WATCHDOG USER GUIDE
REVISION HISTORY¶
| Revision No. | Description |
Date |
|---|---|---|
| 1.0 | 04/21/2023 |
1. Overview¶
Watchdog (WDT) is a hardware or software mechanism that resets the system when it times out. Its core consists of a timer and a reset module. Its working principles are as follows:
- The user pre-sets a timeout period, during which the internal counter of the watchdog must be reset by "feeding the dog"
- If the internal counter value reaches the set timeout period and the watchdog is not fed in time, the watchdog will trigger a system reset and restart the system
The terms "WDT," "watchdog," and "watchdog" used in this document all refer to the timeout reset system function described above. This document describes the hardware watchdog mechanism of the PCUPID series chips.
2. Keyword Description¶
-
Hardware watchdog: An independent watchdog hardware circuit (including timing and reset circuits, built-in SoC). The software periodically writes specific values to the hardware registers. After the timeout, it outputs a hardware reset signal to force the system to restart. It does not rely on the operating system to run, and can trigger a hardware reset even if the CPU crashes.
-
Software watchdog: Based on the software logic simulation of the kernel timer, the user program feeds the watchdog periodically. After the timeout, the kernel API triggers a system restart or alarm. It does not require hardware support and is flexible and customizable. The timeout action cannot be triggered after the CPU crashes.
-
Watchdog timeout: watchdog timeout duration. If the watchdog is not fed within this duration, the hardware watchdog will output a hardware reset signal and the software watchdog will trigger a timeout action.
-
Watchdog pretimeout: Watchdog pretimeout is a pre-warning mechanism within the watchdog mechanism, providing an early warning before the watchdog actually times out. When a pretimeout is triggered, the system receives a warning signal (e.g., an interrupt). However, there is still a buffer period (the interval between pretimeout and actual timeout) for the system to troubleshoot (e.g., log, save critical data) or attempt self-recovery (e.g., kill a troublesome process).
3. Functional Description¶
The Linux kernel supports both high-precision timer-based software watchdogs (softdog) and hardware-based watchdogs, and provides /dev/watchdog* device files for interaction with userspace programs. Applications can periodically feed the watchdog through the /dev/watchdog* devices.
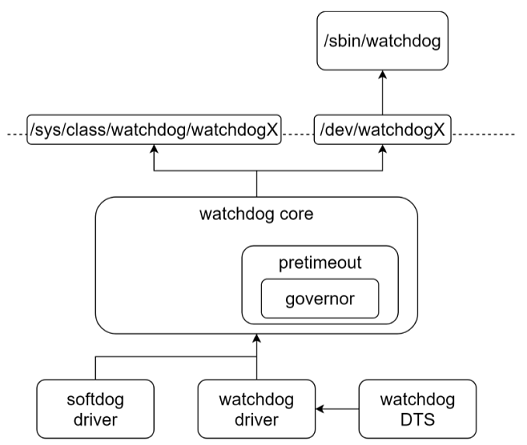
Software watchdog: Linux comes with a function, open on demand, closed by default
Hardware watchdog: SOC built-in, Sigmastar provides drivers, Linux kernel provides devfs watchdog interface, users use ioctl to operate watchdog device
4. Hardware Connection Introduction¶
The hardware watchdog of PCUPID series chips is built into the SOC, with no pins open to the outside world and no need for peripheral hardware circuit connection. The driver writes the register of the SOC to control the watchdog hardware circuit.
5. Uboot Usage Introduction¶
5.1 dts configuration¶
The DTS configuration related to the watchdog driver is as follows:
watchdog: watchdog {
compatible = "sstar,wdt";
reg = <0x1F006000 0x40>;
status = "okay";
};
Watchdog DTS configuration instructions:
| Property | Description | Value | Remarks |
|---|---|---|---|
| compatible | Match the driver for driver registration | "sstar,wdt" | Modification prohibited |
| reg | watchdog register information | Hardware design decision | Modification prohibited |
| status | Select whether to enable the watchdog driver | "ok" or "disable" | Modify as needed, enabled by default |
5.2 uboot config configuration¶
Use make menuconfig to open or close watchdog related config configuration items:
(1) Driver configuration item CONFIG_SSTAR_WDT:
[*] SigmaStar drivers ---> [*] Sigmastar watchdog
(2) Start the watchdog configuration item CONFIG_WATCHDOG_AUTOSTART and the timeout configuration item CONFIG_WATCHDOG_TIMEOUT_MSECS:
[*] Device Drivers ---> [*] Watchdog Timer Support ---> [*] Automatically start watchdog timer [*] Watchdog timeout in msec
Note: If CONFIG_WATCHDOG_AUTOSTART = Y, the watchdog will be started by default when uboot starts, and the timeout period is set by CONFIG_WATCHDOG_TIMEOUT_MSECS. The default value of CONFIG_WATCHDOG_TIMEOUT_MSECS is 2000, in ms, which is 2s
(3) Watchdog configuration item CONFIG_WATCHDOG:
[*] Device Drivers ---> [*] Watchdog Timer Support ---> [*] Enable U-Boot watchdog reset
Note: If this macro is enabled, uboot will feed the dog every second. If CONFIG_WATCHDOG_AUTOSTART is enabled but CONFIG_WATCHDOG is not enabled, the system will reboot after WATCHDOG_TIMEOUT_MSECS ms
(4) Open the wdt command configuration item CONFIG_WATCHDOG:
[*] Command line interface ---> [*] Device access commands ---> [*] wdt
Note: Only when this macro is enabled can the wdt command be executed under uboot
5.3 wdt command parameter description¶
-
View available watchdogs:
wdt list - list watchdog devices Example: SigmaStar # wdt list watchdog (sstar_wdt) SigmaStar#
Note: "watchdog" in the example is the device name, sstar_wdt is not the device name
-
Get/set the current watchdog device:
wdt dev [<name>] - get/set current watchdog device
Parameter Name Description name Without parameters, it gets the name of the watchdog device currently operating. -
Start watchdog:
wdt start <timeout ms> [flags] - start watchdog timer
Parameter Name Description timeout ms Specify the watchdog timeout in milliseconds flags Flags information passed to the watchdog driver. The current driver does not use this parameter. -
Stop watchdog:
wdt stop - stop watchdog timer
-
Reset the watchdog timer:
wdt reset-reset watchdog timer
-
Immediately trigger the watchdog timeout:
wdt expire [flags] - expire watchdog timer immediately
Parameter Name Description flag -f forces trigger timeout; -d delays trigger timeout; -s suppresses logging during trigger timeout. Note: The
wdt expirecommand is used to trigger the watchdog timeout immediately. U-Boot's native implementation sets the timeout to 1ms, which is not supported by current hardware.
5.4 wdt usage examples¶
First turn off the "Auto-start watchdog" and "Auto-feed watchdog" configuration items, then perform the following operations
wdt list → wdt list // Check which watchdog devices are available wdt dev [<name>] → wdt dev watchdog // Use the watchdog named "watchdog" wdt start <timeout ms> [flags] → wdt start 10000 // Set the watchdog timeout to 10s wdt reset → wdt reset //Reset the watchdog timer before the watchdog times out wdt stop → wdt stop // Stop watchdog before watchdog times out
Note: To disable the watchdog timer, disable the CONFIG_WATCHDOG_AUTOSTART configuration item. To disable the automatic watchdog timer, disable the CONFIG_WATCHDOG configuration item. See the uboot config section above for instructions. If these two configuration items are not disabled, the uboot system will automatically ping the watchdog timer at regular intervals, preventing you from testing the wdt start function with this demo.
6. Kernel Usage Introduction¶
6.1 dts configuration¶
The DTS configuration related to the Watchdog driver is as follows:
WDT: watchdog {
compatible = "sstar,wdt";
reg = <0x0 0x1F006000 0x0 0x40>;
interrupts = <GIC_SPI INT_FIQ_WDT IRQ_TYPE_LEVEL_HIGH>;
max-length = <40>;
status = "okay";
};
Watchdog DTS configuration instructions:
| Property | Description | Value | Remarks |
|---|---|---|---|
| compatible | Match the driver for driver registration | "sstar,wdt" | Modification prohibited |
| reg | Set register bank address | Hardware design decision | Modification prohibited |
| interrupts | Specify the hardware interrupt number used by Watchdog | Hardware design decision | Modification prohibited |
| max-length | watchdog count bandwidth | hardware design decision | modification prohibited |
| status | Select whether to enable the Watchdog driver | "ok" or "disable" | Modify as needed, enabled by default |
6.2 kernel config configuration¶
Use make menuconfig to open or close watchdog related config configuration items:
Device Drivers --->
[*] SStar SoC platform drivers --->
<*> watchdog driver
6.3 Usage Introduction¶
6.3.1 How to use devfs¶
Linux provides the /dev/watchdog node for users to use, which can be operated with ioctl. The user program needs to actively enable the watchdog function.
-
Header file: include/uapi/linux/watchdog.h
-
Data structure: struct watchdog_info structure describes the information of the watchdog device
-
ioctl control commands:
-
WDIOC_GETSUPPORT: Gets the functions supported by the watchdog
-
WDIOC_SETOPTIONS: Used to enable or disable the watchdog
-
WDIOC_KEEPALIVE: Keepalive operation
-
WDIOC_SETTIMEOUT: Set the watchdog timeout
-
WDIOC_GETPRETIMEOUT: Get the watchdog timeout
-
The header file watchdog.h is as follows:
#ifndef _UAPI_LINUX_WATCHDOG_H #define _UAPI_LINUX_WATCHDOG_H #include <linux/ioctl.h> #include <linux/types.h> #define WATCHDOG_IOCTL_BASE 'W' struct watchdog_info { __u32 options; /* Options the card/driver supports */ __u32 firmware_version; /* Firmware version of the card */ __u8 identity[32]; /* Identity of the board */ }; #define WDIOC_GETSUPPORT _IOR(WATCHDOG_IOCTL_BASE, 0, struct watchdog_info) #define WDIOC_GETSTATUS _IOR(WATCHDOG_IOCTL_BASE, 1, int) #define WDIOC_GETBOOTSTATUS _IOR(WATCHDOG_IOCTL_BASE, 2, int) #define WDIOC_GETTEMP _IOR(WATCHDOG_IOCTL_BASE, 3, int) #define WDIOC_SETOPTIONS _IOR(WATCHDOG_IOCTL_BASE, 4, int) #define WDIOC_KEEPALIVE _IOR(WATCHDOG_IOCTL_BASE, 5, int) #define WDIOC_SETTIMEOUT _IOWR(WATCHDOG_IOCTL_BASE, 6, int) #define WDIOC_GETTIMEOUT _IOR(WATCHDOG_IOCTL_BASE, 7, int) #define WDIOC_SETPRETIMEOUT _IOWR(WATCHDOG_IOCTL_BASE, 8, int) #define WDIOC_GETPRETIMEOUT _IOR(WATCHDOG_IOCTL_BASE, 9, int) #define WDIOC_GETTIMELEFT _IOR(WATCHDOG_IOCTL_BASE, 10, int) #define WDIOF_UNKNOWN -1 /* Unknown flag error */ #define WDIOS_UNKNOWN -1 /* Unknown status error */ #define WDIOF_OVERHEAT 0x0001 /* Reset due to CPU overheat */ #define WDIOF_FANFAULT 0x0002 /* Fan failed */ #define WDIOF_EXTERN1 0x0004 /* External relay 1 */ #define WDIOF_EXTERN2 0x0008 /* External relay 2 */ #define WDIOF_POWERUNDER 0x0010 /* Power bad/power fault */ #define WDIOF_CARDRESET 0x0020 /* Card previously reset the CPU */ #define WDIOF_POWEROVER 0x0040 /* Power over voltage */ #define WDIOF_SETTIMEOUT 0x0080 /* Set timeout (in seconds) */ #define WDIOF_MAGICCLOSE 0x0100 /* Supports magic close char */ #define WDIOF_PRETIMEOUT 0x0200 /* Pretimeout (in seconds), get/set */ #define WDIOF_ALARMONLY 0x0400 /* Watchdog triggers a management or other external alarm not a reboot */ #define WDIOF_KEEPALIVEPING 0x8000 /* Keep alive ping reply */ #define WDIOS_DISABLECARD 0x0001 /* Turn off the watchdog timer */ #define WDIOS_ENABLECARD 0x0002 /* Turn on the watchdog timer */ #define WDIOS_TEMPPANIC 0x0004 /* Kernel panic on temperature trip */ #endif /* _UAPI_LINUX_WATCHDOG_H */
6.4. SampleCode¶
6.4.1. Start Watchdog¶
Enable the/dev/watchdog device, and watchdog will be started.
The reference code is as follows:
int wdt_fd = -1; wdt_fd = open("/dev/watchdog", O_WRONLY); if (wdt_fd == -1) { // fail to open watchdog device }
6.4.2. Stop Watchdog¶
The reference code is as follows:
int option = WDIOS_DISABLECARD; ioctl(wdt_fd, WDIOC_SETOPTIONS, &option); if (wdt_fd != -1) { close(wdt_fd); wdt_fd = -1; }
6.4.3. Set Timeout¶
Set the timeout in seconds using the standard IOCTL command WDIOC_SETTIMEOUT, with a recommended timeout of more than 5 seconds. The reference code is as follows:
#define WATCHDOG_IOCTL_BASE 'W' #define WDIOC_SETTIMEOUT _IOWR(WATCHDOG_IOCTL_BASE, 6, int) int timeout = 20; ioctl(wdt_fd, WDIOC_SETTIMEOUT, &timeout);
6.4.4. Feed Watchdog¶
Feed the dog using the standard IOCTL command WDIOC_KEEPALIVE, and the feeding interval should be smaller than the timeout period. The reference code is as follows:
#define WATCHDOG_IOCTL_BASE 'W' #define WDIOC_KEEPALIVE _IOR(WATCHDOG_IOCTL_BASE, 5, int) ioctl(wdt_fd, WDIOC_KEEPALIVE, 0);
6.4.5. demo¶
#include <stdio.h> #include <iwatchdog.h> #include <unistd.h> #include <fcntl.h> #include <string.h> #include <errno.h> #include <sys/ioctl.h> #include <linux/watchdog.h> int main() { int fd = open("/dev/watchdog", O_WRONLY); if (fd < 0) { perror("Failed to open /dev/watchdog"); return -1; } if (ioctl(fd, WDIOC_SETOPTIONS, WDIOS_ENABLECARD) < 0) { perror("Failed to enable watchdog"); close(fd); return -1; } while (1) { if (write(fd, "V", 1) != 1) { // Reset watchdog timer perror("Failed to reset watchdog timer"); break; } sleep(1); // Sleep for a while before resetting again } close(fd); return 0; }
6.4.6 Test Cases¶
The test cases of hardware watchdog in kernel: <Kernel>drivers/sstar/watchdog/ut/wdt_ut.c
Example: # wdt_ut start 10 /* After starting watchdog, the system will continuously feed the dog, so the system will not restart after 10 seconds*/ # wdt_ut reset 10 /* After starting watchdog, the system will not feed the dog, so the system will restart after 10 seconds*/