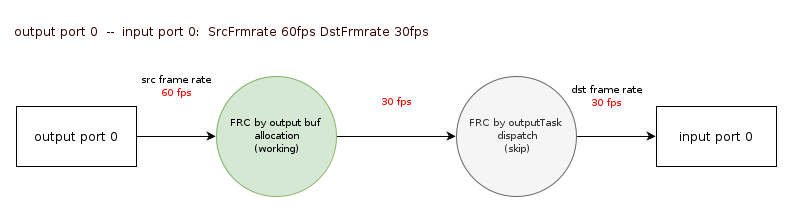
Figure 1-5:one-to-one binding frame rate control
1.6.2.2. One-to-multi Binding
As shown in Figure 1-6, one-to-multi binding frame rate control.
-
Assume that ISP Output Port0 is bound to SCL Input Port0 and Port1, and the frame rate control is 60:30 and 60:15 respectively. That is, the output frame rate of ISP Output Port is 60fps, and the user expects the input frame rate of SCL Input Port0 to be 30fps and the input frame rate of SCL Input Port1 to be 15fps.
-
MI_SYS will calculate the actual frame rate of the ISP and SCL ports respectively, assuming that the actual frame rate is consistent with the frame rate set by the user.
-
At the ISP Output Port, MI_SYS traverses SCL Input Port0 and Port1, and calculates the maximum input frame rate required by the next stage, which is 30fps. Since the ISP real frame rate of 60fps is greater than the maximum expected frame rate of 30fps, MI_SYS will actively drop frames, reducing the ISP Output Port frame rate from 60fps to 30fps. (The green part indicates frame drop)
-
At SCL Input Port0, the frame rate output by the previous ISP is the real frame rate of SCL Input Port0, that is, 30fps, which is consistent with the expected frame rate of SCL Input Port0, so MI_SYS will not drop frames.
-
At SCL Input Port1, the frame rate output by the previous ISP is the real frame rate of SCL Input Port0, which is 30fps. This is inconsistent with the expected frame rate of SCL Input Port0, so MI_SYS actively drops frames to reduce the frame rate to 15fps. (The green part indicates frame drop)
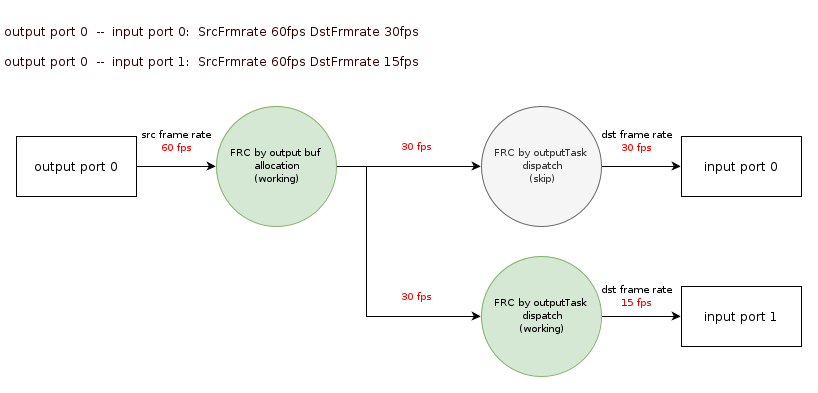
Figure 1-6:one-to-multi binding frame rate control.
1.6.2.3. One-to-multi and set UserDepth
As shown in Figure 1-7, One-to-multi and set UserDepth.
-
When UserDepth is set for ISP Output Port, it indicates that the user needs to get ISP output data, and MI_SYS needs to keep the latest data for the user, so ISP Output Port is required to always output the latest data.
-
In this scenario, MI_SYS will not perform frame rate control on the ISP Output Port.
-
At SCL Input Port0, the frame rate output by the previous ISP is the real frame rate of SCL Input Port0, which is 60fps, which is inconsistent with the expected frame rate of SCL Input Port0. Therefore, MI_SYS actively drops frames to reduce the frame rate to 30fps. (The green part indicates frame drop)
-
At SCL Input Port1, the frame rate output by the previous ISP is the real frame rate of SCL Input Port0, which is 60fps. This is inconsistent with the expected frame rate of SCL Input Port0, so MI_SYS actively drops frames to reduce the frame rate to 15fps. (The green part indicates frame drop)
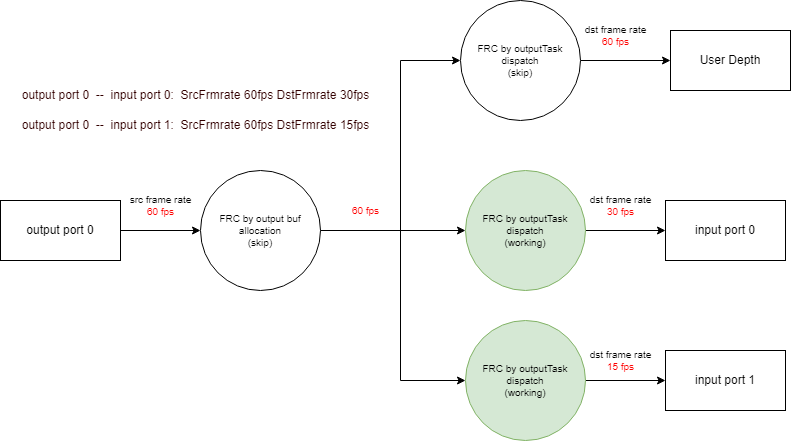
Figure 1-7:One-to-multi and set UserDepth
1.6.2.4. Vdec frame rate control in NVR scenarios
As shown in Figure 1-8, Vdec frame rate control in NVR.
-
Since NVR requires users to input code streams to Vdec, it is difficult to strictly ensure that the speed of code streams is balanced, which is different from the scenario where the data source of IPC is strictly controlled by interrupts. If users cannot ensure the stability of the input frame rate, they can use the function of automatically calculating the frame rate provided by MI. This function is automatically enabled when u32SrcFrmrate is set to -1. At this time, MI will strictly follow u32DstFrmrate to decide whether to allocate Buffer to Vdec.
-
The user obtains the bitstream data from the network and inputs it into the Vdec Input Ringpool, sets the Vdec Output Port to bind the Disp Input Port. Due to the large fluctuation of the network bitstream, the frame rate control can be set to -1:30 and the Bind Type to FRAME Mode.
-
MI_SYS will perform frame rate control at the Vdec Ouput Port, allocating a buffer to Vdec every 1000ms/30 = 33.3 ms to ensure that the output frame rate of the Vdec Output Port can be stabilized at 30fps, avoiding frame rate fluctuations caused by the network.
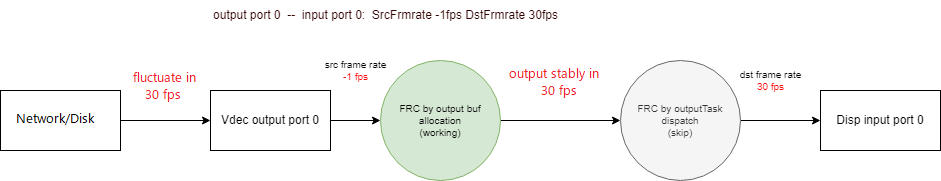
Figure 1-8:Vdec frame rate control in NVR
Tips:
NVR products can query the current ChnPort legacy frames through the API interface of MI_VDEC to dynamically select two strategies to achieve better results
The function of automatically calibrating the real frame rate of previous Output when Vdec Bind is in the next stage is no longer effective.
NVR provides the function of double-speed playback. When the timing of the subsequent Disp cannot keep up, it is necessary to actively drop frames before inputting the Disp. If the Vdec decoding speed is faster than the Disp display timing, the proportional frame drop function provided by MI can be used to achieve the desired frame rate by setting the ratio of u32SrcFrmrate and u32DstFrmrate.
1.6.3. Suspend to RAM¶
Suspend to RAM (STR) is a power management mode in Linux. Its core principle is to save the current operating status of the system (including memory data, CPU registers, hardware registers, etc.) to the memory, while shutting down or reducing the power consumption of most hardware devices.
When waking up, the system quickly resumes from memory to its pre-suspend state.
MI STR is developed based on the Linux PM framework. From the perspective of Linux PM, MI STR has only one PM device (MI SYS). The suspend/resume of other modules is managed by MI SYS and does not directly interact with Linux PM.
For applications, STR is insensitive. Applications can trigger the STR process through echo mem > /sys/power/state. The STR process is shown in Figure 1-9:
Figure 1-9 Suspend to RAM flow
1.6.4. MI SYS MMA¶
MI SYS MMA is a physical memory pool that is specifically used to provide physical memory for input and output multimedia data to the MI module.
When the MI pipeline starts to flow out, the MI module will apply for MMA Buffer from MI SYS for multimedia data input/output. MI SYS will control the transfer of MMA Buffer between MI modules based on the binding relationship between modules. At the same time, MI SYS also provides an application program interface that allows applications to obtain the MMA Buffer in the pipeline and perform read and write operations.
Users can view the usage of the MMA memory pool by using the following command (refer to 5.15. mma_heap_name0 for more information):
cat /proc/mi_modules/mi_sys_mma/mma_heap_name0
1.6.5. MI SYS DMABUF¶
The Linux dma-buf subsystem provides a framework for sharing hardware (DMA) access buffers between multiple device drivers and subsystems, and for synchronizing asynchronous hardware access.
MI_SYS implements the dma heap memory pool based on the dma-buf subsystem to connect to Linux drivers such as V4L2 and DRM, and supports applications to apply for dmabuf and read and write dmabuf. At the same time, it also implements the dmabuf allocator for the Input/Output Port of the MI module.
The application can Enqueue/Dequeue dmabuf to dmabuf allocator, and dmabuf allocator will pass the physical address information of dmabuf to the MI module to enable the MI module to read and write dmabuf.
Applications can use MI SYS dmabuf as input/output of V4L2 and DRM drivers to implement streaming between MI modules and V4L2 and DRM drivers.
The MI SYS DMABUF usage process is shown in Figure 1-10:
-
The application requests dmabuf from the dma heap and fills it with image data. After enqueueing dmabuf to the dmabuf allocator of the MI module, it calls poll() to wait for the MI module to complete the processing.
-
The MI module gets the dmabuf from the allocator, and after completing the data access, it wakes up the application, and the application then dequeues the dmabuf from the dmabuf allocator.
-
Finally, the application enqueues the dmabuf to the DRM driver to display the image.
For detailed design, please refer to Setup FILE->ISP->SCL->FILE streaming scenario based on DMABUF
Figure 1-10 MI_SYS DMA BUF flow
Tips:
Since dmabuf programming is difficult, it is recommended to use the MI SYS DMABUF function only when you need to connect to V4L2, DRM and other drivers that require dmabuf. The default is to use MI SYS MMA Buffer.
MI SYS DMABUF is implemented by encapsulating MI SYS MMA using the Linux dmabuf framework, and the underlying physical memory is still the MMA Buffer.
1.7. Development Flow¶
1.7.1. build configure¶
-
Enter the alkaid project root directory, make menuconfig, go to Generic Options → Interface Compile Config, and turn on the compilation of the MI_SYS module.
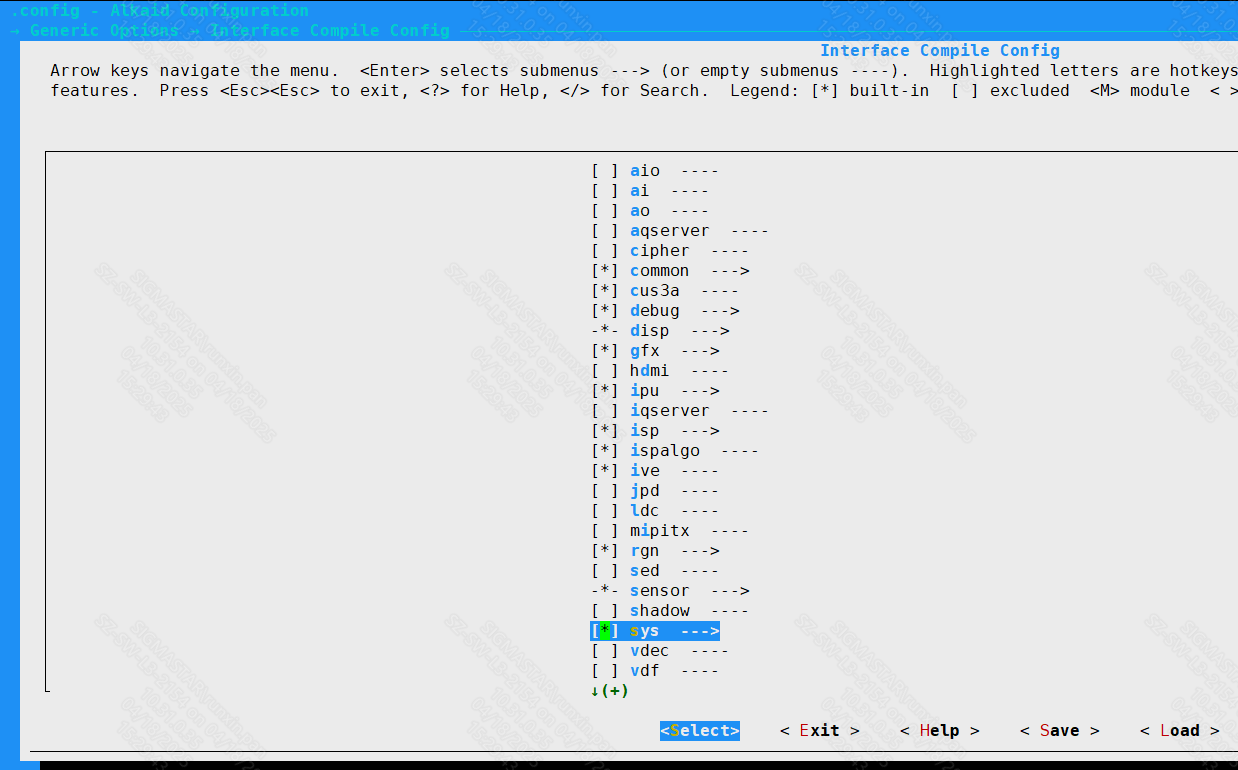
Figure 1-11 MI_SYS compile option
-
Enter the sys option to configure some optional functions of MI_SYS, such as dmabuf, meta pool, etc.
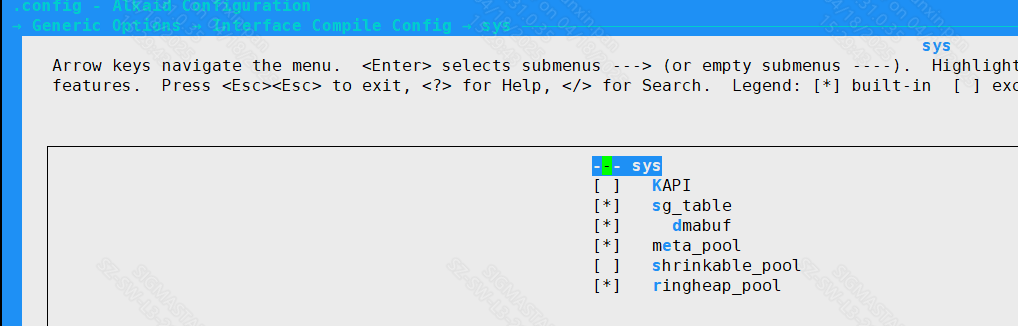
Figure 1-12 MI_SYS dmabuf compile option
-
Go to Generic Options and select MI suspend to RAM and standby to enable the STR function.
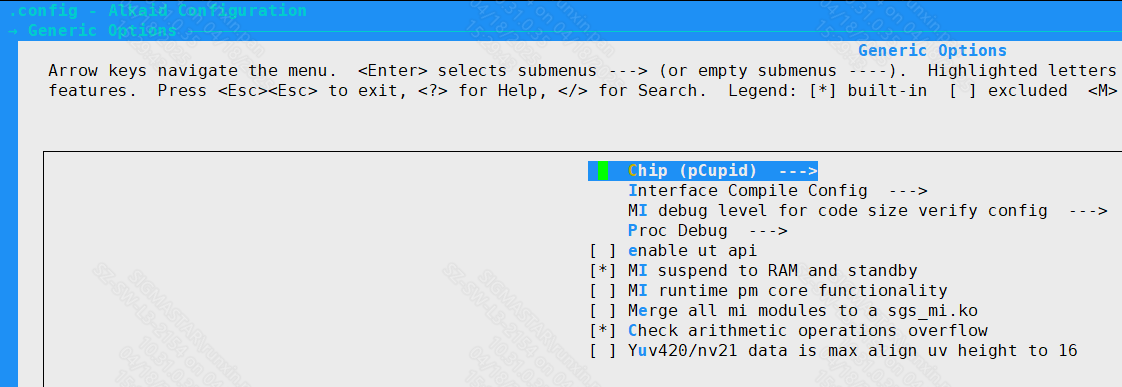
Figure 1-13 MI_SYS STR compile option
-
Save and exit menuconfig, recompile SDK, and burn it to the chip.
After the compilation is complete, libmi_sys.so, libmi_sys.a, mi_sys.h, mi_sys_datatype.h, and mi_sys_sideband_datatype.h will be generated in the project/release/ directory.
After the burning is complete, you can find mi_sys.ko under /config/modules/$(KERNEL_VERSION)/ on the board.
1.7.2 API Call Flow¶
First, make sure mi_sys.ko and mi_common.ko are loaded into the kernel normally.
The MI SYS user API call flow is shown in Figure 1-14: MI_SYS API call flow:
Figure 1-14 MI_SYS API call flow
-
Init the MI System.
-
Init all MI modules on pipeline.
-
Bind the front-end and back-end MI modules according to the scene requirements and set the frame rate control parameters;
-
Set Output Port depth.
-
Call poll() and wait for Output Port finish output data.
-
Get MI module Output Port buffer.
-
Read the Output Port buffer.
-
Release the Output port buffer back to MI module.
-
Exit the MI System.
1.8. example code¶
1.8.1. Setup FILLE->ISP->SCL->FILE pipeline¶
This example implements the application reading the 1920x1080_1920_yuyv422.yuv file, inputting the file to the ISP, binding the ISP to the SCL, and finally obtaining the output image from the SCL Output Port and saving it as ./1280x720_1280_yuyv422.yuv.
The example focuses on showing how to use the MI_SYS API to implement the binding between MI modules and the input and output of the module ports.
#include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> #include <string.h> #include <signal.h> #include <unistd.h> #include <fcntl.h> #include <pthread.h> #include <sys/ioctl.h> #include <poll.h> #include "mi_sensor.h" #include "mi_sensor_datatype.h" #include "mi_vif.h" #include "mi_vif_datatype.h" #include "mi_isp.h" #include "mi_isp_datatype.h" #include "mi_scl.h" #include "mi_scl_datatype.h" #include "mi_common.h" #include "mi_common_datatype.h" #include "mi_sys.h" #include "mi_sys_datatype.h" #include "sys/mman.h" static MI_BOOL bExit = FALSE; #define ISP_INPUT_FILE_PATH "./1920x1080_1920_yuyv422.yuv" #define INPUT_WIDTH 1920 #define INPUT_HEIGH 1080 #define INPUT_PIXEL E_MI_SYS_PIXEL_FRAME_YUV422_YUYV #define INPUT_SIZE (INPUT_WIDTH * INPUT_HEIGH * 2) #define SCL_OUTPUT_FILE_PATH "./1280x720_1280_yuyv422.yuv" #define OUTPUT_WIDTH 1280 #define OUTPUT_HEIGH 720 #define OUTPUT_PIXEL E_MI_SYS_PIXEL_FRAME_YUV422_YUYV #define OUTPUT_SIZE (OUTPUT_WIDTH * OUTPUT_HEIGH * 2) #define ISP_DEV_ID 0 #define ISP_CHN_ID 0 #define ISP_OUTPUT_PORT_ID 1 #define ISP_INPUT_PORT_ID 0 #define SCL_DEV_ID 1 #define SCL_CHN_ID 0 #define SCL_OUTPUT_PORT_ID 0 #define SCL_INPUT_PORT_ID 0 MI_S32 IspInit(void) { MI_ISP_DevAttr_t stDevAttr; MI_ISP_ChannelAttr_t stChnAttr; MI_ISP_ChnParam_t stChnParam; MI_ISP_OutPortParam_t stOutPortParam; MI_SYS_ChnPort_t stChnPort; memset(&stDevAttr, 0x0, sizeof(MI_ISP_DevAttr_t)); memset(&stChnAttr, 0x0, sizeof(MI_ISP_ChannelAttr_t)); memset(&stChnParam, 0x0, sizeof(MI_ISP_ChnParam_t)); memset(&stOutPortParam, 0x0, sizeof(MI_ISP_OutPortParam_t)); memset(&stChnPort, 0x0, sizeof(MI_SYS_ChnPort_t)); stDevAttr.u32DevStitchMask = E_MI_ISP_DEVICEMASK_ID0; MI_ISP_CreateDevice(ISP_DEV_ID, &stDevAttr); MI_ISP_CreateChannel(ISP_DEV_ID, ISP_CHN_ID, &stChnAttr); MI_ISP_SetChnParam(ISP_DEV_ID, ISP_CHN_ID, &stChnParam); MI_ISP_StartChannel(ISP_DEV_ID, ISP_CHN_ID); stOutPortParam.stCropRect.u16Width = OUTPUT_WIDTH; stOutPortParam.stCropRect.u16Height = OUTPUT_HEIGH; stOutPortParam.ePixelFormat = OUTPUT_PIXEL; MI_ISP_SetOutputPortParam(ISP_DEV_ID, ISP_CHN_ID, ISP_OUTPUT_PORT_ID, &stOutPortParam); MI_ISP_EnableOutputPort(ISP_DEV_ID, ISP_CHN_ID, ISP_OUTPUT_PORT_ID); stChnPort.eModId = E_MI_MODULE_ID_ISP; stChnPort.u32DevId = ISP_DEV_ID; stChnPort.u32ChnId = ISP_CHN_ID; stChnPort.u32PortId = ISP_OUTPUT_PORT_ID; MI_SYS_SetChnOutputPortDepth(0, &stChnPort, 0, 5); return MI_SUCCESS; } MI_S32 IspDeinit(void) { MI_ISP_DisableOutputPort(ISP_DEV_ID, ISP_CHN_ID, ISP_OUTPUT_PORT_ID); MI_ISP_StopChannel(ISP_DEV_ID, ISP_CHN_ID); MI_ISP_DestroyChannel(ISP_DEV_ID, ISP_CHN_ID); MI_ISP_DestoryDevice(ISP_DEV_ID); return MI_SUCCESS; } int SclInit(void) { MI_SCL_DevAttr_t stDevAttr; MI_SCL_ChannelAttr_t stChnAttr; MI_SCL_ChnParam_t stChnParam; MI_SCL_OutPortParam_t stOutPortParam; MI_SYS_ChnPort_t stChnPort; memset(&stDevAttr, 0x0, sizeof(MI_SCL_DevAttr_t)); memset(&stChnAttr, 0x0, sizeof(MI_SCL_ChannelAttr_t)); memset(&stChnParam, 0x0, sizeof(MI_SCL_ChnParam_t)); memset(&stOutPortParam, 0x0, sizeof(MI_SCL_OutPortParam_t)); memset(&stChnPort, 0x0, sizeof(MI_SYS_ChnPort_t)); stDevAttr.u32NeedUseHWOutPortMask = E_MI_SCL_HWSCL0; MI_SCL_CreateDevice(SCL_DEV_ID, &stDevAttr); MI_SCL_CreateChannel(SCL_DEV_ID, SCL_CHN_ID, &stChnAttr); stChnParam.eRot = E_MI_SYS_ROTATE_NONE; MI_SCL_SetChnParam(SCL_DEV_ID, SCL_CHN_ID, &stChnParam); MI_SCL_StartChannel(SCL_DEV_ID, SCL_CHN_ID); MI_SCL_GetOutputPortParam(SCL_DEV_ID, SCL_CHN_ID, SCL_OUTPUT_PORT_ID, &stOutPortParam); stOutPortParam.stSCLOutCropRect.u16Width = OUTPUT_WIDTH; stOutPortParam.stSCLOutCropRect.u16Height = OUTPUT_HEIGH; stOutPortParam.stSCLOutputSize.u16Width = OUTPUT_WIDTH; stOutPortParam.stSCLOutputSize.u16Height = OUTPUT_HEIGH; stOutPortParam.stSCLOutputSize.u16Width = OUTPUT_WIDTH; stOutPortParam.stSCLOutputSize.u16Height = OUTPUT_HEIGH; stOutPortParam.ePixelFormat = OUTPUT_PIXEL; MI_SCL_SetOutputPortParam(SCL_DEV_ID, SCL_CHN_ID, SCL_OUTPUT_PORT_ID, &stOutPortParam); MI_SCL_EnableOutputPort(SCL_DEV_ID, SCL_CHN_ID, SCL_OUTPUT_PORT_ID); stChnPort.eModId = E_MI_MODULE_ID_SCL; stChnPort.u32DevId = SCL_DEV_ID; stChnPort.u32ChnId = SCL_CHN_ID; stChnPort.u32PortId = SCL_OUTPUT_PORT_ID; MI_SYS_SetChnOutputPortDepth(0, &stChnPort, 3, 5); return MI_SUCCESS; } MI_S32 SclDeinit(void) { MI_SCL_DisableOutputPort(SCL_DEV_ID, SCL_CHN_ID, SCL_OUTPUT_PORT_ID); MI_SCL_StopChannel(SCL_DEV_ID, SCL_CHN_ID); MI_SCL_DestroyChannel(SCL_DEV_ID, SCL_CHN_ID); MI_SCL_DestroyDevice(SCL_DEV_ID); return MI_SUCCESS; } MI_S32 IspBindScl(void) { MI_SYS_ChnPort_t stSrcChnPort; MI_SYS_ChnPort_t stDstChnPort; stSrcChnPort.eModId = E_MI_MODULE_ID_ISP; stSrcChnPort.u32DevId = ISP_DEV_ID; stSrcChnPort.u32ChnId = ISP_CHN_ID; stSrcChnPort.u32PortId = ISP_OUTPUT_PORT_ID; stDstChnPort.eModId = E_MI_MODULE_ID_SCL; stDstChnPort.u32DevId = SCL_DEV_ID; stDstChnPort.u32ChnId = SCL_CHN_ID; stDstChnPort.u32PortId = SCL_INPUT_PORT_ID; MI_SYS_BindChnPort(0, &stSrcChnPort, &stDstChnPort, 10, 5, E_MI_SYS_BIND_TYPE_FRAME_BASE, 0); return MI_SUCCESS; } MI_U32 IspUnbindScl(void) { MI_SYS_ChnPort_t stSrcChnPort; MI_SYS_ChnPort_t stDstChnPort; stSrcChnPort.eModId = E_MI_MODULE_ID_ISP; stSrcChnPort.u32DevId = ISP_DEV_ID; stSrcChnPort.u32ChnId = ISP_CHN_ID; stSrcChnPort.u32PortId = ISP_OUTPUT_PORT_ID; stDstChnPort.eModId = E_MI_MODULE_ID_SCL; stDstChnPort.u32DevId = SCL_DEV_ID; stDstChnPort.u32ChnId = SCL_CHN_ID; stDstChnPort.u32PortId = SCL_INPUT_PORT_ID; MI_SYS_UnBindChnPort(0, &stSrcChnPort, &stDstChnPort); return MI_SUCCESS; } int GetSclOutputData(void) { MI_SYS_ChnPort_t stSclOutputPort; MI_S32 s32Ret = MI_SUCCESS; MI_S32 s32Fd; MI_SYS_BufInfo_t stBufInfo; MI_SYS_BUF_HANDLE hHandle; FILE *pFile = NULL; struct pollfd fds = {0}; // dump scl output to file pFile = fopen(SCL_OUTPUT_FILE_PATH, "w"); if (pFile == NULL) { printf("open yuv file failed!\n"); bExit = TRUE; return -1; } stSclOutputPort.eModId = E_MI_MODULE_ID_SCL; stSclOutputPort.u32DevId = SCL_DEV_ID; stSclOutputPort.u32ChnId = SCL_CHN_ID; stSclOutputPort.u32PortId = SCL_OUTPUT_PORT_ID; // get scl output port fd s32Ret = MI_SYS_GetFd(&stSclOutputPort, &s32Fd); if(MI_SUCCESS != s32Ret) { printf("MI_SYS_GetFd fail 0x%x\n", s32Ret); fclose(pFile); return s32Ret; } fds.fd = s32Fd; fds.events = POLLIN; while(!bExit) { s32Ret = poll(&fds, 1, 5000); if (s32Ret <= 0 || fds.revents & POLLERR) { printf("select failed! ret=0x%x, revent=0x%x\n", s32Ret, fds.revents); } else { s32Ret = MI_SYS_ChnOutputPortGetBuf(&stSclOutputPort, &stBufInfo, &hHandle); if (s32Ret != MI_SUCCESS) { printf("get scl output buf fail 0x%x\n", s32Ret); continue; } fseek(pFile, 0, SEEK_SET); fwrite(stBufInfo.stFrameData.pVirAddr[0], 1, OUTPUT_SIZE, pFile); MI_SYS_ChnOutputPortPutBuf(hHandle); } } MI_SYS_CloseFd(s32Fd); fclose(pFile); return 0; } void *IspInputThread(void *arg) { MI_SYS_BufConf_t stBufConf; MI_SYS_BufInfo_t stBufInfo; MI_SYS_ChnPort_t stIspInputPort; MI_SYS_BUF_HANDLE hHandle; FILE *pFile = NULL; MI_S32 s32ReadSize = 0; memset(&stBufConf, 0x0, sizeof(MI_SYS_BufConf_t)); memset(&stIspInputPort, 0, sizeof(MI_SYS_ChnPort_t)); stBufConf.eBufType = E_MI_SYS_BUFDATA_FRAME; stBufConf.stFrameCfg.eFormat = INPUT_PIXEL; stBufConf.stFrameCfg.u16Width = INPUT_WIDTH; stBufConf.stFrameCfg.u16Height = INPUT_HEIGH; stIspInputPort.eModId = E_MI_MODULE_ID_ISP; stIspInputPort.u32DevId = ISP_DEV_ID; stIspInputPort.u32ChnId = ISP_CHN_ID; stIspInputPort.u32PortId = ISP_INPUT_PORT_ID; pFile = fopen(ISP_INPUT_FILE_PATH, "rb"); if (pFile == NULL) { printf("open yuv file failed!\n"); } while(!bExit) { fseek(pFile, 0L, SEEK_SET); if (MI_SUCCESS == MI_SYS_ChnInputPortGetBuf(&stIspInputPort, &stBufConf, &stBufInfo, &hHandle, 1000)) { s32ReadSize = fread(stBufInfo.stFrameData.pVirAddr[0], 1, INPUT_SIZE, pFile); if (s32ReadSize > 0) { MI_SYS_ChnInputPortPutBuf(hHandle, &stBufInfo, FALSE); } else { printf("read file error %d\n", s32ReadSize); MI_SYS_ChnInputPortPutBuf(hHandle, &stBufInfo, TRUE); } } else { printf("get isp input buf fail\n"); } // 10fps usleep(100 * 1000); } fclose(pFile); return NULL; } void SignalHandler(int signo) { printf("Exit app \n"); bExit = TRUE; } int main(int argc, char *argv[]) { pthread_t IspThreadHandle; signal(SIGINT, SignalHandler); // must call MI_SYS_Init() before any other MI API MI_SYS_Init(0); IspInit(); SclInit(); IspBindScl(); pthread_create(&IspThreadHandle, NULL, IspInputThread, NULL); printf("ctrl+c to exit the app\n"); GetSclOutputData(); pthread_join(IspThreadHandle, NULL); IspUnbindScl(); SclDeinit(); IspDeinit(); // call MI_SYS_Exit() when we exit MI_SYS_Exit(0); }
1.8.2. Setup FILE->ISP->SCL->FILE pipeline base on dmabuf¶
The logic of this example is similar to that of 1.8.1. Setup FILLE->ISP->SCL->FILE pipeline.
The difference is that this example uses the MI SYS DMABUF interface to complete the image input of ISP and the image output of SCL.
#include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> #include <string.h> #include <signal.h> #include <unistd.h> #include <fcntl.h> #include <pthread.h> #include <sys/ioctl.h> #include <poll.h> #include "mi_sensor.h" #include "mi_sensor_datatype.h" #include "mi_vif.h" #include "mi_vif_datatype.h" #include "mi_isp.h" #include "mi_isp_datatype.h" #include "mi_scl.h" #include "mi_scl_datatype.h" #include "mi_common.h" #include "mi_common_datatype.h" #include "mi_sys.h" #include "mi_sys_datatype.h" #include "sys/mman.h" typedef struct{ MI_U64 len; MI_U32 fd; MI_U32 fd_flags; MI_U64 heap_flags; } dma_heap_allocation_data; #define DMA_HEAP_IOC_MAGIC 'H' #define DMA_HEAP_IOCTL_ALLOC _IOWR(DMA_HEAP_IOC_MAGIC, 0, dma_heap_allocation_data) struct dma_buf_sync { MI_U64 flags; }; #define DMA_BUF_SYNC_READ (1 << 0) #define DMA_BUF_SYNC_START (0 << 2) #define DMA_BUF_SYNC_END (1 << 2) #define DMA_BUF_BASE 'b' #define DMA_BUF_IOCTL_SYNC _IOW(DMA_BUF_BASE, 0, struct dma_buf_sync) static MI_BOOL bExit = FALSE; #define ISP_INPUT_FILE_PATH "./1920x1080_1920_yuyv422.yuv" #define INPUT_WIDTH 1920 #define INPUT_HEIGH 1080 #define INPUT_PIXEL E_MI_SYS_PIXEL_FRAME_YUV422_YUYV #define INPUT_SIZE (INPUT_WIDTH * INPUT_HEIGH * 2) #define SCL_OUTPUT_FILE_PATH "./1280x720_1280_yuyv422.yuv" #define OUTPUT_WIDTH 1280 #define OUTPUT_HEIGH 720 #define OUTPUT_PIXEL E_MI_SYS_PIXEL_FRAME_YUV422_YUYV #define OUTPUT_SIZE (OUTPUT_WIDTH * OUTPUT_HEIGH * 2) #define ISP_DEV_ID 0 #define ISP_CHN_ID 0 #define ISP_OUTPUT_PORT_ID 1 #define ISP_INPUT_PORT_ID 0 #define SCL_DEV_ID 1 #define SCL_CHN_ID 0 #define SCL_OUTPUT_PORT_ID 0 #define SCL_INPUT_PORT_ID 0 int AllocDmabuf(int len) { int dma_heap_fd; int ret; dma_heap_allocation_data data = { .len = len, .fd = 0, .fd_flags = O_RDWR, .heap_flags = 0, }; // open mma dma heap dma_heap_fd = open("/dev/mma", O_RDWR); if (dma_heap_fd <= 0) { printf("failed, open /dev/mma return fail %d\n", dma_heap_fd); return -1; } // alloc dmabuf from mma dma heap ret = ioctl(dma_heap_fd, DMA_HEAP_IOCTL_ALLOC, &data); if (ret != 0) { perror("alloc dmabuf fail\n"); data.fd = -1; } close(dma_heap_fd); return data.fd; } void FreeDmabuf(int fd) { close(fd); } int IspInit(void) { MI_ISP_DevAttr_t stDevAttr; MI_ISP_ChannelAttr_t stChnAttr; MI_ISP_ChnParam_t stChnParam; MI_ISP_OutPortParam_t stOutPortParam; MI_SYS_ChnPort_t stChnPort; memset(&stDevAttr, 0x0, sizeof(MI_ISP_DevAttr_t)); memset(&stChnAttr, 0x0, sizeof(MI_ISP_ChannelAttr_t)); memset(&stChnParam, 0x0, sizeof(MI_ISP_ChnParam_t)); memset(&stOutPortParam, 0x0, sizeof(MI_ISP_OutPortParam_t)); memset(&stChnPort, 0x0, sizeof(MI_SYS_ChnPort_t)); stDevAttr.u32DevStitchMask = E_MI_ISP_DEVICEMASK_ID0; MI_ISP_CreateDevice(ISP_DEV_ID, &stDevAttr); MI_ISP_CreateChannel(ISP_DEV_ID, ISP_CHN_ID, &stChnAttr); MI_ISP_SetChnParam(ISP_DEV_ID, ISP_CHN_ID, &stChnParam); MI_ISP_StartChannel(ISP_DEV_ID, ISP_CHN_ID); stOutPortParam.stCropRect.u16Width = OUTPUT_WIDTH; stOutPortParam.stCropRect.u16Height = OUTPUT_HEIGH; stOutPortParam.ePixelFormat = OUTPUT_PIXEL; MI_ISP_SetOutputPortParam(ISP_DEV_ID, ISP_CHN_ID, ISP_OUTPUT_PORT_ID, &stOutPortParam); MI_ISP_EnableOutputPort(ISP_DEV_ID, ISP_CHN_ID, ISP_OUTPUT_PORT_ID); stChnPort.eModId = E_MI_MODULE_ID_ISP; stChnPort.u32DevId = ISP_DEV_ID; stChnPort.u32ChnId = ISP_CHN_ID; stChnPort.u32PortId = ISP_INPUT_PORT_ID; MI_SYS_CreateChnInputPortDmabufCusAllocator(&stChnPort); return MI_SUCCESS; } MI_S32 IspDeinit(void) { MI_SYS_ChnPort_t stChnPort; stChnPort.eModId = E_MI_MODULE_ID_ISP; stChnPort.u32DevId = ISP_DEV_ID; stChnPort.u32ChnId = ISP_CHN_ID; stChnPort.u32PortId = ISP_INPUT_PORT_ID; MI_SYS_DestroyChnInputPortDmabufCusAllocator(&stChnPort); MI_ISP_DisableOutputPort(ISP_DEV_ID, ISP_CHN_ID, ISP_OUTPUT_PORT_ID); MI_ISP_StopChannel(ISP_DEV_ID, ISP_CHN_ID); MI_ISP_DestroyChannel(ISP_DEV_ID, ISP_CHN_ID); MI_ISP_DestoryDevice(ISP_DEV_ID); return MI_SUCCESS; } int SclInit(void) { MI_SCL_DevAttr_t stDevAttr; MI_SCL_ChannelAttr_t stChnAttr; MI_SCL_ChnParam_t stChnParam; MI_SCL_OutPortParam_t stOutPortParam; MI_SYS_ChnPort_t stChnPort; memset(&stDevAttr, 0x0, sizeof(MI_SCL_DevAttr_t)); memset(&stChnAttr, 0x0, sizeof(MI_SCL_ChannelAttr_t)); memset(&stChnParam, 0x0, sizeof(MI_SCL_ChnParam_t)); memset(&stOutPortParam, 0x0, sizeof(MI_SCL_OutPortParam_t)); memset(&stChnPort, 0x0, sizeof(MI_SYS_ChnPort_t)); stDevAttr.u32NeedUseHWOutPortMask = E_MI_SCL_HWSCL0; MI_SCL_CreateDevice(SCL_DEV_ID, &stDevAttr); MI_SCL_CreateChannel(SCL_DEV_ID, SCL_CHN_ID, &stChnAttr); stChnParam.eRot = E_MI_SYS_ROTATE_NONE; MI_SCL_SetChnParam(SCL_DEV_ID, SCL_CHN_ID, &stChnParam); MI_SCL_StartChannel(SCL_DEV_ID, SCL_CHN_ID); MI_SCL_GetOutputPortParam(SCL_DEV_ID, SCL_CHN_ID, SCL_OUTPUT_PORT_ID, &stOutPortParam); stOutPortParam.stSCLOutCropRect.u16Width = OUTPUT_WIDTH; stOutPortParam.stSCLOutCropRect.u16Height = OUTPUT_HEIGH; stOutPortParam.stSCLOutputSize.u16Width = OUTPUT_WIDTH; stOutPortParam.stSCLOutputSize.u16Height = OUTPUT_HEIGH; stOutPortParam.stSCLOutputSize.u16Width = OUTPUT_WIDTH; stOutPortParam.stSCLOutputSize.u16Height = OUTPUT_HEIGH; stOutPortParam.ePixelFormat = OUTPUT_PIXEL; MI_SCL_SetOutputPortParam(SCL_DEV_ID, SCL_CHN_ID, SCL_OUTPUT_PORT_ID, &stOutPortParam); MI_SCL_EnableOutputPort(SCL_DEV_ID, SCL_CHN_ID, SCL_OUTPUT_PORT_ID); stChnPort.eModId = E_MI_MODULE_ID_SCL; stChnPort.u32DevId = SCL_DEV_ID; stChnPort.u32ChnId = SCL_CHN_ID; stChnPort.u32PortId = SCL_OUTPUT_PORT_ID; MI_SYS_CreateChnOutputPortDmabufCusAllocator(&stChnPort); return MI_SUCCESS; } MI_S32 SclDeinit(void) { MI_SYS_ChnPort_t stChnPort; stChnPort.eModId = E_MI_MODULE_ID_SCL; stChnPort.u32DevId = SCL_DEV_ID; stChnPort.u32ChnId = SCL_CHN_ID; stChnPort.u32PortId = SCL_OUTPUT_PORT_ID; MI_SYS_DestroyChnOutputPortDmabufCusAllocator(&stChnPort); MI_SCL_DisableOutputPort(SCL_DEV_ID, SCL_CHN_ID, SCL_OUTPUT_PORT_ID); MI_SCL_StopChannel(SCL_DEV_ID, SCL_CHN_ID); MI_SCL_DestroyChannel(SCL_DEV_ID, SCL_CHN_ID); MI_SCL_DestroyDevice(SCL_DEV_ID); return MI_SUCCESS; } MI_S32 IspBindScl(void) { MI_SYS_ChnPort_t stSrcChnPort; MI_SYS_ChnPort_t stDstChnPort; stSrcChnPort.eModId = E_MI_MODULE_ID_ISP; stSrcChnPort.u32DevId = ISP_DEV_ID; stSrcChnPort.u32ChnId = ISP_CHN_ID; stSrcChnPort.u32PortId = ISP_OUTPUT_PORT_ID; stDstChnPort.eModId = E_MI_MODULE_ID_SCL; stDstChnPort.u32DevId = SCL_DEV_ID; stDstChnPort.u32ChnId = SCL_CHN_ID; stDstChnPort.u32PortId = SCL_INPUT_PORT_ID; MI_SYS_BindChnPort(0, &stSrcChnPort, &stDstChnPort, 10, 5, E_MI_SYS_BIND_TYPE_FRAME_BASE, 0); return MI_SUCCESS; } MI_U32 IspUnbindScl(void) { MI_SYS_ChnPort_t stSrcChnPort; MI_SYS_ChnPort_t stDstChnPort; stSrcChnPort.eModId = E_MI_MODULE_ID_ISP; stSrcChnPort.u32DevId = ISP_DEV_ID; stSrcChnPort.u32ChnId = ISP_CHN_ID; stSrcChnPort.u32PortId = ISP_OUTPUT_PORT_ID; stDstChnPort.eModId = E_MI_MODULE_ID_SCL; stDstChnPort.u32DevId = SCL_DEV_ID; stDstChnPort.u32ChnId = SCL_CHN_ID; stDstChnPort.u32PortId = SCL_INPUT_PORT_ID; MI_SYS_UnBindChnPort(0, &stSrcChnPort, &stDstChnPort); return MI_SUCCESS; } int GetSclOutputData(void) { MI_SYS_ChnPort_t stSclOutputPort; MI_S32 s32Ret = MI_SUCCESS; MI_S32 s32Fd; MI_SYS_DmaBufInfo_t stDmaBufInfo; FILE *pFile; void *pVaddr; struct pollfd fds = {0}; struct dma_buf_sync sync; memset(&stDmaBufInfo, 0x0, sizeof(stDmaBufInfo)); // dump scl output to file pFile = fopen(SCL_OUTPUT_FILE_PATH, "w"); if (pFile == NULL) { printf("open yuv file failed!\n"); bExit = TRUE; return -1; } s32Fd = AllocDmabuf(OUTPUT_SIZE); if (s32Fd <= 0) { printf("alloc dmabuf fail %d\n", s32Fd); fclose(pFile); return -1; } // mmap dmabuf to user space,so that user can read data from dmabuf pVaddr = mmap(NULL, OUTPUT_SIZE, PROT_WRITE|PROT_READ, MAP_SHARED, s32Fd, 0); if(!pVaddr) { printf("failed, mmap dma-buf return fail\n"); s32Ret = -1; goto EXIT; } stSclOutputPort.eModId = E_MI_MODULE_ID_SCL; stSclOutputPort.u32DevId = SCL_DEV_ID; stSclOutputPort.u32ChnId = SCL_CHN_ID; stSclOutputPort.u32PortId = SCL_OUTPUT_PORT_ID; fds.fd = s32Fd; fds.events = POLLOUT; while(!bExit) { memset(&stDmaBufInfo, 0x0, sizeof(stDmaBufInfo)); stDmaBufInfo.s32Fd[0] = s32Fd; stDmaBufInfo.s32Fd[1] = s32Fd; stDmaBufInfo.eFormat = OUTPUT_PIXEL; stDmaBufInfo.u16Width = OUTPUT_WIDTH; stDmaBufInfo.u16Height = OUTPUT_HEIGH; stDmaBufInfo.u32Stride[0] = OUTPUT_WIDTH * 2; //for yuv422yuyv s32Ret = MI_SYS_ChnOutputPortEnqueueDmabuf(&stSclOutputPort, &stDmaBufInfo); if (s32Ret != MI_SUCCESS) { printf("enqueue scl fail 0x%x\n", s32Ret); continue; } s32Ret = poll(&fds, 1, 5000); if (s32Ret <= 0 || fds.revents & POLLERR) { printf("select failed! ret=0x%x, revent=0x%x\n", s32Ret, fds.revents); s32Ret = MI_SYS_ChnOutputPortDropDmabuf(&stSclOutputPort, &stDmaBufInfo); if (s32Ret != MI_SUCCESS) { printf("drop dmabuf fail,dmabuf maybe hang! 0x%x\n", s32Ret); } } else { s32Ret = MI_SYS_ChnOutputPortDequeueDmabuf(&stSclOutputPort, &stDmaBufInfo); if (s32Ret != MI_SUCCESS || stDmaBufInfo.u32Status != MI_SYS_DMABUF_STATUS_DONE) { printf("scl output dmabuf not done, status = 0x%x ret = 0x%x\n", stDmaBufInfo.u32Status, s32Ret); continue; } fseek(pFile, 0, SEEK_SET); // dmabuf is cached,so must invalid cache before we read dmabuf sync.flags = DMA_BUF_SYNC_READ | DMA_BUF_SYNC_START; ioctl(s32Fd, DMA_BUF_IOCTL_SYNC, &sync); fwrite(pVaddr, 1, OUTPUT_SIZE, pFile); sync.flags = DMA_BUF_SYNC_READ | DMA_BUF_SYNC_END; ioctl(s32Fd, DMA_BUF_IOCTL_SYNC, &sync); } } s32Ret = 0; EXIT: FreeDmabuf(s32Fd); fclose(pFile); return s32Ret; } void *IspInputThread(void *arg) { MI_SYS_ChnPort_t stIspInputPort; MI_SYS_DmaBufInfo_t stDmaBufInfo; MI_U64 u64Pts; FILE *pFile = NULL; MI_S32 s32ReadSize = 0; int dmabuf_fd; void *pVaddr; struct pollfd fds = {0}; int ret; dmabuf_fd = AllocDmabuf(INPUT_SIZE); if (dmabuf_fd <= 0) { printf("alloc dmabuf fail %d\n", dmabuf_fd); return NULL; } // mmap dmabuf to user space,so that user can write data to dmabuf pVaddr = mmap(NULL, INPUT_SIZE, PROT_WRITE|PROT_READ, MAP_SHARED, dmabuf_fd, 0); if(!pVaddr) { printf("failed, mmap dma-buf return fail\n"); goto EXIT; } // read file to dmabuf pFile = fopen(ISP_INPUT_FILE_PATH, "rb"); if (pFile == NULL) { printf("open yuv file failed!\n"); goto EXIT; } fseek(pFile, 0L, SEEK_SET); s32ReadSize = fread(pVaddr, 1, INPUT_SIZE, pFile); fclose(pFile); if (s32ReadSize <= 0) { printf("read file error %d\n", s32ReadSize); goto EXIT; } stIspInputPort.eModId = E_MI_MODULE_ID_ISP; stIspInputPort.u32DevId = ISP_DEV_ID; stIspInputPort.u32ChnId = ISP_CHN_ID; stIspInputPort.u32PortId = ISP_INPUT_PORT_ID; fds.fd = dmabuf_fd; fds.events = POLLOUT; while(!bExit) { memset(&stDmaBufInfo, 0x0, sizeof(stDmaBufInfo)); stDmaBufInfo.s32Fd[0] = dmabuf_fd; stDmaBufInfo.s32Fd[1] = dmabuf_fd; stDmaBufInfo.eFormat = INPUT_PIXEL; stDmaBufInfo.u16Width = INPUT_WIDTH; stDmaBufInfo.u16Height = INPUT_HEIGH; stDmaBufInfo.u32Stride[0] = INPUT_WIDTH * 2; stDmaBufInfo.stContentCropWindow.u16Width = INPUT_WIDTH; stDmaBufInfo.stContentCropWindow.u16Height = INPUT_HEIGH; MI_SYS_GetCurPts(0, &u64Pts); stDmaBufInfo.u64Pts = u64Pts; ret = MI_SYS_ChnInputPortEnqueueDmabuf(&stIspInputPort, &stDmaBufInfo); if (ret != MI_SUCCESS) { printf("enqueue isp fail 0x%x\n", ret); continue; } ret = poll(&fds, 1, 5000); if (ret <= 0 || fds.revents & POLLERR) { printf("select failed, maybe hang! ret=0x%x, revent=0x%x\n", ret, fds.revents); } else { MI_SYS_ChnInputPortDequeueDmabuf(&stIspInputPort, &stDmaBufInfo); } // 10fps usleep(100 * 1000); } EXIT: FreeDmabuf(dmabuf_fd); return NULL; } void SignalHandler(int signo) { printf("Exit app \n"); bExit = TRUE; } int main(int argc, char *argv[]) { pthread_t IspThreadHandle; signal(SIGINT, SignalHandler); // must call MI_SYS_Init() before any other MI API MI_SYS_Init(0); IspInit(); SclInit(); IspBindScl(); pthread_create(&IspThreadHandle, NULL, IspInputThread, NULL); printf("ctrl+c to exit the app\n"); GetSclOutputData(); pthread_join(IspThreadHandle, NULL); IspUnbindScl(); SclDeinit(); IspDeinit(); // call MI_SYS_Exit() when we exit MI_SYS_Exit(0); }
1.8.3. Usage of MI SYS Memory manage APIs¶
This example shows how to use the MI SYS memory management interface to implement read and write operations on mma buf.
The logic of the instance is to apply for mma buf, map mma buf to the user process address space, perform read and write access to mma buf, and finally use bdma to write to mma buf.
Note that when the CPU reads and writes mma buf, it must ensure data consistency between cache and RAM.
MI_S32 main(void) { MI_U32 ret = MI_SUCCESS; MI_PHY phyBufAddr = 0; void * pVirBufAddr = NULL; MI_U32 buffSize = 4096; MI_SYS_Init(0); // alloc mma buf ret = MI_SYS_MMA_Alloc(0, NULL, buffSize, &phyBufAddr); if (ret != MI_SUCCESS) { goto EXIT; } // mmap mma buf phyaddr to user space virtual address ret = MI_SYS_Mmap(phyBufAddr, buffSize, &pVirBufAddr, TRUE); if (ret != MI_SUCCESS) { MI_SYS_MMA_Free(0, phyBufAddr); goto EXIT; } memset(pVirBufAddr, 0x5a, buffSize); // flush cache to make sure that data are truely written to ram MI_SYS_FlushInvCache(pVirBufAddr, buffSize); printf("read from mma buf val=0x%x\n", *(MI_U32 *)pVirBufAddr); // use bdma to write data MI_SYS_MemsetPa(0, phyBufAddr, 0x66, buffSize); // invalid the cache to make sure that we read the data from ram but not cache MI_SYS_FlushInvCache(pVirBufAddr, buffSize); printf("read from mma buf val=0x%x\n", *(MI_U32 *)pVirBufAddr); MI_SYS_Munmap(pVirBufAddr, buffSize); MI_SYS_MMA_Free(0, phyBufAddr); EXIT: MI_SYS_Exit(0); return ret; }
2. API REFERENCE¶
2.1. API Format Description¶
This manual uses information about the Description APIs for the 8 reference domains, which are represented by Table 2-1.
Table 2‑1 : API Format Description
| Label | Function |
|---|---|
| Function | Briefly Description the main features of the API. |
| Syntax | List the header files that should be included in the call API and the prototype declaration of the API. |
| Parameters | List the parameters, parameter descriptions, and parameter properties of the API. |
| Return value | List all possible return values of the API and what it means. |
| Dependency | Lists the header files that the API contains and the library files that the API will link to when the API compiles. |
| Attention | List the things you should be aware of when using the API. |
| Example | List instances that use the API. |
| Related topics | The interface associated with the call context. |
2.2. Feature Module API List¶
As mentioned earlier, we can roughly divide the MI_SYS's API into three broad categories: system functional class, data flow class, memory management class.
Tips:
Only some interfaces of MI_SYS support cross-Soc settings, which all carry the u16SocId parameter. The interfaces that do not carry this parameter do not support cross-Soc settings by default.
Table 2‑2 : API List
| API Name | Function |
|---|---|
| System functional class | |
| MI_SYS_Init | Initialize the MI_SYS system |
| MI_SYS_Exit | Destructing MI_SYS System |
| MI_SYS_GetVersion | Get the system version number of MI |
| MI_SYS_GetCurPts | Get the current timestamp of the MI system |
| MI_SYS_InitPtsBase | Initializing MI System Baseline Timestamp |
| MI_SYS_SyncPts | Synchronized MI system timestamp |
| MI_SYS_SetReg | Set the value of the register, debug with |
| MI_SYS_GetReg | Get the value of the register, debug with |
| MI_SYS_ReadUuid | Get Chip's Unique ID |
| MI_SYS_EnableChnOutputPortLowLatency | Enable or disable output port low latency |
| Data stream class | |
| MI_SYS_BindChnPort | Binding of the data source Output port to the recipient Input port |
| MI_SYS_BindChnPort2 | Binding from the output port of the data source to the recipient Input port, requiring a working mode to be specified |
| MI_SYS_UnBind_ChnPort | The de-binding of the data source Output port to the recipient Input port |
| MI_SYS_GetBindbyDest | Query the corresponding source Output port for the data recipient Input port |
| MI_SYS_ChnInputPortGetBuf | Get the buf of channel input Port |
| MI_SYS_ChnInputPortPutBuf | Add the buf of the channel input Port to the pending queue |
| MI_SYS_ChnOutputPortGetBuf | Get the buf of the channel output Port |
| MI_SYS_ChnOutputPortPutBuf | Release channel outputPort's buf |
| MI_SYS_ChnInputPortGetBufPa | The buf object corresponding to the allocation channel input port, which only returns MIU physical address |
| MI_SYS_ChnInputPortPutBufPa | Add the buf object corresponding to the channel input port to the pending queue, which needs to be used in pair with the function MI_SYS_ChnInputPortGetBufPa |
| MI_SYS_ChnOutputPortGetBufPa | The buf object corresponding to the allocation channel output port, which only returns MIU physical address |
| MI_SYS_ChnOutputPortPutBufPa | Release channel output port corresponding to the buf object, which needs to be used in pair with the function MI_SYS_ChnOutputPortGetBufPa |
| MI_SYS_SetChnOutputPortDepth | Set the depth of the channel OutputPort |
| MI_SYS_ChnPortInjectBuf | Inject output port Buf data into module channel input port |
| MI_SYS_GetFd | Get the file Description character of the current output Port wait event |
| MI_SYS_CloseFd | File Description character to close the current output Port |
| MI_SYS_DupBuf | Duplicate buf object |
| MI_SYS_ChnInputPortSetUserPicture | According to the set frame rate, the buf will be repeatedly input to the current input port and add to the waiting queue |
| MI_SYS_EnableUserPicture | Enable user picture |
| MI_SYS_DisableUserPicture | Disable user picture, release buf |
| MI_SYS_SetChnOutputPortUserFrc | Set the frame rate when user get buffer from output port, which will save bandwidth |
| MI_SYS_SetChnOutputPortBufExtConf | Set the alignment of output buf |
| MI_SYS_SetChnInputPortFrc | Set the input frame rate of InputPort |
| MI_SYS_QueryDevChnPortState | Query the status of Dev/Chn/Port, whether Chn/Port is enabled and Dev has been created |
| MI_SYS_CreateChnInputPortDmabufCusAllocator | Create a linux shared dma buffers manager for input port |
| MI_SYS_DestroyChnInputPortDmabufCusAllocator | Destroy the linux shared dma buffers manager of input port, which needs to be used in pair with the function MI_SYS_CreateChnInputPortDmabufCusAllocator |
| MI_SYS_ChnInputPortEnqueueDmabuf | Enqueue a linux shared dma-buf to input port |
| MI_SYS_ChnInputPortDequeueDmabuf | Dequeue a linux shared dma-buf from input port |
| MI_SYS_CreateChnOutputPortDmabufCusAllocator | Create a linux shared dma buffers manager for output port |
| MI_SYS_DestroyChnOutputPortDmabufCusAllocator | Destroy the linux shared dma buffers manager of output port, which needs to be used in pair with the function MI_SYS_CreateChnOutputPortDmabufCusAllocator |
| MI_SYS_ChnOutputPortEnqueueDmabuf | Enqueue a linux shared dma-buf to output port |
| MI_SYS_ChnOutputPortDequeueDmabuf | Dequeue a linux shared dma-buf from output port |
| MI_SYS_ChnOutputPortDropDmabuf | Drop a specific linux shared dma-buf from output port |
| MI_SYS_GetDmaBuf | Get the physical address from dmabuf fd |
| MI_SYS_PutDmaBuf | Release the physical address returned from MI_SYS_GetDmaBuf |
| MI_SYS_GetSidebandData | Get sideband data from bufhandle,such as frame id |
| Memory management classes | |
| MI_SYS_SetChnMMAConf | Set the MMA pool name for the default allocation of memory for the module device channel Output port |
| MI_SYS_GetChnMMAConf | Get the MMA pool name of the module device channel Output port's default allocated memory |
| MI_SYS_MMA_Alloc | Application requests physical continuous memory from MMA memory management pool |
| MI_SYS_MMA_Free | Memory allocated to the MMA memory management pool in the user state |
| MI_SYS_Mmap | Mapping physical memory to CPU virtual addresses |
| MI_SYS_Munmap | Un-mapping physical memory to virtual addresses |
| MI_SYS_FlushInvCache | Flush cache CPU virtual address |
| MI_SYS_ConfigPrivateMMAPool | Configure private MMA Heap for mold fast |
| MI_SYS_PrivateDevChnHeapAlloc | Request memory from module channel private MMA Pool |
| MI_SYS_PrivateDevChnHeapFree | Free memory from module channel private MMA pool |
| MI_SYS_Va2Pa | Turn CPU virtual address pointer to Physical address |
| MI_SYS_MemcpyPaEx | Copy memory from source memory to destination memory by DMA. src/dst can be different type memory. |
2.3. System functional class API¶
2.3.1. MI_SYS_Init¶
-
Function
MI_SYS initialization, the MI_SYS module provides basic support for other MI modules in the system and needs to be initialized earlier than other MI modules in the system, otherwise other stream types within the module will fail when initialization.
-
Syntax
MI_S32 MI_SYS_Init(MI_U16 u16SocId);
-
Parameters
Parameter Name Description Input/Output u16SocId Specify the target Soc for this operation Input -
Return
-
0 Successful.
-
!0 Failed, please refer to the error code.
-
-
Dependency
-
Head file: mi_sys_datatype.h / mi_sys.h
-
Library files: libmi_sys.a / libmi_sys.so
-
-
Note
-
MI_SYS_Init need to be called earlier than other MI modules in the Init function.
-
The MI_SYS_Init can be called multiple times in the same process, but must be used in pairs with the MI_SYS_Exit.
-
The system needs to configure the configuration parameters of the MMA memory heap within the kernel boot parameters.
-
-
Sample
#define ST_DEFAULT_SOC_ID 0 MI_S32 ST_Sys_Init(void) { MI_SYS_Version_t stVersion; MI_U64 u64Pts = 0; MI_U16 u16SocId = ST_DEFAULT_SOC_ID; MI_U64 u64Uuid; STCHECKRESULT(MI_SYS_Init(u16SocId)); memset(&stVersion, 0x0, sizeof(MI_SYS_Version_t)); STCHECKRESULT(MI_SYS_GetVersion(u16SocId , &stVersion)); ST_INFO("u8Version:%s\n", stVersion.u8Version); STCHECKRESULT(MI_SYS_ReadUuid(u16SocId, &u64Uuid)); INFO("u64Uuid:%llx\n", u64Uuid); STCHECKRESULT(MI_SYS_GetCurPts(u16SocId, &u64Pts)); ST_INFO("u64Pts:0x%llx\n", u64Pts); u64Pts = 0xF1237890F1237890; STCHECKRESULT(MI_SYS_InitPtsBase(u16SocId, u64Pts)); u64Pts = 0xE1237890E1237890; STCHECKRESULT(MI_SYS_SyncPts(u16SocId, u64Pts)); return MI_SUCCESS; } MI_S32 ST_Sys_Exit(void) { MI_U16 u16SocId = ST_DEFAULT_SOC_ID; STCHECKRESULT(MI_SYS_Exit(u16SocId)); return MI_SUCCESS; }Tips:
This example is intended for: MI_SYS_Init / MI_SYS_Exit / MI_SYS_GetVersion / MI_SYS_GetCurPts / MI_SYS_InitPtsBase / MI_SYS_SyncPts / MI_SYS_ReadUuid .
-
Related topics
2.3.2. MI_SYS_Exit¶
-
Function
MI_SYS initialization, before calling MI_SYS_Exit, you need to make sure that all other modules in the system have been de-initialized and that all VBPOOL has been Destroyed or the MI_SYS_Exit will return to failure.
-
Syntax
MI_S32 MI_SYS_Exit (MI_U16 u16SocId);
-
Parameters
Parameter Name Description Input/Output u16SocId Specify the target Soc for this operation Input -
Return
-
0 Successful.
-
!0 Failed, please refer to the error code.
-
-
Dependency
-
Head file: mi_sys_datatype.h / mi_sys.h
-
Library files: libmi_sys.a / libmi_sys.so
-
-
Note
-
MI_SYS_Exit Before calling, make sure that all other modules in the system have been deinitialized.
-
MI_SYS_Exit Before calling, you need to make sure that all created VBPOOL in the system has been successfully destroyed.
-
-
Sample
Refer to the
Samplein MI_SYS_init. -
Related topics
2.3.3. MI_SYS_GetVersion¶
-
Function
Get the system version number of MI.
-
Syntax
MI_S32 MI_SYS_GetVersion (MI_U16 u16SocId, MI_SYS_Version_t *pstVersion);
-
Parameters
Parameter Name Description Input/Output u16SocId Specify the target Soc for this operation Input pstVersion System version number returns data structure pointer Output -
Return
-
0 Successful.
-
!0 Failed, please refer to the error code.
-
-
Dependency
-
Head file: mi_sys_datatype.h / mi_sys.h
-
Library files: libmi_sys.a / libmi_sys.so
-
-
Sample
Refer to the
Samplein MI_SYS_init.
2.3.4. MI_SYS_GetCurPts¶
-
Function
Get the current timestamp of the MI system.
-
Syntax
MI_S32 MI_SYS_GetCurPts (MI_U16 u16SocId, MI_U64 *pu64Pts);
-
Parameters
Parameter Name Description Input/Output u16SocId Specify the target Soc for this operation Input pu64Pts The system's current timestamp returns address Output -
Return
-
0 Successful.
-
!0 Failed, please refer to the error code.
-
-
Dependency
-
Head file: mi_sys_datatype.h / mi_sys.h
-
Library files: libmi_sys.a / libmi_sys.so
-
-
Sample
Refer to the
Samplein MI_SYS_init.
2.3.5. MI_SYS_InitPtsBase¶
-
Function
Initializing MI System Baseline Timestamp.
-
Syntax
MI_S32 MI_SYS_InitPtsBase (MI_U16 u16SocId, MI_U64 u64PtsBase);
-
Parameters
Parameter Name Description Input/Output u16SocId Specify the target Soc for this operation Input u64PtsBase Set system timestamp baseline Input -
Return
-
0 Successful.
-
!0 Failed, please refer to the error code.
-
-
Dependency
-
Head file: mi_sys_datatype.h / mi_sys.h
-
Library files: libmi_sys.a / libmi_sys.so
-
-
Sample
Refer to the
Samplein MI_SYS_init.
2.3.6. MI_SYS_SyncPts¶
-
Function
Synchronized MI system timestamp.
-
Syntax
MI_S32 MI_SYS_SyncPts (MI_U16 u16SocId, MI_U64 u64Pts);
-
Parameters
Parameter Name Description Input/Output u16SocId Specify the target Soc for this operation Input u64Pts Fine-tuned system timestamp baseline Input -
Return
-
0 Successful.
-
!0 Failed, please refer to the error code.
-
-
Dependency
-
Head file: mi_sys_datatype.h / mi_sys.h
-
Library files: libmi_sys.a / libmi_sys.so
-
-
Sample
Refer to the
Samplein MI_SYS_init.
2.3.7. MI_SYS_SetReg¶
-
Function
Set the value of the register.
-
Syntax
MI_S32 MI_SYS_SetReg (MI_U16 u16SocId, MI_U32 u32RegAddr, MI_U16 u16Value,MI_U16 u16Mask);
-
Parameters
Parameter Name Description Input/Output u16SocId Specify the target Soc for this operation Input u32RegAddr Register Bus Address Input u16Value 16bit register value to be written Input u16Mask This time the Mask ingests the bar for the register value Input -
Return
-
0 Successful.
-
!0 Failed, please refer to the error code.
-
-
Dependency
-
Head file: mi_sys_datatype.h / mi_sys.h
-
Library files: libmi_sys.a / libmi_sys.so
-
2.3.8. MI_SYS_GetReg¶
-
Function
Get the value of the register, debug with.
-
Syntax
MI_S32 MI_SYS_GetReg (MI_U16 u16SocId, MI_U32 u32RegAddr, MI_U16 *pu16Value);
-
Parameters
Parameter Name Description Input/Output u16SocId Specify the target Soc for this operation Input u32RegAddr Register Bus Address Input pu16Value To read back to 16bit register value return address Output -
Return
-
0 Successful.
-
!0 Failed, please refer to the error code.
-
-
Dependency
-
Head file: mi_sys_datatype.h / mi_sys.h
-
Library files: libmi_sys.a / libmi_sys.so
-
2.3.9. MI_SYS_ReadUuid¶
-
Function
Get Chip's Unique ID.
-
Syntax
MI_S32 MI_SYS_ReadUuid (MI_U16 u16SocId, MI_U64 *u64Uuid);
-
Parameters
Parameter Name Description Input/Output u16SocId Specify the target Soc for this operation Input u64Uuid Get a pointer to the chip unique ID value Output -
Return
-
0 Successful.
-
!0 Failed, please refer to the error code.
-
-
Dependency
-
Head file: mi_sys_datatype.h / mi_sys.h
-
Library files: libmi_sys.a / libmi_sys.so
-
-
Sample
Refer to the
Samplein MI_SYS_init.
2.3.10. MI_SYS_EnableChnOutputPortLowLatency¶
-
Function
Enable or disable output port low latency.
-
Syntax
MI_S32 MI_SYS_EnableChnOutputPortLowLatency(MI_U16 u16SocId, MI_SYS_ChnPort_t *pstChnPort,MI_BOOL bEnable , MI_U32 u32Param);
-
Parameters
Parameter Name Parameter meaning Input/Output u16SocId Specify the target Soc for this operation Input pstChnPort A pointer to the output port of the module channel Input bEnable TRUE: enable; FALSE: disable, in default. Input u32Param Low Latency parameter, which is determined by specific modules. It is used to configure the Line Count. The buffer of frame is sent to user or backward once the count of lines is written, instead of waiting for the whole frame done. Input -
Return
-
0 Successful.
-
!0 Failed, please refer to the error code.
-
-
Dependency
-
Head file: mi_sys_datatype.h / mi_sys.h
-
Library files: libmi_sys.a / libmi_sys.so
-
-
Note
When bEnable is true, u32Param must be greater than 0; otherwise the setting is invalid.
-
Sample
MI_SYS_ChnPort_t stChnPort; MI_U16 u16SocId = ST_DEFAULT_SOC_ID; stChnPort.eModId = E_MI_MODULE_ID_ISP; stChnPort.u32DevId = 0; stChnPort.u32ChnId = 0; stChnPort.u32PortId = 0; MI_SYS_EnableChnOutputPortLowLatency(u16SocId, &stChnPort,TRUE , 100); MI_SYS_EnableChnOutputPortLowLatency(u16SocId, &stChnPort,FALSE , 0);
2.4. Data flow class API¶
2.4.1. MI_SYS_BindChnPort¶
-
Function
Binding of the data source Output port to the data receiver Input port.
-
Syntax
MI_S32 MI_SYS_BindChnPort(MI_U16 u16SocId, MI_SYS_ChnPort_t *pstSrcChnPort, MI_SYS_ChnPort_t *pstDstChnPort,MI_U32 u32SrcFrmrate, MI_U32 u32DstFrmrate, MI_SYS_BindType_e eBindType, MI_U32 u32BindParam)
-
Parameters
Parameter Name Parameter meaning Input/Output u16SocId Specify the target Soc for this operation Input pstSrcChnPort A pointer to the source port configuration information data structure Input pstDstChnPort A pointer to the destination configuration information data structure Input u32SrcFrmrate Frame rate of source port configuration Input u32DstFrmrate Frame rate of destination port configuration Input eBindType For the operating modes of the connection between the source port and the destination port, please refer to the MI_SYS_BindType_e Input u32BindParam Additional parameters to be brought in for different operating modes Input -
Return
-
0 Successful.
-
!0 Failed, please refer to the error code.
-
-
Dependency
-
Head file: mi_sys_datatype.h / mi_sys.h
-
Library files: libmi_sys.a / libmi_sys.so
-
-
Note
-
The source port must be a channel Output port.
-
The destination port must be a channel Input port.
-
The same source port can be bound to multiple destination ports.
-
The same destination port can only be bound to one source port and it must have not been bound before.
-
MI_SYS_BindChnPort can be called multiple times when pstSrcChnPort, pstDstChnPort and eBindType are the same to reset u32SrcFrmrate and u32DstFrmrate that need to be modified. User can also modify u32SrcFrmrate and u32DstFrmrate through MI_SYS_SetChnInputPortFrc.
-
The old version of this function prototype declaration was different from the current version.
-
The usage scenarios of eBindType and u32BindParam are as follows.
eBindType Applicable Scenario E_MI_SYS_BIND_TYPE_SW_LOW_LATENCY u32BindParam represents low latency value, unit: ms E_MI_SYS_BIND_TYPE_HW_RING In the chip before Maruko, u32BindParam represents ring buffer depth, currently only vpe and venc (h264/h265) support this mode, only one channel.
In Maruko and later chips, u32BindParam is not used yet.E_MI_SYS_BIND_TYPE_REALTIME u32BindParam unused. Used scene: jpe imi, only support one channel; vif->isp, support one channel; isp->scl, support multiple channels E_MI_SYS_BIND_TYPE_FRAME_BASE u32BindParam unused. Use this frame mode by default. -
The frame rate control Strategy of MI_SYS_BindChnPort is E_MI_SYS_FRC_STRATEGY_BY_PERIOD by default. If MI_SYS_SetChnInputPortFrc has been called to set other frame rate control Strategy, this strategy will be overwritten.
-
-
Sample
MI_SYS_ChnPort_t stSrcChnPort; MI_SYS_ChnPort_t stDstChnPort; MI_U32 u32SrcFrmrate; MI_U32 u32DstFrmrate; MI_SYS_BindType_e eBindType; MI_U32 u32BindParam; MI_U16 u16SocId = ST_DEFAULT_SOC_ID; // a. When the type of connection between ISP and VENC is E_MI_SYS_BIND_TYPE_FRAME_BASE, the code is as follows: stSrcChnPort.eModId = E_MI_MODULE_ID_ISP; stSrcChnPort.u32DevId = 0; stSrcChnPort.u32ChnId = 0; stSrcChnPort.u32PortId = 0; stDstChnPort.eModId = E_MI_MODULE_ID_VENC; stDstChnPort.u32DevId = 0; stDstChnPort.u32ChnId = 0; stDstChnPort.u32PortId = 0; u32SrcFrmrate = 30; u32DstFrmrate = 30; eBindType = E_MI_SYS_BIND_TYPE_FRAME_BASE; u32BindParam = 0; STCHECKRESULT(MI_SYS_BindChnPort(u16SocId, &stSrcChnPort, &stDstChnPort, u32SrcFrmrate, u32DstFrmrate, eBindType, u32BindParam)); // b. When the type of connection between ISP and VENC is E_MI_SYS_BIND_TYPE_REALTIME, the code is as follows: stSrcChnPort.eModId = E_MI_MODULE_ID_ISP; stSrcChnPort.u32DevId = 0; stSrcChnPort.u32ChnId = 0; stSrcChnPort.u32PortId = 0; stDstChnPort.eModId = E_MI_MODULE_ID_VENC; stDstChnPort.u32DevId = 1; stDstChnPort.u32ChnId = 0; stDstChnPort.u32PortId = 0; u32SrcFrmrate = 30; u32DstFrmrate = 30; eBindType = E_MI_SYS_BIND_TYPE_REALTIME; u32BindParam = 0; STCHECKRESULT(MI_SYS_BindChnPort(u16SocId, &stSrcChnPort, &stDstChnPort, u32SrcFrmrate, u32DstFrmrate, eBindType, u32BindParam)); // c. When the type of connection between ISP and VENC is E_MI_SYS_BIND_TYPE_HW_RING, the code is as follows: tSrcChnPort.eModId = E_MI_MODULE_ID_ISP; stSrcChnPort.u32DevId = 0; stSrcChnPort.u32ChnId = 0; stSrcChnPort.u32PortId = 0; stDstChnPort.eModId = E_MI_MODULE_ID_VENC; stDstChnPort.u32DevId = 0; stDstChnPort.u32ChnId = 0; stDstChnPort.u32PortId = 0; u32SrcFrmrate = 30; u32DstFrmrate = 30; eBindType = E_MI_SYS_BIND_TYPE_HW_RING; u32BindParam = 1080;//Suppose ISP output resolution is 1920*1080, and ring buffer depth is 1080 STCHECKRESULT(MI_SYS_BindChnPort(u16SocId, &stSrcChnPort, &stDstChnPort, u32SrcFrmrate, u32DstFrmrate, eBindType, u32BindParam));
-
Related topics
2.4.2. MI_SYS_BindChnPort2¶
-
Function
Binding of the data source Output port to the data receiver Input port requires additional operating mode.
-
Syntax
#define MI_SYS_BindChnPort2 MI_SYS_BindChnPort
-
Parameters
Same as MI_SYS_BindChnPort
-
Return
-
0 Successful.
-
!0 Failed, please refer to the error code.
-
-
Dependency
-
Head file: mi_sys_datatype.h / mi_sys.h
-
Library files: libmi_sys.a / libmi_sys.so
-
-
Note
-
The source port must be a channel Output port.
-
The destination port must be a channel Input port.
-
The same source port can be bound to multiple destination ports.
-
The same destination port can only be bound to one source port and it must have not been bound before.
-
MI_SYS_BindChnPort2 can be called multiple times when pstSrcChnPort, pstDstChnPort and eBindType are the same to reset u32SrcFrmrate and u32DstFrmrate that need to be modified. User can also modify u32SrcFrmrate and u32DstFrmrate through MI_SYS_SetChnInputPortFrc.
-
The old version did not provide this interface. If the interface is not found, there is no need to set it.
-
The usage scenarios of eBindType and u32BindParam are as follows.
eBindType Applicable Scenario E_MI_SYS_BIND_TYPE_SW_LOW_LATENCY u32 Bind Param represents low latency value, unit: ms E_MI_SYS_BIND_TYPE_HW_RING In the chip before Maruko, u32BindParam represents ring buffer depth, currently only vpe and venc (h264/h265) support this mode, only one channel.
In Maruko and later chips, u32BindParam is not used yet.E_MI_SYS_BIND_TYPE_REALTIME u32BindParam unused. Used scene: jpe imi, only support one channel; vif->isp, support one channel; isp->scl, support multiple channels E_MI_SYS_BIND_TYPE_FRAME_BASE u32BindParam unused. Use this frame mode by default. -
The frame rate control Strategy of MI_SYS_BindChnPort2 is E_MI_SYS_FRC_STRATEGY_BY_PERIOD by default. If MI_SYS_SetChnInputPortFrc has been called to set other frame rate control Strategy, this strategy will be overwritten.
-
-
Sample
Same as MI_SYS_BindChnPort
-
Related topics
2.4.3. MI_SYS_UnBind_ChnPort¶
-
Function
De-binding between the data source Output port to the data receiver Input port.
-
Syntax
MI_S32 MI_SYS_UnBindChnPort(MI_U16 u16SocId, MI_SYS_ChnPort_t *pstSrcChnPort, *pstDstChnPort);
-
Parameters
Parameter Name Description Input/Output u16SocId Specify the target Soc for this operation Input pstSrcChnPort The source port configures the information data structure pointer. Input pstDstChnPort The destination port configures the information data structure pointer. Input -
Return
-
0 Successful.
-
!0 Failed, please refer to the error code.
-
-
Dependency
-
Head file: mi_sys_datatype.h / mi_sys.h
-
Library files: libmi_sys.a / libmi_sys.so
-
-
Note
-
The source port must be a channel Output port.
-
The destination port must be a channel Input port.
-
The source and destination ports must have been bound before.
-
-
Related topics
2.4.4. MI_SYS_GetBindbyDest¶
-
Function
Query the corresponding source Output port for the data recipient Input port.
-
Syntax
MI_S32 MI_SYS_GetBindbyDest (MI_U16 u16SocId, MI_SYS_ChnPort_t *pstDstChnPort, *pstSrcChnPort, MI_SYS_BindType_e *peBindType);
-
Parameters
Parameter Name Description Input/Output u16SocId Specify the target Soc for this operation Input pstSrcChnPort The source port configures the information data structure pointer. Input pstDstChnPort The destination port configures the information data structure pointer. Input -
Return
-
0 Successful.
-
!0 Failed, please refer to the error code.
-
-
Dependency
-
Head file: mi_sys_datatype.h / mi_sys.h
-
Library files: libmi_sys.a / libmi_sys.so
-
-
Note
-
The destination port must be a channel Input port.
-
The target port must have been bound before.
-
2.4.5. MI_SYS_ChnInputPortGetBuf¶
-
Function
The buf object corresponding to the allocation channel input port.
-
Syntax
MI_S32 MI_SYS_ChnInputPortGetBuf (MI_SYS_ChnPort_tMI_SYS_ChnPort_t *pstChnPort,MI_SYS_BufConf_t *pstBufConf, MI_SYS_BufInfo_tMI_SYS_BufInfo_t *pstBufInfo, MI_SYS_BUF_HANDLE *phHandle , MI_S32 s32TimeOutMs);
-
Parameters
Parameter Name Description Input/Output pstChnPort A pointer to the input port of the module channel Input pstBufConf Memory configuration information to be allocated Input pstPortBuf Return buf pointer Output phHandle Get the handle of input Port Buf Output s32TimeOutMs Milliseconds waiting for timeout, >=0 is the specific time; <0 is 20ms, which is the default value Input -
Return
-
0 Successful.
-
!0 Failed, please refer to the error code.
-
-
Dependency
-
Head file: mi_sys_datatype.h / mi_sys.h
-
Library files: libmi_sys.a / libmi_sys.so
-
-
Sample
MI_SYS_ChnPort_t stIspChnInput; MI_SYS_BUF_HANDLE hHandle = 0; MI_SYS_BufConf_t stBufConf; MI_SYS_BufInfo_t stBufInfo; MI_SYS_ChnPortFrcAttr_t stFrcAttr; struct timeval stTv; MI_U16 u16Width = 1920, u16Height = 1080; FILE *fp = NULL; memset(&stIspChnInput, 0x0, sizeof(MI_SYS_ChnPort_t)); memset(&stBufConf, 0x0, sizeof(MI_SYS_BufConf_t)); memset(&stBufInfo, 0x0, sizeof(MI_SYS_BufInfo_t)); stIspChnInput.eModId = E_MI_MODULE_ID_ISP; stIspChnInput.u32DevId = 0; stIspChnInput.u32ChnId = 0; stIspChnInput.u32PortId = 0; fp = fopen("/mnt/ispport0_1920x1080_pixel0_737.raw","rb"); if(fp == NULL) { printf("file %s open fail\n", "/mnt/ispport0_1920x1080_pixel0_737.raw"); return 0; } stFrcAttr. eType = E_MI_SYS_FRC_TYPE_USERINJECT; stFrcAttr. eStrategy = E_MI_SYS_FRC_STRATEGY_BY_RATIO; stFrcAttr. u32SrcFrameRate = 30; stFrcAttr. u32DstFrameRate = 15; if(MI_SUCCESS != MI_SYS_SetChnInputPortFrc(&stIspChnInput, &stFrcAttr)) { printf ("MI_SYS_SetChnInputPortFrc failed\n "); return 0; } while(1) { stBufConf.eBufType = E_MI_SYS_BUFDATA_FRAME; gettimeofday(&stTv, NULL); stBufConf.u64TargetPts = stTv.tv_sec*1000000 + stTv.tv_usec; stBufConf.stFrameCfg.eFormat = E_MI_SYS_PIXEL_FRAME_YUV422_YUYV; stBufConf.stFrameCfg.eFrameScanMode = E_MI_SYS_FRAME_SCAN_MODE_PROGRESSIVE; stBufConf.stFrameCfg.u16Width = u16Width; stBufConf.stFrameCfg.u16Height = u16Height; if(MI_SUCCESS == MI_SYS_ChnInputPortGetBuf(&stIspChnInput,&stBufConf,&stBufInfo,&hHandle,0)) { if(fread(stBufInfo.stFrameData.pVirAddr[0], u16Width*u16Height*2, 1, fp) <= 0) { fseek(fp, 0, SEEK_SET); } MI_SYS_ChnInputPortPutBuf(hHandle,&stBufInfo, FALSE); } } -
Related topics
2.4.6. MI_SYS_ChnInputPortPutBuf¶
-
Function
Add the buf object corresponding to the channel input port to the pending queue.
-
Syntax
MI_S32 MI_SYS_ChnInputPortPutBuf (MI_SYS_BUF_HANDLE hHandle, MI_SYS_BufInfo_tMI_SYS_BufInfo_t *pstBufInfo, MI_BOOL bDropBuf);
-
Parameters
Parameter Name Description Input/Output hHandle Current buf's Handle Input pstBufInfo Buf pointer to be submitted Input bDropBuf Whether to discard buf directly without submitting to the pending queue Input -
Return
-
0 Successful.
-
!0 Failed, please refer to the error code.
-
-
Dependency
-
Head file: mi_sys_datatype.h / mi_sys.h
-
Library files: libmi_sys.a / libmi_sys.so
-
-
Sample
Refer to the
samplein MI_SYS_ChnInputPortGetBuf. -
Related topics
2.4.7. MI_SYS_ChnOutputPortGetBuf¶
-
Function
The buf object corresponding to the allocation channel input port.
-
Syntax
MI_S32 MI_SYS_ChnOutputPortGetBuf (MI_SYS_ChnPort_tMI_SYS_ChnPort_t *pstChnPort, MI_SYS_BufInfo_t MI_SYS_BufInfo_t *pstBufInfo , MI_SYS_BUF_HANDLE *phHandle);
-
Parameters
Parameter Name Description Input/Output pstChnPort A pointer to the input port of the module channel Input pstBufInfo Return buf pointer Output phHandle Get the handle of outputPort Buf Output -
Return
-
0 Successful.
-
!0 Failed, please refer to the error code.
-
-
Dependency
-
Head file: mi_sys_datatype.h / mi_sys.h
-
Library files: libmi_sys.a / libmi_sys.so
-
-
Sample
MI_SYS_ChnPort_t stChnPort; MI_SYS_BufInfo_t stBufInfo; MI_SYS_BUF_HANDLE stBufHandle; MI_SYS_FrameBufExtraConfig_t stBufExtraConf = {0}; MI_S32 s32Ret = MI_SUCCESS; MI_S32 s32Fd = 0; fd_set read_fds; struct timeval TimeoutVal; char szFileName[128]; int fd = 0; MI_U32 u32GetFramesCount = 0; MI_BOOL _bWriteFile = TRUE; MI_U16 u16SocId = ST_DEFAULT_SOC_ID; stChnPort.eModId = E_MI_MODULE_ID_SCL; stChnPort.u32DevId = 0; stChnPort.u32ChnId = SCL_CHN_FOR_VDF; stChnPort.u32PortId = 0; s32Ret = MI_SYS_GetFd(&stChnPort, &s32Fd); if(MI_SUCCESS != s32Ret) { ST_ERR("MI_SYS_GetFd 0, error, %X\n", s32Ret); return NULL; } stBufExtraConf. u16BufHAlignment = 16; stBufExtraConf. u16BufVAlignment = 2; s32Ret = MI_SYS_SetChnOutputPortBufExtConf(&stChnPort, &stBufExtraConf); if (MI_SUCCESS != s32Ret) { ST_ERR("MI_SYS_SetChnOutputPortBufExtConf err:%x, chn:%d,port:%d\n", s32Ret, stChnPort.u32ChnId, stChnPort.u32PortId); return NULL; } s32Ret = MI_SYS_SetChnOutputPortUserFrc(&stChnPort, 30, 15); if (MI_SUCCESS != s32Ret) { ST_ERR("MI_SYS_ SetChnOutputPortUserFrc err:%x, chn:%d,port:%d\n", s32Ret, stChnPort.u32ChnId, stChnPort.u32PortId); return NULL; } sprintf(szFileName, "scl%d.es", stChnPort.u32ChnId); printf("start to record %s\n", szFileName); fd = open(szFileName, O_RDWR | O_CREAT | O_TRUNC, S_IRUSR | S_IWUSR | S_IRGRP | S_IROTH); if (fd < 0) { ST_ERR("create %s fail\n", szFileName); } while (1) { FD_ZERO(&read_fds); FD_SET(s32Fd, &read_fds); TimeoutVal.tv_sec = 1; TimeoutVal.tv_usec = 0; s32Ret = select(s32Fd + 1, &read_fds, NULL, NULL, &TimeoutVal); if(s32Ret < 0) { ST_ERR("select failed!\n"); // usleep(10 * 1000); continue; } else if(s32Ret == 0) { ST_ERR("get scl frame time out\n"); //usleep(10 * 1000); continue; } else { if(FD_ISSET(s32Fd, &read_fds)) { s32Ret = MI_SYS_ChnOutputPortGetBuf(&stChnPort, &stBufInfo, &stBufHandle); if(MI_SUCCESS != s32Ret) { //ST_ERR("MI_SYS_ChnOutputPortGetBuf err, %x\n", s32Ret); continue; } // save one Frame YUV data if (fd > 0) { if(_bWriteFile) { write(fd, stBufInfo.stFrameData.pVirAddr[0], stBufInfo.stFrameData.u16Height * stBufInfo.stFrameData.u32Stride[0] + stBufInfo.stFrameData.u16Height * stBufInfo.stFrameData.u32Stride[1] /2); } } ++u32GetFramesCount; printf("channelId[%u] u32GetFramesCount[%u]\n", stChnPort.u32ChnId, u32GetFramesCount); MI_SYS_ChnOutputPortPutBuf(stBufHandle); } } } if (fd > 0) { close(fd); fd = -1; } MI_SYS_SetChnOutputPortDepth(u16SocId, &stChnPort, 0, 3); printf("exit record\n"); return NULL; -
Related topics
2.4.8. MI_SYS_ChnOutputPortPutBuf¶
-
Function
Release channel output port corresponding to buf object.
-
Syntax
MI_S32 MI_SYS_ChnOutputPortPutBuf (MI_SYS_BUF_HANDLE hBufHandle);
-
Parameters
Parameter Name Description Input/Output hBufHandle Handle for buf to be submitted Input -
Return
-
0 Successful.
-
!0 Failed, please refer to the error code.
-
-
Dependency
-
Head file: mi_sys_datatype.h / mi_sys.h
-
Library files: libmi_sys.a / libmi_sys.so
-
-
Sample
Refer to the sample in MI_SYS_ChnOutputPortGetBuf.
-
Related topics
2.4.9. MI_SYS_ChnInputPortGetBufPa¶
-
Function
The buf object corresponding to the allocation channel input port, which only returns MIU physical address.
-
Syntax
MI_S32 MI_SYS_ChnInputPortGetBufPa (MI_SYS_ChnPort_tMI_SYS_ChnPort_t *pstChnPort,MI_SYS_BufConf_t *pstBufConf, MI_SYS_BufInfo_tMI_SYS_BufInfo_t *pstBufInfo, MI_SYS_BUF_HANDLE *phHandle , MI_S32 s32TimeOutMs);
-
Parameters
Parameter Name Description Input/Output pstChnPort A pointer to the input port of the module channel Input pstBufConf Configuration information of the memory to be allocated Input pstPortBuf Return buf pointer Output phHandle Get the handle of input Port Buf Output s32TimeOutMs Milliseconds waiting for timeout, >=0 is the specific time; <0 is 20ms, which is the default value Input -
Return
-
0 Successful.
-
!0 Failed, please refer to the error code.
-
-
Dependency
-
Head file: mi_sys_datatype.h / mi_sys.h
-
Library files: libmi_sys.a / libmi_sys.so
-
-
Note
The difference with MI_SYS_ChnInputPortGetBuf: Only phyAddr can be used in pstBufInfo obtained by MI_SYS_ChnInputPortGetBufPa, while phyAddr and pVirAddr in pstBufInfo obtained by MI_SYS_ChnInputPortGetBuf can be used.
-
Sample
MI_SYS_ChnPort_t stIspChnInput; MI_SYS_BUF_HANDLE hHandle = 0; MI_SYS_BufConf_t stBufConf; MI_SYS_BufInfo_t stBufInfo; struct timeval stTv; MI_U16 u16Width = 1920, u16Height = 1080; FILE *fp = NULL; void *pVirAddr = NULL; MI_U16 u16SocId = ST_DEFAULT_SOC_ID; memset(&stIspChnInput, 0x0, sizeof(MI_SYS_ChnPort_t)); memset(&stBufConf, 0x0, sizeof(MI_SYS_BufConf_t)); memset(&stBufInfo, 0x0, sizeof(MI_SYS_BufInfo_t)); stVpeChnInput.eModId = E_MI_MODULE_ID_ISP; stVpeChnInput.u32DevId = 0; stVpeChnInput.u32ChnId = 0; stVpeChnInput.u32PortId = 0; fp = fopen("/mnt/ispport0_1920x1080_pixel0_737.raw", "rb"); if (fp == NULL) { printf("file %s open fail\n", "/mnt/ispport0_1920x1080_pixel0_737.raw"); return 0; } while (1) { stBufConf.eBufType = E_MI_SYS_BUFDATA_FRAME; gettimeofday(&stTv, NULL); stBufConf.u64TargetPts = stTv.tv_sec * 1000000 + stTv.tv_usec; stBufConf.stFrameCfg.eFormat = E_MI_SYS_PIXEL_FRAME_YUV422_YUYV; stBufConf.stFrameCfg.eFrameScanMode = E_MI_SYS_FRAME_SCAN_MODE_PROGRESSIVE; stBufConf.stFrameCfg.u16Width = u16Width; stBufConf.stFrameCfg.u16Height = u16Height; if (MI_SUCCESS == MI_SYS_ChnInputPortGetBufPa(&stIspChnInput, &stBufConf, &stBufInfo, &hHandle, 0)) { pVirAddr = MI_SYS_Mmap(stBufInfo.stFrameData.phyAddr[0], stBufInfo.stFrameData.u32BufSize, &pVirAddr, TRUE); assert(pVirAddr); if (fread(pVirAddr, u16Width * u16Height * 2, 1, fp) <= 0) { fseek(fp, 0, SEEK_SET); } MI_SYS_Munmap(pVirAddr, stBufInfo.stFrameData.u32BufSize); MI_SYS_ChnInputPortPutBufPa(hHandle, &stBufInfo, FALSE); } } -
Related topics
2.4.10. MI_SYS_ChnInputPortPutBufPa¶
-
Function
Add the buf object corresponding to the channel input port to the pending queue, which needs to be used in pair with the function MI_SYS_ChnInputPortGetBufPa.
-
Syntax
MI_S32 MI_SYS_ChnInputPortPutBufPa (MI_SYS_BUF_HANDLE hHandle ,MI_SYS_BufInfo_t *pstPortBuf, MI_BOOL bDropBuf);
-
Parameters
Parameter Name Description Input/Output hHandle Current buf's Idr Handle Input pstPortBuf Buf pointer to be submitted Input bDropBuf Drop direct waiver of modifications to buf Input -
Return
-
0 Successful.
-
!0 Failed, please refer to the error code.
-
-
Dependency
-
Head file: mi_sys_datatype.h / mi_sys.h
-
Library files: libmi_sys.a / libmi_sys.so
-
-
Note
The difference with MI_SYS_ChnInputPortPutBuf: Only phyAddr can be used in pstBufInfo submitted by MI_SYS_ChnInputPortPutBufPa, while phyAddr and pVirAddr in pstBufInfo submitted by MI_SYS_ChnInputPortPutBuf can be used.
-
Sample
Please refer to the
samplein MI_SYS_ChnOutputPortGetBufPa -
Related topics
2.4.11. MI_SYS_ChnOutputPortGetBufPa¶
-
Function
The buf object corresponding to the allocation channel output port, which only returns MIU physical address.
-
Syntax
MI_S32 MI_SYS_ChnOutputPortGetBufPa (MI_SYS_ChnPort_tMI_SYS_ChnPort_t *pstChnPort, MI_SYS_BufInfo_t MI_SYS_BufInfo_t *pstBufInfo , MI_SYS_BUF_HANDLE *phHandle);
-
Parameters
Parameter Name Description Input/Output pstChnPort A pointer to the input port of the module channel Input pstBufInfo Return buf pointer Output phHandle Get the handle of outputPort Buf Output -
Return
-
0 Successful.
-
!0 Failed, please refer to the error code.
-
-
Dependency
-
Head file: mi_sys_datatype.h / mi_sys.h
-
Library files: libmi_sys.a / libmi_sys.so
-
-
Note
The difference with MI_SYS_ChnOutputPortGetBuf: Only phyAddr can be used in pstBufInfo obtained by MI_SYS_ChnOutputPortGetBufPa, while phyAddr and pVirAddr in pstBufInfo obtained by MI_SYS_ChnOutputPortGetBuf can be used.
-
Sample
MI_SYS_ChnPort_t stChnPort; MI_SYS_BufInfo_t stBufInfo; MI_SYS_BUF_HANDLE stBufHandle; MI_S32 s32Ret = MI_SUCCESS; MI_S32 s32Fd = 0; fd_set read_fds; struct timeval TimeoutVal; char szFileName[128]; int fd = 0; MI_U32 u32GetFramesCount = 0; MI_BOOL _bWriteFile = TRUE; void *pVirAddr = NULL; MI_U16 u16SocId = ST_DEFAULT_SOC_ID; stChnPort.eModId = E_MI_MODULE_ID_SCL; stChnPort.u32DevId = 0; stChnPort.u32ChnId = SCL_CHN_FOR_VDF; stChnPort.u32PortId = 0; s32Ret = MI_SYS_GetFd(&stChnPort, &s32Fd); if (MI_SUCCESS != s32Ret) { ST_ERR("MI_SYS_GetFd 0, error, %X\n", s32Ret); return NULL; } s32Ret = MI_SYS_SetChnOutputPortDepth(u16SocId, &stChnPort, 2, 3); if (MI_SUCCESS != s32Ret) { ST_ERR("MI_SYS_SetChnOutputPortDepth err:%x, chn:%d,port:%d\n", s32Ret, stChnPort.u32ChnId, stChnPort.u32PortId); return NULL; } sprintf(szFileName, "scl%d.es", stChnPort.u32ChnId); printf("start to record %s\n", szFileName); fd = open(szFileName, O_RDWR | O_CREAT | O_TRUNC, S_IRUSR | S_IWUSR | S_IRGRP | S_IROTH); if (fd < 0) { ST_ERR("create %s fail\n", szFileName); } while (1) { FD_ZERO(&read_fds); FD_SET(s32Fd, &read_fds); TimeoutVal.tv_sec = 1; TimeoutVal.tv_usec = 0; s32Ret = select(s32Fd + 1, &read_fds, NULL, NULL, &TimeoutVal); if (s32Ret < 0) { ST_ERR("select failed!\n"); // usleep(10 * 1000); continue; } else if (s32Ret == 0) { ST_ERR("get scl frame time out\n"); //usleep(10 * 1000); continue; } else { if (FD_ISSET(s32Fd, &read_fds)) { s32Ret = MI_SYS_ChnOutputPortGetBuf(&stChnPort, &stBufInfo, &stBufHandle); if (MI_SUCCESS != s32Ret) { //ST_ERR("MI_SYS_ChnOutputPortGetBuf err, %x\n", s32Ret); continue; } pVirAddr = MI_SYS_Mmap(stBufInfo.stFrameData.phyAddr[0], stBufInfo.stFrameData.u32BufSize, &pVirAddr, TRUE); assert(pVirAddr); // save one Frame YUV data if (fd > 0) { if (_bWriteFile) { write(fd, pVirAddr, stBufInfo.stFrameData.u16Height * stBufInfo.stFrameData.u32Stride[0] + stBufInfo.stFrameData.u16Height * stBufInfo.stFrameData.u32Stride[1] / 2); } } ++u32GetFramesCount; printf("channelId[%u] u32GetFramesCount[%u]\n", stChnPort.u32ChnId, u32GetFramesCount); MI_SYS_Munmap(pVirAddr, stBufInfo.stFrameData.u32BufSize); MI_SYS_ChnOutputPortPutBufPa(stBufHandle); } } } if (fd > 0) { close(fd); fd = -1; } MI_SYS_SetChnOutputPortDepth(u16SocId, &stChnPort, 0, 3); printf("exit record\n"); return NULL; -
Related topics
2.4.12. MI_SYS_ChnOutputPortPutBufPa¶
-
Function
Release channel output port corresponding to the buf object, which needs to be used in pair with the function MI_SYS_ChnOutputPortGetBufPa.
-
Syntax
MI_S32 MI_SYS_ChnOutputPortPutBufPa (MI_SYS_BUF_HANDLE hBufHandle);
-
Parameters
Parameter Name Description Input/Output hBufHandle Handle for buf to be submitted Input -
Return
-
0 Successful.
-
!0 Failed, please refer to the error code.
-
-
Dependency
-
Head file: mi_sys_datatype.h / mi_sys.h
-
Library files: libmi_sys.a / libmi_sys.so
-
-
Note
The difference with MI_SYS_ChnOutputPortPutBuf: Only phyAddr can be used in the pstBufInfo corresponding to the handle submitted by MI_SYS_ChnOutputPortPutBufPa, and both phyAddr and pVirAddr in the pstBufInfo corresponding to the handle submitted by MI_SYS_ChnOutputPortPutBuf can be used.
-
Sample
Please refer to the sample in MI_SYS_ChnOutputPortGetBufPa
-
Related topics
2.4.13. MI_SYS_SetChnOutputPortDepth¶
-
Function
Set the number of system bufs corresponding to the channel output port and the number of bufs that users can get.
-
Syntax
MI_S32 MI_SYS_SetChnOutputPortDepth(MI_U16 u16SocId, MI_SYS_ChnPort_tMI_SYS_ChnPort_t *pstChnPort, MI_U32 u32UserFrameDepth, MI_U32 u32BufQueueDepth);
-
Parameters
Parameter Name Description Input/Output u16SocId Specify the target Soc for this operation Input pstChnPort A pointer to the output port of the module channel Input u32UserFrameDepth Set the maximum number of buf that the output user can get Input u32BufQueueDepth Set the maximum number of buf for this output system Input -
Return
-
0 Successful.
-
!0 Failed, please refer to the error code.
-
-
Dependency
-
Head file: mi_sys_datatype.h / mi_sys.h
-
Library files: libmi_sys.a / libmi_sys.so
-
-
Note
-
u32UserFrameDepth defaults to 0, u32BufQueueDepth defaults to 4.
-
After using OutputPortBuf (MI_SYS_ChnOutputPortGetBuf / MI_SYS_ChnOutputPortPutBuf no longer need to be called), it is recommended to set u32UserFrameDepth to 0, which can reduce the buffers of output buf and save memory.
-
u32UserFrameDepth must be less than or equal to u32BufQueueDepth.
-
When u32UserFrameDepth is equal to u32BufQueueDepth and the number of user fifo queue buffers is equal to u32BufQueueDepth, the current output port will stop working.
-
When the output port is not bound to the later stage, to make the current output port work, u32UserFrameDepth must be set greater than 0.
-
If the output port is bound by realtime mode or ring mode, the u32UserFrameDepth of the current output port must be set to 0.
-
For other restrictions, please refer to vif/isp/scl/venc/jpd API.
-
-
Sample
Please refer to the
samplein MI_SYS_ChnOutputPortGetBuf
2.4.14. MI_SYS_ChnPortInjectBuf¶
-
Function
Plug the acquired output Port buf into the specified input Port Buf Queue.
-
Syntax
MI_S32 MI_SYS_ChnPortInjectBuf(MI_SYS_BUF_HANDLE hHandle, *pstChnPort);
-
Parameters
Parameter Name Description Input/Output hHandle Obtained outputPort Buf handle Input pstChnPort A pointer to the input port of the module channel Input -
Return
-
0 Successful.
-
!0 Failed, please refer to the error code.
-
-
Dependency
-
Head file: mi_sys_datatype.h / mi_sys.h
-
Library files: libmi_sys.a / libmi_sys.so
-
-
Note
After calling MI_SYS_ChnPortInjectBuf, user can no longer display the release handle.
-
Sample
Please refer to the
samplein MI_SYS_ChnOutputPortGetBuf -
Related topics
2.4.15. MI_SYS_GetFd¶
-
Function
Get the file Description Number for the current output Port waiting-up event.
-
Syntax
MI_S32 MI_SYS_GetFd(MI_SYS_ChnPort_tMI_SYS_ChnPort_t *pstChnPort, MI_S32 *ps32Fd);
-
Parameters
Parameter Name Description Input/Output pstChnPort Port information structure pointer Input ps32Fd File Description for waiting for event Output -
Return
-
0 Successful.
-
!0 Failed, please refer to the error code.
-
-
Dependency
-
Head file: mi_sys_datatype.h / mi_sys.h
-
Library files: libmi_sys.a / libmi_sys.so
-
-
Note
-
Need to be used in pairs with MI_SYS_CloseFd.
-
It is recommended to use the fd + select to extract the data, so that the MI_SYS only enable thread when the corresponding port has data, the efficiency is more efficient than use while + sleep loop to take data.
-
-
Sample
Please refer to the
samplein MI_SYS_ChnOutputPortGetBuf -
Related topics
2.4.16. MI_SYS_CloseFd¶
-
Function
File Description Number to close the current output Port.
-
Syntax
MI_S32 MI_SYS_CloseFd(MI_S32 s32ChnPortFd);
-
Parameters
Parameter Name Description Input/Output s32ChnPortFd File Description Members for waiting for event Input -
Return
-
0 Successful.
-
!0 Failed, please refer to the error code.
-
-
Dependency
-
Head file: mi_sys_datatype.h / mi_sys.h
-
Library files: libmi_sys.a / libmi_sys.so
-
-
Sample
Please refer to the
samplein MI_SYS_ChnOutputPortGetBuf -
Related topics
2.4.17. MI_SYS_DupBuf¶
-
Function
Duplicate buf object.
-
Syntax
MI_S32 MI_SYS_DupBuf (MI_SYS_BUF_HANDLE srcBufHandle , MI_SYS_BUF_HANDLE *pDupTargetBufHandle);
-
Parameters
Parameter Name Description Input/Output srcBufHandle Source buf object Input pDupTargetBufHandle Return buf object pointer Output -
Return
-
0 Successful.
-
!0 Failed, please refer to the error code.
-
-
Dependency
-
Head file: mi_sys_datatype.h / mi_sys.h
-
Library files: libmi_sys.a / libmi_sys.so
-
-
Sample
int test0() { MI_SYS_ChnPort_t stChnPort; MI_SYS_BufInfo_t stBufInfo; MI_SYS_BUF_HANDLE bufHandle ,DupTargetBufHandle; MI_S32 s32Ret; stChnPort.eModId = E_MI_MODULE_ID_ISP; stChnPort.u32DevId = 0; stChnPort.u32ChnId = 0; stChnPort.u32PortId = 0; s32Ret = MI_SYS_ChnOutputPortGetBuf (&stChnPort,&stBufInfo,&bufHandle); if(s32Ret != MI_SUCCESS) return 0; s32Ret = MI_SYS_DupBuf(bufHandle, &DupTargetBufHandle); if(s32Ret != MI_SUCCESS) { MI_SYS_ChnOutputPortPutBuf(bufHandle); return 0; } stChnPort.eModId = E_MI_MODULE_ID_SCL; stChnPort.u32DevId = 0; stChnPort.u32ChnId = 0; stChnPort.u32PortId = 0; MI_SYS_ChnPortInjectBuf(DupTargetBufHandle , &stChnPort); *************************** continue to use the stBufInfo *************************** MI_SYS_ChnOutputPortPutBuf(bufHandle); return 1; } int test1() { MI_SYS_ChnPort_t stChnPort; MI_SYS_BufInfo_t stBufInfo; MI_SYS_BufConf_t stBufConf; MI_SYS_BUF_HANDLE bufHandle ,DupTargetBufHandle; MI_S32 s32Ret; stChnPort.eModId = E_MI_MODULE_ID_SCL; stChnPort.u32DevId = 0; stChnPort.u32ChnId = 0; stChnPort.u32PortId = 0; memset(&stBufConf , 0 , sizeof(stBufConf)); stBufConf.eBufType = E_MI_SYS_BUFDATA_FRAME; stBufConf.stFrameCfg.eFormat = E_MI_SYS_PIXEL_FRAME_YUV_SEMIPLANAR_422; stBufConf.stFrameCfg.u16Height = 1080; stBufConf.stFrameCfg.u16Width = 1920; stBufConf.stFrameCfg.eFrameScanMode = E_MI_SYS_FRAME_SCAN_MODE_PROGRESSIVE; s32Ret = MI_SYS_ChnInputPortGetBuf (&stChnPort,&stBufConf,&stBufInfo,&bufHandle ,0); if(s32Ret != MI_SUCCESS) return 0; *************************** Fill stBufInfo *************************** s32Ret = MI_SYS_DupBuf(bufHandle, &DupTargetBufHandle); if(s32Ret != MI_SUCCESS) { MI_SYS_ChnInputPortPutBuf(bufHandle); return 0; } MI_SYS_ChnInputPortPutBuf(DupTargetBufHandle , & stChnPort , FALSE); *************************** continue to use the stBufInfo *************************** return 1; } -
Related topics
2.4.18. MI_SYS_ChnInputPortSetUserPicture¶
-
Function
According to the set frame rate, the buf will be repeatedly input to the current input port and add to the waiting queue.
-
Syntax
MI_SYS_ChnInputPortSetUserPicture(MI_SYS_BUF_HANDLE BufHandle , MI_SYS_BufInfo_t *pstBufInfo, MI_SYS_UserPictureInfo_t *pstUserPictureInfo);
-
Parameters
Parameter Name Description Input/Output BufHandle Current buf's Handle Input pstBufInfo Buf pointer to be submitted Input pstUserPictureInfo Pointer for setting frame rate information to the driver Input -
Return
-
0 Successful.
-
!0 Failed, please refer to the error code.
-
-
Dependency
-
Head file: mi_sys_datatype.h / mi_sys.h
-
Library files: libmi_sys.a / libmi_sys.so
-
-
Note
The Input port for enable user picture cannot be bound and needs to be enabled.
-
Sample
int test0() { MI_SYS_ChnPort_t stChnPort; MI_SYS_BufConf_t stBufConf; MI_SYS_BufInfo_t stBufInfo; MI_SYS_BUF_HANDLE bufHandle; MI_SYS_UserPictureInfo_t stUserPictureInfo; memset(&stChnPort , 0 , sizeof(stChnPort)); memset(&stBufConf, 0 , sizeof(stBufConf)); memset(&stBufInfo, 0 , sizeof(stBufInfo)); stChnPort.eModId = E_MI_MODULE_ID_ISP; stChnPort.u32DevId = 0; stChnPort.u32ChnId = 0; stChnPort.u32PortId =0; stBufConf.eBufType = E_MI_SYS_BUFDATA_FRAME; stBufConf.stFrameCfg.u16Width = 1920; stBufConf.stFrameCfg.u16Height = 1080; stBufConf.stFrameCfg.eFormat = E_MI_SYS_PIXEL_FRAME_YUV422_YUYV; MI_SYS_ChnInputPortGetBuf(&stChnPort , & stBufConf , & stBufInfo , & bufHandle , 100); /*************************** Fill the stBufInfo with data ***************************/ stUserPictureInfo.u32SrcFrc = 30;// 30 frames per second MI_SYS_ChnInputPortSetUserPicture( bufHandle , & stBufInfo , & stUserPictureInfo); MI_SYS_EnableUserPicture(bufHandle); …… …… …… MI_SYS_DisableUserPicture(bufHandle); return 0; } -
Related topics
2.4.19. MI_SYS_EnableUserPicture¶
-
Function
Enable user picture.
-
Syntax
MI_S32 MI_SYS_EnableUserPicture(MI_SYS_BUF_HANDLE BufHandle);
-
Parameters
Parameter Name Description Input/Output BufHandle Handle of bufinfo set to the driver through MI_SYS_ChnInputPortSetUserPicture Input -
Return
-
0 Successful.
-
!0 Failed, please refer to the error code.
-
-
Dependency
-
Head file: mi_sys_datatype.h / mi_sys.h
-
Library files: libmi_sys.a / libmi_sys.so
-
-
Sample
Please refer to the
samplein MI_SYS_ChnInputPortSetUserPicture -
Related topics
2.4.20. MI_SYS_DisableUserPicture¶
-
Function
Turn off user picture function and release buf.
-
Syntax
MI_S32 MI_SYS_DisableUserPicture(MI_SYS_BUF_HANDLE BufHandle);
-
Parameters
Parameter Name Description Input/Output BufHandle Handle of bufinfo set to the driver through MI_SYS_ChnInputPortSetUserPicture Input -
Return
-
0 Successful.
-
!0 Failed, please refer to the error code.
-
-
Dependency
-
Head file: mi_sys_datatype.h / mi_sys.h
-
Library files: libmi_sys.a / libmi_sys.so
-
-
Sample
Please refer to the
samplein MI_SYS_ChnInputPortSetUserPicture -
Related topics
2.4.21. MI_SYS_SetChnOutputPortUserFrc¶
-
Function
Set buf framerate of output port.
-
Syntax
MI_S32 MI_SYS_SetChnOutputPortUserFrc((MI_SYS_ChnPort_t *pstChnPort, MI_U32 u32SrcFrmrate, MI_U32 u32DstFrmrate);
-
Parameters
Parameter Name Description Input/Output pstChnPort Port information structure pointer Input u32SrcFrmrate Source buf framerate of OutPutPort Input u32DstFrmrate OutputPort buf framerate Input -
Return
-
0 Successful.
-
!0 Failed, please refer to the error code.
-
-
Dependency
-
Head file: mi_sys_datatype.h / mi_sys.h
-
Library files: libmi_sys.a / libmi_sys.so
-
-
Sample
Please refer to the
samplein MI_SYS_ChnOutputPortGetBuf -
Related topics
2.4.22. MI_SYS_SetChnOutputPortBufExtConf¶
-
Function
Set the alignment of outputBuf.
-
Syntax
MI_S32 MI_SYS_SetChnOutputPortBufExtConf(MI_SYS_ChnPort_t *pstChnPort, MI_SYS_FrameBufExtraConfig_t *pstBufExtraConf);
-
Parameters
Parameter Name Description Input/Output pstChnPort Port information structure pointer Input pstBufExtraConf OutPutPort Buf alignment paramter structure pointer Input -
Return
-
0 Successful.
-
!0 Failed, please refer to the error code.
-
-
Dependency
-
Head file: mi_sys_datatype.h, mi_sys.h
-
Library files: libmi_sys.a / libmi_sys.so
-
-
Note
-
U16BufHAlignment must be aligned to 16.
-
To cancel user Settings, set u16BufHAlignment and u16BufVAlignment to 0, and set the user Settings to call the interface again.
-
-
Sample
Please refer to the
samplein MI_SYS_ChnOutputPortGetBuf -
Related topics
2.4.23. MI_SYS_SetChnInputPortFrc¶
-
Function
Set the InputPort input frame rate.
-
Syntax
MI_S32 MI_SYS_SetChnInputPortFrc(MI_SYS_ChnPort_t *pstChnPort, MI_SYS_ChnPortFrcAttr_t *pstFrcAttr);
-
Parameters
Parameter Name Description Input/Output pstChnPort Port information structure pointer Input pstFrcAttr Buf framerate paramter structure pointer Input -
Return
-
0 Successful.
-
!0 Failed, please refer to the error code.
-
-
Dependency
-
Head file: mi_sys_datatype.h, mi_sys.h
-
Library files: libmi_sys.a / libmi_sys.so
-
-
Note
-
This interface will overwrite its default Frc strategy when invoked after MI_SYS_BindChnPort2.
-
Before setting the Frc type to E_MI_SYS_FRC_TYPE_USERINJECT, please ensure that InputPort is not bound to any other OutputPort.
-
-
Sample
Please refer to the
samplein MI_SYS_ChnOutputPortGetBuf -
Related topics
2.4.24. MI_SYS_QueryDevChnPortState¶
-
Function
Query the status of Dev/Chn/Port, whether Chn/Port is enabled and Dev has been created. When the status of Dev/Chn is queried, Chn/Port id of pstChnPort need to be set to -1.
-
Syntax
MI_S32 MI_SYS_QueryDevChnPortState(MI_SYS_ChnPort_t *pstChnPort, MI_BOOL bIsInputPort, MI_SYS_ChnPortState_t *pstState);
-
Parameters
Parameter Name Description Input/Output pstChnPort Port information structure pointer Input bIsInputPort Whether it is Input Port Input pstState Whether Chn/Port is enabled and Dev has been created Output -
Return
-
0 Chn/Port is enabled and Dev has been created.
-
!0 Failed, please refer to the error code.
-
-
Related topics
2.4.25. MI_SYS_CreateChnInputPortDmabufCusAllocator¶
-
Function
Create a linux shared dma buffers manager for input port to implement the input port as an linux dma-buf importer.
-
Syntax
MI_S32 MI_SYS_CreateChnInputPortDmabufCusAllocator(MI_SYS_ChnPort_t *pstChnPort);
-
Parameters
Parameter Name Description Input/Output pstChnPort Port information structure pointer Input -
Return
-
0 Successful.
-
!0 Failed, please refer to the error code.
-
-
Dependency
-
Head file: mi_sys_datatype.h, mi_sys.h
-
Library files: libmi_sys.a / libmi_sys.so
-
-
Note
- This function is only available on linux system, and the linux kernel requires the CONFIG_DMABUF_HEAPS option to be enabled
-
Sample
MI_SYS_DmaBufInfo_t * alloc_dmabuf(int dev_fd, MI_U32 u32Width, MI_U32 u32Height, MI_SYS_PixelFormat_e eFormat) { MI_SYS_DmaBufInfo_t *pstDmaBufInfo = NULL; dma_heap_allocation_data data = { .len = 0, .fd = 0, .fd_flags = 2, .heap_flags = 0, }; pstDmaBufInfo = malloc(sizeof(MI_SYS_DmaBufInfo_t)); if(pstDmaBufInfo) { data.len = u32Width * u32Height * 4; s32Ret = ioctl(dev_fd, DMA_HEAP_IOCTL_ALLOC, &data); if(data.fd <= 0) { DBG_ERR("failed, alloc dma-buf return fail"); free(pstDmaBufInfo); return NULL; } memset(&stDmaBufInfo, 0, sizeof(MI_SYS_DmaBufInfo_t)); stDmaBufInfo.s32Fd[0] = data.fd; stDmaBufInfo.s32Fd[1] = data.fd; stDmaBufInfo.u16Width = u32Width; stDmaBufInfo.u16Height = u32Height; stDmaBufInfo.u32Stride[0] = u32Width; stDmaBufInfo.u32Stride[1] = stDmaBufInfo.u32Stride[0]; stDmaBufInfo.eFormat = eFormat; MI_SYS_GetCurPts(0, &stDmaBufInfo.u64Pts); } return pstDmaBufInfo; } MI_S32 free_dmabuf(MI_SYS_DmaBufInfo_t *pstDmaBufInfo) { if(pstDmaBufInfo) { close(pstDmaBufInfo->s32Fd[0]); free(pstDmaBufInfo); } return MI_SUCCESS; } int main(int argc, char *argv[]) { MI_SYS_ChnPort_t stChnPort; MI_SYS_DmaBufInfo_t *pstDmaBufInfo = NULL; MI_U32 u32Width = 1920; MI_U32 u32Height = 10280; MI_SYS_PixelFormat_e eFormat = E_MI_SYS_PIXEL_FRAME_ARGB8888; MI_U32 datalen = u32Width * u32Height * 4; void *pVaddr = NULL; MI_S32 fd = -1; fd = open("/dev/mma", O_RDWR); if (fd <= 0) { DBG_ERR("failed, open /dev/mma return fail\n"); return -1; } memset(&stChnPort, 0, sizeof(MI_SYS_ChnPort_t)); stChnPort.eModId = E_MI_MODULE_ID_OS; stChnPort.u32DevId = 0; stChnPort.u32ChnId = 0; stChnPort.u32PortId = 0; s32Ret = MI_SYS_CreateChnInputPortDmabufCusAllocator(&stChnPort); if (MI_SUCCESS != s32Ret) { DBG_ERR("failed, create input port dma-buf heap return fail\n"); goto CLOSE_FD; } s32Ret = MI_SYS_CreateChnOutputPortDmabufCusAllocator(&stChnPort); if (MI_SUCCESS != s32Ret) { DBG_ERR("failed, create output port dma-buf heap return fail\n"); goto DESTROY_1; } pstDmaBufInfo = alloc_dmabuf(fd, u32Width, u32Height, eFormat); if(!pstDmaBufInfo) { DBG_ERR("alloc dmabuf failed\n") goto DESTROY_2; } pVaddr = mmap(NULL, datalen, PROT_WRITE|PROT_READ, MAP_SHARED, pstDmaBufInfo->s32Fd[0], 0); if(!pVaddr) { DBG_ERR("failed, mmap dma-buf return fail"); free_dmabuf(pstDmaBufInfo); goto DESTROY_2; } memset(pVaddr, 0xFE, datalen); s32Ret = MI_SYS_ChnInputPortEnqueueDmabuf(&stChnPort, pstDmaBufInfo); if (MI_SUCCESS != s32Ret) { DBG_ERR("failed, enqueue dma-buf return fail\n"); free_dmabuf(pstDmaBufInfo); } else { usleep(30*1000); s32Ret = MI_SYS_ChnInputPortDequeueDmabuf(&stChnPort, pstDmaBufInfo); if (MI_SUCCESS != s32Ret) { DBG_ERR("failed, dequeue dma-buf return fail\n"); } free_dmabuf(pstDmaBufInfo); } pstDmaBufInfo = alloc_dmabuf(fd, u32Width, u32Height, eFormat); if(!pstDmaBufInfo) { DBG_ERR("alloc dmabuf failed\n") goto DESTROY_2; } pVaddr = mmap(NULL, datalen, PROT_WRITE|PROT_READ, MAP_SHARED, pstDmaBufInfo->s32Fd[0], 0); if(!pVaddr) { DBG_ERR("failed, mmap dma-buf return fail"); free_dmabuf(pstDmaBufInfo); goto DESTROY_2; } memset(pVaddr, 0x7F, datalen); s32Ret = MI_SYS_ChnOutputPortEnqueueDmabuf(&stChnPort, pstDmaBufInfo); if (MI_SUCCESS != s32Ret) { DBG_ERR("failed, enqueue dma-buf return fail\n"); free_dmabuf(pstDmaBufInfo); } else { usleep(30*1000); s32Ret = MI_SYS_ChnOutputPortDequeueDmabuf(&stChnPort, pstDmaBufInfo); if (MI_SUCCESS != s32Ret) { DBG_ERR("failed, dequeue dma-buf return fail\n"); s32Ret = MI_SYS_ChnOutputPortDropDmabuf(&stChnPort, pstDmaBufInfo); if(MI_SUCCESS != s32Ret) { DBG_ERR("failed, drop dma-buf return fail\n"); } } free_dmabuf(pstDmaBufInfo); } MI_PHY phyAddr = 0; s32Ret = MI_SYS_GetDmaBuf(pstDmaBufInfo->s32Fd[0], &phyAddr); if (MI_SUCCESS != s32Ret) { DBG_ERR("failed, MI_SYS_GetDmaBuf return fail\n"); goto DESTROY_2; } s32Ret = MI_SYS_PutDmaBuf(phyAddr); if (MI_SUCCESS != s32Ret) { DBG_ERR("failed, MI_SYS_PutDmaBuf return fail\n"); goto DESTROY_2; } DESTROY_2: MI_SYS_DestroyChnOutputPortDmabufCusAllocator(&stChnPort); DESTROY_1: MI_SYS_DestroyChnInputPortDmabufCusAllocator(&stChnPort); CLOSE_FD: close(fd); } return 0; -
Related topics
MI_SYS_DestroyChnInputPortDmabufCusAllocator
2.4.26. MI_SYS_DestroyChnInputPortDmabufCusAllocator¶
-
Function
Destroy the linux shared dma buffers manager of input port.
-
Syntax
MI_S32 MI_SYS_DestroyChnInputPortDmabufCusAllocator(MI_SYS_ChnPort_t *pstChnPort);
-
Parameters
Parameter Name Description Input/Output pstChnPort Port information structure pointer Input -
Return
-
0 Successful.
-
!0 Failed, please refer to the error code.
-
-
Dependency
-
Head file: mi_sys_datatype.h, mi_sys.h
-
Library files: libmi_sys.a / libmi_sys.so
-
-
Note
- This function is only available on linux system, and the linux kernel requires the CONFIG_DMABUF_HEAPS option to be enabled
-
Sample
Please refer to the
samplein MI_SYS_CreateChnInputPortDmabufCusAllocator -
Related topics
MI_SYS_CreateChnInputPortDmabufCusAllocator
2.4.27. MI_SYS_ChnInputPortEnqueueDmabuf¶
-
Function
Enqueue a linux dma-buf to input port.
-
Syntax
MI_S32 MI_SYS_ChnInputPortEnqueueDmabuf(MI_SYS_ChnPort_t *pstChnPort, MI_SYS_DmaBufInfo_t *pstDmaBufInfo);
-
Parameters
Parameter Name Description Input/Output pstChnPort Port information structure pointer Input pstDmaBufInfo The linux dma-buf information data structure pointer Input -
Return
-
0 Successful.
-
!0 Failed, please refer to the error code.
-
-
Dependency
-
Head file: mi_sys_datatype.h, mi_sys.h
-
Library files: libmi_sys.a / libmi_sys.so
-
-
Note
- This function is only available on linux system, and the linux kernel requires the CONFIG_DMABUF_HEAPS option to be enabled
-
Sample
Please refer to the
samplein MI_SYS_CreateChnInputPortDmabufCusAllocator -
Related topics
MI_SYS_CreateChnInputPortDmabufCusAllocator
2.4.28. MI_SYS_ChnInputPortDequeueDmabuf¶
-
Function
Dequeue a finished linux dma-buf from input port.
-
Syntax
MI_S32 MI_SYS_ChnInputPortDequeueDmabuf(MI_SYS_ChnPort_t *pstChnPort, MI_SYS_DmaBufInfo_t *pstDmaBufInfo);
-
Parameters
Parameter Name Description Input/Output pstChnPort Port information structure pointer Input pstDmaBufInfo The linux dma-buf information data structure pointer Output -
Return
-
0 Successful.
-
!0 Failed, please refer to the error code.
-
-
Dependency
-
Head file: mi_sys_datatype.h, mi_sys.h
-
Library files: libmi_sys.a / libmi_sys.so
-
-
Note
- This function is only available on linux system, and the linux kernel requires the CONFIG_DMABUF_HEAPS option to be enabled
-
Sample
Please refer to the
samplein MI_SYS_CreateChnInputPortDmabufCusAllocator -
Related topics
MI_SYS_CreateChnInputPortDmabufCusAllocator
2.4.29. MI_SYS_CreateChnOutputPortDmabufCusAllocator¶
-
Function
Create a linux shared dma buffers manager for output port to implement the output port as an linux dma-buf importer.
-
Syntax
MI_S32 MI_SYS_CreateChnOutputPortDmabufCusAllocator(MI_SYS_ChnPort_t *pstChnPort);
-
Parameters
Parameter Name Description Input/Output pstChnPort Port information structure pointer Input -
Return
-
0 Successful.
-
!0 Failed, please refer to the error code.
-
-
Dependency
-
Head file: mi_sys_datatype.h, mi_sys.h
-
Library files: libmi_sys.a / libmi_sys.so
-
-
Note
- This function is only available on linux system, and the linux kernel requires the CONFIG_DMABUF_HEAPS option to be enabled
-
Sample
Please refer to the
samplein MI_SYS_CreateChnInputPortDmabufCusAllocator -
Related topics
MI_SYS_DestroyChnOutputPortDmabufCusAllocator
MI_SYS_ChnOutputPortEnqueueDmabuf
2.4.30. MI_SYS_DestroyChnOutputPortDmabufCusAllocator¶
-
Function
Destroy the linux shared dma buffers manager of output port.
-
Syntax
MI_S32 MI_SYS_DestroyChnOutputPortDmabufCusAllocator(MI_SYS_ChnPort_t *pstChnPort);
-
Parameters
Parameter Name Description Input/Output pstChnPort Port information structure pointer Input -
Return
-
0 Successful.
-
!0 Failed, please refer to the error code.
-
-
Dependency
-
Head file: mi_sys_datatype.h, mi_sys.h
-
Library files: libmi_sys.a / libmi_sys.so
-
-
Note
- This function is only available on linux system, and the linux kernel requires the CONFIG_DMABUF_HEAPS option to be enabled
-
Sample
Please refer to the
samplein MI_SYS_CreateChnInputPortDmabufCusAllocator -
Related topics
MI_SYS_CreateChnOutputPortDmabufCusAllocator
MI_SYS_ChnOutputPortEnqueueDmabuf
2.4.31. MI_SYS_ChnOutputPortEnqueueDmabuf¶
-
Function
Enqueue a linux dma-buf to output port.
-
Syntax
MI_S32 MI_SYS_ChnOutputPortEnqueueDmabuf(MI_SYS_ChnPort_t *pstChnPort, MI_SYS_DmaBufInfo_t *pstDmaBufInfo);
-
Parameters
Parameter Name Description Input/Output pstChnPort Port information structure pointer Input pstDmaBufInfo The linux dma-buf information data structure pointer Input -
Return
-
0 Successful.
-
!0 Failed, please refer to the error code.
-
-
Dependency
-
Head file: mi_sys_datatype.h, mi_sys.h
-
Library files: libmi_sys.a / libmi_sys.so
-
-
Note
- This function is only available on linux system, and the linux kernel requires the CONFIG_DMABUF_HEAPS option to be enabled
-
Sample
Please refer to the
samplein MI_SYS_CreateChnInputPortDmabufCusAllocator -
Related topics
MI_SYS_CreateChnOutputPortDmabufCusAllocator
MI_SYS_DestroyChnOutputPortDmabufCusAllocator
2.4.32. MI_SYS_ChnOutputPortDequeueDmabuf¶
-
Function
Dequeue a finished linux dma-buf from output port.
-
Syntax
MI_S32 MI_SYS_ChnOutputPortDequeueDmabuf(MI_SYS_ChnPort_t *pstChnPort, MI_SYS_DmaBufInfo_t *pstDmaBufInfo);
-
Parameters
Parameter Name Description Input/Output pstChnPort Port information structure pointer Input pstDmaBufInfo The linux dma-buf information data structure pointer Output -
Return
-
0 Successful.
-
!0 Failed, please refer to the error code.
-
-
Dependency
-
Head file: mi_sys_datatype.h, mi_sys.h
-
Library files: libmi_sys.a / libmi_sys.so
-
-
Note
- This function is only available on linux system, and the linux kernel requires the CONFIG_DMABUF_HEAPS option to be enabled
-
Sample
Please refer to the
samplein MI_SYS_CreateChnInputPortDmabufCusAllocator -
Related topics
MI_SYS_CreateChnOutputPortDmabufCusAllocator
MI_SYS_DestroyChnOutputPortDmabufCusAllocator
2.4.33. MI_SYS_ChnOutputPortDropDmabuf¶
-
Function
Drop a specific linux dma-buf from output port.
-
Syntax
MI_S32 MI_SYS_ChnOutputPortDropDmabuf(MI_SYS_ChnPort_t *pstChnPort, MI_SYS_DmaBufInfo_t *pstDmaBufInfo);
-
Parameters
Parameter Name Description Input/Output pstChnPort Port information structure pointer Input pstDmaBufInfo The linux dma-buf information data structure pointer Input -
Return
-
0 Successful.
-
!0 Failed, please refer to the error code.
-
-
Dependency
-
Head file: mi_sys_datatype.h, mi_sys.h
-
Library files: libmi_sys.a / libmi_sys.so
-
-
Note
- This function is only available on linux system, and the linux kernel requires the CONFIG_DMABUF_HEAPS option to be enabled
-
Sample
Please refer to the
samplein MI_SYS_CreateChnInputPortDmabufCusAllocator -
Related topics
MI_SYS_CreateChnOutputPortDmabufCusAllocator
MI_SYS_DestroyChnOutputPortDmabufCusAllocator
2.4.34. MI_SYS_GetDmaBuf¶
-
Function
Get the physical address from dmabuf fd. This will increase the reference count of dmabuf fd, so it should be released by MI_SYS_PutDmaBuf to decrease the reference count of dmabuf fd.
-
Syntax
MI_S32 MI_SYS_GetDmaBuf(MI_S32 s32Fd, MI_PHY *pPhyAddr);
-
Parameters
Parameter Name Description Input/Output s32Fd A linux dmabuf fd Input pPhyAddr The corresponding physical address of input dmabuf fd Output -
Return
-
0 Successful.
-
!0 Failed, please refer to the error code.
-
-
Dependency
-
Head file: mi_sys_datatype.h, mi_sys.h
-
Library files: libmi_sys.a / libmi_sys.so
-
-
Note
- This function is only available on linux system, and the linux kernel requires the CONFIG_DMABUF_HEAPS option to be enabled
-
Sample
Please refer to the
samplein MI_SYS_CreateChnInputPortDmabufCusAllocator -
Related topics
2.4.35. MI_SYS_PutDmaBuf¶
-
Function
Release the physical address returned from MI_SYS_GetDmaBuf.
-
Syntax
MI_S32 MI_SYS_PutDmaBuf(MI_PHY phyAddr);
-
Parameters
Parameter Name Description Input/Output phyAddr The physical address returned from MI_SYS_GetDmaBuf Input -
Return
-
0 Successful.
-
!0 Failed, please refer to the error code.
-
-
Dependency
-
Head file: mi_sys_datatype.h, mi_sys.h
-
Library files: libmi_sys.a / libmi_sys.so
-
-
Note
- This function is only available on linux system, and the linux kernel requires the CONFIG_DMABUF_HEAPS option to be enabled
-
Sample
Please refer to the
samplein MI_SYS_CreateChnInputPortDmabufCusAllocator -
Related topics
2.4.36. MI_SYS_GetSidebandData¶
-
Function
Get the side band data of the image, such as the frame ID
-
Syntax
MI_S32 MI_SYS_GetSidebandData(MI_SYS_BUF_HANDLE handle, MI_U32 u32DataType, MI_SYS_SidebandData_t *pstSidebandData)
-
Parameters
Parameter Name Description Input/Output bufHandle bufHandle returned by MI_SYS_ChnOutputPortGetBuf()/MI_SYS_ChnInputPortGetBuf() Input u32DataType Data type Input pstSidebandData The pointer that points to MI_SYS_SidebandData_t Input -
Return
-
0 Successful.
-
!0 Failed, please refer to the error code.
-
-
Dependency
-
Head file: mi_sys_datatype.h, mi_sys.h
-
Library files: libmi_sys.a / libmi_sys.so
-
-
Note
-
User must call MI_SYS_GetSidebandData() before calling MI_SYS_ChnOutputPortPutBuf(). Otherwise, the API will return error.
-
The value of u32DataType can be:
Parameter Value Description Memory Size MI_SYS_SIDEBAND_DATA_FRAMEID Get the frame id of an image sizeof(MI_U32) MI_SYS_SIDEBAND_DATA_AEINFO Get the AE Info of an image with only one sensor sizeof(mi_SYS_SidebandData_AeInfo_t)
-
-
Sample
MI_S32 s32Ret = MI_SUCCESS; MI_SYS_ChnPort_t stChnPort; MI_SYS_BufInfo_t stBufInfo; MI_SYS_BUF_HANDLE stBufHandle; MI_SYS_SidebandData_t stSideband; MI_SYS_SidebandData_AeInfo_t stAeInfo; MI_U32 frame_id = 0; stChnPort.eModId = E_MI_MODULE_ID_ISP; stChnPort.u32DevId = 0; stChnPort.u32ChnId = 0; stChnPort.u32PortId = 0; s32Ret = MI_SYS_ChnOutputPortGetBuf(&stChnPort, &stBufInfo,&stBufHandle); if(MI_SUCCESS != s32Ret) { return; } stSideband.pVirAddr = &frame_id; stSideband.u32Size = sizeof(frame_id); s32Ret = MI_SYS_GetSidebandData(stBufHandle, MI_SYS_SIDEBAND_DATA_FRAMEID, &stSideband); if(MI_SUCCESS != s32Ret) { printf("error 0x%x\n", s32Ret); return; } printf("frame id:%d\n", frame_id); stSideband.pVirAddr = &stAeInfo; stSideband.u32Size = sizeof(stAeInfo); S32Ret = MI_SYS_GetSidebandData(stBufHandle, MI_SYS_SIDEBAND_DATA_AEINFO, &stSideband); if (MI_SUCCESS != s32Ret) { printf("error 0x%x\n", s32Ret); return; } printf("ae info gain:%d, shutter:%d ispgain:%d sensor id:%d\n", stAeInfo.u32SnrGain, stAeInfo.u32Shutter, \ stAeInfo.u32IspGain, StAeInfo.u8SnrId); MI_SYS_ChnOutputPortPutBuf(stBufHandle);
2.5. Memory Management Class API¶
2.5.1. MI_SYS_SetChnMMAConf¶
-
Function
Set the MMA pool name of the module device channel Output default allocation memory.
-
Syntax
MI_S32 MI_SYS_SetChnMMAConf (MI_U16 u16SocId, MI_ModuleId_e eModId, MI_U32 u32DevId, MI_U32 u32ChnId, MI_U8 *pu8MMAHeapName);
-
Parameters
Parameter Name Description Input/Output u16SocId Specify the target Soc for this operation Input eModId Module ID to be configured Input u32DevId Device ID to be configured Input u32ChnId Channel number to be configured Input pu8MMAHeapName Set MMA heap name Input -
Return
-
0 Successful.
-
!0 Failed, please refer to the error code.
-
-
Dependency
-
Head file: mi_sys_datatype.h / mi_sys.h
-
Library files: libmi_sys.a / libmi_sys.so
-
-
Note
If MI_SYS_SetChnMMAConf setting is not called or the pu8MMAHeapName value is set to NULL, the default mma_heap_name0 is used.
-
Sample
MI_ModuleId_e eVifModeId = E_MI_MODULE_ID_VIF; MI_VIF_DEV vifDev = 0; MI_VIF_CHN vifChn = 0; MI_U16 u16SocId = ST_DEFAULT_SOC_ID; MI_SYS_SetChnMMAConf(u16SocId, eVifModeId, vifDev, vifChn, "mma_heap_name0");
2.5.2. MI_SYS_GetChnMMAConf¶
-
Function
Get the MMA pool name of the module device channel Output port's default allocated memory.
-
Syntax
MI_S32 MI_SYS_GetChnMMAConf (u16SocId, MI_ModuleId_e eModId, MI_U32 u32DevId, MI_U32 u32ChnId, void *pu8MMAHeapName, MI_U32 u32Length);
-
Parameters
Parameter Name Description Input/Output u16SocId Specify the target Soc for this operation Input eModId Module ID to be configured Input u32DevId Device ID to be configured Input u32ChnId Channel number to be configured Input pu8MMAHeapName MMA heap name to be abtained Output u32Length Length of the memory pointed by pu8MMAHeapName, the max 64Byte Input -
Return
-
0 Successful.
-
!0 Failed, please refer to the error code.
-
-
Dependency
-
Head file: mi_sys_datatype.h / mi_sys.h
-
Library files: libmi_sys.a / libmi_sys.so
-
-
Related topics
2.5.3. MI_SYS_MMA_Alloc¶
-
Function
Request the allocation of memory directly to the MMA Memory Manager.
-
Syntax
MI_S32 MI_SYS_MMA_Alloc(MI_U16 u16SocId, MI_U8 *pstMMAHeapName, MI_U32 u32BlkSize ,MI_PHY *phyAddr);
-
Parameters
Parameter Name Description Input/Output u16SocId Specify the target Soc for this operation Input pstMMAHeapName Target MMA heapname Input u32BlkSize The size of the block byte to sedated Input phyAddr Physical address of memory block returned Output -
Return
-
0 Successful.
-
!0 Failed, please refer to the error code.
-
-
Dependency
-
Head file: mi_sys_datatype.h / mi_sys.h
-
Library files: libmi_sys.a / libmi_sys.so
-
-
Note
-
Allocated from the default heap, when pstMMAHeapName is NULL.
-
u32BlkSize recommends aligning 64Byte, as the flush cache line is 64Byte.
-
The phyAddr system has ensured 64 byte alignment. If you need to offset phyAddr again, you also need to align it with 64Byte.
-
-
Sample
MI_PHY phySrcBufAddr = 0; void *pVirSrcBufAddr = NULL; MI_U32 srcBuffSize = 1920 * 1980 * 3 / 2; MI_U16 u16SocId = ST_DEFAULT_SOC_ID; srcBuffSize = ALIGN_UP(srcBuffSize, 64); ret = MI_SYS_MMA_Alloc(u16SocId, NULL, srcBuffSize, &phySrcBufAddr); if(ret != MI_SUCCESS) { printf("alloc src buff failed\n"); return -1; } ret = MI_SYS_Mmap(phySrcBufAddr, srcBuffSize, &pVirSrcBufAddr, TRUE); if(ret != MI_SUCCESS) { MI_SYS_MMA_Free(u16SocId, phySrcBufAddr); printf("mmap src buff failed\n"); return -1; } memset(pVirSrcBufAddr, 0, srcBuffSize); MI_SYS_FlushInvCache(pVirSrcBufAddr,srcBuffSize); MI_SYS_Munmap(pVirSrcBufAddr, srcBuffSize); MI_SYS_MMA_Free(u16SocId, phySrcBufAddr); -
Related topics
2.5.4. MI_SYS_MMA_Free¶
-
Function
Memory allocated before being released directly to mmA Memory Manager.
-
Syntax
MI_S32 MI_SYS_MMA_Free(MI_U16 u16SocId, MI_U64 phyAddr);
-
Parameters
Parameter Name Description Input/Output u16SocId Specify the target Soc for this operation Input phyAddr Physical address of memory to be freed Input -
Return
-
0 Successful.
-
!0 Failed, please refer to the error code.
-
-
Dependency
-
Head file: mi_sys_datatype.h / mi_sys.h
-
Library files: libmi_sys.a / libmi_sys.so
-
-
Sample
Please refer to the
samplein MI_SYS_MMA_Alloc -
Related topics
2.5.5. MI_SYS_Mmap¶
-
Function
Mapping any physical memory to the CPU virtual address space for the current user-state process.
-
Syntax
MI_S32 MI_SYS_Mmap(MI_U64 u64PhyAddr, MI_U32 u32Size, void **ppVirtualAddress, MI_BOOL bCache);
-
Parameters
Parameter Name Description Input/Output u64PhyAddr Physical address to be mapped Input u32Size The length of the physical address to be mapped Input ppVirtualAddress Pointer to store the CPU virtual address pointer Output bCache Whether map into cache or un-cache Input -
Return
-
0 Successful.
-
!0 Failed, please refer to the error code.
-
-
Dependency
-
Head file: mi_sys_datatype.h / mi_sys.h
-
Library files: libmi_sys.a / libmi_sys.so
-
-
Note
-
The physical address is the SStar memory controller address.
-
The physical address is recommended to be 64Byte aligned.
-
The physical address length is recommended to be 64Byte aligned.
-
Physical memory must fall completely outside the memory range managed by MMA or from the memory managed by Linux kernel
-
-
Sample
Please refer to the
samplein MI_SYS_MMA_Alloc -
Related topics
2.5.6. MI_SYS_FlushInvCache¶
-
Function
Flush cache.
-
Syntax
MI_S32 MI_SYS_FlushInvCache(MI_VOID *pVirtualAddress, MI_U32 u32Size);
-
Parameters
Parameter Name Description Input/Output pVirtualAddress Previously MI_SYS_Mmap returned CPU virtual address Input u32Size The length of the cache to be flush Input -
Return
-
0 Successful.
-
!0 Failed, please refer to the error code.
-
-
Dependency
-
Head file: mi_sys_datatype.h / mi_sys.h
-
Library files: libmi_sys.a / libmi_sys.so
-
-
Note
-
The physical address to flush cache is recommended to be 64Byte aligned.
-
The mapping length to flush cache is recommended to be 64Byte aligned.
-
The map memory range to flush cache must be previously obtained through the MI_SYS_Mmap API.
-
The mapping memory for flush cache should be MI_SYS_Mmap in the way of cache, nocache way without flush cache.
-
-
Sample
Please refer to the
samplein MI_SYS_MMA_Alloc -
Related topics
2.5.7. MI_SYS_Munmap¶
-
Function
Cancel the mapping of physical memory to the virtual address..
-
Syntax
MI_S32 MI_SYS_Munmap(MI_VOID *pVirtualAddress, MI_U32 u32Size);
-
Parameters
Parameter Name Description Input/Output pVirtualAddress Previously MI_SYS_Mmap returned CPU virtual address Input u32Size The length of the map to be unmapped Input -
Return
-
0 Successful.
-
!0 Failed, please refer to the error code.
-
-
Dependency
-
Head file: mi_sys_datatype.h / mi_sys.h
-
Library files: libmi_sys.a / libmi_sys.so
-
-
Note
-
The virtual address to be unmapped is recommended to be 64Byte aligned.
-
The mapping length to be unmapped is recommended to be 64Byte aligned.
-
The range of mapped memory to be canceled must be previously obtained through the MI_SYS_Mmap API.
-
-
Sample
Please refer to the
samplein MI_SYS_MMA_Alloc -
Related topics
2.5.8. MI_SYS_MemsetPa¶
-
Function
Fill the entire physical memory with the DMA hardware module.
-
Syntax
MI_S32 MI_SYS_MemsetPa(MI_U16 u16SocId, MI_PHY phyPa, MI_U32 u32Val, MI_U32 u32Lenth);
-
Parameters
Parameter Name Description Input/Output u16SocId Specify the target Soc for this operation Input phyPa The physical address of the padding Input u32Val Fill value of 4bytes size Input u32Lenth Fill size, in byte Input -
Return
-
0 Successful.
-
!0 Failed, please refer to the error code.
-
-
Dependency
-
Head file: mi_sys_datatype.h / mi_sys.h
-
Library files: libmi_sys.a / libmi_sys.so
-
-
Sample
MI_PHY phySrcBufAddr = 0; MI_PHY phyDstBufAddr = 0; void *pVirSrcBufAddr = NULL; void *pVirDstBufAddr = NULL; MI_U32 buffSize = 1920 * 1980 * 3 / 2; MI_U16 u16SocId = ST_DEFAULT_SOC_ID; buffSize = ALIGN_UP(buffSize, 4096); ret = MI_SYS_MMA_Alloc(u16SocId, NULL, buffSize, &phySrcBufAddr); if(ret != MI_SUCCESS) { printf("alloc src buff failed\n"); return -1; } ret = MI_SYS_MMA_Alloc(u16SocId, NULL, buffSize, &phyDstBufAddr); if(ret != MI_SUCCESS) { MI_SYS_MMA_Free(u16SocId, phySrcBufAddr); printf("alloc dts buff failed\n"); return -1; } MI_SYS_MemsetPa(u16SocId, phySrcBufAddr, 0xffffffff, buffSize); MI_SYS_MemsetPa(u16SocId, phyDstBufAddr, 0x00, buffSize); MI_SYS_MemcpyPa(u16SocId, phyDstBufAddr, phySrcBufAddr, buffSize); MI_SYS_MMA_Free(u16SocId, phySrcBufAddr); MI_SYS_MMA_Free(u16SocId, phyDstBufAddr); -
Related topics
2.5.9. MI_SYS_MemcpyPa¶
-
Function
Copy the source memory data to the target memory via the DMA hardware module.
-
Syntax
MI_S32 MI_SYS_MemcpyPa(MI_U6 u16SocId, MI_PHY phyDst, MI_PHY phySrc, MI_U32 u32Lenth);
-
Parameters
Parameter Name Description Input/Output u16SocId Specify the target Soc for this operation Input phyDst Destination physical address Input phySrc Source physical address Input u32Lenth Copy size, in byte Input -
Return
-
0 Successful.
-
!0 Failed, please refer to the error code.
-
-
Dependency
-
Head file: mi_sys_datatype.h / mi_sys.h
-
Library files: libmi_sys.a / libmi_sys.so
-
-
Sample
Please refer to the
samplein MI_SYS_MemsetPa -
Related topics
2.5.10. MI_SYS_BufFillPa¶
-
Function
Fill some of the physical memory with the DMA hardware module.
-
Syntax
MI_S32 MI_SYS_BufFillPa(MI_U16 u16SocId, MI_SYS_FrameData_t *pstBuf, MI_U32 u32Val, MI_SYS_WindowRect_t *pstRect);
-
Parameters
Parameter Name Description Input/Output u16SocId Specify the target Soc for this operation Input pstBuf The structure of the filled frame data Description Input u32Val Fill value Input pstRect The extent of the data populated Input -
Return
-
0 Successful.
-
!0 Failed, please refer to the error code.
-
-
Dependency
-
Head file: mi_sys_datatype.h / mi_sys.h
-
Library files: libmi_sys.a / libmi_sys.so
-
The meanings of bits in u32Val are different as the format changes:
Format Parameter Description E_MI_SYS_PIXEL_FRAME_YUV_SEMIPLANAR_422
E_MI_SYS_PIXEL_FRAME_YUV_SEMIPLANAR_420
E_MI_SYS_PIXEL_FRAME_YUV_SEMIPLANAR_420_NV21
E_MI_SYS_PIXEL_FRAME_YUV422_PLANAR
E_MI_SYS_PIXEL_FRAME_YUV420_PLANARBit 0-7: V
Bit 8-15: Y
Bit 16-23: UE_MI_SYS_PIXEL_FRAME_YUV422_YUYV
E_MI_SYS_PIXEL_FRAME_YUV422_UYVY
E_MI_SYS_PIXEL_FRAME_YUV422_YVYU
E_MI_SYS_PIXEL_FRAME_YUV422_VYUY
E_MI_SYS_PIXEL_FRAME_ARGB8888
E_MI_SYS_PIXEL_FRAME_ABGR8888All bits are valid E_MI_SYS_PIXEL_FRAME_ARGB1555
E_MI_SYS_PIXEL_FRAME_ARGB4444
E_MI_SYS_PIXEL_FRAME_RGB565
E_MI_SYS_DATA_PRECISION_16BPPThe lowest 16 bits are valid E_MI_SYS_PIXEL_FRAME_RGB888
E_MI_SYS_PIXEL_FRAME_BGR888The lowest 24 bits are valid E_MI_SYS_DATA_PRECISION_8BPP
E_MI_SYS_PIXEL_FRAME_I8The lowest 8 bits are valid E_MI_SYS_DATA_PRECISION_10BPP The lowest 10 bits are valid E_MI_SYS_DATA_PRECISION_12BPP The lowest 12 bits are valid E_MI_SYS_DATA_PRECISION_14BPP The lowest 14 bits are valid E_MI_SYS_PIXEL_FRAME_I2 The lowest 2 bits are valid E_MI_SYS_PIXEL_FRAME_I4 The lowest 4 bits are valid
-
-
Note
-
The pstRect data range is based on the first address of the pstBuf Description as the first address (0, 0), and the width and height are partially filled with the ePixel Format in pstBuf to calculate the size of the memory data moved by each pixel.
-
PstBuf in u16Width, u16 Height, phyAddr, u32Stride, ePixelFormat is required, the rest of the value is meaningless.
-
-
Sample
MI_S32 ret = 0; MI_SYS_WindowRect_t rect; MI_SYS_FrameData_t stSysFrame; MI_U16 u16SocId = ST_DEFAULT_SOC_ID; memcpy(&stSysFrame, &buf->stFrameData, sizeof(MI_SYS_FrameData_t)); if(pRect) { rect.u16X = pRect->left; rect.u16Y = pRect->top; rect.u16Height = pRect->bottom-pRect->top; rect.u16Width = pRect->right-pRect->left; } else { rect.u16X = 0; rect.u16Y = 0; rect.u16Height = stSysFrame.u16Height; rect.u16Width = stSysFrame.u16Width; } DBG_INFO("rect %d %d %d %d \n", rect.u16X, rect.u16Y , rect.u16Width, rect.u16Height); ret = MI_SYS_ BufFillPa(u16SocId, &stSysFrame, u32ColorVal, &rect); return ret; -
Related topics
2.5.11. MI_SYS_BufBlitPa¶
-
Function
Copy parts of the source memory data to parts of the target memory through the DMA hardware module.
-
Syntax
MI_S32 MI_SYS_BufBlitPa(MI_U16 u16SocId, MI_SYS_FrameData_t *pstDstBuf, MI_SYS_WindowRect_t *pstDstRect, MI_SYS_FrameData_t *pstSrcBuf, MI_SYS_WindowRect_t *pstSrcRect);
-
Parameters
Parameter Name Description Input/Output u16SocId Specify the target Soc for this operation Input pstDstBuf Target memory physical first address Input pstDstRect The area of the target memory copy Input pstSrcBuf Source memory physical first address Input pstSrcRect Area of the source memory copy Input -
Return
-
0 Successful.
-
!0 Failed, please refer to the error code.
-
-
Dependency
-
Head file: mi_sys_datatype.h / mi_sys.h
-
Library files: libmi_sys.a / libmi_sys.so
-
-
Note
-
The pstDStRect/pstSrcRect data range is based on the first address of pstDstBuf/pstSrcBuf Buf Description as the first address (0,0), and the width and height are partially populated with ePixelFormat to calculate the size of memory data moved by each pixel.
-
PstDdbuf/pstSrcBuf in u16Width, u16 Height, phyAddr, u32Stride, e32Cre, ePixelFormat is required, the rest of the value is meaningless.
-
The area portion of the source memory or target memory exceeds its original range and will only copy the data on which it is not exceeded.
-
-
Sample
MI_S32 ret = MI_SUCCESS; vdisp_copyinfo_plane_t *plane; MI_SYS_FrameData_t stSrcFrame, stDstFrame; MI_SYS_WindowRect_t stSrcRect, stDstRect; MI_U16 u16SocId = ST_DEFAULT_SOC_ID; plane = ©info->plane[0]; stSrcFrame.ePixelFormat = E_MI_SYS_PIXEL_FRAME_I8; stSrcFrame.phyAddr[0] = plane->src_paddr; stSrcFrame.u16Width = plane->width; stSrcFrame.u16Height = plane->height; stSrcFrame.u32Stride[0] = plane->src_stride; stDstFrame.ePixelFormat = E_MI_SYS_PIXEL_FRAME_I8; stDstFrame.phyAddr[0] = plane->dst_paddr; stDstFrame.u16Width = plane->width; stDstFrame.u16Height = plane->height; stDstFrame.u32Stride[0] = plane->dst_stride; stSrcRect.u16X = 0; stSrcRect.u16Y = 0; stSrcRect.u16Height = stSrcFrame.u16Height; stSrcRect.u16Width = stSrcFrame.u16Width; stDstRect.u16X = 0; stDstRect.u16Y = 0; stDstRect.u16Height = stDstFrame.u16Height; stDstRect.u16Width = stDstFrame.u16Width; ret = MI_SYS_BufBlitPa(u16SocId, &stDstFrame, &stDstRect, &stSrcFrame, &stSrcRect); return ret;
-
Related topics
2.5.12. MI_SYS_ConfigPrivateMMAPool¶
-
Function
Configure private MMA Heap.
-
Syntax
MI_S32 MI_SYS_ConfigPrivateMMAPool(MI_U16 u16SocId, MI_SYS_GlobalPrivPoolConfig_t *pstGlobalPrivPoolConf);
-
Parameters
Parameter Name Description Input/Output u16SocId Specify the target Soc for this operation Input pstGlobalPrivPoolConf Configure private MMA Heap for modules Input -
Return
-
0 Successful.
-
!0 Failed, please refer to the error code.
-
-
Dependency
-
Head file: mi_sys_datatype.h / mi_sys.h
-
Library files: libmi_sys.a / libmi_sys.so
-
-
Note
-
Device private MMA Heap and channel private MMA Heap cannot coexist.
-
It is recommended to create a private MMA heap for each module after MI_SYS_init.
-
When pstGlobalPrivPoolConf-bCreate is TRUE, create a private POOL, destroy the private POOL when it is FALSE
-
Various eConfigType use scenarios are as follows:
eConfigType Applicable Scenario E_MI_SYS_VPE_TO_VENC_PRIVATE_RING_POOL Set up a private ring heap pool for scl and venc ports bound to E_MI_SYS_BIND_TYPE_HW_RIN mode.
Note: Mi_Sys2.0 indicates the settings between vpe and venc ports. Be abandoned in Maruko and later chips.E_MI_SYS_PRE_CHN_PRIVATE_POOL Set up a private heap pool for the module channel E_MI_SYS_PRE_DEV_PRIVATE_POOL Set up a private heap pool for module devices E_MI_SYS_PER_CHN_PORT_OUTPUT_POOL Set heap pool for module output port, after which the output buf priority of the port is assigned E_MI_SYS_PER_DEV_PRIVATE_RING_POOL Set up a private ring heap pool for module devices. In Maruko and later chips, it needs to apply the ring pool with this enum type before binding with HW_Ring mode.
-
-
Sample
Suppose the scene is: Two streams under IPC, one main Stream H265 maximum resolution 1920 x 1080, and all the way Sub Stream H264 max resolution is 720 x 576.
VENC Creat MMA Heap:
//Main Sream: //Create private MMA heap with size of 38745760 for Channel 1 MI_SYS_GlobalPrivPoolConfig_t stConfig; MI_U16 u16SocId = ST_DEFAULT_SOC_ID; memset(&stConfig , 0 ,sizeof(stConfig)); stConfig.eConfigType = E_MI_SYS_PER_CHN_PRIVATE_POOL; stConfig.bCreate = TRUE; stConfig.uConfig.stPreChnPrivPoolConfig.eModule = E_MI_MODULE_ID_VENC; stConfig.uConfig.stPreChnPrivPoolConfig.u32Devid = 0; stConfig.uConfig.stPreChnPrivPoolConfig.u32Channel= 1; stConfig.uConfig.stPreChnPrivPoolConfig.u32PrivateHeapSize = 38745760; MI_SYS_ConfigPrivateMMAPool(u16SocId, &stConfig); //Sub Stream: // Create private MMA heap with size of 805152 for Channel 2 stConfig.eConfigType = E_MI_SYS_PER_CHN_PRIVATE_POOL; stConfig.bCreate = TRUE; stConfig.uConfig.stPreChnPrivPoolConfig.eModule = E_MI_MODULE_ID_VENC; stConfig.uConfig.stPreChnPrivPoolConfig.u32Devid = 0; stConfig.uConfig.stPreChnPrivPoolConfig.u32Channel= 2; stConfig.uConfig.stPreChnPrivPoolConfig.u32PrivateHeapSize = 805152; MI_SYS_ConfigPrivateMMAPool(u16SocId, &stConfig);
VENC Destroyed MMA Heap:
// Main Sream: //Destroyed private MMA heap of Channel 1 stConfig.eConfigType = E_MI_SYS_PER_CHN_PRIVATE_POOL; stConfig.bCreate = FALSE; stConfig.uConfig.stPreChnPrivPoolConfig.eModule = E_MI_MODULE_ID_VENC; stConfig.uConfig.stPreChnPrivPoolConfig.u32Devid = 0; stConfig.uConfig.stPreChnPrivPoolConfig.u32Channel= 1; MI_SYS_ConfigPrivateMMAPool(&stConfig); //Sub Stream: //Destroyed private MMA heap of Channel 2 stConfig.eConfigType = E_MI_SYS_PER_CHN_PRIVATE_POOL; stConfig.bCreate = FALSE; stConfig.uConfig.stPreChnPrivPoolConfig.eModule = E_MI_MODULE_ID_VENC; stConfig.uConfig.stPreChnPrivPoolConfig.u32Devid = 0; stConfig.uConfig.stPreChnPrivPoolConfig.u32Channel= 2; MI_SYS_ConfigPrivateMMAPool(u16SocId, &stConfig);
ISP Creat MMA Heap:
//Creat private MMA Heap with size of 0x4f9200 for Device 0 stConfig.eConfigType = E_MI_SYS_PER_DEV_PRIVATE_POOL; stConfig.bCreate = TRUE; stConfig.uConfig.stPreDevPrivPoolConfig.eModule = E_MI_MODULE_ID_ISP; stConfig.uConfig.stPreDevPrivPoolConfig.u32Devid = 0; MI_SYS_ConfigPrivateMMAPool(u16SocId, &stConfig);
ISP Destroyed MMA Heap:
//Destroyed private MMA Heap of Device 0 stConfig.eConfigType = E_MI_SYS_PER_DEV_PRIVATE_POOL; stConfig.bCreate = FALSE; stConfig.uConfig.stPreDevPrivPoolConfig.eModule = E_MI_MODULE_ID_ISP; stConfig.uConfig.stPreChnPrivPoolConfig.u32Devid = 0; MI_SYS_ConfigPrivateMMAPool(u16SocId, &stConfig);
Creat SCL -> VENC ring MMA Heap:
stConfig.eConfigType = E_MI_SYS_VPE_TO_VENC_PRIVATE_RING_POOL; stConfig.bCreate = TRUE; stConfig.uConfig. stPreVpe2VencRingPrivPoolConfig.u32VencInputRingPoolStaticSize = 8*1024*1024; MI_SYS_ConfigPrivateMMAPool(u16SocId, &stConfig);
Destroyed SCL -> VENC ring MMA Heap:
stConfig.eConfigType = E_MI_SYS_VPE_TO_VENC_PRIVATE_RING_POOL; stConfig.bCreate = FALSE; MI_SYS_ConfigPrivateMMAPool(u16SocId, &&stConfig);
Create SCL ring MMA Heap:
stConfig.eConfigType = E_MI_SYS_PER_DEV_PRIVATE_RING_POOL; stConfig.bCreate = TRUE; stConfig.uConfig.stpreDevPrivRingPoolConfig.eModule = E_MI_MODULE_ID_SCL; stConfig.uConfig.stpreDevPrivRingPoolConfig.u32Devid = 0; stConfig.uConfig.stpreDevPrivRingPoolConfig.u16MaxWidth = 2560; stConfig.uConfig.stpreDevPrivRingPoolConfig.u16MaxHeight = 1440; stConfig.uConfig.stpreDevPrivRingPoolConfig.u16RingLine = 720; MI_SYS_ConfigPrivateMMAPool(u16SocId, &stConfig);
Destroyed SCL ring MMA Heap
stConfig.eConfigType = E_MI_SYS_PER_DEV_PRIVATE_RING_POOL; stConfig.bCreate = FALSE; MI_SYS_ConfigPrivateMMAPool(u16SocId, &stConfig);
Different resolutions or enable different function have different sizes to match, detail parameters should be calculated according to the scene and specifications.
-
Related topics
2.5.13. MI_SYS_PrivateDevChnHeapAlloc¶
-
Function
Request memory from module channel private MMA Pool.
-
Syntax
MI_S32 MI_SYS_PrivateDevChnHeapAlloc(MI_U16 u16SocId, MI_ModuleId_e eModule, MI_U32 u32Devid, MI_S32 s32ChnId, MI_U8 *pu8BufName, MI_U32 u32blkSize, MI_PHY *pphyAddr, MI_BOOL bTailAlloc);
-
Parameters
Parameter Name Description Input/Output u16SocId Specify the target Soc for this operation Input eModule Module ID Input u32Devid The device ID of the module Input s32ChnId Channel ID of the module Input pu8BufName When applying for the name of private memory, pass null, use the "app-privAlloc" as the default name Input u32blkSize Request the size of private memory Input pphyAddr Physical address of allocated private memory Output bTailAlloc Whether to apply from the tail of the channel private pool Input -
Return
-
0 Successful.
-
!0 Failed, please refer to the error code.
-
-
Dependency
-
Head file: mi_sys_datatype.h / mi_sys.h
-
Library files: libmi_sys.a / libmi_sys.so
-
-
Note
When using this interface, make sure that you have applied E_MI_SYS_PRE_CHN_PRIVATE_POOL type of private memory pool using MI_SYS_ConfigPrivateMMAPool first.
-
Sample
MI_PHY *pphyAddr = NULL; MI_SYS_GlobalPrivPoolConfig_t stConfig; MI_U16 u16SocId = ST_DEFAULT_SOC_ID; Memset(&stConfig , 0 ,sizeof(stConfig)); stConfig.eConfigType = E_MI_SYS_PER_CHN_PRIVATE_POOL; stConfig.bCreate = TRUE; stConfig.uConfig.stPreChnPrivPoolConfig. eModule = E_MI_MODULE_ID_VENC; stConfig.uConfig.stPreChnPrivPoolConfig. u32Devid = 0; stConfig.uConfig.stPreChnPrivPoolConfig. u32Channel= 1; stConfig.uConfig.stPreChnPrivPoolConfig. u32PrivateHeapSize = 38745760; MI_SYS_ConfigPrivateMMAPool(u16SocId, &stConfig); ret = MI_SYS_PrivateDevChnHeapAlloc(u16SocId, E_MI_MODULE_ID_VENC, 0, 1, NULL, 4096, pphyAddr, FALSE); if(ret != MI_SUCCESS) { MI_SYS_ConfigPrivateMMAPool(u16SocId, &stConfig); printf("alloc buff from chn private heap failed\n"); return -1; } //do something... MI_SYS_PrivateDevChnHeapFree(u16SocId, E_MI_MODULE_ID_VENC, 0, 1, *pphyAddr); MI_SYS_ConfigPrivateMMAPool(u16SocId, &stConfig); -
Related topics
2.5.14. MI_SYS_PrivateDevChnHeapFree¶
-
Function
Free memory from module channel private MMA Pool.
-
Syntax
MI_S32 MI_SYS_PrivateDevChnHeapFree(MI_U16 u16SocId, MI_ModuleId_e eModule, MI_U32 u32Devid, MI_S32 s32ChnId, MI_PHY phyAddr);
-
Parameters
Parameter Name Description Input/Output u16SocId Specify the target Soc for this operation Input eModule Module ID Input u32Devid The device ID of the module Input s32ChnId Channel ID of the module Input phyAddr Physical address for memory that needs to be freed Input -
Return
-
0 Successful.
-
!0 Failed, please refer to the error code.
-
-
Dependency
-
Head file: mi_sys_datatype.h / mi_sys.h
-
Library files: libmi_sys.a / libmi_sys.so
-
-
Note
When using this interface, make sure that you have applied a private memory pool of E_MI_SYS_PRE_CHN_PRIVATE_POOL type using the MI_SYS_ConfigPrivateMMAPool first. Otherwise it will apply memory from the heap mma_heap_name0.
-
Sample
Please refer to the
samplein MI_SYS_PrivateDevChnHeapAlloc -
Related topics
2.5.15. MI_SYS_Va2Pa¶
-
Function
Turn CPU virtual address pointer to Physical address.
-
Syntax
MI_S32 MI_SYS_Va2Pa (void *pVirtualAddress, MI_PHY *pPhyAddr);
-
Parameters
Parameter Name Description Input/Output pVirtualAddress CPU virtual address pointer Input pPhyAddr Pointer to store the physical address of the memory block Output -
Return
-
0 Successful.
-
!0 Failed, please refer to the error code.
-
-
Dependency
-
Head file: mi_sys_datatype.h / mi_sys.h
-
Library files: libmi_sys.a / libmi_sys.so
-
-
Note
When using the interface, make sure that the input CPU virtual address is valid and points to the address space allocated in MI.
-
Sample
MI_PHY phySrcBufAddr = 0; MI_PHY phyAddrVa2Pa = 0; void *pVirSrcBufAddr = NULL; MI_U32 srcBuffSize = 1920 * 1980 * 3 / 2; MI_U16 u16SocId = ST_DEFAULT_SOC_ID; srcBuffSize = ALIGN_UP(srcBuffSize, 4096); ret = MI_SYS_MMA_Alloc(u16SocId, NULL, srcBuffSize, &phySrcBufAddr); if(ret != MI_SUCCESS) { printf("alloc src buff failed\n"); return -1; } ret = MI_SYS_Mmap(phySrcBufAddr, srcBuffSize, &pVirSrcBufAddr, TRUE); if(ret != MI_SUCCESS) { MI_SYS_MMA_Free(u16SocId, phySrcBufAddr); printf("mmap src buff failed\n"); return -1; } MI_SYS_Va2Pa(pVirSrcBufAddr, &phyAddrVa2Pa); assert(phySrcBufAddr == phyAddrVa2Pa); memset(pVirSrcBufAddr, 0, srcBuffSize); MI_SYS_FlushInvCache(pVirSrcBufAddr,srcBuffSize); MI_SYS_Munmap(pVirSrcBufAddr, srcBuffSize); MI_SYS_MMA_Free(u16SocId, phySrcBufAddr); -
Related topics
2.5.16. MI_SYS_MemcpyPaEx¶
-
Function
Copy memory from source memory to destination memory by DMA. src/dst can be different type memory.
-
Syntax
MI_S32 MI_SYS_MemcpyPaEx(MI_U16 u16SocId, MI_SYS_MemcpyDirect_e eMemcpyDirect, MI_PHY phyDst, MI_PHY phySrc, MI_U32 u32Lenth);
-
Parameters
Parameter Name Description Input/Output u16SocId Specify the target Soc for this operation Input eMemcpyDirect memcpy directions Input phyDst destination memory address Input phySrc source memory address Input u32Lenth copy length(byte) Input -
Related topics
3. DATA TYPE¶
3.1. Description of data structure Description Format¶
This manual uses information about the five reference domain Description data types, which act as information about the reference domain Description data types, as shown in Table 3-1.
Table 3‑1 : Data Structure Description Format Description
| Label | Function |
|---|---|
| Description | Briefly describe the main function of data type. |
| Define | List the definition statement of the data type |
| Members | List the data structure of the members and meanings. |
| Note | List things that should be in Note when using data types. |
| Related data types and interfaces | List the other data types and interfaces associated with this data type. |
3.2. List of data structures¶
Relevant data types and data structures are defined as follows:
Table 3‑2 : Summary of Data Structures
| Data Structures | definition |
|---|---|
| MI_ModuleId_e | Define module ID enumeration type |
| MI_SYS_PixelFormat_e | Define pixel enumeration type |
| MI_SYS_CompressMode_e | Define compression enumeration type |
| MI_SYS_FrameTileMode_e | Define Tile format enumeration type |
| MI_SYS_FieldType_e | Define Field Enumeration Type |
| MI_SYS_BufDataType_e | Define module ID enumeration type |
| MI_SYS_FrameIspInfoType_e | Define types of ISP info enumerations carried by frame data |
| MI_SYS_ChnPort_t | Define module device channel structure |
| MI_SYS_MetaData_t | Define the structure for MetaData |
| MI_SYS_RawData_t | Structure of Define Stream RawData |
| MI_SYS_WindowRect_t | Structure of Define Window coordinates |
| MI_SYS_FrameData_t | Structure of Define Stream FrameData |
| MI_SYS_BufInfo_t | Buf Information Structure |
| MI_SYS_FrameBufExtraConfig_t | Define Structure sits additionally configured by Stream Frame buffer |
| MI_SYS_BufFrameConfig_t | Frame buf configuration information structure |
| MI_SYS_BufRawConfig_t | Raw buf configuration information structure |
| MI_SYS_MetaDataConfig_t | Meta buf configuration information structure |
| MI_SYS_BufConf_t | Configure the Buf information structure |
| MI_SYS_Version_t | Sys version information structure |
| MI_VB_PoolListConf_t | Structure of DescribeVB Pool list information |
| MI_SYS_BindType_e | Enumeration type of Pre- and Post-Level Working Mode of Define |
| MI_SYS_FrameData_PhySignalType | Enumeration type of buffer type to which Describe frame data belongs |
| MI_SYS_InsidePrivatePoolType_e | Describe the created enumeration type of private MMA POOL type |
| MI_SYS_PerChnPrivHeapConf_t | Define the structure describing channel private MMA Pool |
| MI_SYS_PerDevPrivHeapConf_t | Define the structure describing the device's private MMA Pool |
| MI_SYS_PerVpe2VencRingPoolConff_t | Define the structure describing private Ring MMA Pool between SCL and VENC. Mi_Sys2.0 indicates the settings between vpe and venc ports. |
| MI_SYS_PerChnPortOutputPool_t | Define the private MMA Pool structure describing output port |
| MI_SYS_PerDevPrivRingPoolConf_t | Define the private MMA Pool structure describing output port. |
| MI_SYS_GlobalPrivPoolConfig_t | Define the structure describing private MMA Pool |
| MI_SYS_FrameIspInfo_t | Define the structure of ISP info in frame data |
| MI_SYS_FbcData_t | Define data structure for frame buffer compress |
| MI_SYS_BufFrameMultiPlaneConfig_t | MultiPlane Frame buf configuration information structure |
| MI_SYS_FrameDataSubPlane_t | Structure of Define Stream SubPlane FrameData |
| MI_SYS_BufFrameMetaConfig_t | Define structure of frame meta data |
| MI_SYS_FrameDataMultiPlane_t | Structure of Define Stream MultiPlane FrameData |
| MI_SYS_UserPictureInfo_t | Define the structure describing user picture info |
| MI_SYS_FrcStrategy_e | Define the enum describing Frc strategy |
| MI_SYS_FrcType_e | Define the enum describing Frc type |
| MI_SYS_ChnPortFrcAttr_t | Define the structure describing Frc attribute |
| MI_SYS_BindAttr_t | Define the structure describing bind attribute |
| MI_SYS_DmaBufInfo_t | Define the structure describing the linux dma-buf related information |
| MI_SYS_MemcpyDirect_e | Dma memory copy direction, now support DRAM & PM-SRAM dual-direct |
| MI_SYS_ChnPortState_t | Define the structure describing the ChnPort State |
3.2.1. MI_ModuleId_e¶
-
Description
Define Module ID enumeration type.
-
Definition
typedef enum { E_MI_MODULE_ID_IVE = 0, E_MI_MODULE_ID_VDF = 1, E_MI_MODULE_ID_VENC = 2, E_MI_MODULE_ID_RGN = 3, E_MI_MODULE_ID_AI = 4, E_MI_MODULE_ID_AO = 5, E_MI_MODULE_ID_VIF = 6, E_MI_MODULE_ID_VPE = 7, E_MI_MODULE_ID_VDEC = 8, E_MI_MODULE_ID_SYS = 9, E_MI_MODULE_ID_FB = 10, E_MI_MODULE_ID_HDMI = 11, E_MI_MODULE_ID_DIVP = 12, E_MI_MODULE_ID_GFX = 13, E_MI_MODULE_ID_VDISP = 14, E_MI_MODULE_ID_DISP = 15, E_MI_MODULE_ID_OS = 16, E_MI_MODULE_ID_IAE = 17, E_MI_MODULE_ID_MD = 18, E_MI_MODULE_ID_OD = 19, E_MI_MODULE_ID_SHADOW = 20, E_MI_MODULE_ID_WARP = 21, E_MI_MODULE_ID_UAC = 22, E_MI_MODULE_ID_LDC = 23, E_MI_MODULE_ID_SD = 24, E_MI_MODULE_ID_PANEL = 25, E_MI_MODULE_ID_CIPHER = 26, E_MI_MODULE_ID_SNR = 27, E_MI_MODULE_ID_WLAN =28, E_MI_MODULE_ID_IPU = 29, E_MI_MODULE_ID_MIPITX = 30, E_MI_MODULE_ID_GYRO = 31, E_MI_MODULE_ID_JPD = 32, E_MI_MODULE_ID_ISP = 33, E_MI_MODULE_ID_SCL = 34, E_MI_MODULE_ID_WBC = 35, E_MI_MODULE_ID_DSP = 36, E_MI_MODULE_ID_PCIE = 37, E_MI_MODULE_ID_DUMMY = 38, E_MI_MODULE_ID_NIR = 39, E_MI_MODULE_ID_DPU = 40, E_MI_MODULE_ID_HVP = 41, E_MI_MODULE_ID_HDMIRX = 42, E_MI_MODULE_ID_PSPI = 43, //E_MI_MODULE_ID_SED = 29, E_MI_MODULE_ID_MAX, } MI_ModuleId_e; -
Members
Module ID Module ID HEX Value Members Name Module 0 0x00 E_MI_MODULE_ID_IVE Module ID for Image Intelligent Operator IVE 1 0x01 E_MI_MODULE_ID_VDF Module ID of Video Intelligent Algorithm Framework Module VDF 2 0x02 E_MI_MODULE_ID_VENC Module ID for video coding module VENC 3 0x03 E_MI_MODULE_ID_RGN MODULE ID FOR OSD OVERLAY AND MASKING MODULE REG 4 0x04 E_MI_MODULE_ID_AI Module ID for Audio Input Module AI 5 0x05 E_MI_MODULE_ID_AO Module ID for audio Output Module AO 6 0x06 E_MI_MODULE_ID_VIF Video InputVIF's Module ID 7 0x07 E_MI_MODULE_ID_VPE Module ID of the video image processing module VPE 8 0x08 E_MI_MODULE_ID_VDEC Module ID for video decoding VEDC 9 0x09 E_MI_MODULE_ID_SYS Module ID of System Module SYS 10 0x0A E_MI_MODULE_ID_FB SStar UI shows the module ID of the FrameBuffer Device module 11 0x0B E_MI_MODULE_ID_HDMI HMDI Module ID 12 0x0C E_MI_MODULE_ID_DIVP Module ID for video DI and post-processing module DIVP 13 0x0D E_MI_MODULE_ID_GFX Module ID of 2D Graphics Processing Acceleration Module GFX 14 0x0E E_MI_MODULE_ID_VDISP Image Puzzle Module VDISP Module ID 15 0x0F E_MI_MODULE_ID_DISP Video display module ID of module DISP 16 0x10 E_MI_MODULE_ID_OS RTOS System Module ID 17 0x11 E_MI_MODULE_ID_IAE Module ID for Audio Smart Operator IAE 18 0x12 E_MI_MODULE_ID_MD Module ID of the motion detection module MD 19 0x13 E_MI_MODULE_ID_OD Block ingesting module ID for the OD of the detection module 20 0x14 E_MI_MODULE_ID_SHADOW Module ID for virtual MI framework SHADOW 21 0x15 E_MI_MODULE_ID_WARP Module ID of the image malformation correction algorithm WARP 22 0x16 E_MI_MODULE_ID_UAC Module ID for USB Aduio Class-specific ALSA devices 23 0x17 E_MI_MODULE_ID_LDC Module ID of image malformation correction algorithm LDC 24 0x18 E_MI_MODULE_ID_SD Module ID for image zoom function 25 0x19 E_MI_MODULE_ID_PANEL The display of panel's module ID 26 0x1A E_MI_MODULE_ID_CIPHER Chip encrypts CIPHER's module ID 27 0x1B E_MI_MODULE_ID_SNR Sensor module ID 28 0x1C E_MI_MODULE_ID_WLAN Module ID for wireless communication network Wi-Fi 29 0x1D E_MI_MODULE_ID_IPU Module ID for image recognition processing IPU 30 0x1E E_MI_MODULE_ID_MIPITX Send data module IDs using THE MIPI protocol 31 0x1F E_MI_MODULE_ID_GYRO Module ID of the gyroscope 32 0x20 E_MI_MODULE_ID_JPD Module ID processed by JPD 33 0x21 E_MI_MODULE_ID_ISP Module ID for ISP 34 0x22 E_MI_MODULE_ID_SCL Module ID for image scaling 35 0x23 E_MI_MODULE_ID_WBC Module ID for video writeback 36 0X24 E_MI_MODULE_ID_DSP Module ID for DSP 37 0X25 E_MI_MODULE_ID_PCIE Module ID for PCIE 38 0X26 E_MI_MODULE_ID_DUMMY Module ID for internal test function
3.2.2. MI_SYS_PixelFormat_e¶
-
Description
Define Pixel enumeration type.
-
Definition
typedef enum { E_MI_SYS_PIXEL_FRAME_YUV422_YUYV = 0, E_MI_SYS_PIXEL_FRAME_ARGB8888, E_MI_SYS_PIXEL_FRAME_ABGR8888, E_MI_SYS_PIXEL_FRAME_BGRA8888, E_MI_SYS_PIXEL_FRAME_RGB565, E_MI_SYS_PIXEL_FRAME_ARGB1555, E_MI_SYS_PIXEL_FRAME_ARGB4444, E_MI_SYS_PIXEL_FRAME_I2, E_MI_SYS_PIXEL_FRAME_I4, E_MI_SYS_PIXEL_FRAME_I8, E_MI_SYS_PIXEL_FRAME_YUV_SEMIPLANAR_422, E_MI_SYS_PIXEL_FRAME_YUV_SEMIPLANAR_420, E_MI_SYS_PIXEL_FRAME_YUV_SEMIPLANAR_420_NV21, E_MI_SYS_PIXEL_FRAME_YUV_TILE_420, E_MI_SYS_PIXEL_FRAME_YUV422_UYVY, E_MI_SYS_PIXEL_FRAME_YUV422_YVYU, E_MI_SYS_PIXEL_FRAME_YUV422_VYUY, E_MI_SYS_PIXEL_FRAME_YUV422_PLANAR, E_MI_SYS_PIXEL_FRAME_YUV420_PLANAR, E_MI_SYS_PIXEL_FRAME_FBC_420, E_MI_SYS_PIXEL_FRAME_RGB_BAYER_BASE, E_MI_SYS_PIXEL_FRAME_RGB_BAYER_NUM = E_MI_SYS_PIXEL_FRAME_RGB_BAYER_BASE + E_MI_SYS_DATA_PRECISION_MAX*E_MI_SYS_PIXEL_BAYERID_MAX-1, E_MI_SYS_PIXEL_FRAME_RGB888, E_MI_SYS_PIXEL_FRAME_BGR888, E_MI_SYS_PIXEL_FRAME_GRAY8, E_MI_SYS_PIXEL_FRAME_RGB101010, E_MI_SYS_PIXEL_FRAME_RGB888_PLANAR, E_MI_SYS_PIXEL_FRAME_FORMAT_MAX, } MI_SYS_PixelFormat_e; -
Members
Members Name Description E_MI_SYS_PIXEL_FRAME_YUV422_YUYV YUV422_YUYV format E_MI_SYS_PIXEL_FRAME_ARGB8888 ARGB8888 format E_MI_SYS_PIXEL_FRAME_ABGR8888 ABGR8888 format E_MI_SYS_PIXEL_FRAME_BGRA8888 BGRA8888 format E_MI_SYS_PIXEL_FRAME_RGB565 RGB565 format E_MI_SYS_PIXEL_FRAME_ARGB1555 ARGB1555 format E_MI_SYS_PIXEL_FRAME_ARGB4444 ARGB4444 format E_MI_SYS_PIXEL_FRAME_I2 2 bpp format E_MI_SYS_PIXEL_FRAME_I4 4 bpp format E_MI_SYS_PIXEL_FRAME_I8 8 bpp format E_MI_SYS_PIXEL_FRAME_YUV_SEMIPLANAR_422 YUV422 semi-planar format E_MI_SYS_PIXEL_FRAME_YUV_SEMIPLANAR_420 YUV420sp nv12 format E_MI_SYS_PIXEL_FRAME_YUV_SEMIPLANAR_420_NV21 YUV420sp nv21 format E_MI_SYS_PIXEL_FRAME_TILE_420 Internal custom TILE format E_MI_SYS_PIXEL_FRAME_YUV422_UYVY YUV422_UYVY format E_MI_SYS_PIXEL_FRAME_YUV422_YVYU YUV422_YVYU format E_MI_SYS_PIXEL_FRAME_YUV422_VYUY YUV422_VYUY format E_MI_SYS_PIXEL_FRAME_YUV422_PLANAR YUV422_PLANAR format E_MI_SYS_PIXEL_FRAME_YUV420_PLANAR YUV420_PLANAR format E_MI_SYS_PIXEL_FRAME_FBC_420 Internal customer format E_MI_SYS_PIXEL_FRAME_RGB_BAYER_BASE RGB raw data combined format base num value E_MI_SYS_PIXEL_FRAME_RGB_BAYER_NUM RGB raw data combined format max num value E_MI_SYS_PIXEL_FRAME_RGB888 RGB888 format E_MI_SYS_PIXEL_FRAME_BGR888 BGR888 format E_MI_SYS_PIXEL_FRAME_GRAY8 8bit gray format E_MI_SYS_PIXEL_FRAME_RGB101010 RGB101010 format E_MI_SYS_PIXEL_FRAME_RGB888_PLANAR RGB888_PLANER format E_MI_SYS_PIXEL_FRAME_FORMAT_MAX Enum max value -
Note
-
E_MI_SYS_PIXEL_FRAME_RGB_BAYER_BASE, E_MI_SYS_PIXEL_FRAME_RGB_BAYER_NUM is available in the RGB raw data combination format. In this format, the bit bit ePixPrecision and the orderee eBayerId provided by the sensor generate an enum value in the RGB raw data combination format from RGB_BAYER_PIXEL macro.
-
RGB_BAYER_PIXEL macro definition: #define RGB_BAYER_PIXEL(BitMode, PixelID) (E_MI_SYS_PIXEL_FRAME_RGB_BAYER_BASE+ BitMode*E_MI_SYS_PIXEL_BAYERID_MAX+ PixelID), the range of values: (E_MI_SYSAME_BASE_RGB_FRAME_FRAME_RGB_FRAME_PIXER_RGB_PIXER)
A small example of the use is provided below, and for more detailed information, please refer to the API documentation for the corresponding module.
static MI_SYS_PixelFormat_e getRawType(STUB_SensorType_e sensorType) { MI_SYS_PixelFormat_e eRawType = E_MI_SYS_PIXEL_FRAME_RGB_BAYER_NUM; MI_SNR_PlaneInfo_t stSnrPlane0Info; memset(&stSnrPlane0Info, 0x0, sizeof(MI_SNR_PlaneInfo_t)); MI_SNR_GetPlaneInfo(E_MI_SNR_PAD_ID_0, 0, &stSnrPlane0Info); eRawType = (MI_SYS_PixelFormat_e)RGB_BAYER_PIXEL(stSnrPlane0Info.ePixPrecision, stSnrPlane0Info.eBayerId); return eRawType; } -
3.2.3. MI_SYS_CompressMode_e¶
-
Description
Define Compression enumeration type.
-
Definition
typedef enum { E_MI_SYS_COMPRESS_MODE_NONE,//no compress E_MI_SYS_COMPRESS_MODE_SEG,//compress unit is 256 bytes as a segment E_MI_SYS_COMPRESS_MODE_LINE,//compress unit is the whole line E_MI_SYS_COMPRESS_MODE_FRAME,//compress unit is the whole frame E_MI_SYS_COMPRESS_MODE_TO_8BIT, E_MI_SYS_COMPRESS_MODE_TO_6BIT, E_MI_SYS_COMPRESS_MODE_IFC, E_MI_SYS_COMPRESS_MODE_SFBC0, E_MI_SYS_COMPRESS_MODE_SFBC1, E_MI_SYS_COMPRESS_MODE_SFBC2, E_MI_SYS_COMPRESS_MODE_BUTT, //number } MI_SYS_CompressMode_e; -
Members
Members Name Description E_MI_SYS_COMPRESS_MODE_NONE Uncompressed video formats E_MI_SYS_COMPRESS_MODE_SEG Segment compressed video format E_MI_SYS_COMPRESS_MODE_LINE Line-compressed video format, compressed by one segment of behavior E_MI_SYS_COMPRESS_MODE_FRAME Frame-compressed video format that compresses a frame of data E_MI_SYS_COMPRESS_MODE_TO_8BIT Compress pixel to 8-bit E_MI_SYS_COMPRESS_MODE_TO_6BIT Pixel compressed to 6bit E_MI_SYS_COMPRESS_MODE_IFC Arm frame buffer compression E_MI_SYS_COMPRESS_MODE_SFBC0 Sigmastar compression method 0 E_MI_SYS_COMPRESS_MODE_SFBC1 Sigmastar compression method 1 E_MI_SYS_COMPRESS_MODE_SFBC2 Sigmastar compression method 2 E_MI_SYS_COMPRESS_MODE_BUTT Number of video compression methods
3.2.4. MI_SYS_FrameTileMode_e¶
-
Description
Define Tile Format enumeration type.
-
Definition
typedef enum { E_MI_SYS_FRAME_TILE_MODE_NONE = 0, E_MI_SYS_FRAME_TILE_MODE_16x16, // tile mode 16x16 E_MI_SYS_FRAME_TILE_MODE_16x32, // tile mode 16x32 E_MI_SYS_FRAME_TILE_MODE_32x16, // tile mode 32x16 E_MI_SYS_FRAME_TILE_MODE_32x32, // tile mode 32x32 E_MI_SYS_FRAME_TILE_MODE_128x32, // tile mode 128x32 E_MI_SYS_FRAME_TILE_MODE_128x64, // tile mode 128x64 E_MI_SYS_FRAME_TILE_MODE_64x4, // tile mode 64x4 E_MI_SYS_FRAME_TILE_MODE_MAX } MI_SYS_FrameTileMode_e; -
Members
Members Name Description E_MI_SYS_FRAME_TILE_MODE_NONE None E_MI_SYS_FRAME_TILE_MODE_16x16 16x16 mode E_MI_SYS_FRAME_TILE_MODE_16x32 16x32 mode E_MI_SYS_FRAME_TILE_MODE_32x16 32x16 mode E_MI_SYS_FRAME_TILE_MODE_32x32 32x32 mode E_MI_SYS_FRAME_TILE_MODE_128x32 128x32 mode E_MI_SYS_FRAME_TILE_MODE_128x64 128x64 mode E_MI_SYS_FRAME_TILE_MODE_64x4 64x4 mode
3.2.5. MI_SYS_FieldType_e¶
-
Description
Define Enumeration type.
-
Definition
typedef enum { E_MI_SYS_FIELDTYPE_NONE, //< no field. E_MI_SYS_FIELDTYPE_TOP, //< Top field only. E_MI_SYS_FIELDTYPE_BOTTOM, //< Bottom field only. E_MI_SYS_FIELDTYPE_BOTH, //< Both fields. E_MI_SYS_FIELDTYPE_NUM } MI_SYS_FieldType_e; -
Members
Members Name Description E_MI_SYS_FIELDTYPE_NONE None E_MI_SYS_FIELDTYPE_TOP Top field only E_MI_SYS_FIELDTYPE_BOTTOM Bottom field only E_MI_SYS_FIELDTYPE_BOTH Both fields
3.2.6. MI_SYS_BufDataType_e¶
-
Description
Define Module ID enumeration type.
-
Definition
typedef enum { E_MI_SYS_BUFDATA_RAW = 0, E_MI_SYS_BUFDATA_FRAME, E_MI_SYS_BUFDATA_META, E_MI_SYS_BUFDATA_MULTIPLANE, E_MI_SYS_BUFDATA_FBC, E_MI_SYS_BUFDATA_MAX } MI_SYS_BufDataType_e; -
Members
Members Name Description E_MI_SYS_BUFDATA_RAW Raw data type E_MI_SYS_BUFDATA_FRAME Frame data type E_MI_SYS_BUFDATA_META Meta data type E_MI_SYS_BUFDATA_MULTIPLANE Multiplane data type E_MI_SYS_BUFDATA_FBC FBC data type E_MI_SYS_BUFDATA_MAX Number of data types
3.2.7. MI_SYS_FrameIspInfoType_e¶
-
Description
Define types of ISP info enumerations carried by frame data.
-
Definition
typedef enum { E_MI_SYS_FRAME_ISP_INFO_TYPE_NONE, E_MI_SYS_FRAME_ISP_INFO_TYPE_GLOBAL_GRADIENT } MI_SYS_FrameIspInfoType_e; -
Members
Members Name Description E_MI_SYS_FRAME_ISP_INFO_TYPE_NONE NONE E_MI_SYS_FRAME_ISP_INFO_TYPE_GLOBAL_GRADIENT Global gradient data types for ISPs
3.2.8. MI_SYS_ChnPort_t¶
-
Description
Define Module equipment channel structure.
-
Definition
typedef struct MI_SYS_ChnPort_s { MI_ModuleId_e eModId; MI_U32 u32DevId; MI_U32 u32ChnId; MI_U32 u32PortId; } MI_SYS_ChnPort_t; -
Members
Members Name Description eModId Module id u32DevId Device id u32ChnId Channel id u32PortId Port id
3.2.9. MI_SYS_MetaData_t¶
-
Description
Define Structure of the Code Stream MetaData.
-
Definition
typedef struct MI_SYS_MetaData_s { union { MI_PTR pVirAddr; MI_PTR64 p64VirAddr; }; MI_PHY phyAddr;//notice that this is miu bus addr,not cpu bus addr. MI_U32 u32Size; MI_U32 u32ExtraData; /*driver special flag*/ MI_ModuleId_e eDataFromModule; } MI_SYS_MetaData_t; -
Members
Members Name Description pVirAddr Data storage virtual address (the p64VirAddr member variable is forbidden) phyAddr Data storage physical address u32Size Data size u32ExtraData driver special flag eDataFromModule Data from which module
3.2.10. MI_SYS_RawData_t¶
-
Description
Define Structure of The Stream RawData.
-
Definition
typedef struct MI_SYS_RawData_s { union { MI_PTR pVirAddr; MI_PTR64 p64VirAddr; }; MI_PHY phyAddr;//notice that this is miu bus addr,not cpu bus addr. MI_U32 u32BufSize; MI_U32 u32ContentSize; MI_BOOL bEndOfFrame; MI_U64 u64SeqNum; } MI_SYS_RawData_t; -
Members
Members Name Description pVirAddr The virtual address of the stream package (the p64VirAddr member variable is forbidden) phyAddr The physical address of the stream package u32BufSize Buf size u32ContentSize Data actually takes up buf size bEndOfFrame Whether the current frame ends. (Reserved parameter) currently only supports frame-by-frame transmission in frame mode. u64SeqNum Frame number of the current frame -
Note
-
Currently only support the transmission of data by frame, each time need to transfer a complete frame of data.
-
When the stream frame data comes with PTS, the decoded Output data Output is the same PTS. When PTS is 1, do not refer to the system clock Output data frame.
-
3.2.11. MI_SYS_WindowRect_t¶
-
Description
Define window Structure of coordinates.
-
Definition
typedef struct MI_SYS_WindowRect_s { MI_U16 u16X; MI_U16 u16Y; MI_U16 u16Width; MI_U16 u16Height; } MI_SYS_WindowRect_t; -
Members
Members Name Description u16X The value of the horizontal direction of the window start position. u16Y The value of the vertical direction of the window start position. u16Width Window width. u16Height Window height.
3.2.12. MI_SYS_FrameData_t¶
-
Description
Define Structure of The Stream FrameData.
-
Definition
//N.B. in MI_SYS_FrameData_t should never support u32Size, //for other values are enough,and not support u32Size is general standard method. typedef struct MI_SYS_FrameData_s { MI_SYS_FrameTileMode_e eTileMode; MI_SYS_PixelFormat_e ePixelFormat; MI_SYS_CompressMode_e eCompressMode; MI_SYS_FrameScanMode_e eFrameScanMode; MI_SYS_FieldType_e eFieldType; MI_SYS_FrameData_PhySignalType ePhylayoutType; MI_U16 u16Width; MI_U16 u16Height; //in case ePhylayoutType equal to REALTIME_FRAME_DATA, pVirAddr would be MI_SYS_REALTIME_MAGIC_PADDR and phyAddr would be MI_SYS_REALTIME_MAGIC_VADDR union { MI_PTR pVirAddr[3]; MI_PTR64 p64VirAddr[3]; }; MI_PHY phyAddr[3];//notice that this is miu bus addr,not cpu bus addr. MI_U32 u32Stride[3]; MI_U32 u32BufSize;//total size that allocated for this buffer,include consider alignment. MI_U16 u16RingBufRealTotalHeight;///Valid in case RINGBUF_FRAME_DATA, u16RingBufRealTotalHeight must be LGE than u16Height MI_SYS_FrameIspInfo_t stFrameIspInfo;//isp info of each frame MI_SYS_WindowRect_t stContentCropWindow; MI_U32 u32MetaDataTypeMask; MI_PHY phyMetaDataAddr[MI_SYS_MAX_METADATA_CNT]; MI_U32 u32MetaDataSize[MI_SYS_MAX_METADATA_CNT]; } MI_SYS_FrameData_t; -
Members
Members Name Description eTileMode Tile mode ePixelFormat Pixel format eCompressMode Compressed format eFrameScanMode Frame scan module eFieldType File type ePhylayoutType The type of buffer that the frame belongs to u16Width Frame width u16Height Frame height pVirAddr Virtual address (the p64VirAddr member variable is forbidden) phyAddr Physical address u32Stride Number of bytes per row of pictures u32BufSize The actual buf size assigned by Sys to the current frame u16RingBufRealTotalHeight The true height of frame data when ring mode stFrameIspInfo ISP info struct stContentCropWindow Crop info struct u32MetaDataTypeMask Meta data type mask phyMetaDataAddr Meta data address u32MetaDataSize Meta data size
3.2.13. MI_SYS_BufInfo_t¶
-
Description
Define Structure of code flow information.
-
Definition
typedef struct MI_SYS_BufInfo_s { MI_U64 u64Pts; MI_U64 u64SidebandMsg; MI_SYS_BufDataType_e eBufType; MI_U32 u32SequenceNumber; MI_U32 bEndOfStream : 1; MI_U32 bUsrBuf : 1; MI_U32 bDrop : 1; MI_U32 bCrcCheck : 1; MI_U32 u32IrFlag : 2; // For Window Hello Usage: 0x00/off, 0x01/on, 0x02/invalid MI_U32 u32Reserved : 26; union { MI_SYS_FrameData_t stFrameData; MI_SYS_RawData_t stRawData; MI_SYS_MetaData_t stMetaData; MI_SYS_FrameDataMultiPlane_t stFrameDataMultiPlane; MI_SYS_FbcData_t stFbcData; }; MI_ModuleId_e eDataSource; } MI_SYS_BufInfo_t; -
Members
Members Name Description u64Pts Timestamp u64SidebandMsg Side band message eBufType Buf type u32SequenceNumber Sequence number Bit field Bit 0 bEndOfStream Whether all the information has been sent Bit 1 bUsrBuf Whether user used buf Bit 2 bDrop Whether to drop buf Bit 3 bCrcCkeck Whether to enable crc verification Bit 4-5 u32IrFlag Ir flag bit Bit 6-31 u32Reserved Reserved bit Union stFrameData Frame data format structure stRawData Raw data format structure stMetaData Meta data format structure stFrameDataMultiPlane Multi-Frame collection data format structure stFbcData Frame buffer compressed data structure eDataSource Data Source
3.2.14. MI_SYS_FrameBufExtraConfig_t¶
-
Description
Define Structure sits additionally configured by Stream Frame buffer.
-
Definition
typedef struct MI_SYS_FrameBufExtraConfig_s { //Buf alignment requirement in horizontal MI_U16 u16BufHAlignment; //Buf alignment requirement in vertical MI_U16 u16BufVAlignment; //Buf alignment requirement in chroma MI_U16 u16BufChromaAlignment; // Buf alignment requirement after compress MI_U16 u16BufCompressAlignment; // Buf Extra add after alignment MI_U16 u16BufExtraSize; //Clear padding flag MI_BOOL bClearPadding; } MI_SYS_FrameBufExtraConfig_t; -
Members
Members Name Description u16BufHAlignment Horizontal alignment values u16BufVAlignment Vertical alignment values u16BufChromaAlignment Chroma buffer size alignment value u16BufCompressAlignment Compress buffer size alignment value u16BufExtraSize Buffer size extra allocation value bClearPadding Whether to blacken the edge of the buffer
3.2.15. MI_SYS_BufFrameConfig_t¶
-
Description
Define Structure of the Code Stream Frame buffer configuration.
-
Definition
typedef struct MI_SYS_BufFrameConfig_s { MI_U16 u16Width; MI_U16 u16Height; MI_SYS_FrameScanMode_e eFrameScanMode;// MI_SYS_PixelFormat_e eFormat; MI_SYS_CompressMode_e eCompressMode; MI_U32 u32MetaDataTypeMask; MI_U32 u32MetaDataSize[MI_SYS_MAX_METADATA_CNT]; } MI_SYS_BufFrameConfig_t; -
Members
Members Name Description u16Width Frame width u16Height Frame height eFrameScanMode Frame Scan Mode eFormat Frame pixel format eCompressMode Frame compress mode u32MetaDataTypeMask Meta data type mask u32MetaDataSize Meta data size
3.2.16. MI_SYS_BufRawConfig_t¶
-
Description
Define Structure of the code flow raw buffer configuration.
-
Definition
typedef struct MI_SYS_BufRawConfig_s { MI_U32 u32Size; } MI_SYS_BufRawConfig_t; -
Members
Members Name Description u32Size Buf Size
3.2.17. MI_SYS_MetaDataConfig_t¶
-
Description
Define Structure of the code flow meta buffer configuration.
-
Definition
typedef struct MI_SYS_MetaDataConfig_s { MI_U32 u32Size; } MI_SYS_MetaDataConfig_t; -
Members
Members Name Description u32Size Buf Size
3.2.18. MI_SYS_BufConf_t¶
-
Description
Define Structure of the Flow Port Buf configuration.
-
Definition
typedef struct MI_SYS_BufConf_s { MI_SYS_BufDataType_e eBufType; MI_U32 u32Flags; // 0 or MI_SYS_MAP_VA MI_U64 u64TargetPts; MI_BOOL bDirectBuf; // Direct alloc buffer by Others. MI_BOOL bCrcCheck; union { MI_SYS_BufFrameConfig_t stFrameCfg; MI_SYS_BufRawConfig_t stRawCfg; MI_SYS_MetaDataConfig_t stMetaCfg; MI_SYS_BufFrameMultiPlaneConfig_t stMultiPlaneCfg; MI_SYS_BufFrameMetaConfig_t stFrameMetaCfg; // support frame buffer has alloced by Others. MI_SYS_FbcDataConfig_t stFbcCfg; }; } MI_SYS_BufConf_t; -
Members
Members Name Description eBufType Buf type u32Flags Buf is map kernel space va or not u64TargetPts Set buf pts bDirectBuf Direct alloc buffer by Others bCrcCheck Buf enable crc check or not Union stFrameCfg Set data format parameter of Frame stRawCfg Set data format parameter of Raw stMetaCfg Set data format parameter of Meta stMultiPlaneCfg Set data format parameter of multi-Frame stFrameMetaCfg Frame meta data config stFbcCfg Fbc data config
3.2.19. MI_SYS_Version_t¶
-
Description
Define Sys version structure information.
-
Definition
typedef struct MI_SYS_Version_s { MI_U8 u8Version[128]; } MI_SYS_Version_t; -
Members
Members Name Description u8Version[128] Describe sys version information string buf
3.2.20. MI_VB_PoolListConf_t¶
-
Description
Define DescribeVB Pool Structure of linked information.
-
Definition
typedef struct MI_VB_PoolListConf_s { MI_U32 u32PoolListCnt; MI_VB_PoolConf_t stPoolConf[MI_VB_POOL_LIST_MAX_CNT]; } MI_VB_PoolListConf_t; -
Members
Members Name Description u32PoolListCnt VB pool list number of Members stPoolConf VB pool linked table Members configuration information
3.2.21. MI_SYS_BindType_e¶
-
Description
Define Front and rear operating modes.
-
Definition
typedef enum { E_MI_SYS_BIND_TYPE_FRAME_BASE = 0x00000001, E_MI_SYS_BIND_TYPE_SW_LOW_LATENCY = 0x00000002, E_MI_SYS_BIND_TYPE_REALTIME = 0x00000004, E_MI_SYS_BIND_TYPE_HW_AUTOSYNC = 0x00000008, E_MI_SYS_BIND_TYPE_HW_RING = 0x00000010 } MI_SYS_BindType_e; -
Members
Members Name Description E_MI_SYS_BIND_TYPE_FRAME_BASE frame mode, default how to work E_MI_SYS_BIND_TYPE_SW_LOW_LATENCY Low latency working E_MI_SYS_BIND_TYPE_REALTIME How hardware is directly connected E_MI_SYS_BIND_TYPE_HW_AUTOSYNC Front and rear handshake level, buffer size consistent with image resolution E_MI_SYS_BIND_TYPE_HW_RING Front and rear handshake levels, ring buffer depth can be trated less than the image resolution is high -
Note
-
Older versions of MI SYS do not provide this function, if not found, do not have to set.
-
The FRAME_BASE and HW_RING types use DRAM, and the REALTIME type uses SRAM.
-
Due to underlying restrictions, input ports bound by HW_RING or REALTIME cannot use MI_SYS_ChnInputPortGetBuf/ MI_SYS_ChnInputPortPutBuf, and output ports cannot use MI_SYS_ChnOutputPortGetBuf/ MI_SYS_ChnOutputPortPutBuf.
-
Comparison of memory size used by different bindtypes: FRAME_BASE type > HW_RING type > REALTIME type.
-
3.2.22. MI_SYS_FrameData_PhySignalType¶
-
Description
Describe frame data Enumerated types of buffer types that are affiliated.
-
Definition
typedef enum { REALTIME_FRAME_DATA, RINGBUF_FRAME_DATA, NORMAL_FRAME_DATA, AUTOSYNC_FRAME_DATA, } MI_SYS_FrameData_PhySignalType; -
Members
Members Name Description REALTIME_FRAME_DATA In E_MI_SYS_BIND_TYPE_REALTIME mode RINGBUF_FRAME_DATA The resulting frame data NORMAL_FRAME_DATA In E_MI_SYS_BIND_TYPE_HW_RING mode AUTOSYNC_FRAME_DATA In E_MI_SYS_BIND_TYPE_HW_AUTOSYNC mode -
Note
Older versions of MI SYS do not provide this function, if not found, do not have to set.
3.2.23. MI_SYS_InsidePrivatePoolType_e¶
-
Description
Descripe the created enumeration type of private MMA POOL type.
-
Definition
typedef enum { E_MI_SYS_SCL_TO_VENC_PRIVATE_RING_POOL = 0, E_MI_SYS_PER_CHN_PRIVATE_POOL=1, E_MI_SYS_PER_DEV_PRIVATE_POOL=2, E_MI_SYS_PER_CHN_PORT_OUTPUT_POOL=3, E_MI_SYS_PER_DEV_PRIVATE_RING_POOL=4, } MI_SYS_InsidePrivatePoolType_e; -
Members
Members Name Description E_MI_SYS_VPE_TO_VENC_PRIVATE_RING_POOL Private Ring Pool Type for SCL and VENC.
mi_sys2.0 indicates VPE and VENC. Be abandoned in Maruko and later chips.E_MI_SYS_PER_CHN_PRIVATE_POOL Channel Private Pool Type E_MI_SYS_PER_DEV_PRIVATE_POOL Device Private Pool Type E_MI_SYS_PER_CHN_PORT_OUTPUT_POOL Output Port Private Pool Type E_MI_SYS_PER_DEV_PRIVATE_RING_POOL Device Private Ring Pool Type
In Maruko and later chips, it need to apply the ring pool with this enum type before binding with HW_Ring mode. -
Note
Older versions of MI SYS do not provide this function, if not found, do not have to set.
3.2.24. MI_SYS_PerChnPrivHeapConf_t¶
-
Description
Define the structure describing channel private MMA Pool.
-
Definition
typedef struct MI_PerChnPrivHeapConf_s { MI_ModuleId_e eModule; MI_U32 u32Devid; MI_U32 u32Channel; MI_U8 u8MMAHeapName[MI_MAX_MMA_HEAP_LENGTH]; MI_U32 u32PrivateHeapSize; } MI_SYS_PerChnPrivHeapConf_t; -
Members
Members Name Description eModule Module ID u32Devid Device ID u32Channel Channel ID u8MMAHeapName Mma heap name u32PrivateHeapSize Private pool size
3.2.25. MI_SYS_PerDevPrivHeapConf_t¶
-
Description
Define the structure describing the device's private MMA Pool.
-
Definition
typedef struct MI_PerDevPrivHeapConf_s { MI_ModuleId_e eModule; MI_U32 u32Devid; MI_U32 u32Reserve; MI_U8 u8MMAHeapName[MI_MAX_MMA_HEAP_LENGTH]; MI_U32 u32PrivateHeapSize; } MI_SYS_PerDevPrivHeapConf_t; -
Members
Members Name Description eModule Module ID u32Devid Device ID u32Reserve Reserved u8MMAHeapName Mma heap name u32PrivateHeapSize Private pool size
3.2.26. MI_SYS_PerVpe2VencRingPoolConff_t¶
-
Description
Define the structure describing private Ring MMA Pool between SCL and VENC. mi_sys2.0 indicates between VPE and VENC. Be abandoned in Maruko and later chips.
-
Definition
typedef struct MI_SYS_PerVpe2VencRingPoolConf_s { MI_U32 u32VencInputRingPoolStaticSize; MI_U8 u8MMAHeapName[MI_MAX_MMA_HEAP_LENGTH]; } MI_SYS_PerVpe2VencRingPoolConf_t; -
Members
Members Name Description u32VencInputRingPoolStaticSize Private pool size u8MMAHeapName Mma heap name
3.2.27. MI_SYS_PerChnPortOutputPool_t¶
-
Description
Define the private MMA Pool structure describing output port.
-
Definition
typedef struct MI_SYS_PerChnPortOutputPool_s { MI_ModuleId_e eModule; MI_U32 u32Devid; MI_U32 u32Channel; MI_U32 u32Port; MI_U8 u8MMAHeapName[MI_MAX_MMA_HEAP_LENGTH]; MI_U32 u32PrivateHeapSize; } MI_SYS_PerChnPortOutputPool_t; -
Members
Members Name Description eModule Module ID u32Devid Device ID u32Channel Channel ID u32Port Port ID u8MMAHeapName Mma heap name u32PrivateHeapSize Private pool size
3.2.28. MI_SYS_PerDevPrivRingPoolConf_t¶
-
Description
Define the private MMA Pool structure describing output port.
-
Definition
typedef struct MI_SYS_PerDevPrivRingPoolConf_s { MI_ModuleId_e eModule; MI_U32 u32Devid; MI_U16 u16MaxWidth; MI_U16 u16MaxHeight; MI_U16 u16RingLine; MI_U8 u8MMAHeapName[MI_MAX_MMA_HEAP_LENGTH]; }MI_SYS_PerDevPrivRingPoolConf_t; -
Members
Members Name Description eModule Module ID u32Devid Device ID u16MaxWidth The max width of Ring Pool u16MaxHeight The max Height of Ring Pool u16RingLine Ring Pool total line u8MMAHeapName Mma heap name
3.2.29. MI_SYS_GlobalPrivPoolConfig_t¶
-
Description
Define the structure describing private MMA Pool.
-
Definition
typedef struct MI_SYS_GlobalPrivPoolConfig_s { MI_SYS_InsidePrivatePoolType_e eConfigType; MI_BOOL bCreate; union { MI_SYS_PerChnPrivHeapConf_t stPreChnPrivPoolConfig; MI_SYS_PerDevPrivHeapConf_t stPreDevPrivPoolConfig; MI_SYS_PerVpe2VencRingPoolConf_t stPreVpe2VencRingPrivPoolConfig; MI_SYS_PerChnPortOutputPool_t stPreChnPortOutputPrivPool; MI_SYS_PerDevPrivRingPoolConf_t stpreDevPrivRingPoolConfig; }uConfig; } MI_SYS_GlobalPrivPoolConfig_t; -
Members
Members Name Description eConfigType Private pool type bCreate Whether Create PrivatePool.true: Creat false: Destroyed uConfig Structures of different types of private pool
3.2.30. MI_SYS_FrameIspInfo_t¶
-
Description
Define the structure of ISP info in frame data.
-
Definition
typedef struct MI_SYS_FrameIspInfo_s { MI_SYS_FrameIspInfoType_e eType; union { MI_U32 u32GlobalGradient; }uIspInfo; } MI_SYS_FrameIspInfo_t; -
Members
Members Name Description eType ISP info type uIspInfo ISP info union
3.2.31. MI_SYS_FbcData_t¶
-
Description
Define data structure for frame buffer compress.
-
Definition
typedef struct MI_SYS_FbcData_s { MI_SYS_FrameTileMode_e eTileMode; MI_SYS_PixelFormat_e ePixelFormat; MI_SYS_CompressMode_e eCompressMode; MI_SYS_FrameData_PhySignalType ePhylayoutType; MI_U16 u16Width; MI_U16 u16Height; union { MI_PTR pVirAddr[2]; MI_PTR64 p64VirAddr[2]; }; MI_PHY phyAddr[2]; // notice that this is miu bus addr,not cpu bus addr. MI_U32 u32Stride[2]; MI_U32 u32BufSize; // total size that allocated for this buffer,include consider alignment. /* * ----------------- ---------------- * | | ^ * | | | * u16RingBufStartLine --> | |---- | * | | ^ | * | Ring | | | * | | u16Height | * | Heap | | | * | | | u16RingHeapTotalLines * | | v | * u16RingBufEndLine --> | |---- | * | | | * | | v * ----------------- ---------------- */ MI_U16 u16RingBufStartLine; MI_U16 u16RingBufEndLine; MI_U16 u16RingHeapTotalLines; MI_PHY phyFbcTableAddr[2]; MI_U32 u32FbcTableSize[2]; MI_SYS_FrameIspInfo_t stFrameIspInfo; } MI_SYS_FbcData_t; -
Members
Members Name Description eTileMode Tile format type ePixelFormat Pixel enumeration type eCompressMode Compression mode ePhylayoutType Frame data buffer type u16Width Frame data width u16Height Frame data height pVirAddr[2] Frame data buffer virtual address (the p64VirAddr member variable is forbidden) phyAddr[2] Frame data buffer physical address u32Stride[2] Bytes occupied by each row of Frame data u32BufSize Frame data buffer size u16RingBufStartLine Ring buffer start line u16RingBufEndLine Ring buffer end line u16RingHeapTotalLines Ring buffer total line phyFbcTableAddr[2] Convert Fbc data to nv12 table, currently only supports to nv12. u32FbcTableSize[2] Convert Fbc data to nv12 table size. stFrameIspInfo The Isp information of FrameData.
3.2.32. MI_SYS_BufFrameMultiPlaneConfig_t¶
-
Description
Define Structure of the code flow multiplane buffer configuration.
-
Definition
typedef struct MI_SYS_BufFrameMultiPlaneConfig_s { MI_U8 u8SubPlaneNum; MI_SYS_BufFrameConfig_t stFrameCfgs[MI_SYS_MAX_SUB_PLANE_CNT]; }MI_SYS_BufFrameMultiPlaneConfig_t; -
Members
Members Name Description u8SubPlaneNum Buf count stFrameCfg Define Structure of the code flow frame buffer configuration.
3.2.33. MI_SYS_FrameDataSubPlane_t¶
-
Description
Define Structure of The Stream SubPlane FrameData.
-
Definition
typedef struct MI_SYS_FrameDataSubPlane_s { MI_SYS_PixelFormat_e ePixelFormat; MI_SYS_CompressMode_e eCompressMode; MI_U64 u64FrameId; MI_U16 u16Width; MI_U16 u16Height; union { MI_PTR pVirAddr[2]; MI_PTR64 p64VirAddr[2]; }; MI_PHY phyAddr[2]; MI_U16 u16Stride[2]; MI_U32 u32BufSize; MI_SYS_FrameData_PhySignalType ePhySignalType; } MI_SYS_FrameDataSubPlane_t; -
Members
Members Name Description ePixelFormat Pixel format eCompressMode Compressed format u64FrameId Frame id u16Width Frame width u16Height Frame height pVirAddr Virtual address (the p64VirAddr member variable is forbidden) phyAddr Physical address u16Stride Number of bytes per row of pictures u32BufSize The actual buf size assigned by Sys to the current frame ePhySignalType The physical signal Type of data
3.2.34. MI_SYS_BufFrameMetaConfig_t¶
-
Description
Define structure of frame meta data.
-
Definition
typedef struct MI_SYS_BufFrameMetaConfig_s { MI_U16 u16Width; MI_U16 u16Height; MI_SYS_FrameScanMode_e eFrameScanMode; // MI_SYS_PixelFormat_e eFormat; MI_SYS_CompressMode_e eCompressMode; union { MI_PTR pVirAddr[3]; MI_PTR64 p64VirAddr[3]; }; MI_PHY phyAddr[3]; MI_U16 u32Stride[3]; MI_U32 u32BufSize; } MI_SYS_BufFrameMetaConfig_t; -
Members
Members Name Description u16Width Data width u16Height Data height eFrameScanMode Frame scan mode eFormat Pixel format eCompressMode Compression mode pVirAddr[3] Virtual address (the p64VirAddr member variable is forbidden) phyAddr[3] Physical address u32Stride[3] Bytes occupied by each line of the picture u32BufSize The actual buf size allocated by Sys to the current frame
3.2.35. MI_SYS_FrameDataMultiPlane_t¶
-
Description
Define Structure of the Stream MutiPlane FrameData.
-
Definition
typedef struct MI_SYS_FrameDataMultiPlane_s { MI_U8 u8SubPlaneNum; MI_SYS_FrameDataSubPlane_t stSubPlanes[MI_SYS_MAX_SUB_PLANE_CNT]; } MI_SYS_FrameDataMultiPlane_t; -
Members
Members Name Description u8SubPlaneNum Buf count stSubPlanes Define Structure of the code flow MultiPlane buffer configuration.
3.2.36. MI_SYS_UserPictureInfo_t¶
-
Description
Define the structure describing user picture info.
-
Definition
typedef struct MI_SYS_UserPictureInfo_s { MI_U32 u32SrcFrc; } MI_SYS_UserPictureInfo_t; -
Members
Members Name Description U32SrcFrc Set the frame rate of Input port buf
3.2.37. MI_SYS_FrcStrategy_e¶
-
Description
Define the enum describing Frc strategy.
-
Definition
typedef enum { E_MI_SYS_FRC_STRATEGY_BY_RATIO, E_MI_SYS_FRC_STRATEGY_BY_PERIOD, E_MI_SYS_FRC_STRATEGY_BY_PTS, E_MI_SYS_FRC_STRATEGY_MAX, } MI_SYS_FrcStrategy_e; -
Members
Members Name Description E_MI_SYS_FRC_STRATEGY_BY_RATIO RATIO strategy E_MI_SYS_FRC_STRATEGY_BY_PERIOD PERIOD strategy E_MI_SYS_FRC_STRATEGY_BY_PTS PTS strategy
3.2.38. MI_SYS_FrcType_e¶
-
Description
Define the enum describing Frc type.
-
Definition
typedef enum { E_MI_SYS_FRC_TYPE_PIPELINE, E_MI_SYS_FRC_TYPE_USERINJECT, E_MI_SYS_FRC_TYPE_MAX, } MI_SYS_FrcType_e; -
Members
Members Name Description E_MI_SYS_FRC_TYPE_PIPELINE PIPELINE type E_MI_SYS_FRC_TYPE_USERINJECT USERINJECT type -
Note
- The InputPort which had bound and its Frc type is PIPELINE. The Frc type of InputPort, which is controlled by the user to input Buf and has no binding relationship, is USERINJECT.
3.2.39. MI_SYS_ChnPortFrcAttr_t¶
-
Description
Define the structure describing Frc attribute.
-
Definition
typedef struct MI_SYS_ChnPortFrcAttr_s { MI_SYS_FrcType_e eType; MI_SYS_FrcStrategy_e eStrategy; MI_U32 u32SrcFrameRate; MI_U32 u32DstFrameRate; } MI_SYS_ChnPortFrcAttr_t; -
Members
Members Name Description eType Frc type eStrategy Frc strategy u32SrcFrameRate Source FrameRate u32DstFrameRate Destination FrameRate
3.2.40. MI_SYS_BindAttr_t¶
-
Description
Define the structure describing bind attribute.
-
Definition
typedef struct MI_SYS_BindAttr_s { MI_SYS_BindType_e eBindType; } MI_SYS_BindAttr_t; -
Members
Members Name Description eBindType Front and rear operating modes
3.2.41. MI_SYS_DmaBufInfo_t¶
-
Description
Define the structure describing the linux dma-buf related information.
-
Definition
typedef struct MI_SYS_DmaBufInfo_s { MI_U16 u16Width; MI_U16 u16Height; MI_U32 bEndOfStream; MI_U32 u32SequenceNumber; MI_U64 u64Pts; MI_SYS_PixelFormat_e eFormat; MI_SYS_CompressMode_e eCompressMode; MI_SYS_FrameScanMode_e eFrameScanMode; MI_SYS_FrameTileMode_e eTileMode; MI_SYS_WindowRect_t stContentCropWindow; MI_SYS_FrameExtInfo_t stFrameExtInfo; MI_S32 s32Fd[3]; MI_U32 u32Stride[3]; MI_U32 u32DataOffset[3]; MI_U32 u32Status; } MI_SYS_DmaBufInfo_t; -
Members
Members Name Description u16Width Frame data width u16Height Frame data height bEndOfStream Whether all the information has been sent u32SequenceNumber Sequence number u64Pts Timestamp eFormat Frame pixel format eCompressMode Compression mode eFrameScanMode Frame scan mode eTileMode Tile format type stContentCropWindow Crop info struct stFrameExtInfo Frame isp info struct s32Fd[3] The file descriptor used to associate the linux dma-buf u32Stride[3] Number of bytes per row of pictures u32DataOffset[3] Offset of each component of the frame data (the unit is byte) u32Status Buffer status -
Note
- This datatype is only available on linux system, and the linux kernel requires the CONFIG_DMABUF_HEAPS option to be enabled
3.2.42. MI_SYS_MemcpyDirect_e¶
-
Description
Dma memory copy direction, now support DRAM & PM-SRAM dual-direct.
-
Definition
typedef enum { E_MI_SYS_MEMCPY_DRAM_TO_DRAM, E_MI_SYS_MEMCPY_DRAM_TO_PM_SRAM, E_MI_SYS_MEMCPY_PM_SRAM_TO_DRAM, E_MI_SYS_MEMCPY_DRAM_TO_PM_PSRAM, E_MI_SYS_MEMCPY_PM_PSRAM_TO_DRAM, E_MI_SYS_MEMCPY_DIRECT_MAX, } MI_SYS_MemcpyDirect_e -
Members
Members Name Description E_MI_SYS_MEMCPY_DRAM_TO_PM_SRAM Copy DRAM to PM SRAM E_MI_SYS_MEMCPY_PM_SRAM_TO_DRAM Copy PM SRAM to DRAM E_MI_SYS_MEMCPY_DRAM_TO_PM_PSRAM Copy DRAM to PM PSRAM E_MI_SYS_MEMCPY_PM_PSRAM_TO_DRAM Copy PM PSRAM to DRAM E_MI_SYS_MEMCPY_DRAM_TO_DRAM Copy DRAM to DRAM
3.2.43. MI_SYS_ChnPortState_t¶
-
Description
Define the structure describing the ChnPort State.
-
Definition
typedef struct MI_SYS_ChnPortState_s { MI_BOOL bEnable; } MI_SYS_ChnPortState_t; -
Members
Members Name Description bEnable Chn/Port is enabled and Dev has been created.
3.2.44. MI_SYS_SidebandData_t¶
-
Description
Define the structure to describe Sideband Data information
-
Definition
typedef struct MI_SYS_SidebandData_s { union { MI_PTR pVirAddr; MI_PTR64 p64VirAddr; }; MI_U32 u32Size; } MI_SYS_SidebandData_t; -
Members
Members Name Description pVirAddr Outgoing parameter, used to obtain the address of Sideband Data information in ARM 32-bit architecture. p64VirAddr Outgoing parameter, used to obtain the address of Sideband Data information in ARM 64-bit architecture. u32Size Outgoing parameter, indicating the byte size occupied by the Sideband Data. Please look up MI_SYS_GetSidebandData
3.2.45. MI_SYS_SidebandData_AeInfo_t¶
-
Description
Define the structure to describe the Ae information of Sideband Data
-
Definition
typedef struct MI_SYS_SidebandData_AeInfo_s { MI_U8 u8SnrId; MI_U32 u32IspGain; MI_U32 u32SnrGain; MI_U32 u32Shutter; } MI_SYS_SidebandData_AeInfo_t; -
Members
Members Name Description u8SnrId Sensor ID, indicating the sensor described by AeInfo. u32IspGain The Value of ISP Gain. u32SnrGain The Value of Sensor Gain. u32Shutter The Value of shutter.
4. ERROR CODE¶
4.1. The composition of the error code¶
Mi returns the error code for 4 bytes, a total of 32bits, consisting of five parts as shown in Table 4-1:
Table 4‑1: The composition of the error code
| Position | Bits | Description |
|---|---|---|
| BIT [0-11] | 12bits | The error type that indicates the specific error meaning of the error code. |
| BIT [12-15] | 4bits | Error level, fixed return 2. |
| BIT [16-23] | 8bits | Module ID, which module the error code belongs to. |
| BIT [24-31] | 8bits | Fixed to 0xA0. |
Tips:
We can simply think of the error code as two double bytes (16bits) for quick interpretation, in the case of the error code 0xA0092001:
"A009": Indicates that the error occurred in a module with module ID 9. By looking at the definition of "MI_ModuleId_e", it can be known that it is the MI_SYS module.
"2001": The error type that indicates the error is 1, which means "Device ID is out of legal range".
4.2. The error code list for MI_SYS API¶
MI_SYS APIs return a value of 4 bytes, 0 indicates successful, and other values indicate failed. Please note that all Non-0 return value should be listed in Table 4-2, otherwise it is illegal.
Table 4‑2: MI_SYS error code
| Error Code | Definition | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 0xA0092001 | MI_ERR_SYS_INVALID_DEVID | Device ID out of legal range |
| 0xA0092002 | MI_ERR_SYS_INVALID_CHNID | Channel group number error or invalid area handle |
| 0xA0092003 | MI_ERR_SYS_ILLEGAL_PARAM | Parameter out of legal range |
| 0xA0092004 | MI_ERR_SYS_EXIST | Repeatedly create a device, channel or resource that already exists |
| 0xA0092005 | MI_ERR_SYS_UNEXIST | Trying to use or destroy a device, channel or resource that does not exist |
| 0xA0092006 | MI_ERR_SYS_NULL_PTR | There are null pointers in the function |
| 0xA0092007 | MI_ERR_SYS_NOT_CONFIG | The module is not configured |
| 0xA0092008 | MI_ERR_SYS_NOT_SUPPORT | The parameter or function is not supported |
| 0xA0092009 | MI_ERR_SYS_NOT_PERM | This operation is not permitted, such as trying to modify static configuration parameters |
| 0xA009200C | MI_ERR_SYS_NOMEM | Failed to allocate memory, such as system memory is insufficient |
| 0xA009200D | MI_ERR_SYS_NOBUF | Failed to allocate buffer, such as the requested data buffer is too large |
| 0xA009200E | MI_ERR_SYS_BUF_EMPTY | No data in the buffer |
| 0xA009200F | MI_ERR_SYS_BUF_FULL | Full data in buffer |
| 0xA0092010 | MI_ERR_SYS_NOTREADY | The system has not initialized or loaded the module |
| 0xA0092011 | MI_ERR_SYS_BADADDR | The address is illegal |
| 0xA0092012 | MI_ERR_SYS_BUSY | The system is busy |
| 0xA0092013 | MI_ERR_SYS_CHN_NOT_STARTED | The channel has not been started. |
| 0xA0092014 | MI_ERR_SYS_CHN_NOT_STOPED | The channel has not been stopped |
| 0xA0092015 | MI_ERR_SYS_NOT_INIT | The module has not been initialized |
| 0xA0092016 | MI_ERR_SYS_INITED | The module has been initialized |
| 0xA0092017 | MI_ERR_SYS_NOT_ENABLE | The channel or port has not been enabled |
| 0xA0092018 | MI_ERR_SYS_NOT_DISABLE | The channel or port has not been disabled |
| 0xA0092019 | MI_ERR_SYS_TIMEOUT | Timeout |
| 0xA009201A | MI_ERR_SYS_DEV_NOT_STARTED | The device has not been started |
| 0xA009201B | MI_ERR_SYS_DEV_NOT_STOPED | The device has not been stopped |
| 0xA009201C | MI_ERR_SYS_CHN_NO_CONTENT | There is no content in the channel |
| 0xA009201D | MI_ERR_SYS_NOVASAPCE | Failed to map virtual address |
| 0xA009201E | MI_ERR_SYS_NOITEM | There is no item in RingPool |
| 0xA009201F | MI_ERR_SYS_FAILED | Undefined error |
5. PROCFS INTRODUCTION¶
5.1. mi_infer_graph.py¶
5.1.1. cat¶
-
Debug info
# cat /proc/mi_modules/mi_infer_graph.py
-
Debug info analysis
Sys provides a python script for proc fs to generate runtime information, which can be cat saved to the Linux server, then copy it to the text and run it on the Linux server using pyhton2, and two pictures will be output. The default image format is the simplified version, and one is " infer_DAG ", the other is " perf_static ". One of the output pictures is as follows:

The rectangle represents channel pass name;
The label on the line indicates from which input port to which output port, as well as bind type, source frame rate and dest frame rate.
5.2. mi_graph_contrl¶
5.2.1. cat¶
-
Debug info
# cat /proc/mi_modules/mi_graph_contrl
-
Debug info analysis
The "dump bind" field of the above command indicates mi_infer_graph.py output style, "off" indicates output simplified binding graph, "on" indicates output detailed binding graph.
5.2.2. echo¶
| Function | Control the image style output by Python scripts. |
|---|---|
| Command | echo [command] >/proc/mi_modules/mi_graph_contrl |
| Parameter Description |
[command] Command: dump bind on: control output detailed binding graph dump bind off: control output simplified binding graph |
| Example | output detailed binding graph : # echo dump bind on > /proc/mi_modules/mi_graph_contrl # cat /proc/mi_modules/mi_infer_graph.py |
5.3. debug_level¶
5.3.1. cat/echo¶
-
Debug info
# cat /proc/mi_modules/mi_sys/debug_level 2
-
Debug info analysis
Each module (including the sys module) has its own debug level to control the printing level. The respective printing level is controlled in
/proc/mi_modules/mi_modulename/debug_levelrespectively, where the modulename is shaped like disp, dipp, rgn and so on. The above is just taking/proc/mi_modules/mi_sys/debug_levelas an example.Function Print debug warning level. Command cat /proc/mi_modules/[ModuleName]/debug_level Parameter
Description[ModuleName] Module name
mi_disp / mi_gfx / mi_rgn / mi_vdec / mi_vif / mi_ai / mi_shadow / mi_vdisp / mi_ao / mi_hdmi / mi_sys / mi_vencExample cat /proc/mi_modules/mi_sys/debug_level
2
//The debug warning level of mi_sys is 2 (show warning and error’s information)Function Modify warning level. Command echo [Level] > /proc/mi_modules/[ModuleName]/debug_level Parameter
Description[Level]
0 No debug info (MI_DBG_NONE)
1 Only show error info (MI_DBG_ERR)
2 show level<=2 info (MI_DBG_WRN)
3 show level<=3 info (MI_DBG_API)
4 show level<=4 info (MI_DBG_KMSG)
5 show level<=5 info (MI_DBG_INFO)
6 show level<=6 info (MI_DBG_DEBUG)
7 show level<=7 info (MI_DBG_TRACE)
8 show all info (MI_DBG_ALL)
[ModuleName] Module name
mi_disp / mi_gfx / mi_rgn / mi_vdec / mi_vif / mi_ai / mi_vdisp / mi_ao / mi_hdmi / mi_sys / mi_vencExample echo 1 > /proc/mi_modules/mi_vdec/debug_level
//Modify the warning level of the mi_vdec module to only show error information.
5.4. debug_file¶
5.4.1. echo¶
-
Debug info
# echo mi_sys_impl.c > /proc/mi_modules/mi_sys/debug_file
-
Debug info analysis
When used for debugging, all levels of DBG log Information in the mi_sys_impl.c file can be printed on the serial port.
-
Parameter Description
Parameter Description Command echo [fileName] … > /proc/mi_modules/mi_xxx/debug_file
//Indicates that the DBG log information of all levels in the function fileName can be printed at runtime. Multiple functions can be enabled at the same time, separated by spaces.
echo > /proc/mi_modules/mi_xxx/debug_file
//Indicates to close the printing of all levels of the previously opened function fileName. At this time, the DBG log in the function fileName can only be printed at the level set by /proc/mi_modules/mi_xxx/debug_level.
PS: fileName must belong to the corresponding mi_xxx module.Parameter
Description[mi_xxx] Indicates the name of the MI module, which can be:
mi_disp / mi_gfx / mi_rgn / mi_vdec / mi_vif / mi_ai / mi_shadow / mi_vdisp / mi_ao / mi_hdmi / mi_sys / mi_venc
5.5. debug_func¶
5.5.1. echo¶
-
Debug info
# echo MI_SYS_IMPL_Init > /proc/mi_modules/mi_sys/debug_func
-
Debug info analysis
When used for debugging, all levels of DBG log Information in the MI_SYS_IMPL_Init() function can be printed on the serial port.
-
Parameter Description
Parameter Description Command echo [funcName] … > /proc/mi_modules/mi_xxx/debug_func
//Indicates that the DBG log information of all levels in the function funcName can be printed at runtime. Multiple functions can be enabled at the same time, separated by spaces.echo > /proc/mi_modules/mi_xxx/debug_func
//Indicates to close the printing of all levels of the previously opened function fileName. At this time, the DBG log in the function funcName can only be printed at the level set by /proc/mi_modules/mi_xxx/debug_level.
PS: funcName must belong to the corresponding mi_xxx module.Parameter
Description[mi_xxx] Indicates the name of the MI module, which can be:
mi_disp / mi_gfx / mi_rgn / mi_vdec / mi_vif / mi_ai / mi_shadow / mi_vdisp / mi_ao / mi_venc / mi_hdmi / mi_sys
5.6. module_version_file¶
5.6.1. cat¶
-
Debug info
# cat /proc/mi_modules/mi_ai/module_version_file MStar Module version: project_commit.sdk_commit.build_time c1799df.fd2d52b.20171225180033 # cat /proc/mi_modules/mi_global_info … MStar Module version: project_commit.sdk_commit.build_time cb68bfd.44aca45.20171226100257 …
-
Debug info analysis
xxxx_version_fileprovides a version Information, and/proc/mi_modules/mi_global_infoalso provides a version Information. But it essentially refers to the version Information of the mi_sys module. The above are just examples of mi_ai and mi_global_info. Each module has its own version file. -
Parameter Description
Parameter Description Version Info project_commit When the module compiles ko, the project commit information of the whole package. If the commit based on the module changes when ko is replaced separately, then the commit obtained in the version of ko will also change accordingly. sdk_commit When the module compiles ko, the sdk commit information of the whole package. If the commit based on the module changes when ko is replaced separately, then the commit obtained in the version of ko will also change accordingly. build_time Time refers to the actual build time, accurate to seconds, even if make clean; When you build image as a whole, the time of each ko will also be different.
5.7. show threads¶
5.7.1. echo¶
-
Debug info
# echo show_threads > /proc/mi_modules/mi_sys/mi_sys0

-
Debug info analysis
View the call stack status of all current threads.
-
This command can help Query & locate deadlock problems.
-
This Command prints a lot, so you’d better to print it in kmsg to avoid contamination by other information.
-
5.8. debug_frc¶
5.8.1. echo¶
-
Debug info
# echo debug_frc on 12 0 0 0 0 "out" > /proc/mi_modules/mi_sys/mi_sys0
-
Debug info analysis
printk in _MI_SYS_IMPL_Common_WriteProc,
Switch enable debug FRC, Modid:12, Dev:0, Chn:0, Pass:0, Port:0, BufType:1. Enable frame rate control debug switch.
-
Parameter Description
Parameter Description Command Switch enable debug FRC: echo debug_frc on [Modid] [Devid] [Chnid] [Passid] [Portid] [in/out] > /proc/mi_modules/mi_sys/mi_sys0
//Open the frame rate control debug switch.
Switch disable debug FRC:echo debug_frc off > /proc/mi_modules/mi_sys/mi_sys0
//Close the frame rate control debug switch.Parameter
Description[Modid] : module id
[Devid] : device id
[Chnid] : channel id
[Passid] : pass id
[Portid] : port id
[in/out] : input/output direction
5.9. set_outputport_depth¶
5.9.1. echo¶
-
Debug info
# echo set_ouputport_depth 6 0 0 0 0 0 2 4 > /proc/mi_modules/mi_sys/mi_sys0
-
Parameter Description
Parameter Description Command Set output port depth:
echo set_ouputport_depth [Modid] [Devid] [Chnid] [Passid] [Portid] [u32userFrameDepth] [u32BufQueueDepth] > /proc/mi_modules/mi_sys/mi_sys0Parameter
Description[Modid] : module id
[Devid] : device id
[Chnid] : channel id
[Passid] : pass id
[Portid] : port id
[u32userFrameDepth]: Set the maximum number of bufs that the output user can get.
[u32BufQueueDepth]: Set the maximum number of bufs for this output system.
5.10. set_thread_priority¶
5.10.1. echo¶
-
Debug info
# echo set_thread_priority 4 0 99 > /proc/mi_modules/mi_sys/mi_sys0 # echo set_thread_priority 8 849 99 > /proc/mi_modules/mi_sys/mi_sys0
-
Parameter Description
Parameter Description Command Set work_thread_priority by module id: echo set_thread_priority [Modid] [Devid] [u32Priority] > /proc/mi_modules/mi_sys/mi_sys0
Set_thread_priority by pid:echo set_thread_priority 8 [pid] [u32Priority] > /proc/mi_modules/mi_sys/mi_sys0Parameter
Description[Modid] : module id
[Devid] : device id
[u32Priority] : Thread level to be set.
[pid] : Thread pid
5.11. mmu debug¶
5.11.1. echo¶
-
Debug info
# echo debug_mmu debug_log 1 1 1 33,34 > /proc/mi_modules/mi_sys/mi_sys0
-
Parameter Description
Parameter Description Command Enable/disable alloc/free buf log:
echo debug_mmu debug_log [enable/disable] [enable/disable free] [enable/disable alloc] [module id list] > /proc/mi_modules/mi_sys/mi_sys0Parameter
Description[enable/disable] :enable or disable
[module id list]: module list, Separated by commas -
Example
1.echo debug_mmu debug_log 1 --- enable alloc/free buf log 2.echo debug_mmu debug_log 1 0 --- enable alloc buf log 3.echo debug_mmu debug_log 1 1 0 --- enable free buf log 4.echo debug_mmu debug_log 1 1 1 4,6 --- enable ai & vif alloc/free buf log 5.echo debug_mmu debug_log 1 0 1 4,6 --- enable ai & vif alloc buf log 6.echo debug_mmu debug_log 1 1 0 4,6 --- enable ai & vif free buf log
-
Note
Enable mmu debug, please refer to MODPARAM.JSON INTRODUCTION
5.12. set_inputport_pattern¶
5.12.1. echo¶
-
Debug info
# echo set_inputPort_pattern 33 0 0 0 0 1 > /proc/mi_modules/mi_sys/mi_sys0
-
Debug info analysis
Set to enable ModId33 DevId0 ChnId0 PassId0 InputPortId0, at this time, ModId33 module in pipeline only keeps one buf data to pass data to the post-module (The bindtype of ModId33 and post-module need to be set frame mode), which is used for debugging to locate which ModId's buf data is faulty.
-
Parameter Description
Parameter Description Command echo set_inputport_pattern [Modid] [Devid] [ChnId] [PassId] [InputPortId] [bEnable] > /proc/mi_modules/mi_sys/mi_sys0
//Set a certain inputPort of ModId to retain only a piece of buf data to transfer data to the subsequent ModId (the bindType of the ModId and the subsequent ModId need to be set to frame mode), which is used for debugging to locate which ModId's buf data is faulty.Parameter
Description[Modid] : module id.
[Devid] : device id.
[ChnId] : channel id.
[PassId] : pass id.
[inputPortId] : inputPort Id.
[bEnable] : Whether to enable, 0/1.
5.13. mi_sys0¶
5.13.1. cat¶
-
Debug info
# cat /proc/mi_modules/mi_sys/mi_sys0
-
Debug info analysis
This command shows the relevant information processed by the data stream buf of each modId module when the current device is in the pipeline.
-
Parameter Description
Parameter Description (mod-dev-chn info) module module Id, which can be:
mi_disp / mi_gfx / mi_rgn / mi_vdec / mi_ai / mi_shadow / mi_vdisp / mi_ao / mi_hdmi / mi_sys / mi_venc / mi_vifdevId device Id chn channel Id pre
(Consult whether the
current modId can handle the handleinfo of buf)suc The number of times that the current modId has successfully preprocessed buf. busy The number of times that the current modId has successfully preprocessed buf. drop The number of drop operations performed by the current modId on the preprocessed buf. Enq
(Add buf to handleinfo
in the queue of the current modId)run The current modId enqueue operation returns the number of times in the running state. done The current modId has been processed to complete the number of bufs in the queue. retry The current number of modId retrying to process buf in the queue. drop The number of times the current modId drops the pending buf in the queue. bar cmdq related checkin
(inputport buf handleinfo)run The number of times that the current modId processed the inputport buf operation to return to the running state. done The current modId has processed the number of bufs in the inputport. retry The current modId retry to process the coefficient of inputport buf. drop The number of times the current modId drops the pending input port buf. checkout
(outputport buf handleinfo)run The current modId processing outputport buf operation returns the number of times in the running state. done The number of times that the current modId has been processed to complete the buf in the outputport. retry The current number of modId retries to process the outputport buf. drop The number of times the current modId drops the pending outputport buf.
5.14. miu_protect¶
5.14.1. cat¶
-
Debug info
# cat /proc/mi_modules/mi_sys_mma/miu_protect ============= start miu_protect_info ================== kernel protect enabled LX : cpu_start_addr:0x20c00000 size:0xe300000 miu_index miuBlockIndex start_cpu_bus_pa length 0x0 0x00 0x20c00000 0x460000 KernelProtect IP white list: clientId name 43 MIU_CLIENT_MIPS_RW 50 MIU_CLIENT_NAND_RW 82 MIU_CLIENT_USB_UHC0_RW 83 MIU_CLIENT_USB_UHC1_RW 84 MIU_CLIENT_USB_UHC2_RW 18 MIU_CLIENT_G3D_RW 140 MIU_CLIENT_USB3_RW 129 MIU_CLIENT_SDIO_RW 165 MIU_CLIENT_SATA_RW 133 MIU_CLIENT_USB_UHC3_RW 225 MIU_CLIENT_USB30_1_RW 226 MIU_CLIENT_USB30_2_RW 5 MIU_CLIENT_BDMA_RW 14 MIU_CLIENT_EMAC_RW -
Debug info analysis
This command shows the related Information of miu protect.
-
Parameter Description
Parameter Description LX
(Take only one LX for example, LX represents memory corresponding to linux image)cpu_start_addr The starting CPU addr corresponding to this LX. size The size corresponding to this LX. Information about the range of a certain kernel protect miu_index Index number miuBlockIndex Total 4 miu range’s index information. start_cpu_bus_pa The starting cpu bus addr of this LX. length The length of the range. KernelProtect IP white list clientId Miu protect IP id in IP whitelist (The global id from the perspective of undivided group). name The actual name of the IP corresponding to the clientId.
5.15. mma_heap_name0¶
5.15.1. cat¶
-
Debug info
# cat /proc/mi_modules/mi_sys_mma/mma_heap_name0 heap_info: heap_name pa_start length avail mma_heap_name0 40000000 1f000000 1b238000 heap_param: mmuEnable addsize_before addsize_after delayUnmap freeEntryNum 1 0 0 0 361 main_chunk_mgr: vpa_start length avail used HighPeak LowPeak 60000000 20000000 1c238000 3dc8000 40c5000 d40000 ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------ offset length used_flag task_name pid Module 0 300000 1 CMDMEM -1 mi_sys 300000 1000 1 sys-logConfig -1 mi_sys 301000 40000 1 sys-logBuffer -1 mi_sys 341000 1fb000 1 vif0-out0-0 867 mi_vif 53c000 1fb000 1 vif0-out0-0 867 mi_vif 737000 1fb000 1 vif0-out0-0 867 mi_vif 932000 3fa000 1 mma_heap_codec -1 mi_sys d2c000 21000 1 ven_mv_0 867 mi_venc d4d000 23000 1 ven_fcty_0 867 mi_venc d70000 12000 1 ven_fctc_0 867 mi_venc d82000 41000 1 ven_rdo_0 867 mi_venc dc3000 1000 1 ven_inst_0 867 mi_venc dc4000 1000 1 venc-algo-m 867 mi_venc dc5000 60000 0 NA -1 mi_sys e25000 a3000 1 ISP_STATIS 867 mi_isp ec8000 1000 1 ISP_WDR 867 mi_isp ec9000 22000 1 DNR_INFO1 867 mi_isp eeb000 32a000 1 DNR_INFO0 867 mi_isp 1215000 6000 1 ISP_IDX_CMDQ 867 mi_isp 121b000 10000 1 ISP_CMDQ 867 mi_isp 122b000 4000 1 ISP_MLOAD 867 mi_isp 122f000 152000 1 RingHeapAlloc -1 mi_sys 1381000 1a6000 0 NA -1 mi_sys 1527000 4000 1 ISP_MLOAD 867 mi_isp 152b000 3f5000 1 venc-ring-mem0 867 mi_venc 1920000 3b1000 1 ven_rec_0_0 867 mi_venc 1cd1000 2fd000 0 NA -1 mi_sys 1fce000 2000000 1 venc-ring-mem1 867 mi_venc 3fce000 2fd000 1 scl0-out0-0 867 mi_scl 42cb000 1bd35000 0 NA -1 mi_sys (mma_heap_codec)sub_chunk_mgr: vpa_start length avail used HighPeak LowPeak 60932000 3fa000 2df000 11b000 11b000 0 ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------ offset length used_flag task_name pid Module 0 ea000 1 vcodec_dev -1 mi_venc ea000 31000 1 ven_work_ven_ta -1 mi_venc 11b000 2df000 0 NA -1 mi_sys (CMDMEM)sub_chunk_mgr: vpa_start length avail 60000000 300000 195000 ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------ offset length used_flag cmdq_id pid ModDev 0 20000 0 -1 -1 NA 20000 16b000 1 1 0 mi_isp0 20000 16b000 1 1 0 mi_scl0 20000 16b000 1 1 0 mi_venc8 18b000 175000 0 -1 -1 NA -
Debug info analysis
The cat information corresponds to the basic information and current status of the mma heap.
-
Parameter Description
Parameter Description heap_info heap_name The name of mma heap. pa_start The start PA of the heap. length The whole length of mma heap. avail The total amount of unused memory remaining in the heap.. heap_param mmuEnable Enable mmu addrsize_before Set the size of the reserved application before the application buf. addrsize_after Set the size of the reserved application after the application buf. delayUnmap Whether to enable the delayed unmap currently applied for buf when buf free, when it is applied again next time, first unmap and then map.
1: Enable to delay unmap
0: Disable to delay unmapfreeEntryNum Free entry number main_chunk_mgr vpa_start Main chunk mgr start address. It name “vpa_start” when mmu is enable, or it will name “pa_start”. length The entire mma vpa length managed by chunk mgr. Since the entire mma heap is used as a chunk mgr, when mmu is turned off, the value is equal to mma heap length; When mmu is turned on, the value is greater than mma heap length. avail The total amount of unused memory remaining in chunk mgr (heap). used The total amount of used memory remaining in chunk mgr (heap). HighPeak The peak memory counted over a period of time. LowPeak The valley memory counted over a period of time. offset The offset of this chunk in chunk mgr. length The length of this chunk. used_flag Whether the chunk is allocated. If yes, the value is 1; otherwise, the value is 0. task_name If the used flag is 1, then task_name stores which task uses it; otherwise, it is an invalid value NA. pid Invalid at present. Module Which Module used the chunk. (mma_heap_codec)
sub_chunk_mgr(mma_heap_codec)
sub_chunk_mgrThe sub chunk mgr of main chunk mgr. It is the chunk name “mma_heap_codec” in main chunk mgr.
About the parameter of this chunk mgr, please refer to the parameter of main chunk mgr.
It doesn’t show information of sub chunk mgr by default. After set one command, it perhaps show more than one sub chunk mgr, or show nothing for sub chunk mgr.
The command is: echo show_privMma 1 > /proc/mi_modules/mi_sys/mi_sys0(CMDMEM)sub_chunk_mgr (CMDMEM)
sub_chunk_mgrThe sub chunk mgr of main chunk mgr. It is the chunk name “CMDMEM” in main chunk mgr. This sub chunk mgr is show by default, it show the cmdq mma buf usage. vpa_start (CMDMEM)
sub chunk mgr start address. It name “vpa_start” when mmu is enable, or it will name “pa_start”.length The length of mma buf cmdq used. avail The total amount of unused memory remaining in CMDMEM chunk mgr. offset The offset of this chunk in chunk mgr. length The length of this chunk. used_flag Whether the chunk is allocated. If yes, the value is 1; otherwise, the value is 0. cmdq_id The cmdq id witch use the chunk. pid Invalid at present. ModDev The module name and device id witch use the cmdq buf.
5.15.2. echo¶
| Function | Dump the data of the specified offset and length to the specified path. |
|---|---|
| Command | echo [Path] [Offset] [Length] > /proc/mi_modules/mi_sys_mma/mma_heap_name[Num] |
| Parameter Description |
[Path] The path to save the file, only need to provide the path, do not provide the specific file name, the system will automatically generate the corresponding file name according to the parameter. [Offset] Dump data from the offset of the mma heap, which must be 64B aligned. [Length] The total amount of data dumped in the mma heap, must be 64B aligned. [Num] The number corresponding to mma head, mma_heap_name0 can be viewed through cat /proc/cmdline at present. |
| Example | echo /mnt/ 0 64 > /proc/mi_modules/mi_sys_mma/mma_heap_name0 //Dump mma__mma_heap_name0__0__64.bin file under /mnt. |
5.16. imi_mma_heap¶
5.16.1. cat¶
-
Debug info
# cat /proc/mi_modules/mi_sys_mma/imi_mma_heap mma heap nameheap_base_cpu_bus_addr length chunk_mgr_avail mmuEnable addsize_before addsize_after bMmuDelayUnmap free_entry_num imi_mma_heap 20000000 43800 26800 0 0 0 0 0 chunk_mgr info: offset length avail used HighPeak LowPeak 0 43800 26800 1d000 1d000 0 each chunk info: offset length used_flag task_name pid Module 0 1d000 1 SRAM -1 mi_venc 1d000 26800 0 NA -1 mi_sys -
Debug info analysis
The cat information corresponds to the basic information and current status of the mma heap.
-
Parameter Description
Parameter Description heap basic info mma heap name mma heap name heap_base_cpu_bus_addr The unused amount of allocations in allocator. length The length of heap. chunk_mgr_avail The total amount of unused memory remaining in heap. mmuEnable Whether Mma heap support HW_MMU. 1 means enable, 0 means disable. addrsize_before Set the reserved memory space size before the requested buf. addrsize_after Set the reserved memory space size after the requested buf. bMmuDelayUnmap Whether to delay unmap the current alloced buf when buf free is applied.When alloc buf next time, firstly unmap before mapping.
1: enable delaying unmap
0: disable delaying unmapfree_entry_num the free entry num chunk_mgr info offset The offset of chunk mgr. Since the entire mma heap is used as a chunk mgr, this value is always 0. length The length of chunk mgr. Since the entire mma heap is used as a chunk mgr, this value is always mma heap length. avail The total free memory length in chunk mgr. used The total used memory length in chunk mgr. HighPeak The statistical memory peak value voer a period of time. LowPeak The statistical memory valley value voer a period of time. each chunk info (Information and usage of each chunk in chunk mgr) offset The offset of this chunk in chunk mgr. length The length of this chunk. used_flag Whether the chunk is allocated. If yes, the value is 1; otherwise, the value is 0. task_name If the used flag is 1, then task_name stores which task uses it; otherwise, it is an invalid value NA. pid current of the chunk -> tgid Module The module of the chunk
5.17. meta¶
5.17.1. cat¶
-
Debug info
# cat /proc/mi_modules/mi_sys_mma/meta =================== start meta_info ========================= basic info: total page count:16 each meta data size:256 total_count_with_metadatasize 256 total_free_count_with_metadatasize:254 meta info : ref_cnt=3 each allocation info: offset_in_pool length phy_addr va_in_kern real_used_flag 0x0 0x100 0x2336000 c1736000 0 0x100 0x100 0x2336100 c1736100 0 0x200 0x100 0x2336200 c1736200 0 0x300 0x100 0x2336300 c1736300 0 0x400 0x100 0x2336400 c1736400 0 0x500 0x100 0x2336500 c1736500 0 0x600 0x100 0x2336600 c1736600 0 0x700 0x100 0x2336700 c1736700 0 0x800 0x100 0x2336800 c1736800 0 0x900 0x100 0x2336900 c1736900 0 0xa00 0x100 0x2336a00 c1736a00 0 …… =================== end meta_info ================================
-
Debug info analysis
Once meta allocator has been used (There is only one meta allocator),
/proc/mi_modules/mi_sys_mma/metafile will be generated, and the corresponding memory will allocate to be used.
5.17.2. echo¶
| Function | Dump the data of the specified offset and length to the specified path. |
|---|---|
| Command | echo [Path] [Offset] [Length] > /proc/mi_modules/mi_sys_mma/ vb_pool_global |
| Parameter Description |
[Path] The path to save the file, only need to provide the path, do not provide the specific file name, the system will automatically generate the corresponding file name according to the parameter. [Offset] From which offset of the allocator to start dump data, it is the logical offset of the allocator. [Length] The size of the total amount of data dumped in the allocator. |
| Example | echo /mnt 0 1024 > /proc/mi_modules/mi_sys_mma/meta //Dump meta_0_1024.bin under /mnt. |
5.18. mi_module_name_devid¶
5.18.1. cat¶
-
Debug info
cat /proc/mi_modules/mi_disp/mi_disp0
-
Debug info analysis
The result of the cat operation is divided into two parts. The first part is the general Debug Information provided by MI_SYS for the device, which is provided from four perspectives: device, channel, input port, and output port; the second part is the private information of the device . The content of each module will explain the private Information elsewhere, here only the general Information will be explained from the SYS perspective.
Take cat /proc/mi_modules/mi_vdisp/mi_vdisp0 as an example to get the above result.
-
Parameter Description
Parameter Description Common info for device ChnNum The channel number EnChnNum The enabled channel number PassNum The pass number InPortNum The input port number OutPortNum The output port number CollectSize The total size of allocator contained in AllocatorCollection CMDQ kickoff counter PassId The pass Id using cmdq in the device. CmdqId The cmdq Id TotalKickoff The current kickoff times of the cmdq. kickoffFence The current kickoff fence value of the cmdq. Idle The current Idle times of kickoff in the cmdq. DevId The device Id. current_buf_size The currnet used buf size of the device Peak_buf_size The used buf peak value of the device. each dev buf info offset The offset from buf. length The length of buf. used_flag The flag of recording whether buf is used. task_name The name of task using the buf. Common info for channel(only dump enabled channel) ChnId The channel Id. PassNum The pass Id EnInPNum The enabled input port number EnOutPNum The enabled output port number. MMAHeapName If SetChnMMAConf, the value is the corresponding mma heap name; otherwise, the value is NULL. current_buf_size The current used buf size. Peak_buf_size The current used buf peak value of the channel. user_pid The task pid of the channel. each chn buf info offset The offset from buf used by the channel. length The buf length used_flag The flag of recording whether buf is used. task_name The name of task using the buf. chn pass pipeline delay in us (can be only used in IPC currently, which uses vif as first input) Flow OnPreProcessInputTask: MI PASS determines whether the current task needs to be processed, and if it can be configured for the output buffer.
EnqueueInputTask: Hand over the input task to MI PASS to start processing.
BarrierInputTask: Insert CMDQ synchronization instructions (such as waitevent, polling engine done).
CheckInputTaskStatus: Check whether the input task is completed and the completion status (success, failure, etc).
DequeueInputTask: Notify MI PASS to release the resources associated with the input task.
OnPollingAsyncOutputTaskConfig: For MI Pass with asynchronous input and output, or MI Pass with only output without input, MI SYS queries whether there is an independent output buf request requirement.
EnqueueAsyncOutputTask: Hand over the asynchronous output task to MI PASS for processing.
BarrierAsyncOutputTask: Insert cmdq synchronization instructions for asynchronous output tasks.
CheckOutputTaskStatus: Check whether the output task is completed and the completion status (success, failure, etc).
DequeueOutputTask: Notify MI PASS to release the resources associated with the output task.
FinDMADispatch: MI SYS transfers the buffer in the output task of MI PASS to the input queue of the bound post-level MI PASS.Min The minimum delay elapsed from Buffer generation (generally the time when vif starts to process the buffer) to the flow corresponding to the MI PASS. Max The maximum delay elapsed from Buffer generation (generally the time when vif starts to process the buffer) to the flow corresponding to the MI PASS. Avg The average delay elapsed from Buffer generation (generally the time when vif starts to process the buffer) to the flow corresponding to the MI PASS. Diff The current delay elapsed from Buffer generation (generally the time when vif starts to process the buffer) to the flow corresponding to the MI PASS. Input port common info(only dump enabled Input port) ChnId Input port channel id PassId Input port pass id PortId Input port id SrcFrmrate Src frame rate DstFrmrate Dst frame rate user_buf_quota The quota of buff count UsrInjectQ_cnt The buff count of UsrInjectBufQueu UsrInjectQ_size The buff size of UsrInjectBufQueue BindInQ_cnt The buff count of BindInputBufQueue BindInQ_size The buff size of BindInputBufQueue WorkingQ_cnt The buff count of WorkingQueue WorkingQ_size The buff count of WorkingQueue usrLockedInjectCnt The buff count currently taken by user Input port bind info(only dump enabled Input port) ChnId Channel id PortId Input port id bind_module_id The id of the module where the output port is bound to the input port bind_module_name The name of the module where the output port is bound to the input port bind_ChnId The id of the channel where the output port is bound to the input port. bind_PortId The id of the port where the output port is bound to the input port. Output port common info (only dump enabled Output port) ChnId Output port channel id PortId Output port id BufCntQuota The quota of buff count usrLockedCnt The buff count actually taken by user in UsrGetFifoBufQueue totalOutPortInUsed totalOutputPortInUsed buff count DrvBkRefFifoQ_cnt DrvBkRefFifoQueue buff count DrvBkRefFifoQ_size DrvBkRefFifoQueue buff count UsrGetFifoQ_cnt UsrGetFifoBufQueue buff count UsrGetFifoQ_size UsrGetFifoBufQueue buff size WorkingQ_cnt WorkingQueue buff count WorkingQ_size WorkingQueue buff size Output port BindPeerInputPortList info(only dump enabled Output port) ChnId Output port channel id PortId Output port id bind_module_id The id of the module where one of the input ports binded to the output port(here referred to as the binded input port) bind_module_name The name of the module where the binded input port is located bind_ChnId The channel id where the binded input port is located bind_PortId The portid where the binded input port is located
5.18.2. echo¶
| Function | Get help information of the module. |
|---|---|
| Command | echo help > /proc/mi_modules/[ModName]/[ModID] |
| Parameter Description |
[ModName] Module name mi_disp / mi_gfx / mi_rgn / mi_vdec / mi_scl / mi_ai / mi_isp / mi_shadow / mi_vdisp / mi_ao / mi_hdmi / mi_sys / mi_venc / mi_vif [ModID] The corresponding file in the module is generally the module name + number Such as mi_disp0, mi_gfx0, mi_rgn0 |
| Example | echo help > /proc/mi_modules/mi_disp/mi_disp0 //Get help information of mi_disp0. |
5.19. mem_stat¶
5.19.1. cat¶
-
Debug info
# cat /proc/mi_modules/mi_sys_mma/mem_stat mi_sys CMDMEM c0000 TotalSize 101000 AllTotalSize 101000 -
Debug info analysis
Print the memory status of mi sys.
-
Parameter Description
Parameter Description Mem_stat mi_sys Owned mi_sys module CMDMEM Cmd memory size sys-logBuffer The maximum buf size applied to sys log sys-logConfig The buf size allocated (applied) to sys log TotalSize The size used by ModuleUsdTotalSize AllTotalSize Total size
6. MODPARAM.JSON INTRODUCTION¶
6.1. The json file content¶
{
"E_MI_MODULE_ID_SYS" :
{
"cmdQBufSize" : 400
},
"E_MI_MODULE_ID_DISP" :
{
"threadPriority" : 98,
"debugFilePath" : "",
"u64CpuMaskAffinity" : "0x0"
},
"E_MI_MODULE_ID_MIPITX" :
{
"threadPriority" : 70
},
"E_MI_MODULE_ID_PANEL" :
{
"debugFilePath" : ""
},
"E_MI_MODULE_ID_FB" :
{
"default_reserved_mem_name": "fb"
}
}
The modparam.json is under /config, when sys is initialized, the json file will be loaded.
6.2. SYS common paramaters and paramater description¶
| Parameters | Default | Support chip | Customer configuration | Function |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| bEnableMmu | True | Souffle and later chip | Y | Enable or disable hw mmu |
| g_bEnableMiuProtect | TRUE | Souffle and later chip | Y | Enable or disable miu protect |
| bEnableCmdqReset | FALSE | Souffle and later chip | Y | Enable or disable cmdq reset |
| default_config_path | "ABABABABABABABABABAB" | Souffle and later chip | Y | Path of json file |
| config_ini_path | "/misc/config.ini" | Souffle and later chip | Y | Path of ini file |
| mmu_vpa_length | "0x0" | Souffle and later chip | N | Configurate mmu vpa length to reduce kernel memory's using. |
| cmdQBufSize | 1024 | Souffle and later chip | Y | Size of cmdq buf |
| entrySize | 0 | Souffle and later chip | N | Configurate mmu entry size |
| debugMmu | 0 | Souffle and later chip | Y | Enable or disable mmu debug code |
| gMmuStartPfn | 0 | Souffle and later chip | N | Configurate mmu start address |
6.3. Example of parameter usage¶
The sys only needs to focus on this ModuleId called E_MI_MODULE_ID_SYS.
6.3.1. cmdQBufSize¶
The parameter represents the cmdqbuf size. For example, "cmdQBufSize" : 400 shows cmdq buf is 400K. Please modify cmdQBufSize if you need to change the cmdq buf.
6.3.2. bEnableMmu¶
The parameter represents whether the mmu is enabled. To disable bEnableMmu, please add bEnableMmu:0, since the default value is 1.
Example:
"E_MI_MODULE_ID_SYS" :
{
"cmdQBufSize" : 400,
" bEnableMmu” : 0
},