MI ISP API
REVISION HISTORY¶
| Revision No. | Description |
Date |
|---|---|---|
| 3.0 | 12/04/2020 | |
| 3.1 | 07/25/2021 | |
| 08/25/2021 | ||
| 3.2 | 11/23/2021 | |
| 3.3 | 02/17/2022 | |
| 3.4 | 03/21/2022 | |
| 3.5 | 05/23/2022 | |
| 3.6 | 08/03/2022 | |
| 3.7 | 10/28/2022 | |
| 3.8 | 12/01/2022 | |
| 3.9 | 1/11/2023 | |
| 3.10 | 02/14/2023 | |
| 3.11 | 04/10/2024 | |
| 3.11 | 04/27/2024 |
1. Overview¶
1.1. Module description¶
ISP (Image Signal Processing) realizes HDR, 3D/2D noise reduction, 3A algorithm, WDR and other related functions.
Keyword
-
Device
Hardware device.
-
channel
Time division multiplexed channel on device.
-
DNR
Digital Noise Reduction.
2D Noise Reduction: average a pixel with surrounding pixels, and the noise will be reduced after that, but the picture will be blurred;
3D Noise Reduction: add time domain processing, 2D noise reduction only considers one frame of image, while 3D noise reduction considers the time domain relationship between frames, and averages each pixel in time domain.
-
3A algorithm
AE (Auto Exposure), AWB (Auto White Balance), and AF(Auto Focus).
-
IQ
IQ (Image Quality) is a quality evaluation standard for images captured by cameras, covering multiple aspects such as resolution, color reproduction, contrast, noise, dynamic range, gamma correction, lens distortion, etc.
-
HDR
High-Dynamic Range.
According to the LDR (Low-Dynamic Range) of different exposure times, the final HDR image is synthesized using the LDR image with the best detail corresponding to each exposure time. It can better reflect the visual effects in the real environment.
-
WDR
Wide Dynamic Range.
After turning it on, the bright and dark parts of the scene can be seen clearly. The wide dynamic range is the ratio of the brightest and the darkest signal value that the image can distinguish.
-
Rotation
Rotate the original image around the center point by 0°/90°/180°/270°.
-
mirror
Horizontal mirror flip.
-
Flip
Mirror up and down.
-
Crop
Crop the image.
-
seg
Segment module.
-
Compress
Compress mode, compress data transmission to save bandwidth.
-
IR
IR Data of RGBIR sensor.
-
AIISP
Somewhere in the ISP pipeline, an AI (artificial intelligence) algorithm is used to optimize the image before it is sent back to the ISP for further processing. The purpose is to use the powerful computing power of AI to supplement the ISP and obtain higher quality images.
1.2. Basic Structure¶
Simply put, ISP receives the input image from the front end, processes it through the ISP's internal functional modules, and outputs the processed image.
Input Stage
There are two forms of ISP input:
-
Direct connection to the front-end IP hardware (such as VIF), directly sending data to the ISP, this mode is called realtime. In this mode, only one channel of data from the front end is supported, and multiple channels of data are not supported.
-
Read from the system memory in the form of a buffer. The data source of the buffer can be written by the front-end IP, or directly poured in by the user through the MI_SYS interface. This mode is called framemode. In this mode, multiple channels of data from the front end can be supported to be input simultaneously, and the ISP processes these multiple channels of data in the form of time-division multiplexing.
Process Stage
-
ISP pipeline is the main processing process of ISP, which involves multiple hardware functions. The functions of each generation of chips are inconsistent, so it is not expanded in detail here. For details, please refer to 1.3. Function Introduction and 1.5. Chip Differences
-
CUS3A runs the 3A algorithm. It obtains image statistics from the ISP pipeline, sends them to the 3A algorithm to get the results, and then sends them back to the ISP pipeline. For details of this part, please refer to: AE/AWB/AF Interface
-
IQ is used to control image quality. Users use specific tools to manually or automatically adjust image quality. It obtains parameters from the ISP pipeline and sets new parameters to the ISP pipeline, thereby affecting image quality. For details of this part, please refer to: ISP Software Development Reference and ISP API Tuning SOP
Output Stage
There are also two output forms for images processed by ISP:
-
Direct connection to the back-end IP hardware (such as SCL or LDC), that is, realtime, which can be output to multiple back-end IPs at the same time.
-
Written to the system memory in the form of a buffer, that is, framemode, the user and the back-end module can directly obtain the content from the output buffer.
Note that realtime and framemode can be used at the same time when outputting.
1.3. Functions Introduction¶
MI_ISP supports the following functions:
-
Rotate, flip and mirror the image
-
Crop the image
-
HDR fusion of the input long and short exposure images
-
De-noise the image in the temporal and spatial domains (3DNR)
-
Apply the 3A algorithm to adjust the image effect
-
Perform WDR processing on the image
-
Adjust the IQ parameters to obtain different image quality and effects
-
Correct the image distortion through the built-in 1D-LDC
-
Convert the input bayer format image to YUV format
Note that not every generation of chips has all the functions described above. For details, please refer to 1.5. Chip Differences
1.4. Application scenarios¶
MI_ISP can be applied to the following scenarios:
-
Pure linux scenario
In the linux environment, you can develop based on the API interface provided by MI_ISP.
-
Pure rtos scenario
In the rtos environment, applications can be developed based on the API interface provided by MI_ISP.
-
Dualos scenario
In the dualos environment, applications running on the linux side and applications running on the rtos side can be developed based on the MI_ISP API.
1.5. Chip Differences¶
The chip described in this document is Pcupid
1.5.1. Specifications¶
Both ‘\’ and ‘N’ means this function is not supported.
-
Module function specifications
Function Tiramisu Mochi Muffin Maruko Opera Souffle Pcupid Dev Number 1 1 2 1 1 1 1 Chn Number 32 32 32 4 5 4 4 Port Number 3 2 3 3 3 4 3 DNR Range 0-2 0-7 0-2 0-6 0-2 0-5 0-2 InputCrop Y Y Y Y Y Y Y 3A Y N Y Y Y Y Y 2F HDR Y N Y Y Y Y N 3F HDR N N N N N Y N Rotation Y N Y Y Y Y N mirror Y N Y Y Y Y N flip Y N Y Y Y Y N WDR Y Y Y Y Y Y Y OutPutCrop Y Y Y Y Y Y Y IR Y N Y Y Y Y Y Compress Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Seg N N Y N N N N Max Pixel Rate 4K30 4K60 4K60 4K30 6M30 16M30 2M30 -
Input specifications
Input Tiramisu Mochi Muffin Maruko Opera Souffle Pcupid Pixel yuv422 YUYV Y N Y Y N Y Y yuv422 UYVY Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Bayer Y N Y Y Y Y Y Compress NONE Y Y Y Y Y Y Y TO_8BIT Y N Y Y Y Y Y TO_6BIT N Y N N N N N SFBC0 N Y N N N N N Crop Y Y Y Y Y Y Y resolution MAX 4208 3840 4068 3840 2688 4680 1920 MIN 320x256(Enable AE)
16x16(Disable AE)16x16 320x256(Enable AE)
16x16(Disable AE)320x256(Enable AE)
16x16(Disable AE)320x256(Enable AE)
16x16(Disable AE)128x120(Enable AE)
16x16(Disable AE)320x256(Enable AE)
16x16(Disable AE)Pixel Alignment (WxH) 2x2 2x2 2x2 2x2 2x2 2x2 2x2 2x2 -
Output specifications
Output Tiramisu Mochi Muffin Maruko Opera Souffle Pcupid Pixel ARGB8888 N Y N Y Y Y Y ABGR8888 N N N Y Y Y Y BGRA8888 N N N Y Y Y Y yuv420SP NV12 Y Y Y Y Y Y Y yuv420SP NV21 N Y N Y Y Y Y yuv420 Planer N Y N Y Y Y Y yuv422 YUYV Y Y Y Y Y Y Y yuv422 YVYU Y Y Y Y Y Y Y yuv422 VYUY Y Y Y Y Y Y Y yuv422 UYVY Y Y Y Y Y Y Y yuv422 SP N Y N Y Y Y Y yuv422 Planer N Y N Y Y Y Y Compress NONE Y Y Y Y Y Y Y 10TO6 N Y N Y Y Y N Crop Y Y Y Y Y Y Y IR Y N Y Y Y Y Y Pixel Alignment (WxH) 2x2 2x2 2x2 2x2 2x2 2x2 2x2
1.5.2. Flow chart¶
1.5.2.1. Tiramisu
Note:
-
Tiramisu only has a device0, and each device supports up to 16 channels.
-
Only YUV422_yuyv / uyvy and Bayer format input are supported, Bayer format can support 3DNR and 3a functions.
1.5.2.2. Muffin
Note:
-
Muffin has Device0 and Device1, and each Device supports up to 16 channels.
-
Only supports YUV422_YUYV/UYVY and bayer format input.
-
After enabling AI ISP through MI_ISP_SetCustSegAttr, it supports app to take out the buffer from before 3DNR/before WDR/before RGB2YUV, and send it back to before 3DNR/before WDR/before RGB2YUV after processing.
-
Before 3DNR is the data before entering the DNR module.
1.5.2.3. Mochi
Note:
-
Mochi only has a device0, and each device supports up to 16 channels.
-
Only YUV422_uyvy format input are supported.
-
Do not support HDR/Rotation/Mirror/Flip.
1.5.2.4. Maruko
Note:
-
Maruko only has a device0, and each device supports up to 16 channels.
-
Only YUV422_yuyv / uyvy and Bayer format input are supported, Bayer format can support 3DNR/3A/Rot functions.
1.5.2.5. Opera
Note:
-
Opera only has a device0, and each device supports up to 5 channels.
-
Only YUV422_UYVY and Bayer input format are supported, and only Bayer format can support 3DNR/3A/Rot functions.
1.5.2.6. Souffle
Note:
-
Souffle only has a device0, and each device supports up to 4 channels.
-
Only YUV422_YUYV / YUV422_UYVY and Bayer input format are supported, and only Bayer format can support 3DNR/3A/Rot functions.
1.5.2.7. Pcupid
Note:
-
Pcupid only has a device0, and each device supports up to 4 channels.
-
Only YUV422_YUYV / YUV422_UYVY and Bayer input format are supported, and only Bayer format can support 3DNR/3A functions.
-
Do not support HDR/Rotation/Mirror/Flip.
1.6. Working principle¶
NA
1.7. Interface calling¶
The interface call of MI_ISP is divided into the following steps:
-
Initialize MI_SYS
-
Create MI_ISP Device
-
Create MI_ISP Channel
-
Set the parameters of MI_ISP Channel
-
Start MI_ISP Channel
-
Set the parameters of MI_ISP Output port
-
Enable MI_ISP Output port
-
Set the MI_ISP Output port depth
-
If MI_ISP has front-end and back-end modules, call MI_SYS interface to bind MI_ISP with front-end and back-end modules
-
Front-end or SYS pushes stream to ISP, SYS gets stream from ISP or ISP pushes stream to back-end
-
Disable the enabled MI_ISP Output port
-
Stop MI_ISP Channel
-
Destroy MI_ISP Channel
-
Destroy MI_ISP Device
-
Deinitialize MI_SYS
1.8. Example¶
1.8.1 Example 1¶
The first example introduces the initialization and deinitialization procedures of the MI_ISP module.
#include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> #include <string.h> #include <signal.h> #include <unistd.h> #include "mi_sys.h" #include "mi_isp.h" #define ExecFunc(_func_,_ret_) \ if((_func_) != (_ret_)) \ { \ printf("[ %d ] exec function is failed\n",__LINE__); \ exit(-1); \ } \ else \ { \ printf("[ %d ] exec function is success\n",__LINE__);\ } MI_S32 IspModuleInit(MI_ISP_DEV ispDevId, MI_ISP_CHANNEL ispChnId, MI_ISP_PORT ispPortId) { // create isp device MI_ISP_DevAttr_t ispDevAttr; memset(&ispDevAttr, 0x0, sizeof(MI_ISP_DevAttr_t)); ispDevAttr.u32DevStitchMask = 0; ExecFunc(MI_ISP_CreateDevice(ispDevId, &ispDevAttr), MI_SUCCESS); // create isp channel MI_ISP_ChannelAttr_t ispChnAttr; memset(&ispChnAttr, 0x0, sizeof(MI_ISP_ChannelAttr_t)); ExecFunc(MI_ISP_CreateChannel(ispDevId, ispChnId, &ispChnAttr), MI_SUCCESS); // set isp channel param MI_ISP_ChnParam_t ispChnParam; memset(&ispChnParam, 0x0, sizeof(MI_ISP_ChnParam_t)); ispChnParam.eHDRType = E_MI_ISP_HDR_TYPE_OFF; ispChnParam.e3DNRLevel = E_MI_ISP_3DNR_LEVEL1; ispChnParam.eRot = E_MI_SYS_ROTATE_90; ExecFunc(MI_ISP_SetChnParam(ispDevId, ispChnId, &ispChnParam), MI_SUCCESS); // start isp channel ExecFunc(MI_ISP_StartChannel(ispDevId, ispChnId), MI_SUCCESS); // set isp output port param MI_ISP_OutPortParam_t ispOutputParam; memset(&ispOutputParam, 0x0, sizeof(MI_ISP_OutPortParam_t)); ispOutputParam.ePixelFormat = E_MI_SYS_PIXEL_FRAME_YUV_SEMIPLANAR_420; ExecFunc(MI_ISP_SetOutputPortParam(ispDevId, ispChnId, ispPortId, &ispOutputParam), MI_SUCCESS); // enable isp output port ExecFunc(MI_ISP_EnableOutputPort(ispDevId, ispChnId, ispPortId), MI_SUCCESS); // set isp output port depth MI_SYS_ChnPort_t chnPort; chnPort.eModId = E_MI_MODULE_ID_ISP; chnPort.u32DevId = ispDevId; chnPort.u32ChnId = ispChnId; chnPort.u32PortId = ispPortId; ExecFunc(MI_SYS_SetChnOutputPortDepth(0, &chnPort, 1, 4), MI_SUCCESS); return MI_SUCCESS; } MI_S32 IspModuleDeinit(MI_ISP_DEV ispDevId, MI_ISP_CHANNEL ispChnId, MI_ISP_PORT ispPortId) { ExecFunc(MI_ISP_DisableOutputPort(ispDevId, ispChnId,ispPortId), MI_SUCCESS); ExecFunc(MI_ISP_StopChannel(ispDevId,ispChnId), MI_SUCCESS); ExecFunc(MI_ISP_DestroyChannel(ispDevId, ispChnId), MI_SUCCESS); ExecFunc(MI_ISP_DestoryDevice(ispDevId), MI_SUCCESS); return MI_SUCCESS; } MI_BOOL bExit = FALSE; void signalHandler(int signo) { printf("ctrl +c is input \n"); bExit = TRUE; return; } int main(int argc, char **argv) { MI_ISP_DEV ispDevId = 0; MI_ISP_CHANNEL ispChnId = 0; MI_ISP_PORT ispPortId = 1; ExecFunc(MI_SYS_Init(0), MI_SUCCESS); ExecFunc(IspModuleInit(ispDevId, ispChnId, ispPortId), MI_SUCCESS); signal(SIGINT, signalHandler); while (!bExit) { sleep(1); } ExecFunc(IspModuleDeinit(ispDevId, ispChnId, ispPortId), MI_SUCCESS); ExecFunc(MI_SYS_Exit(0), MI_SUCCESS); return 0; }
1.8.2. Example 2¶
The second example uses a classic pipeline, namely sensor -> vif -> isp -> scl, where framemode is used to connect vif->isp, and realitme is used to connect isp->scl. For the flow of the front-end and back-end modules, only the demo code is given here without much explanation. For in-depth understanding, please refer to the corresponding documents: sensor, vif, scl
#include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> #include <string.h> #include <signal.h> #include <unistd.h> #include "mi_sensor.h" #include "mi_sensor_datatype.h" #include "mi_vif.h" #include "mi_isp.h" #include "mi_scl.h" #include "mi_sys.h" #define ExecFunc(_func_,_ret_) \ if((_func_) != (_ret_)) \ { \ printf("[ %d ] exec function is failed\n",__LINE__); \ exit(-1); \ } \ else \ { \ printf("[ %d ] exec function is success\n",__LINE__);\ } typedef struct { MI_SYS_ChnPort_t srcChnPort; MI_SYS_ChnPort_t dstChnPort; MI_U32 srcFrmrate; MI_U32 dstFrmrate; MI_SYS_BindType_e bindType; MI_U32 bindParam; } Sys_BindInfo_t; MI_S32 SysBind(Sys_BindInfo_t *pstBindInfo) { ExecFunc(MI_SYS_BindChnPort2(0, &pstBindInfo->srcChnPort, &pstBindInfo->dstChnPort, pstBindInfo->srcFrmrate, pstBindInfo->dstFrmrate, pstBindInfo->bindType, pstBindInfo->bindParam), MI_SUCCESS); printf("\n"); printf("src(%d-%d-%d-%d) dst(%d-%d-%d-%d) %d...\n", pstBindInfo->srcChnPort.eModId, pstBindInfo->srcChnPort.u32DevId, pstBindInfo->srcChnPort.u32ChnId, pstBindInfo->srcChnPort.u32PortId, pstBindInfo->dstChnPort.eModId, pstBindInfo->dstChnPort.u32DevId, pstBindInfo->dstChnPort.u32ChnId, pstBindInfo->dstChnPort.u32PortId, pstBindInfo->bindType); printf("\n"); return MI_SUCCESS; } MI_S32 SysUnBind(Sys_BindInfo_t *pstBindInfo) { ExecFunc(MI_SYS_UnBindChnPort(0, &pstBindInfo->srcChnPort, &pstBindInfo->dstChnPort), MI_SUCCESS); return MI_SUCCESS; } MI_S32 SnrModuleInit(MI_SNR_PADID snrPadId, MI_U8 resIdx, MI_BOOL useHdr) { MI_SNR_SetPlaneMode(snrPadId, useHdr); MI_SNR_SetRes(snrPadId, resIdx); MI_SNR_Enable(snrPadId); return 0; } MI_S32 SnrModuleDeInit(MI_SNR_PADID snrPadId) { MI_SNR_Disable(snrPadId); return 0; } MI_S32 VifModuleInit(MI_SNR_PADID snrPadId, MI_VIF_DEV vifDevId) { MI_U8 vifGroupId = vifDevId; MI_VIF_PORT vifPort = 0; MI_U32 planeId = 0; MI_SNR_PADInfo_t snrPad0Info; MI_SNR_PlaneInfo_t snrPlane0Info; memset(&snrPad0Info, 0x0, sizeof(MI_SNR_PADInfo_t)); memset(&snrPlane0Info, 0x0, sizeof(MI_SNR_PlaneInfo_t)); MI_VIF_GroupAttr_t vifGroupAttr; memset(&vifGroupAttr, 0x0, sizeof(MI_VIF_GroupAttr_t)); ExecFunc(MI_SNR_GetPadInfo(snrPadId, &snrPad0Info), MI_SUCCESS); ExecFunc(MI_SNR_GetPlaneInfo(snrPadId, planeId, &snrPlane0Info), MI_SUCCESS); vifGroupAttr.eIntfMode = (MI_VIF_IntfMode_e)snrPad0Info.eIntfMode; vifGroupAttr.eWorkMode = E_MI_VIF_WORK_MODE_1MULTIPLEX; vifGroupAttr.eHDRType = (MI_VIF_HDRType_e)snrPad0Info.eHDRMode; vifGroupAttr.eClkEdge = E_MI_VIF_CLK_EDGE_DOUBLE; ExecFunc(MI_VIF_CreateDevGroup(vifGroupId, &vifGroupAttr), MI_SUCCESS); MI_VIF_DevAttr_t vifDevAttr; memset(&vifDevAttr, 0x0, sizeof(MI_VIF_DevAttr_t)); vifDevAttr.stInputRect.u16X = snrPlane0Info.stCapRect.u16X; vifDevAttr.stInputRect.u16Y = snrPlane0Info.stCapRect.u16Y; vifDevAttr.stInputRect.u16Width = snrPlane0Info.stCapRect.u16Width; vifDevAttr.stInputRect.u16Height = snrPlane0Info.stCapRect.u16Height; if(snrPlane0Info.eBayerId >= E_MI_SYS_PIXEL_BAYERID_MAX) { vifDevAttr.eInputPixel = snrPlane0Info.ePixel; } else { vifDevAttr.eInputPixel = (MI_SYS_PixelFormat_e)RGB_BAYER_PIXEL(snrPlane0Info.ePixPrecision, snrPlane0Info.eBayerId); } printf("setchnportattr (%d,%d,%d,%d) \n", vifDevAttr.stInputRect.u16X, vifDevAttr.stInputRect.u16Y, vifDevAttr.stInputRect.u16Width, vifDevAttr.stInputRect.u16Height); ExecFunc(MI_VIF_SetDevAttr(vifDevId, &vifDevAttr), MI_SUCCESS); ExecFunc(MI_VIF_EnableDev(vifDevId), MI_SUCCESS); MI_VIF_OutputPortAttr_t vifPortInfo; memset(&vifPortInfo, 0, sizeof(MI_VIF_OutputPortAttr_t)); vifPortInfo.stCapRect.u16X = 0; vifPortInfo.stCapRect.u16Y = 0; vifPortInfo.stCapRect.u16Width = snrPlane0Info.stCapRect.u16Width; vifPortInfo.stCapRect.u16Height = snrPlane0Info.stCapRect.u16Height; vifPortInfo.stDestSize.u16Width = snrPlane0Info.stCapRect.u16Width; vifPortInfo.stDestSize.u16Height = snrPlane0Info.stCapRect.u16Height; printf("sensor bayerid %d, bit mode %d \n", snrPlane0Info.eBayerId, snrPlane0Info.ePixPrecision); vifPortInfo.ePixFormat = vifDevAttr.eInputPixel; //stVifPortInfo.u32FrameModeLineCount for lowlantancy mode vifPortInfo.eFrameRate = E_MI_VIF_FRAMERATE_FULL; ExecFunc(MI_VIF_SetOutputPortAttr(vifDevId, vifPort, &vifPortInfo), MI_SUCCESS); ExecFunc(MI_VIF_EnableOutputPort(vifDevId, vifPort), MI_SUCCESS); MI_SYS_ChnPort_t chnPort; chnPort.eModId = E_MI_MODULE_ID_VIF; chnPort.u32DevId = vifDevId; chnPort.u32ChnId = 0; chnPort.u32PortId = 0; MI_SYS_SetChnOutputPortDepth(0, &chnPort, 1, 4); return MI_SUCCESS; } MI_S32 VifModuleDeinit(MI_VIF_DEV VifDevId) { MI_U8 u8VifGroupId = VifDevId; MI_VIF_PORT vifPort = 0; ExecFunc(MI_VIF_DisableOutputPort(VifDevId, vifPort), MI_SUCCESS); ExecFunc(MI_VIF_DisableDev(VifDevId), MI_SUCCESS); ExecFunc(MI_VIF_DestroyDevGroup(u8VifGroupId), MI_SUCCESS); return MI_SUCCESS; } MI_S32 IspModuleInit(MI_ISP_DEV ispDevId, MI_ISP_CHANNEL ispChnId, MI_ISP_PORT ispPortId, MI_SNR_PADID snrPadId) { // create isp device MI_ISP_DevAttr_t ispDevAttr; memset(&ispDevAttr, 0x0, sizeof(MI_ISP_DevAttr_t)); ispDevAttr.u32DevStitchMask = 0; ExecFunc(MI_ISP_CreateDevice(ispDevId, &ispDevAttr), MI_SUCCESS); // create isp channel MI_ISP_ChannelAttr_t ispChnAttr; memset(&ispChnAttr, 0x0, sizeof(MI_ISP_ChannelAttr_t)); ispChnAttr.u32SensorBindId = (1 << snrPadId); ExecFunc(MI_ISP_CreateChannel(ispDevId, ispChnId, &ispChnAttr), MI_SUCCESS); // set isp channel param MI_ISP_ChnParam_t ispChnParam; memset(&ispChnParam, 0x0, sizeof(MI_ISP_ChnParam_t)); ispChnParam.eHDRType = E_MI_ISP_HDR_TYPE_OFF; ispChnParam.e3DNRLevel = E_MI_ISP_3DNR_LEVEL1; ispChnParam.eRot = E_MI_SYS_ROTATE_90; ExecFunc(MI_ISP_SetChnParam(ispDevId, ispChnId, &ispChnParam), MI_SUCCESS); // start isp channel ExecFunc(MI_ISP_StartChannel(ispDevId, ispChnId), MI_SUCCESS); // set isp output port param MI_ISP_OutPortParam_t ispOutputParam; memset(&ispOutputParam, 0x0, sizeof(MI_ISP_OutPortParam_t)); ispOutputParam.ePixelFormat = E_MI_SYS_PIXEL_FRAME_YUV_SEMIPLANAR_420; ExecFunc(MI_ISP_SetOutputPortParam(ispDevId, ispChnId, ispPortId, &ispOutputParam), MI_SUCCESS); // enable isp output port ExecFunc(MI_ISP_EnableOutputPort(ispDevId, ispChnId, ispPortId), MI_SUCCESS); // set isp output port depth MI_SYS_ChnPort_t chnPort; chnPort.eModId = E_MI_MODULE_ID_ISP; chnPort.u32DevId = ispDevId; chnPort.u32ChnId = ispChnId; chnPort.u32PortId = ispPortId; ExecFunc(MI_SYS_SetChnOutputPortDepth(0, &chnPort, 1, 4), MI_SUCCESS); return MI_SUCCESS; } MI_S32 IspModuleDeinit(MI_ISP_DEV ispDevId, MI_ISP_CHANNEL ispChnId, MI_ISP_PORT ispPortId) { ExecFunc(MI_ISP_DisableOutputPort(ispDevId, ispChnId,ispPortId), MI_SUCCESS); ExecFunc(MI_ISP_StopChannel(ispDevId,ispChnId), MI_SUCCESS); ExecFunc(MI_ISP_DestroyChannel(ispDevId, ispChnId), MI_SUCCESS); ExecFunc(MI_ISP_DestoryDevice(ispDevId), MI_SUCCESS); return MI_SUCCESS; } MI_S32 SclModuleInit(MI_SCL_DEV sclDevId, MI_SCL_CHANNEL sclChnId, MI_SYS_WindowSize_t *pDstSize) { MI_SCL_DevAttr_t sclDevAttr; MI_SCL_ChannelAttr_t sclChnAttr; MI_SCL_ChnParam_t sclChnParam; MI_SCL_OutPortParam_t sclOutputParam; memset(&sclDevAttr, 0x0, sizeof(MI_SCL_DevAttr_t)); memset(&sclChnAttr, 0x0, sizeof(MI_SCL_ChannelAttr_t)); sclDevAttr.u32NeedUseHWOutPortMask = E_MI_SCL_HWSCL0; ExecFunc(MI_SCL_CreateDevice(sclDevId, &sclDevAttr), MI_SUCCESS); ExecFunc(MI_SCL_CreateChannel(sclDevId, sclChnId, &sclChnAttr), MI_SUCCESS); memset(&sclChnParam, 0x0, sizeof(MI_SCL_ChnParam_t)); sclChnParam.eRot = E_MI_SYS_ROTATE_NONE; ExecFunc(MI_SCL_SetChnParam(sclDevId, sclChnId, &sclChnParam), MI_SUCCESS); ExecFunc(MI_SCL_StartChannel(sclDevId, sclChnId), MI_SUCCESS); memset(&sclOutputParam, 0x0, sizeof(MI_SCL_OutPortParam_t)); memcpy(&sclOutputParam.stSCLOutputSize, pDstSize, sizeof(MI_SYS_WindowSize_t)); sclOutputParam.ePixelFormat = E_MI_SYS_PIXEL_FRAME_YUV_SEMIPLANAR_420; sclOutputParam.eCompressMode = E_MI_SYS_COMPRESS_MODE_NONE; sclOutputParam.bMirror = FALSE; sclOutputParam.bFlip = FALSE; ExecFunc(MI_SCL_SetOutputPortParam((MI_SCL_DEV)sclDevId, sclChnId, 0, &sclOutputParam), MI_SUCCESS); ExecFunc(MI_SCL_EnableOutputPort((MI_SCL_DEV)sclDevId, sclChnId, 0), MI_SUCCESS); MI_SYS_ChnPort_t chnPort; chnPort.eModId = E_MI_MODULE_ID_SCL; chnPort.u32DevId = sclDevId; chnPort.u32ChnId = sclChnId; chnPort.u32PortId = 0; ExecFunc(MI_SYS_SetChnOutputPortDepth(0, &chnPort, 1, 4), MI_SUCCESS); return MI_SUCCESS; } MI_S32 SclModuleDeinit(MI_SCL_DEV sclDevId, MI_SCL_CHANNEL sclChnId) { ExecFunc(MI_SCL_DisableOutputPort(sclDevId, sclChnId,0), MI_SUCCESS); ExecFunc(MI_SCL_StopChannel(sclDevId,sclChnId), MI_SUCCESS); ExecFunc(MI_SCL_DestroyChannel(sclDevId, sclChnId), MI_SUCCESS); ExecFunc(MI_SCL_DestroyDevice(sclDevId), MI_SUCCESS); return MI_SUCCESS; } MI_BOOL bExit = FALSE; void signalHandler(int signo) { printf("ctrl +c is input \n"); bExit = TRUE; return; } int main(int argc, char **argv) { ExecFunc(MI_SYS_Init(0), MI_SUCCESS); MI_SNR_PADID snrPadId = 0; MI_U32 planeId = 0; MI_SNR_PlaneInfo_t snrPlaneInfo; memset(&snrPlaneInfo, 0, sizeof(MI_SNR_PlaneInfo_t)); ExecFunc(SnrModuleInit(snrPadId, 0, FALSE), MI_SUCCESS); ExecFunc(MI_SNR_GetPlaneInfo(snrPadId, planeId, &snrPlaneInfo), MI_SUCCESS); MI_VIF_DEV vifDevId = 0; ExecFunc(VifModuleInit(snrPadId, vifDevId), MI_SUCCESS); MI_ISP_DEV ispDevId = 0; MI_ISP_CHANNEL ispChnId = 0; MI_ISP_PORT ispPortId = 0; ExecFunc(IspModuleInit(ispDevId, ispChnId, ispPortId, snrPadId), MI_SUCCESS); Sys_BindInfo_t vifIspBindInfo; memset(&vifIspBindInfo, 0x0, sizeof(Sys_BindInfo_t)); vifIspBindInfo.srcChnPort.eModId = E_MI_MODULE_ID_VIF; vifIspBindInfo.srcChnPort.u32DevId = vifDevId; vifIspBindInfo.srcChnPort.u32ChnId = 0; vifIspBindInfo.srcChnPort.u32PortId = 0; vifIspBindInfo.dstChnPort.eModId = E_MI_MODULE_ID_ISP; vifIspBindInfo.dstChnPort.u32DevId = ispDevId; vifIspBindInfo.dstChnPort.u32ChnId = ispChnId; vifIspBindInfo.dstChnPort.u32PortId = 0; vifIspBindInfo.srcFrmrate = 30; vifIspBindInfo.dstFrmrate = 30; vifIspBindInfo.bindType = (MI_SYS_BindType_e)E_MI_SYS_BIND_TYPE_FRAME_BASE; ExecFunc(SysBind(&vifIspBindInfo), MI_SUCCESS); MI_SCL_DEV sclDevId = 0; MI_SCL_DEV sclChnId = 0; MI_SYS_WindowSize_t sclDstSize; sclDstSize.u16Width = snrPlaneInfo.stCapRect.u16Width; sclDstSize.u16Height = snrPlaneInfo.stCapRect.u16Height; SclModuleInit(sclDevId, sclChnId, &sclDstSize); Sys_BindInfo_t ispSclBindInfo; ispSclBindInfo.srcChnPort.eModId = E_MI_MODULE_ID_ISP; ispSclBindInfo.srcChnPort.u32DevId = ispDevId; ispSclBindInfo.srcChnPort.u32ChnId = ispChnId; ispSclBindInfo.srcChnPort.u32PortId = ispPortId; ispSclBindInfo.dstChnPort.eModId = E_MI_MODULE_ID_SCL; ispSclBindInfo.dstChnPort.u32DevId = sclDevId; ispSclBindInfo.dstChnPort.u32ChnId = sclChnId; ispSclBindInfo.dstChnPort.u32PortId = 0; ispSclBindInfo.srcFrmrate = 30; ispSclBindInfo.dstFrmrate = 30; ispSclBindInfo.bindType = E_MI_SYS_BIND_TYPE_REALTIME; ExecFunc(SysBind(&ispSclBindInfo), MI_SUCCESS); signal(SIGINT, signalHandler); while (!bExit) { sleep(1); } ExecFunc(SysUnBind(&ispSclBindInfo), MI_SUCCESS); ExecFunc(SclModuleDeinit(sclDevId, sclChnId), MI_SUCCESS); ExecFunc(SysUnBind(&vifIspBindInfo), MI_SUCCESS); ExecFunc(IspModuleDeinit(ispDevId, ispChnId, ispPortId), MI_SUCCESS); ExecFunc(VifModuleDeinit(vifDevId), MI_SUCCESS); ExecFunc(SnrModuleDeInit(snrPadId), MI_SUCCESS); ExecFunc(MI_SYS_Exit(0), MI_SUCCESS); return 0; }
2. API REFERENCE¶
This function module provides the following APIs:
| API Name | Function |
|---|---|
| MI_ISP_CreateDevice | Create an ISP device |
| MI_ISP_DestroyDevice | Destroy an ISP device |
| MI_ISP_CreateChannel | Create an ISP channel |
| MI_ISP_DestroyChannel | Destroy an ISP channel |
| MI_ISP_SetInputPortCrop | Set ISP input port cropping parameter |
| MI_ISP_GetInputPortCrop | Get ISP input port cropping parameter |
| MI_ISP_SetChnParam | Set ISP channel parameter |
| MI_ISP_GetChnParam | Get ISP channel parameter |
| MI_ISP_StartChannel | Start ISP channel |
| MI_ISP_StopChannel | Stop ISP channel |
| MI_ISP_SetOutputPortParam | Set ISP output port parameter |
| MI_ISP_GetOutputPortParam | Get ISP output port parameter |
| MI_ISP_EnableOutputPort | Enable ISP output channel |
| MI_ISP_DisableOutputPort | Disable ISP output port |
| MI_ISP_Alloc_IQDataBuf | Allocate IQ data buffer |
| MI_ISP_Free_IQDataBuf | Release IQ data buffer |
| MI_ISP_CallBackTask_Register | Register ISP callback interface |
| MI_ISP_CallBackTask_Unregister | Unregister ISP callback interface |
| MI_ISP_SkipFrame | Set skip FrameNum |
| MI_ISP_LoadPortZoomTable | Load ISP port Zoom Table |
| MI_ISP_StartPortZoom | Start ISP port Zoom |
| MI_ISP_StopPortZoom | Stop ISP port Zoom |
| MI_ISP_GetPortCurZoomAttr | Get ISP port current Zoom attribute |
| MI_ISP_SetCustSegAttr | Set AI ISP attribute. |
| MI_ISP_GetCustSegAttr | Get AI ISP attribute |
| MI_ISP_GetCustSegBuf | Get AI ISP buffer |
| MI_ISP_PutCustSegBuf | Release AI ISP buffer |
| MI_ISP_GetSubChnId | Get ISP subchannel ID |
| MI_ISP_SetSubChnParam | Set ISP subchannel parameter |
| MI_ISP_GetSubChnParam | Get ISP subchannel parameter |
| MI_ISP_SetChnOverlapAttr | Set ISP channel overlap attribute |
| MI_ISP_GetChnOverlapAttr | Get ISP channel overlap attribute |
2.1. MI_ISP_CreateDevice¶
-
Description
Create an ISP device.
-
Syntax
MI_S32 MI_ISP_CreateDevice(MI_ISP_DEV DevId, MI_ISP_DevAttr_t *pstDevAttr);
-
Parameter
Parameter name Description Input/Output DevId ISP device ID Input pstDevAttr ISP device attribute pointer. Static attribute. Input -
Return value
-
MI_SUCCESS (0) successful.
-
Non-Zero: failed, see error code for details.
-
-
Dependence
-
Header: mi_isp_datatype.h, mi_isp.h
-
Library: libmi_isp.a
-
-
Note
-
Make sure that the ISP device is disabled before calling. If it is enabled, please use MI_ISP_DestroyDevice to disable it.
-
In function MI_ISP_CreateDevice, when parameter DevId = MI_ISP_CREATE_MULTI_DEV(MI_ISP_DEV0), isp is working in multi device mode. At this time, isp device 0 and isp device 1 is running in one channel.
-
Only Muffin supports multi device mode.
-
In multi device mode, use parameter DevId = MI_ISP_DEV0 when calling other isp api except MI_ISP_DestroyDevice.
-
-
Example
MI_ISP initialization: MI_S32 ST_IspModuleInit(MI_ISP_DEV IspDevId) { #define ST_MAX_ISP_OUTPORT_NUM (2) MI_ISP_CHANNEL IspChnId = 0; MI_ISP_PORT IspOutPortId =0; MI_ISP_DevAttr_t stCreateDevAttr; memset(&stCreateDevAttr, 0x0, sizeof(MI_ISP_DevAttr_t)); stCreateDevAttr.u32DevStitchMask = E_MI_ISP_DEVICE_ID0; MI_ISP_CreateDevice(IspDevId, &stCreateDevAttr); MI_ISP_ChannelAttr_t stIspChnAttr; memset(&stIspChnAttr, 0x0, sizeof(MI_ISP_ChannelAttr_t)); stIspChnAttr. u32SensorBindId = E_MI_ISP_SENSOR0; MI_ISP_CreateChannel(IspDevId, IspChnId, &stIspChnAttr); MI_SYS_WindowRect_t stInputCropInfo; stInputCropInfo.u16x=0; stInputCropInfo.u16y=0; stInputCropInfo.u16width=0; stInputCropInfo.u16height=0;//width/height==0 no use crop. MI_ISP_SetInputPortCrop(IspDevId, IspChnId, &stInputCropInfo); MI_ISP_ChnParam_t stChnParam; stChnParam.eHDRType = E_MI_ISP_HDR_TYPE_OFF; stChnParam.e3DNRLevel = E_MI_ISP_3DNR_LEVEL2; stChnParam.bMirror = FALSE; stChnParam.bFlip = FALSE; stChnParam.eRot = E_MI_SYS_ROTATE_NONE; //use rot or flip, 3dnr level must more than 0 stChnParam.bY2bEnable = FALSE; MI_ISP_SetChnParam(IspDevId, IspChnId, &stChnParam); MI_ISP_StartChannel(IspDevId, IspChnId); for(IspOutPortId=0; IspOutPortId<ST_MAX_ISP_OUTPORT_NUM; IspOutPortId++) { MI_ISP_OutPortParam_t stIspOutputParam; memset(&stIspOutputParam, 0x0, sizeof(MI_ISP_OutPortParam_t)); stIspOutputParam.stCropRect.u16x=0; stIspOutputParam.stCropRect.u16y=0; stIspOutputParam.stCropRect.u16Width=0; stIspOutputParam.stCropRect.u16Height=0;//width/height use 0, not use crop stIspOutputParam.ePixelFormat = E_MI_SYS_PIXEL_FRAME_YUV_SEMIPLANAR_YUV420; MI_ISP_SetOutputPortParam(IspDevId, IspChnId, IspOutPortId, &stIspOutputParam); MI_ISP_EnableOutputPort(IspDevId, IspChnId, IspOutPortId); } return MI_SUCCESS; }MI_ISP de-initialization:
MI_S32 ST_IspModuleUnInit(MI_ISP_DEV IspDevId) { #define ST_MAX_ISP_OUTPORT_NUM (2) MI_ISP_CHANNEL IspChnId = 0; MI_ISP_PORT IspOutPortId =0; for(IspOutPortId=0; IspOutPortId<ST_MAX_ISP_OUTPORT_NUM; IspOutPortId++) { MI_ISP_DisableOutputPort(IspDevId, IspChnId, IspOutPortId); } MI_ISP_StopChannel(IspDevId, IspChnId); MI_ISP_DestroyChannel(IspDevId, IspChnId); MI_ISP_DestroyDevice(IspDevId); return MI_SUCCESS; } -
Related APIs
2.2. MI_ISP_DestroyDevice¶
-
Description
Destroy an ISP device.
-
Syntax
MI_S32 MI_ISP_DestroyDevice(MI_ISP_DEV DevId);
-
Parameter
Parameter name Description Input/Output DevId ISP device ID Input -
Return value
-
MI_SUCCESS (0) successful.
-
Non-Zero: failed, see error code for details.
-
-
Dependence
-
Header: mi_isp_datatype.h, mi_isp.h
-
Library: libmi_isp.a
-
-
Note
You need to disable all the output ports first, and then stop and destroy the channel to destroy device.
-
Example
See the example of MI_ISP_CreateDevice.
-
Related APIs
2.3. MI_ISP_CreateChannel¶
-
Description
Create an ISP channel.
-
Syntax
MI_S32 MI_ISP_CreateChannel(MI_ISP_DEV DevId, MI_ISP_CHANNEL ChnId, MI_ISP_ChannelAttr_t *pstChAttr);
-
Parameter
Parameter name Description Input/Output DevId ISP device ID. Input ChnId ISP channel ID Input pstChAttr ISP channel attribute pointer Input -
Return value
-
MI_SUCCESS (0) successful.
-
Non-Zero: failed, see error code for details.
-
-
Dependence
-
Header: mi_isp_datatype.h, mi_isp.h
-
Library: libmi_isp.a
-
-
Note
Create device firstly, and then create channel.
-
Example
See the example of MI_ISP_CreateDevice.
-
Related APIs
2.4. MI_ISP_DestroyChannel¶
-
Description
Destroy an ISP channel.
-
Syntax
MI_S32 MI_ISP_DestroyChannel(MI_ISP_DEV DevId, MI_ISP_CHANNEL ChnId);
-
Parameter
Parameter name Description Input/Output DevId ISP device ID. Input ChnId ISP channel ID Input -
Return value
-
MI_SUCCESS (0) successful.
-
Non-Zero: failed, see error code for details.
-
-
Dependence
-
Header: mi_isp_datatype.h, mi_isp.h
-
Library: libmi_isp.a
-
-
Note
You need to disable all the output ports first, and then stop channel, so that you can destroy channel.
-
Example
See the example of MI_ISP_CreateDevice.
-
Related APIs
2.5. MI_ISP_SetInputPortCrop¶
-
Description
Set ISP input port cropping parameter.
-
Syntax
MI_S32 MI_ISP_SetInputPortCrop(MI_ISP_DEV DevId, MI_ISP_CHANNEL ChnId, MI_SYS_WindowRect_t *pstCropInfo);
-
Parameter
Parameter name Description Input/Output DevId ISP device ID. Input ChnId ISP channel ID Input pstCropInfo ISP input port cropping parameter pointer Input -
Return value
-
MI_SUCCESS (0) successful.
-
Non-Zero: failed, see error code for details.
-
-
Dependence
-
Header: mi_isp_datatype.h, mi_isp.h
-
Library: libmi_isp.a
-
-
Note
-
When the input is Dram buffer, the input crop can be supported.
-
Crop x, Crop y, width, height are all aligned with 2.
-
The 3A inside the Isp only counts the information of the cropped area, which will affect the final 3A calculation result of the entire screen.
-
When the input data compression mode is not E_MI_SYS_COMPRESS_MODE_NONE, the input data does not support cropping.
-
2.6. MI_ISP_GetInputPortCrop¶
-
Description
Get ISP input port cropping parameter.
-
Syntax
MI_S32 MI_ISP_GetInputPortCrop(MI_ISP_DEV DevId, MI_ISP_CHANNEL ChnId, MI_SYS_WindowRect_t *pstCropInfo);
-
Parameter
Parameter name Description Input/Output DevId ISP device ID. Input ChnId ISP channel ID Input pstCropInfo ISP input port cropping parameter pointer output -
Return value
-
MI_SUCCESS (0) successful.
-
Non-Zero: failed, see error code for details.
-
-
Dependence
-
Header: mi_isp_datatype.h, mi_isp.h
-
Library: libmi_isp.a
-
2.7. MI_ISP_SetChnParam¶
-
Description
Set ISP channel parameter.
-
Syntax
MI_S32 MI_ISP_SetChnParam(MI_ISP_DEV DevId, MI_ISP_CHANNEL ChnId, MI_ISP_ChnParam_t *pstChnParam);
-
Parameter
Parameter name Description Input/Output DevId ISP device ID. Input ChnId ISP channel ID Input pstChnParam ISP channel parameter pointer Input -
Return value
-
MI_SUCCESS (0) successful.
-
Non-Zero: failed, see error code for details.
-
-
Dependence
-
Header: mi_isp_datatype.h, mi_isp.h
-
Library: libmi_isp.a
-
-
Note
It is recommended to switch the channel parameters when the channel is stopped to avoid mismatch between the buffer and back-end parameters in the channel, which may cause an exception.
-
Example
See the example of MI_ISP_CreateDevice.
-
Related APIs
2.8. MI_ISP_GetChnParam¶
-
Description
Get ISP channel parameter.
-
Syntax
MI_S32 MI_ISP_GetChnParam(MI_ISP_DEV DevId, MI_ISP_CHANNEL ChnId, MI_ISP_ChnParam_t *pstChnParam);
-
Parameter
Parameter name Description Input/Output DevId ISP device ID. Input ChnId ISP channel ID Input pstChnParam ISP channel parameter pointer output -
Return value
-
MI_SUCCESS (0) successful.
-
Non-Zero: failed, see error code for details.
-
-
Dependence
-
Header: mi_isp_datatype.h, mi_isp.h
-
Library: libmi_isp.a
-
-
Related APIs
2.9. MI_ISP_StartChannel¶
-
Description
Start ISP channel.
-
Syntax
MI_S32 MI_ISP_StartChannel(MI_ISP_DEV DevId, MI_ISP_CHANNEL ChnId);
-
Parameter
Parameter name Description Input/Output DevId ISP device ID. Input ChnId ISP channel ID Input -
Return value
-
MI_SUCCESS (0) successful.
-
Non-Zero: failed, see error code for details.
-
-
Dependence
-
Header: mi_isp_datatype.h, mi_isp.h
-
Library: libmi_isp.a
-
-
Example
See the example of MI_ISP_CreateDevice.
-
Related APIs
2.10. MI_ISP_StopChannel¶
-
Description
Stop ISP channel.
-
Syntax
MI_S32 MI_ISP_StopChannel(MI_ISP_DEV DevId, MI_ISP_CHANNEL ChnId);
-
Parameter
Parameter name Description Input/Output DevId ISP device ID. Input ChnId ISP channel ID Input -
Return value
-
MI_SUCCESS (0) successful.
-
Non-Zero: failed, see error code for details.
-
-
Dependence
-
Header: mi_isp_datatype.h, mi_isp.h
-
Library: libmi_isp.a
-
-
Note
You can stop the channel when created, and all the output port will have no data output.
-
Example
See the example of MI_ISP_CreateDevice.
2.11. MI_ISP_SetOutputPortParam¶
-
Description
Set ISP output port parameter.
-
Syntax
MI_S32 MI_ISP_SetOutputPortParam(MI_ISP_DEV DevId, MI_ISP_CHANNEL ChnId, MI_ISP_PORT PortId, MI_ISP_OutPortParam_t *pstOutPortParam);
-
Parameter
Parameter name Description Input/Output DevId ISP device ID. Input ChnId ISP channel ID Input PortId ISP port ID Input pstOutPortParam ISP output port parameter pointer Input -
Return value
-
MI_SUCCESS (0) successful.
-
Non-Zero: failed, see error code for details.
-
-
Dependence
-
Header: mi_isp_datatype.h, mi_isp.h
-
Library: libmi_isp.a
-
-
Note
-
Output port0 can only bind with MI_SCL realtime, output area is the same as input, which has no need to call this API to set.
-
Output port1 support crop, and the output size need to be specified.
-
Output port2 only supports the output of the IR data of the RGBIR sensor. Output W/H is fixed at half of the input W/H, which has no need to call this API to set.
-
Output port3 can only bind with MI_LDC realtime, output area is the same as input, which has no need to call this API to set.
-
-
Example
See the example of MI_ISP_CreateDevice.
2.12. MI_ISP_GetOutputPortParam¶
-
Description
Get ISP output port parameter.
-
Syntax
MI_S32 MI_ISP_GetOutputPortParam(MI_ISP_DEV DevId, MI_ISP_CHANNEL ChnId, MI_ISP_PORT PortId, MI_ISP_OutPortParam_t *pstOutPortParam);
-
Parameter
Parameter name Description Input/Output DevId ISP device ID. Input ChnId ISP channel ID Input PortId ISP port ID Input pstOutPortParam ISP output port parameter pointer output -
Return value
-
MI_SUCCESS (0) successful.
-
Non-Zero: failed, see error code for details.
-
-
Dependence
-
Header: mi_isp_datatype.h, mi_isp.h
-
Library: libmi_isp.a
-
-
Related APIs
2.13. MI_ISP_EnableOutputPort¶
-
Description
Enable ISP output channel.
-
Syntax
MI_S32 MI_ISP_EnableOutputPort(MI_ISP_DEV DevId, MI_ISP_CHANNEL ChnId, MI_ISP_PORT PortId);
-
Parameter
Parameter name Description Input/Output DevId ISP device ID. Input ChnId ISP channel ID Input PortId ISP port ID Input -
Return value
-
MI_SUCCESS (0) successful.
-
Non-Zero: failed, see error code for details.
-
-
Dependence
-
Header: mi_isp_datatype.h, mi_isp.h
-
Library: libmi_isp.a
-
-
Note
-
Output port1 can be enabled only when the attribute is set.
-
Output port2 can only be enabled when using RGBIR sensor.
-
-
Example
See the example of MI_ISP_CreateDevice.
-
Related APIs
2.14. MI_ISP_DisableOutputPort¶
-
Description
Disable ISP output port.
-
Syntax
MI_S32 MI_ISP_DisableOutputPort(MI_ISP_DEV DevId, MI_ISP_CHANNEL ChnId, MI_ISP_PORT PortId);
-
Parameter
Parameter name Description Input/Output DevId ISP device ID. Input ChnId ISP channel ID Input PortId ISP port ID Input -
Return value
-
MI_SUCCESS (0) successful.
-
Non-Zero: failed, see error code for details.
-
-
Dependence
-
Header: mi_isp_datatype.h, mi_isp.h
-
Library: libmi_isp.a
-
2.15. MI_ISP_Alloc_IQDataBuf¶
-
Description
Allocate IQ data buffer.
-
Syntax
MI_S32 MI_ISP_Alloc_IQDataBuf(MI_U32 u32Size,void **pUserVirAddr);
-
Parameter
Parameter name Description Input/Output u32Size IQ data buffer size. Input pUserVirAddr IQ data buffer pointer address Input -
Return value
-
MI_SUCCESS (0) successful.
-
Non-Zero: failed, see error code for details.
-
-
Dependence
-
Header: mi_isp_datatype.h, mi_isp.h
-
Library: libmi_isp.a
-
-
Note
-
It is recommended to use this api to apply for IQ api data to avoid the high risk of cpu loading caused by high frequency calls.
-
A thread applies for an isp data buffer to avoid buffer sharing between threads.
-
-
Example
#define MI_ISP_MAX_DATA_SIZE (80*1024) MI_ISP_Alloc_IQDataBuf(MI_ISP_MAX_DATA_SIZE, &pIspBuffer); MI_ISP_IQ_ColorToGrayType_t *pstColorToGray = (MI_ISP_IQ_ColorToGrayType_t *)pIspBuffer; MI_ISP_IQ_GetColorToGray( Channel, pstColorToGray); if(pstColorToGray->bEnable == SS_TRUE) pstColorToGray->bEnable = SS_FALSE; else pstColorToGray->bEnable = SS_TRUE; MI_ISP_IQ_SetColorToGray( Channel, pstColorToGray); MI_ISP_IQ_ContrastType_t *pstContrast = (MI_ISP_IQ_ContrastType_t *)pIspBuffer; MI_ISP_IQ_GetContrast( Channel, pstContrast); MI_ISP_IQ_SetContrast( Channel, pstContrast); MI_ISP_Free_IQDataBuf(pIspBuffer) -
Related APIs
2.16. MI_ISP_Free_IQDataBuf¶
-
Description
Release IQ data buffer.
-
Syntax
MI_S32 MI_ISP_Free_IQDataBuf(void *pUserBuf);
-
Parameter
Parameter name Description Input/Output pUserBuf IQ request data buffer pointer Input -
Return value
-
MI_SUCCESS (0) successful.
-
Non-Zero: failed, see error code for details.
-
-
Dependence
-
Header: mi_isp_datatype.h, mi_isp.h
-
Library: libmi_isp.a
-
-
Example
See the example of MI_ISP_Alloc_IQDataBuf.
2.17. MI_ISP_CallBackTask_Register¶
-
Description
Register ISP callback interface.
-
Syntax
MI_S32 MI_ISP_CallBackTask_Register(MI_ISP_DEV DevId, MI_ISP_CallBackParam_t *pstCallBackParam);
-
Parameter
Parameter name Description Input/Output DevId ISP device ID. Input pstCallBackParam ISP callback parameter Input -
Return value
-
MI_SUCCESS (0) successful.
-
Non-Zero: failed, see error code for details.
-
-
Dependence
-
Header: mi_isp_datatype.h, mi_isp.h
-
Library: libmi_isp.a
-
-
Note
-
The interface currently only supports calling by kernel mode.
-
Called in pair with MI_ISP_CallBackTask_Unregister.
-
-
Example
MI_S32 _MI_ISP_vsync1(MI_U64 u64Data) { DBG_ERR("DATA %llu \n", u64Data); return 0; } MI_S32 _MI_ISP_vsync2(MI_U64 u64Data) { DBG_ERR("DATA %llu \n", u64Data); return 0; } static MS_S32 _MI_ISP_testRegCallback(void) { MI_ISP_CallBackParam_t stCallBackParam1; MI_ISP_CallBackParam_t stCallBackParam2; memset(&stCallBackParam1, 0x0, sizeof(MI_ISP_CallBackParam_t)); memset(&stCallBackParam2, 0x0, sizeof(MI_ISP_CallBackParam_t)); stCallBackParam1.eCallBackMode = E_MI_ISP _CALLBACK_ISR; stCallBackParam1. eIrqType = E_MI_ISP_IRQ_ISPVSYNC; stCallBackParam1.pfnCallBackFunc = _mi_ISP_vsync1; stCallBackParam1.u64Data = 12; MI_ISP_CallBackTask_Register(&stCallBackParam1); stCallBackParam2.eCallBackMode = E_MI_ISP_CALLBACK_ISR; stCallBackParam2. eIrqType = E_MI_ISP_IRQ_ISPVSYNC; stCallBackParam2.pfnCallBackFunc = _mi_ISP_vsync2; stCallBackParam2.u64Data = 23; MI_ISP_CallBackTask_Register(&stCallBackParam2); return 0; } static MS_S32 _MI_ISP_testUnRegCallback(void) { MI_ISP_CallBackParam_t stCallBackParam1; MI_ISP_CallBackParam_t stCallBackParam2; memset(&stCallBackParam1, 0x0, sizeof(MI_ISP_CallBackParam_t)); memset(&stCallBackParam2, 0x0, sizeof(MI_ISP_CallBackParam_t)); stCallBackParam1.eCallBackMode = E_MI_ISP_CALLBACK_ISR; stCallBackParam1.eIrqType = E_MI_ISP_IRQ_ISPVSYNC; stCallBackParam1.pfnCallBackFunc = _mi_ISP_vsync1; stCallBackParam1.u64Data = 12; MI_ISP_CallBackTask_Unregister(&stCallBackParam1); stCallBackParam2.eCallBackMode = E_MI_ISP_CALLBACK_ISR; stCallBackParam2.eIrqType = E_MI_ISP_IRQ_ISPVSYNC; stCallBackParam2.pfnCallBackFunc = _mi_ISP_vsync2; stCallBackParam2.u64Data = 23; MI_ISP_CallBackTask_Unregister(&stCallBackParam2); return 0; } -
Related APIs
2.18. MI_ISP_CallBackTask_Unregister¶
-
Description
Unregister ISP callback interface
-
Syntax
MI_S32 MI_ISP_CallBackTask_Unregister(MI_ISP_DEV DevId, MI_ISP_CallBackParam_t *pstCallBackParam);
-
Parameter
Parameter name Description Input/Output DevId ISP device ID. Input pstCallBackParam ISP callback parameter Input -
Return value
-
MI_SUCCESS (0) successful.
-
Non-Zero: failed, see error code for details.
-
-
Dependence
-
Header: mi_isp_datatype.h, mi_isp.h
-
Library: libmi_isp.a
-
-
Note
-
The interface currently only supports calling by kernel mode.
-
Called in pair of MI_ISP_CallBackTask_Register.
-
-
Example
See the example of MI_ISP_CallBackTask_Register
2.19. MI_ISP_SkipFrame¶
-
Description
Set to skip Frame count from calling this API.
-
Syntax
MI_S32 MI_ISP_SkipFrame(MI_ISP_DEV DevId,MI_ISP_CHANNEL ChnId, MI_U32 u32FrameNum);
-
Parameter
Parameter name Description Input/Output ChnId ISP channel ID Input u32FrameNum Frame number Input -
Return value
-
MI_SUCCESS (0) successful.
-
Non-Zero: failed, see error code for details.
-
-
Dependence
-
Header: mi_isp_datatype.h, mi_isp.h
-
Library: libmi_isp.a
-
2.20. MI_ISP_LoadPortZoomTable¶
-
Description
Load ISP port Zoom Table.
-
Syntax
MI_S32 MI_ISP_LoadPortZoomTable(MI_ISP_DEV DevId, MI_ISP_CHANNEL ChnId, MI_ISP_ZoomTable_t *pZoomTable);
-
Parameter
Parameter name Description Input/Output DevId ISP device ID. Input ChnId ISP channel ID Input pZoomTable Zoom Table parameter Input -
Return value
-
MI_SUCCESS (0) successful.
-
Non-Zero: failed, see error code for details.
-
-
Dependence
-
Header: mi_isp_datatype.h, mi_isp.h
-
Library: libmi_isp.a
-
-
Note
-
Load zoom table through the interface in advance, each frame applies the zoom parameters in the table in turn to ensure smooth zoom effects.
-
Call MI_ISP_SetOutputPortParam cyclically to set crop, which cannot guarantee the effective setting of each frame and cannot achieve smooth effect.
X0 Y0 W0 H0 SensorId=0 X1 Y1 W1 H1 SensorId=0 X2 Y2 W2 H2 SensorId=1 X3 Y3 W3 H3 SensorId=1 The table contains crop position and corresponding sensorid information, sensorid information supports long and short focus switching scenes.
-
The zoom function is completed by the cooperation of MI_ISP and MI_SCL. MI_ISP is responsible for the 3A effect and the long and short focus switching scenes during the zoom process to notify the sensor driver to switch the sensor. MI_SCL is responsible for cropping and scaling up, so in the zoom scene, MI_SCL can no longer use the crop function.
-
During the operation of Zoom, you cannot load the table repeatedly, please use MI_ISP_StopPortZoom first, and then load table.
-
2.21. MI_ISP_StartPortZoom¶
-
Description
Start ISP port Zoom.
-
Syntax
MI_S32 MI_ISP_StartPortZoom(MI_ISP_DEV DevId, MI_ISP_CHANNEL ChnId, MI_ISP_ZoomAttr_t *pstZoomAttr);
-
Parameter
Parameter name Description Input/Output DevId ISP device ID. Input ChnId ISP channel ID Input pstZoomAttr Zoom Table parameter Input -
Return value
-
MI_SUCCESS (0) successful.
-
Non-Zero: failed, see error code for details.
-
-
Dependence
-
Header: mi_isp_datatype.h, mi_isp.h
-
Library: libmi_isp.a
-
-
Note
X0 Y0 W0 H0 SensorId=0 X1 Y1 W1 H1 SensorId=0 X2 Y2 W2 H2 SensorId=1 X3 Y3 W3 H3 SensorId=1 -
u32FromEntryIndex and u32ToEntryIndex are any one of index 0~3 in the table.
-
When u32FromEntryIndex != u32ToEntryIndex, apply crop parameters from u32FromEntryIndex to u32ToEntryIndex frame by frame.
-
When u32FromEntryIndex == u32ToEntryIndex, it will stop at the current u32FromEntryIndex parameter.
-
When MI detects that the sensorid of the next entry is inconsistent with the current sensor id, the sensor driver will be notified of the sensor driver after the current frame is finished, and switch to the corresponding sensor.
-
-
Related APIs
2.22. MI_ISP_StopPortZoom¶
-
Description
Stop ISP port Zoom.
-
Syntax
MI_S32 MI_ISP_StopPortZoom(MI_ISP_DEV DevId, MI_ISP_CHANNEL ChnId);
-
Parameter
Parameter name Description Input/Output DevId ISP device ID. Input ChnId ISP channel ID Input -
Return value
-
MI_SUCCESS (0) successful.
-
Non-Zero: failed, see error code for details.
-
-
Dependence
-
Header: mi_isp_datatype.h, mi_isp.h
-
Library: libmi_isp.a
-
-
Note
Called in pair with MI_ISP_StartPortZoom.
2.23. MI_ISP_GetPortCurZoomAttr¶
-
Description
Get ISP port current Zoom attribute.
-
Syntax
MI_S32 MI_ISP_GetPortCurZoomAttr(MI_ISP_DEV DevId, MI_ISP_CHANNEL ChnId, MI_ISP_ZoomAttr_t *pstZoomAttr);
-
Parameter
Parameter name Description Input/Output DevId ISP device ID. Input ChnId ISP channel ID Input pstZoomAttr Zoom attribute output -
Return value
-
MI_SUCCESS (0) successful.
-
Non-Zero: failed, see error code for details.
-
-
Dependence
-
Header: mi_isp_datatype.h, mi_isp.h
-
Library: libmi_isp.a
-
2.24. MI_ISP_SetCustSegAttr¶
-
Description
Set AI ISP attribute.
-
Syntax
MI_S32 MI_ISP_SetCustSegAttr(MI_ISP_DEV DevId, MI_ISP_CHANNEL ChnId, MI_ISP_CustSegAttr_t *pstCustSegAttr);
-
Parameter
Parameter name Description Input/Output DevId ISP device ID. Input ChnId ISP channel ID Input pstCustSegAttr AI ISP attribute Input -
Return value
-
MI_SUCCESS (0) successful.
-
Non-Zero: failed, see error code for details.
-
-
Dependence
-
Header: mi_isp_datatype.h, mi_isp.h
-
Library: libmi_isp.a
-
-
Note
-
When the value of pstCustSegAttr→eMode is E_MI_ISP_CUST_SEG_MODE_INSERT or E_MI_ISP_CUST_SEG_MODE_REPLACE, AI ISP is enabled. MI ISP will be divided into pass0, pass1 and pass2 internally, and the functions are composed of hdr, 3dnr, wdr, rgb2yuv. Pass1 specifically provides raw buffer to the app.
-
When AI ISP is enabled, isp rotation/mirror/flip is not supported.
-
MI_ISP_SetCustSegAttr should be called after MI_ISP_CreateChannel and before MI_ISP_StartChannel and MI_ISP_SetOutputPortParam.
-
The combination of Pass0 and pass2 is as follows, which can be represented by MI_ISP_CustSegAttr_t. Note: The pass0 module serial number must be smaller than pass2.
Pass0: HDR, HDR→3DNR, HDR→3DNR→WDR, HDR→3DNR→WDR→RGB2YUV
Pass2: RGB2YUV, WDR→RGB2YUV, 3DNR→WDR→RGB2YUV, HDR→3DNR→WDR→RGB2YUV
E_MI_ISP_SEG_HDR output is before 3DNR.
E_MI_ISP_SEG_3DNR contains DNR Rotation/mirror/flip, and the output is before WDR.
E_MI_ISP_SEG_WDR output is before RGB2YUV.
-
pstCustSegAttr→eMode, pstCustSegAttr→eFrom and pstCustSegAttr→eTo are used to describe the functional composition of pass1.
E_MI_ISP_CUST_SEG_MODE_INSERT: Insert the app image in HDR→3DNR→WDR→RGB2YUV to process pass1.
E_MI_ISP_CUST_SEG_MODE_REPLACE: Replace the function of HDR, 3DNR, WDR, RGB2YUV. You can replace only 3DNR or WDR, or replace both of them.
For example:
-
eFrom= E_MI_ISP_SEG_3DNR, eTo= E_MI_ISP_SEG_WDR, eMode= E_MI_ISP_CUST_SEG_MODE_INSERT
-
eFrom= E_MI_ISP_SEG_3DNR, eTo= E_MI_ISP_SEG_WDR, eMode= E_MI_ISP_CUST_SEG_MODE_REPLACE
-
eFrom= E_MI_ISP_SEG_3DNR, eTo= E_MI_ISP_SEG_3DNR, eMode= E_MI_ISP_CUST_SEG_MODE_REPLACE
-
eFrom= E_MI_ISP_SEG_HDR, eTo= E_MI_ISP_SEG_HDR, eMode= E_MI_ISP_CUST_SEG_MODE_REPLACE
-
eFrom= E_MI_ISP_SEG_RGB2YUV, eTo= E_MI_ISP_SEG_RGB2YUV, eMode= E_MI_ISP_CUST_SEG_MODE_REPLACE
-
-
-
Example
MI_ISP initialization:
MI_S32 ST_IspModuleInit(MI_ISP_DEV IspDevId) { MI_ISP_CHANNEL IspChnId = 0; MI_ISP_PORT IspOutPortId =1; MI_ISP_DevAttr_t stCreateDevAttr; memset(&stCreateDevAttr, 0x0, sizeof(MI_ISP_DevAttr_t)); stCreateDevAttr.u32DevStitchMask = E_MI_ISP_DEVICE_ID0; MI_ISP_CreateDevice(IspDevId, &stCreateDevAttr); MI_ISP_ChannelAttr_t stIspChnAttr; memset(&stIspChnAttr, 0x0, sizeof(MI_ISP_ChannelAttr_t)); stIspChnAttr. u32SensorBindId = E_MI_ISP_SENSOR0; MI_ISP_CreateChannel(IspDevId, IspChnId, &stIspChnAttr); MI_SYS_WindowRect_t stInputCropInfo; stInputCropInfo.u16x=0; stInputCropInfo.u16y=0; stInputCropInfo.u16width=0; stInputCropInfo.u16height=0;//width/height==0 no use crop. MI_ISP_SetInputPortCrop(IspDevId, IspChnId, & stInputCropInfo); MI_ISP_ChnParam_t stChnParam; stChnParam.eHDRType = E_MI_ISP_HDR_TYPE_OFF; stChnParam.e3DNRLevel = E_MI_ISP_3DNR_LEVEL2; stChnParam.bMirror = FALSE; stChnParam.bFlip = FALSE; stChnParam.eRot = E_MI_SYS_ROTATE_NONE; stChnParam.bY2bEnable = FALSE; MI_ISP_SetChnParam(IspDevId, IspChnId, & stChnParam); MI_ISP_CustSegAttr_t stCustSegAttr; memset(&stCustSegAttr, 0x0, sizeof(MI_ISP_CustSegAttr_t)); stCustSegAttr.eMode = E_MI_ISP_CUST_SEG_MODE_INSERT; stCustSegAttr.eFrom = E_MI_ISP_SEG_3DNR; stCustSegAttr.eTo = E_MI_ISP_SEG_WDR; stCustSegAttr.stInputParam.ePixelFormat = RGB_BAYER_PIXEL(E_MI_SYS_DATA_PRECISION_12BPP, E_MI_SYS_PIXEL_BAYERID_GR); stCustSegAttr.stOutputParam.ePixelFormat = stCustSegAttr.stInputParam.ePixelFormat; MI_ISP_SetCustSegAttr(enDevId,enChnId, &stCustSegAttr); MI_ISP_StartChannel(IspDevId, IspChnId); MI_ISP_OutPortParam_t stIspOutputParam; memset(&stIspOutputParam, 0x0, sizeof(MI_ISP_OutPortParam_t)); stIspOutputParam.stCropRect.u16x=0; stIspOutputParam.stCropRect.u16y=0; stIspOutputParam.stCropRect.u16Width=0; stIspOutputParam.stCropRect.u16Height=0;//width/height use 0, not use crop stIspOutputParam.ePixelFormat = E_MI_SYS_PIXEL_FRAME_YUV_SEMIPLANAR_YUV420; MI_ISP_SetOutputPortParam(IspDevId, IspChnId, IspOutPortId, &stIspOutputParam); MI_ISP_EnableOutputPort(IspDevId, IspChnId, IspOutPortId); return MI_SUCCESS; }Get raw:
MI_SYS_BUF_HANDLE hBufHandle = NULL; MI_SYS_BufInfo_t stInputBufInfo; MI_SYS_BufInfo_t stOutputBufInfo; MI_U8 *pSrcData = NULL, *pDstData = NULL; memset(&stInputBufInfo, 0, sizeof(MI_SYS_BufInfo_t)); memset(&stOutputBufInfo, 0, sizeof(MI_SYS_BufInfo_t)); s32Ret = MI_ISP_GetCustSegBuf(stChnPort.u32DevId, stChnPort.u32ChnId, &hBufHandle, &stInputBufInfo, &stOutputBufInfo, 200); if(s32Ret == MI_SUCCESS) { pSrcData = stInputBufInfo.stFrameData->pVirAddr[0]; pDstData = stOutputBufInfo.stFrameData->pVirAddr[0]; memcpy(pDstData, pSrcData, stOutputBufInfo.stFrameData.u32BufSize); memset(pDstData, 0, stOutputBufInfo.stFrameData.u32BufSize/4); MI_ISP_PutCustSegBuf(stChnPort.u32DevId, stChnPort.u32ChnId, hBufHandle); }
2.25. MI_ISP_GetCustSegAttr¶
-
Description
Get AI ISP attributes.
-
Syntax
MI_S32 MI_ISP_GetCustSegAttr(MI_ISP_DEV DevId, MI_ISP_CHANNEL ChnId, MI_ISP_CustSegAttr_t *pstCustSegAttr);
-
Parameter
Parameter name Description Input/Output DevId ISP device ID. Input ChnId ISP channel ID Input pstCustSegAttr API ISP attribute output -
Return value
-
MI_SUCCESS (0) successful.
-
Non-Zero: failed, see error code for details.
-
-
Dependence
-
Header: mi_isp_datatype.h, mi_isp.h
-
Library: libmi_isp.a
-
2.26. MI_ISP_GetCustSegBuf¶
-
Description
Get AI ISP buffer.
-
Syntax
MI_S32 MI_ISP_GetCustSegBuf(MI_ISP_DEV DevId, MI_ISP_CHANNEL ChnId,MI_SYS_BUF_HANDLE *pBufHandle, MI_SYS_BufInfo_t *pstInputBufInfo, MI_SYS_BufInfo_t *pstOutputBufInfo, MI_S32 s32MilliSec);
-
Parameter
| Parameter name | Description | Input/Output |
|---|---|---|
| DevId | ISP device ID. | Input |
| ChnId | ISP channel ID | Input |
| pBufHandle, | Pass1 input/output Buf handle | Output |
| pstInputBufInfo | Pass1 input buffer | Output |
| pstOutputBufInfo | Pass1 output buffer | Output |
| s32MilliSec | Timeout, unit: ms | Input |
-
Return value
-
MI_SUCCESS (0) successful.
-
Non-Zero: failed, see error code for details.
-
-
Dependence
-
Header: mi_isp_datatype.h, mi_isp.h
-
Library: libmi_isp.a
-
-
Note
Used in pairs with MI_ISP_PutCustSegBuf.
-
Example
Refer to the example of MI_ISP_SetCustSegAttr.
2.27. MI_ISP_PutCustSegBuf¶
-
Description
Release AI ISP buffer.
-
Syntax
MI_S32 MI_ISP_PutCustSegBuf(MI_ISP_DEV DevId, MI_ISP_CHANNEL ChnId, MI_SYS_BUF_HANDLE bufHandle);
-
Parameter
Parameter name Description Input/Output DevId ISP device ID. Input ChnId ISP channel ID Input pBufHandle, Pass1 input/output Buf handle Input -
Return value
-
MI_SUCCESS (0) successful.
-
Non-Zero: failed, see error code for details.
-
-
Dependence
-
Header: mi_isp_datatype.h, mi_isp.h
-
Library: libmi_isp.a
-
-
Note
-
Used in pairs with MI_ISP_GetCustSegBuf.
-
MI_ISP_PutCustSegBuf should be called in the order as MI_ISP_GetCustSegBuf gets buffer.
-
-
Example
Refer to the example of MI_ISP_SetCustSegAttr.
2.28. MI_ISP_GetSubChnId¶
-
Description
Get ISP subchannel ID
-
Syntax
MI_S32 MI_ISP_GetSubChnId(MI_ISP_DEV DevId, MI_ISP_CHANNEL MainChnId, MI_ISP_BindSnrId_e eSensorBindId, MI_U32 *pu32SubChnId);
-
Parameter
Parameter name Description Input/Output DevId ISP device ID. Input MainChnId ISP channel ID Input eSensorBindId Sensor ID of subchannel binding Input pu32SubChnId ISP subchannel ID Output -
Return value
-
MI_SUCCESS (0) successful.
-
Non-Zero: failed, see error code for details.
-
-
Dependence
-
Header: mi_isp_datatype.h, mi_isp.h
-
Library: libmi_isp.a
-
-
Note
-
In the scene of Stitch, an MI_ISP channel will bind multiple sensors, when IQ wants to control the corresponding sensors, you need to input MI_ISP dev ID, MI_ISP channel ID and sensor ID to get the corresponding subchannel ID, that is, the channel used by IQ.
-
In other cases, the channel used by IQ is the same as MI_ISP channel ID.
-
2.29. MI_ISP_SetSubChnParam¶
-
Description
Set ISP subchannel parameter.
-
Syntax
MI_S32 MI_ISP_SetSubChnParam(MI_ISP_DEV DevId, MI_ISP_CHANNEL ChnId, MI_ISP_SUB_CHANNEL SubChnId, MI_ISP_ChnParam_t *pstChnParam);
-
Parameter
Parameter name Description Input/Output DevId ISP device ID. Input MainChnId ISP channel ID Input SubChnId ISP subchannel ID Input pstChnParam ISP subchannel parameter pointer Intput -
Return value
-
MI_SUCCESS (0) successful.
-
Non-Zero: failed, see error code for details.
-
-
Dependence
-
Header: mi_isp_datatype.h, mi_isp.h
-
Library: libmi_isp.a
-
-
Note
-
It is recommended to switch the sub channel parameters when the channel is stopped to avoid mismatch between the buffer and back-end parameters in the channel, which may cause an exception.
-
Make sure width/height of input and output to be the same between sub channels when setting eRot. E_MI_SYS_ROTATE_90/ E_MI_SYS_ROTATE_270, or E_MI_SYS_ROTATE_NONE/ E_MI_SYS_ROTATE_180.
-
2.30. MI_ISP_GetSubChnParam¶
-
Description
Get ISP subchannel parameter.
-
Syntax
MI_S32 MI_ISP_GetSubChnParam(MI_ISP_DEV DevId, MI_ISP_CHANNEL ChnId, MI_ISP_SUB_CHANNEL SubChnId, MI_ISP_ChnParam_t *pstChnParam);
-
Parameter
Parameter name Description Input/Output DevId ISP device ID. Input MainChnId ISP channel ID Input SubChnId ISP sub channel ID Input pstChnParam ISP sub channel parameter pointer Output -
Return value
-
MI_SUCCESS (0) successful.
-
Non-Zero: failed, see error code for details.
-
-
Dependence
-
Header: mi_isp_datatype.h, mi_isp.h
-
Library: libmi_isp.a
-
2.31. MI_ISP_SetChnOverlapAttr¶
-
Description
Set ISP channel overlap attribute
-
Syntax
MI_S32 MI_ISP_SetChnOverlapAttr(MI_ISP_DEV DevId, MI_ISP_CHANNEL ChnId, MI_ISP_Overlap_e eOverlap);
-
Parameter
Parameter name Description Input/Output DevId ISP device ID Input ChnId ISP channel ID Input eOverlap overlap Input -
Return value
-
MI_SUCCESS (0) successful.
-
Non-Zero: failed, see error code for details.
-
-
Dependence
-
Header: mi_isp_datatype.h, mi_isp.h
-
Library: libmi_isp.a
-
-
Note
-
Overlay is used to merge left and right of image smoothly.
-
Overlay can only take effect when parameter DevId = MI_ISP_CREATE_MULTI_DEV(MI_ISP_DEV0) in calling MI_ISP_CreateDevice, and value of parameter pstChAttr->u32SensorBindId is one sensor in calling MI_ISP_CreateChannel.
-
E_MI_ISP_OVERLAP_128 will read more 128 pixels. E_MI_ISP_OVERLAP_256 will read more 256 pixels.
-
When eOverlap = E_MI_ISP_OVERLAP_256, run as below.
-
2.32. MI_ISP_GetChnOverlapAttr¶
-
Description
Get ISP channel overlap attribute
-
Syntax
MI_S32 MI_ISP_GetChnOverlapAttr(MI_ISP_DEV DevId, MI_ISP_CHANNEL ChnId, MI_ISP_Overlap_e *peOverlap);
-
Parameter
Parameter name Description Input/Output DevId ISP device ID. Input ChnId ISP channel ID Input peOverlap overlap Output -
Return value
-
MI_SUCCESS (0) successful.
-
Non-Zero: failed, see error code for details.
-
-
Dependence
-
Header: mi_isp_datatype.h, mi_isp.h
-
Library: libmi_isp.a
-
3. ISP Data type¶
Video input related data type definition is as following:
| Data type | Description |
|---|---|
| MI_ISP_DEV | Define ISP device type |
| MI_ISP_CHANNEL | Define ISP channel type |
| MI_ISP_PORT | Define ISP port type |
| MI_ISP_DevMaskId_e | Define the device ID used by the mask for the ISP device |
| MI_ISP_DevAttr_t | Define ISP device attribute parameter |
| MI_ISP_HDRType_e | Define HDR switch mode |
| MI_ISP_3DNR_Level_e | Define 3DNR setting level |
| MI_ISP_BindSnrId_e | Define the sensor ID bound to the ISP |
| MI_ISP_SYNC3A_e | Synchronize 3A parameters of each channel |
| MI_ISP_IQApiHeader_t | Define IQ api data type |
| MI_ISP_VersionPara_t | Define ISP special parameter version |
| MI_ISP_CustIQParam_t | Define ISP initialization parameter |
| MI_ISP_ChannelAttr_t | Define ISP channel static attribute parameter |
| MI_ISP_ChnParam_t | Define ISP channel dynamic attribute parameter |
| MI_ISP_OutPortParam_t | Define ISP output port parameter |
| MI_ISP_CALLBK_FUNC | Define callback function type |
| MI_ISP_CallBackMode_e | Define callback mode |
| MI_ISP_IrqType_e | Define hardware interrupt type |
| MI_ISP_CallBackParam_t | Define callback parameter |
| MI_ISP_ZoomEntry_t | Define the Zoom cell entry type |
| MI_ISP_ZoomTable_t | Define Zoom Table type |
| MI_ISP_ZoomAttr_t | Define Zoom attribute |
| MI_ISP_CustSegAttr_t | Define AI ISP attribute |
| MI_ISP_CustSegInPortParam_t | Pass1 input port attribute |
| MI_ISP_CustSegOutPortParam_t | Pass1 output port attribute |
| MI_ISP_CustSegMode_e | AI ISP mode |
| MI_ISP_InternalSeg_e | ISP module name |
| MI_ISP_BufferLayout_e | ISP buffer layout |
| MI_ISP_Overlap_e | ISP overlap. |
| MI_ISP_HDRExposureType_e | Define HDR Exposure Type |
| MI_ISP_HDRFusionType_e | Define HDR Fusion Type |
3.1. MI_ISP_DEV¶
-
Description
Define ISP device type.
-
Definition
typedef MI_U32 MI_ISP_DEV;
3.2. MI_ISP_CHANNEL¶
-
Description
Define ISP channel type.
-
Definition
typedef MI_U32 MI_ISP_CHANNEL;
3.3. MI_ISP_PORT¶
-
Description
Define ISP port type.
-
Definition
typedef MI_U32 MI_ISP_PORT;
3.4. MI_ISP_DevMaskId_e¶
-
Description
Define the device ID used by the mask for the ISP device.
-
Definition
typedef enum { E_MI_ISP_DEVICEMASK_ID0 = 0x0001, E_MI_ISP_DEVICEMASK_ID1 = 0x0002, E_MI_ISP_DEVICEMASK_ID_MAX = 0xffff } MI_ISP_DevMaskId_e; -
Note
Tiramisu, Mochi, Maruko, Souffle and Pcupid only use ISP E_MI_ISP_DEVICEMASK_ID0.
-
Related data type and interface
3.5. MI_ISP_DevAttr_t¶
-
Description
Define ISP device attribute parameter.
-
Definition
typedef struct MI_ISP_DevAttr_s { MI_U32 u32DevStitchMask; //multi ISP dev bitmask by MI_ISP_DevMaskId_e }MI_ISP_DevAttr_t; -
Member
Member name Description u32DevStitchMask ISP DEV ID mask. -
Note
u32DevStitchMask is composed of MI_ISP_DevMaskId_e and bitmask. If the processing speed of an isp device on the channel cannot meet the requirements, you can use this parameter to reuse another Device, but another device can no longer be created.
-
Related data type and interface
3.6. MI_ISP_HDRType_e¶
-
Description
Define HDR switch mode.
-
Definition
typedef enum { E_MI_ISP_HDR_TYPE_OFF, E_MI_ISP_HDR_TYPE_VC, E_MI_ISP_HDR_TYPE_DOL, E_MI_ISP_HDR_TYPE_COMP, E_MI_ISP_HDR_TYPE_LI, E_MI_ISP_HDR_TYPE_COMPVS, E_MI_ISP_HDR_TYPE_DCG, E_MI_ISP_HDR_TYPE_MAX } MI_ISP_HDRType_e; -
Member
Member name Description E_MI_ISP_HDR_TYPE_OFF Turn off HDR E_MI_ISP_HDR_TYPE_VC virtual channel mode HDR, vc0->long,vc1->short E_MI_ISP_HDR_TYPE_DOL Digital Overlap High Dynamic Range E_MI_ISP_HDR_TYPE_COMP Long and Short exposure are merged by sesnor, and isp controls the gain vaule of two frames E_MI_ISP_HDR_TYPE_LI Line interlace HDR E_MI_ISP_HDR_TYPE_COMPVS compressed HDR + Very short E_MI_ISP_HDR_TYPE_DCG Dual conversion gain HDR E_MI_ISP_HDR_TYPE_MAX HDR boundary value -
Note
-
The HDR Type used can be obtained through the MI_SNR_GetPadInfo interface.
-
The HDR function requires the cooperation of MI_VIF and MI_ISP modules, and the same HDR type needs to be set on both sides.
-
E_MI_ISP_HDR_TYPE_DCG and E_MI_ISP_HDR_TYPE_COMPVS are temporarily not supported.
-
Opera series chip support E_MI_ISP_HDR_TYPE_COMP.
-
-
Related data type and interface
3.7. MI_ISP_3DNR_Level_e¶
-
Description
Define 3DNR setting level.
-
Definition
typedef enum { E_MI_ISP_3DNR_LEVEL_OFF, E_MI_ISP_3DNR_LEVEL1, E_MI_ISP_3DNR_LEVEL2, E_MI_ISP_3DNR_LEVEL3, E_MI_ISP_3DNR_LEVEL4, E_MI_ISP_3DNR_LEVEL5, E_MI_ISP_3DNR_LEVEL6, E_MI_ISP_3DNR_LEVEL7, E_MI_ISP_3DNR_LEVEL_NUM }MI_ISP_3DNR_Level_e; -
Note
The higher the level, the better the noise reduction effect and the more buffer consumed.
Chip 3DNR support max level Tiramisu E_MI_ISP_3DNR_LEVEL2 Muffin E_MI_ISP_3DNR_LEVEL2 Mochi E_MI_ISP_3DNR_LEVEL7 Maruko E_MI_ISP_3DNR_LEVEL7 Souffle E_MI_ISP_3DNR_LEVEL5 Pcupid E_MI_ISP_3DNR_LEVEL2 -
Related data type and interface
3.8. MI_ISP_BindSnrId_e¶
-
Description
Define the sensor ID bound to the ISP.
-
Definition
typedef enum { E_MI_ISP_SENSOR_INVALID = 0, E_MI_ISP_SENSOR0 = 0x1, E_MI_ISP_SENSOR1 = 0x2, E_MI_ISP_SENSOR2 = 0x4, E_MI_ISP_SENSOR3 = 0x8, E_MI_ISP_SENSOR4 = 0x10, E_MI_ISP_SENSOR5 = 0x20, E_MI_ISP_SENSOR6 = 0x40, E_MI_ISP_SENSOR7 = 0x80, E_MI_ISP_SENSOR_MAX = 8 }MI_ISP_BindSnrId_e;
3.9. MI_ISP_SYNC3A_e¶
-
Description
Synchronize 3A parameters of each channel.
-
Definition
typedef enum { E_MI_ISP_SYNC3A_NONE = 0x00, E_MI_ISP_SYNC3A_AE = 0x01, E_MI_ISP_SYNC3A_AWB = 0x02, E_MI_ISP_SYNC3A_IQ = 0x04 }MI_ISP_SYNC3A_e; -
Member
Member name Description E_MI_ISP_SYNC3A_NONE Async 3A E_MI_ISP_SYNC3A_AE Sync AE E_MI_ISP_SYNC3A_AWB Sync AWB E_MI_ISP_SYNC3A_IQ Sync IQ parameter setting
3.10. MI_ISP_IQApiHeader_t¶
-
Description
Define IQ api data type.
-
Definition
typedef struct MI_ISP_IQApiHeader_s { MI_U32 u32HeadSize; //Size of MIIspApiHeader_t MI_U32 u32DataLen; //Data length; MI_U32 u32CtrlID; //Function ID MI_U32 u32Channel; //Isp channel number MI_U32 u32DevId; //Isp Device Id MI_S32 s32Ret; //Isp api retuen value } MI_ISP_IQApiHeader_t; -
Member
Member name Description u32HeadSize MI_ISP_IQApiHeader_t struct takes up space u32DataLen Data size u32CtrlID Function corresponding control Id u32Channel Isp channel Id u32DevId Isp device Id s32Ret Interface return value
3.11. MI_ISP_VersionPara_t¶
-
Description
Define ISP special parameter version.
-
Definition
typedef struct MI_ISP_VersionPara_s { MI_U32 u32Revision; MI_U32 u32Size; MI_U8 u8Data[VERSIONPARA_DATA_SIZE]; }MI_ISP_VersionPara_t; -
Member
Member name Description u32Revision Negotiate with IQ team to define the corresponding version number u32Size Data corresponds to effective size u8Data[VERSIONPARA_DATA_SIZE] Store data, the value of VERSIONPARA_DATA_SIZE is 64 -
Related data type and interface
3.12. MI_ISP_CustIQParam_t¶
-
Description
Define ISP initialization parameter.
-
Definition
typedef struct MI_ISP_CustIQParam_s { MI_ISP_VersionPara_t stVersion; }MI_ISP_CustIQParam_t; -
Member
Member name Description stVersion Version parameter -
Note
Some IQ initialization parameters that require ISP customized processing can be set through this parameter. If there is no requirement, you can set all of them to 0.
3.13. MI_ISP_ChannelAttr_t¶
-
Description
Define ISP channel static attribute parameter.
-
Definition
typedef struct MI_ISP_ChannelAttr_s { MI_U32 u32SensorBindId; //bitmask by MI_ISP_BindSnrId_e MI_ISP_CustIQParam_t stIspCustIqParam; MI_U32 u32Sync3AType; //sync 3a bitmask by MI_ISP_SYNC3A_e }MI_ISP_ChannelAttr_t; -
Member
Member name Description u32SensorBindId Sensor Id corresponding to channel binding stIspCustIqParam Isp IQ initialization parameter u32Sync3AType Sync the 3A/IQ parameters between multiple groups of images in the channel -
Note
-
When a multi-sensor splicing scene, one ISP channel needs to process multiple sensor images, you need to set up multiple sensor Id bitmasks through u32SensorBindId, otherwise only the corresponding sensor Id interface is set. If you do not need ISP to do IQ/3A, or the front-end data source is not sensor, you can set it to 0.
-
When multi-sensor splicing scenes, one ISP channel needs to process multiple sensor images, set the 3A/IQ effect synchronization between multiple images through u32Sync3AType to avoid excessive differences in effects between the two images.
-
-
Related data type and interface
3.14. MI_ISP_ChnParam_t¶
-
Description
Define ISP channel dynamic attribute parameter.
-
Definition
typedef struct MI_ISP_ChnParam_s { MI_ISP_HDRType_e eHDRType; MI_ISP_3DNR_Level_e e3DNRLevel; MI_BOOL bMirror; MI_BOOL bFlip; MI_SYS_Rotate_e eRot; MI_BOOL bY2bEnable; } MI_ISP_ChnParam_t; -
Member
Member name Description eHDRType HDR switch parameter e3DNRLevel 3dnr lever bMirror Enable channel mirror bFlip Enable channel flip eRot Channel rotation parameter bY2bEnable Enable the conversion function of yuv to bayer eHDRFusionType HDR Fusion Type u16HDRExposureMask HDR Exposure Type Mask, MI_ISP_HDRExposureType_e Composition -
Note
-
Non Maruko / Souffle chip, when eRot > 0 or bflip = true, e3dnrlevel must be greater than 0.
-
bY2bEnable is only supported by Muffin and only supported when the input port is Frame Mode.
-
Mochi does not support HDR/Mirror/Flip/Rot/Y2bEnable.
-
ISP eHDRType follows Sensor eHDRType and supports up to 3frame HDR sensor. For this purpose, ISP can control different exposure frame fusion or direct output through the combination of eHDRFusionType and u16HDRExposureMask.
-
-
Example
Scenario 1:SENSOR 2frame HDR,ISP 2frame HDR
Sensor VIF ISP eHDRFusionType eHDRFusionType u16HDRExposureMask eHDRFusionType u16HDRExposureMask xx_FUSION_TYPE_2TO1 xx_FUSION_TYPE_2TO1 LS xx_FUSION_TYPE_2TO1 LS Scenario 2:SENSOR 3frame HDR,ISP 2frame HDR
Sensor VIF ISP eHDRFusionType eHDRFusionType u16HDRExposureMask eHDRFusionType u16HDRExposureMask xx_FUSION_TYPE_3TO1 xx_FUSION_TYPE_3TO1 LS / LM / MS xx_FUSION_TYPE_2TO1 LS / LM / MS Scenario 3:SENSOR 3frame HDR,ISP 3frame HDR
Sensor VIF ISP eHDRFusionType eHDRFusionType u16HDRExposureMask eHDRFusionType u16HDRExposureMask xx_FUSION_TYPE_3TO1 xx_FUSION_TYPE_3TO1 LMS xx_FUSION_TYPE_3TO1 LMS Scenario 4:SENSOR 2frame HDR,ISP 2chn Detach export 2frame
Sensor VIF ISP eHDRFusionType eHDRFusionType u16HDRExposureMask eHDRFusionType u16HDRExposureMask xx_FUSION_TYPE_2TO1 xx_FUSION_TYPE_2TO1 LS Chn0 xx_FUSION_TYPE_2TO1 Chn0 L / S Chn1 xx_FUSION_TYPE_2TO1 Chn1 S / L Scenario 5:SENSOR 3frame HDR,ISP 2chn Detach expor 2frame
Sensor VIF ISP eHDRFusionType eHDRFusionType u16HDRExposureMask eHDRFusionType u16HDRExposureMask xx_FUSION_TYPE_3TO1 xx_FUSION_TYPE_3TO1 LS / LM / MS Chn0 xx_FUSION_TYPE_2TO1 Chn0 L / M / S Chn1 xx_FUSION_TYPE_2TO1 Chn1 S / L / M Scenario 6:SENSOR 3frame HDR,ISP 3chn Detach expor 3frame
Sensor VIF ISP eHDRFusionType eHDRFusionType u16HDRExposureMask eHDRFusionType u16HDRExposureMask xx_FUSION_TYPE_3TO1 xx_FUSION_TYPE_3TO1 LMS Chn0 xx_FUSION_TYPE_3TO1 Chn0 L / M / S Chn1 xx_FUSION_TYPE_3TO1 Chn1 M / S / L Chn2 xx_FUSION_TYPE_3TO1 Chn2 S / L / M Scenario 7:SENSOR 3frame HDR,ISP 2chn Detach expor 2frame HDR and 1frame
Sensor VIF ISP eHDRFusionType eHDRFusionType u16HDRExposureMask eHDRFusionType u16HDRExposureMask xx_FUSION_TYPE_3TO1 xx_FUSION_TYPE_3TO1 LMS Chn0 xx_FUSION_TYPE_3TO1 Chn0 LS / LM / MS Chn0 xx_FUSION_TYPE_3TO1 Chn0 M / S / L -
Related data type and interface
3.15. MI_ISP_OutPortParam_t¶
-
Description
Define ISP output port parameter.
-
Definition
typedef struct MI_ISP_OutPortParam_s { MI_SYS_WindowRect_t stCropRect; MI_SYS_PixelFormat_e ePixelFormat; MI_SYS_CompressMode_e eCompressMode; MI_ISP_BufferLayout_e eBufLayout; }MI_ISP_OutPortParam_t; -
Member
Member name Description stCropRect Output crop area ePixelFormat Pixel format eCompressMode Output compress mode eBufLayout Output image buffer layout -
Note
-
eCompressMode support range:
Chip Output compress mode supported Tiramisu E_MI_SYS_COMPRESS_MODE_NONE Muffin E_MI_SYS_COMPRESS_MODE_NONE Mochi E_MI_SYS_COMPRESS_MODE_NONE
E_MI_SYS_COMPRESS_MODE_TO_6BITMaruko E_MI_SYS_COMPRESS_MODE_TO_6BIT Soufffle E_MI_SYS_COMPRESS_MODE_NONE
E_MI_SYS_COMPRESS_MODE_TO_6BITPcupid E_MI_SYS_COMPRESS_MODE_NONE - E_MI_SYS_COMPRESS_MODE_10TO6 limit
Output_Compress_10TO6 Mochi Maruko Soufffle Pixel yuv420SP NV12 Y Y Y yuv422 YUYV Y Y Y Pixel Alignment (WxH) yuv420SP NV12 2x2 2x2 2x2 yuv422 YUYV 2x2 2x2 2x2 -
3.16. MI_ISP_CALLBK_FUNC¶
-
Description
Define callback function type.
-
Definition
typedef MI_S32 (*MI_ISP_CALLBK_FUNC)(MI_U64 u64Data);
-
Related data type and interface
3.17. MI_ISP_CallBackMode_e¶
-
Description
Define callback mode.
-
Definition
typedef enum { E_MI_ISP_CALLBACK_ISR, E_MI_ISP_CALLBACK_MAX, } MI_ISP_CallBackMode_e; -
Member
Member name Description E_MI_ISP_CALLBACK_ISR Hardware interrupt mode callback E_MI_ISP_CALLBACK_MAX Maximum value of callback mode -
Note
Currently only supports ISR callback mode.
-
Related data type and interface
3.18. MI_ISP_IrqType_e¶
-
Description
Define hardware interrupt type.
-
Definition
typedef enum { E_MI_ISP_IRQ_ISPVSYNC, E_MI_ISP_IRQ_ISPFRAMEDONE, E_MI_ISP_IRQ_MAX, } MI_ISP_IrqType_e; -
Member
Member name Description E_MI_ISP_IRQ_ISPVSYNC ISP Vsync interrupt type E_MI_ISP_IRQ_ISPFRAMEDONE ISP Frame done interrupt type E_MI_ISP_IRQ_MAX ISP hardware interrupt type maximum -
Note
-
E_MI_VPE_IRQ_ISPVSYNC: The signal of the first pixel in each frame.
-
E_MI_VPE_IRQ_ISPFRAMEDONE: The signal at the end of each frame written by isp.
-
-
Related data type and interface
3.19. MI_ISP_CallBackParam_t¶
-
Description
Define callback parameter.
-
Definition
typedef struct MI_ISP_CallBackParam_s { MI_ISP_CallBackMode_e eCallBackMode; MI_ISP_IrqType_e eIrqType; MI_ISP_CALLBK_FUNC pfnCallBackFunc; MI_U64 u64Data; } MI_ISP_CallBackParam_t; -
Member
Member name Description eCallBackMode Callback mode eIrqType Hardware interrupt mode type pfnCallBackFunc Callback interface pointer u64Data Callback interface parameter -
Note
None.
-
Related data type and interface
3.20. MI_ISP_ZoomEntry_t¶
-
Description
Define the Zoom cell entry type.
-
Definition
typedef struct MI_ISP_ZoomEntry_s { MI_SYS_WindowRect_t stCropWin; MI_U8 u8ZoomSensorId; } MI_ISP_ZoomEntry_t; -
Member
Member name Description stCropWin Crop position parameter u8ZoomSensorId The sensor Id corresponding to the Crop parameter -
Note
u8ZoomSensorId corresponds to the return value of the pCus_sensor_GetCurSwtichSensorId callback function in the sensor driver.
-
Related data type and interface
3.21. MI_ISP_ZoomTable_t¶
-
Description
Define Zoom Table type.
-
Definition
typedef struct MI_ISP_ZoomTable_s { MI_U32 u32EntryNum; MI_ISP_ZoomEntry_t *pVirTableAddr; } MI_ISP_ZoomTable_t; -
Member
Member name Description u32EntryNum Number of entries in the Zoom Table pVirTableAddr Zoom Table Buffer Pointer -
Related data type and interface
3.22. MI_ISP_ZoomAttr_t¶
-
Description
Define Zoom attribute.
-
Definition
typedef struct MI_ISP_ZoomAttr_s { MI_U32 u32FromEntryIndex; MI_U32 u32ToEntryIndex; MI_U32 u32CurEntryIndex; } MI_ISP_ZoomAttr_t; -
Member
Member name Description u32FromEntryIndex Start to run Zoom entry index u32ToEntryIndex Stop to run Zoom entry index u32CurEntryIndex Index of current Zoom position -
Related data type and interface
3.23. MI_ISP_CustSegAttr_t¶
-
Description
Define AI ISP attribute.
-
Definition
typedef struct MI_ISP_CustSegAttr_s { MI_ISP_CustSegMode_e eMode; MI_ISP_InternalSeg_e eFrom; MI_ISP_InternalSeg_e eTo; MI_ISP_CustSegInPortParam_t stInputParam; MI_ISP_CustSegOutPortParam_t stOutputParam; } MI_ISP_CustSegAttr_t; -
Member
Member name Description eMode Pass1 mode eFrom Head module of Pass1 eTo End module of Pass1 stInputParam Pass1 input port attribute stOutputParam Pass1 output port attribute -
Note
For parameter function, please refer to the description of MI_ISP_SetCustSegAttr.
-
Related data type and interface
3.24. MI_ISP_CustSegInPortParam_t¶
-
Description
Pass1 input port attribute.
-
Definition
typedef struct MI_ISP_CustSegInPortParam_s { MI_SYS_PixelFormat_e ePixelFormat; } MI_ISP_CustSegInPortParam_t; -
Member
Member name Description ePixelFormat Data format -
Note
-
Before 3DNR only supports 12bit bayer and 16bit bayer input and output.
-
Before WDR only supports 16bit bayer input and output.
-
Before RGB2YUV only supports the input and output of E_MI_SYS_PIXEL_FRAME_ARGB8888 and E_MI_SYS_PIXEL_FRAME_RGB101010.
-
-
Related data type and interface
3.25. MI_ISP_CustSegOutPortParam_t¶
-
Description
Pass1 output port attribute.
-
Definition
typedef struct MI_ISP_CustSegOutPortParam_s { MI_SYS_PixelFormat_e ePixelFormat; } MI_ISP_CustSegOutPortParam_t; -
Member
Member name Description ePixelFormat Data format -
Note
-
Before 3DNR only supports 12bit bayer and 16bit bayer input and output.
-
Before WDR only supports 16bit bayer input and output.
-
Before RGB2YUV only supports the input and output of E_MI_SYS_PIXEL_FRAME_ARGB8888 and E_MI_SYS_PIXEL_FRAME_RGB101010.
-
-
Related data type and interface
3.26. MI_ISP_CustSegMode_e¶
-
Description
AI ISP mode.
-
Definition
typedef enum { E_MI_ISP_CUST_SEG_MODE_NONE = 0, E_MI_ISP_CUST_SEG_MODE_INSERT, E_MI_ISP_CUST_SEG_MODE_REPLACE, E_MI_ISP_CUST_SEG_MODE_MAX } MI_ISP_CustSegMode_e; -
Member
Member name Description E_MI_ISP_CUST_SEG_MODE_NONE Disable AI ISP E_MI_ISP_CUST_SEG_MODE_INSERT Insert mode E_MI_ISP_CUST_SEG_MODE_REPLACE Replacement mode E_MI_ISP_CUST_SEG_MODE_MAX Maximum value -
Related data type and interface
3.27. MI_ISP_InternalSeg_e¶
-
Description
ISP module name.
-
Definition
typedef enum { E_MI_ISP_SEG_INVALID = 0, E_MI_ISP_SEG_HDR, // HDR E_MI_ISP_SEG_3DNR, // 3DNR E_MI_ISP_SEG_WDR, // WDR E_MI_ISP_SEG_RGB2YUV, // RGB2YUV E_MI_ISP_SEG_MAX } MI_ISP_InternalSeg_e; -
Member
Member name Description E_MI_ISP_SEG_INVALID Invalid module E_MI_ISP_SEG_HDR HDR module E_MI_ISP_SEG_3DNR DNR,Rotation/mirror/flip module E_MI_ISP_SEG_WDR WDR module E_MI_ISP_SEG_RGB2YUV RGB2YUV module E_MI_ISP_SEG_MAX Maximum value -
Related data type and interface
3.28. MI_ISP_BufferLayout_e¶
-
Description
ISP buffer layout.
-
Definition
typedef enum { E_MI_ISP_BUFFER_LAYOUT_ONE_FRAME, E_MI_ISP_BUFFER_LAYOUT_MULTI_PLANE, E_MI_ISP_BUFFER_LAYOUT_MAX, } MI_ISP_BufferLayout_e; -
Member
Member name Description E_MI_ISP_BUFFER_LAYOUT_ONE_FRAME Data layout in one buffer E_MI_ISP_BUFFER_LAYOUT_MULTI_PLANE Data layout in multi buffer E_MI_ISP_BUFFER_LAYOUT_MAX Maximum value -
Note
-
Only in stitch mode, eBufLayout can set E_MI_ISP_BUFFER_LAYOUT_MULTI_PLANE. In this case, buffer type of output port is E_MI_SYS_BUFDATA_MULTIPLANE. Otherwise E_MI_SYS_BUFDATA_FRAME is output.
-
Only output port 1 supports eBufLayout = E_MI_ISP_BUFFER_LAYOUT_MULTI_PLANE.
-
You can look up E_MI_SYS_BUFDATA_MULTIPLANE and E_MI_SYS_BUFDATA_FRAME in MI SYS API.
-
-
Related data type and interface
3.29. MI_ISP_Overlap_e¶
-
Description
ISP overlap.
-
Definition
typedef enum { E_MI_ISP_OVERLAP_NONE, E_MI_ISP_OVERLAP_128, E_MI_ISP_OVERLAP_256, E_MI_ISP_OVERLAP_MAX } MI_ISP_Overlap_e; -
Member
Member name Description E_MI_ISP_OVERLAP_NONE Disable overlap E_MI_ISP_OVERLAP_128 Read more 128 pixels E_MI_ISP_OVERLAP_256 Read more 256 pixels E_MI_ISP_OVERLAP_MAX Maximum value -
Related data type and interface
3.30. MI_ISP_HDRExposureType_e¶
-
Description
Define HDR Exposure Type.
-
Definition
typedef enum { E_MI_ISP_HDR_EXPOSURE_TYPE_NONE, E_MI_ISP_HDR_EXPOSURE_TYPE_SHORT = 0x1, E_MI_ISP_HDR_EXPOSURE_TYPE_MEDIUM = 0x2, E_MI_ISP_HDR_EXPOSURE_TYPE_LONG = 0x4, E_MI_ISP_HDR_EXPOSURE_TYPE_MAX } MI_ISP_HDRExposureType_e; -
Member
Member name Description E_MI_ISP_HDR_EXPOSURE_TYPE_NONE Disable Exposure Type E_MI_ISP_HDR_EXPOSURE_TYPE_SHORT Short Exposure E_MI_ISP_HDR_EXPOSURE_TYPE_MEDIUM Medium Exposure E_MI_ISP_HDR_EXPOSURE_TYPE_LONG Long Exposure E_MI_ISP_HDR_EXPOSURE_TYPE_MAX MAX Exposure -
Related data type and interface
3.31. MI_ISP_HDRFusionType_e¶
-
Description
Define HDR Fusion Type.
-
Definition
typedef enum { E_MI_ISP_HDR_FUSION_TYPE_NONE, E_MI_ISP_HDR_FUSION_TYPE_2TO1, E_MI_ISP_HDR_FUSION_TYPE_3TO1, E_MI_ISP_HDR_FUSION_TYPE_MAX } MI_ISP_HDRFusionType_e; -
Member
Member name Description E_MI_ISP_HDR_FUSION_TYPE_NONE Disable Fusion Type E_MI_ISP_HDR_FUSION_TYPE_2TO1 2-frame fusion HDR E_MI_ISP_HDR_FUSION_TYPE_3TO1 3-frame fusion HDR E_MI_ISP_HDR_FUSION_TYPE_MAX MAX Fusion Type -
Related data type and interface
4. ISP Error code¶
API error codes are as the table shown below:
| Error code | Macro definition | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 0xA0078001 | MI_ERR_ISP_INVALID_CHNID | Invalid device channel ID |
| 0xA0078002 | MI_ERR_ISP_INVALID_PORTID | Invalid device port ID |
| 0xA0078003 | MI_ERR_ISP_ILLEGAL_PARAM | Illegal parameter |
| 0xA0078004 | MI_ERR_ISP_EXIST | Device has exited |
| 0xA0078005 | MI_ERR_ISP_UNEXIST | Device has not exited |
| 0xA0078006 | MI_ERR_ISP_NULL_PTR | Null pointer parameter |
| 0xA0078008 | MI_ERR_ISP_NOT_SUPPORT | Not supported |
| 0xA0078009 | MI_ERR_ISP_NOT_PERM | Operation is not permitted |
| 0xA007800C | MI_ERR_ISP_NOMEM | Failed to allocate memory |
| 0xA007800D | MI_ERR_ISP_NOBUF | Memory has run out |
| 0xA007800E | MI_ERR_ISP_BUF_EMPTY | Video input buffer is empty |
| 0xA0078010 | MI_ERR_ISP_NOTREADY | Device is not initialized |
| 0xA0078012 | MI_ERR_ISP_BUSY | Device system is busy |
5. PROCFS INTRODUCTION¶
5.1. cat¶
-
Debug info
# cat /proc/mi_modules/mi_isp/mi_isp0
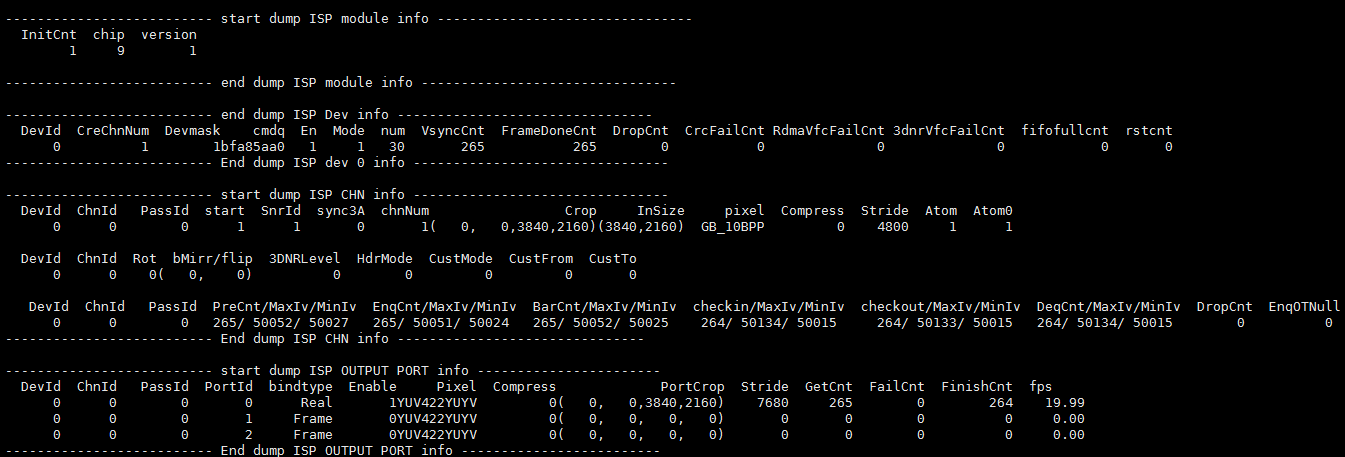
-
Debug info analysis
Record the current ISP usage status and related attributes, you can get this information dynamically, which is convenient for debugging and testing.
-
Parameter Description
Parameter Description ISP Dev info DevId Isp Dev Id CreChnNum Chn number DevMask Stitch Dev Mask cmdq Cmdq pointer En ISR interrupt enable flag Mode ISR interrupt mode num ISR ID VsyncCnt ISR ID FrameDoneCnt ISR Frame Done Cnt DropCnt ISR Frame Drop Cnt crcfailcnt input crc check fail cnt RdmaVfcFailCnt input VFC decompress fail cnt 3dnrVfcFailCnt 3dnr VFC decompress fail cnt fifofullcnt fifo full cnt rstcnt reset hw cnt ISP Chn info DevId Isp Dev Id ChnId Isp Chn Id start Chn Start Flag SnrId Bind sensorId Sync3A Sync 3A type chnNum Muti chn Num Crop Input Crop Size InSize Input Size pixel Input pixel format compress Input compress type Stride Input Buffer Stride Atom Bottom buffers Atom0 There is no buffer at the bottem after the buffer is released Rot Rotation angle bMirror/Flip mirror/flip 3DNRLevel 3DNR Level HdrMode HDR mode CustMode AI ISP Cust Seg mode CustFrom AI ISP From Cust seg CustTo AI ISP to Cust PTMax/Cur Maximum hardware processing time/Current frame hardware processing time PreCnt/EnqCnt/BarCnt/ checkin/checkout/DeqCnt Callback execution times MaxIv/MinIv callback execution interval time DropCnt drop task cnt EnqOTNull Statistics of times that OutBuffer is Null in Enq ISP OutPut Port info DevId Dev Id ChnId Plane id PortID Port Id Bindtype Binding mode with post-level Enable Port enable flag Pixel Port output pixel format compress Port output compress type PortCrop output Crop Size Stride Output Stride GetCnt Count of getting Output buffers Failcnt Count of failed to get Output buffers FinishCnt Count of finished output buffers fps Output port frame rate
5.2. echo¶
# echo help > /proc/mi_modules/mi_isp/mi_isp0
Echo help can view the available commands.
| Function | Stop the specified channel. |
|---|---|
| Command | echo stopchnl [ChnID] [ON/OFF] > /proc/mi_modules/mi_isp/mi_isp0 |
| Parameter Description |
[ChnId] Channel id [ON/OFF] ON: stop chn OFF: start chn |
| Example | echo stopchnl 0 ON > /proc/mi_modules/mi_isp/mi_isp0 |
| Function | Dump the output data of the selected channel and save it in /path. |
|---|---|
| Command | echo dumptaskfile [chnid, Cnt, /path/, bOnlyDumpResChange, bdumpport] > /proc/mi_modules/mi_isp/mi_isp0 |
| Parameter Description |
Chnid: Channel id |
| Cnt: Dump count | |
| Path: Path to store dump files | |
| bOnlyDumpResChange: Blurred images may be generated when switching resolutions. The dump command and switching resolution operations are not easy to perform together. You can set this parameter first, and then switch the resolution. After the program recognizes it, the buffer after the resolution change will be dumped. (Optional) | |
| Bdumpport: Only dump a certain portid, the default is to dump all the ports in the output. (Optional) | |
| Example | echo dumptaskfile 0 1 /mnt > /proc/mi_modules/mi_isp/mi_isp0 |
| Function | Set Dev atomvalue |
|---|---|
| Command | echo setatom [chnid AtomValue] > /proc/mi_modules/mi_isp/mi_isp0 |
| Parameter Description |
chnid: chnel id AtomValue: The maximum number of buffers held by the Driver in input realtime mode |
| Example | echo setatom 0 3 > /proc/mi_modules/mi_isp/mi_isp0 ps: Increase the atom when the bottom layer is stuck, add a buffer to the driver, and re-trig to see if it recovers, or increase it when the frame is dropped to see if the frame can be full. |
| Function | Clear the input/output/done of the specified channel portbuffer. |
|---|---|
| Command | echo clearbuf [chnid, portid bClearInput, bclearoutput, bcleardonebuff] > /proc/mi_modules/mi_isp/mi_isp0 |
| Parameter Description |
Chnid: channel id Portid: port id bClearInput: Clear input buffer bclearoutput: Clear output buffer bcleardonebuff: Clear done buffer |
| Example | echo clearbuf 0 0 1 0 0 > /proc/mi_modules/mi_isp/mi_isp0 |
| Function | Set debug level |
|---|---|
| Command | echo debuglv [level] >/proc/mi_modules/mi_isp/mi_isp0 echo debuglv [chnid][level] >/proc/mi_modules/mi_isp/mi_isp0 |
| Parameter Description |
Chnid: channel id Level: Single level parameter: 1:isp api,2:flow,4:check irq done Double level parameter: 1:check buffer,2:check loop,4:check frame pts,8:check fence done,16:check func time,32:check sidebandmsg,64:check zoominfo |
| Example | echo debuglv 4 > /proc/mi_modules/mi_isp/mi_isp0 //Open check irq done related MI print echo debuglv 0 3 > /proc/mi_modules/mi_isp/mi_isp0 // Open channel0 level3 printing to print buffer info and loop info |
| Function | Drop frame count |
|---|---|
| Command | echo skipframe [chnid, skipnum] > /proc/mi_modules/mi_isp/mi_isp0 |
| Parameter Description |
Chnid: channel id skipnum: drop frame count |
| Example | echo skipframe 0 60 > /proc/mi_modules/mi_isp/mi_isp0 |
| Function | Clear Bind Q buffer |
|---|---|
| Command | echo clearbindq [chnid bclear] > /proc/mi_modules/mi_isp/mi_isp0 |
| Parameter Description |
Chnid: channel id bclear: Whether to clear |
| Example | echo clearbindq 0 1 > /proc/mi_modules/mi_isp/mi_isp0 //Clear channel0 bindQ buffer The ISP BindQ is full and the front-end cannot get the buffer, and judge whether the ISP is too slow. Clear bindQ and observe whether it will accumulate. If it is, the ISP is too slow, if not, the previous exception is not consumed. |
| Function | Set the print frame rate, print if it is lower than this value |
|---|---|
| Command | echo fpsth [chnid portid fpsint fpsfloat] > /proc/mi_modules/mi_isp/mi_isp0 |
| Parameter Description |
Chnid: channel id Portid: port id fpsint: Frame rate integer bits fpsfloat: Frame rate demical bits |
| Example | echo fpsth 0 0 30 30 > /proc/mi_modules/mi_isp/mi_isp0 //Print the fps which is less than 30.30 in channel0 port0 |
| Function | Set the print pts, print if it is exceeding PTS interval |
|---|---|
| Command | echo ptsth [chnid portid minptsinterval maxptsinterval] > /proc/mi_modules/mi_isp/mi_isp0 |
| Parameter Description |
Chnid: channel id Portid: port id minptsinterval: pts interval min value maxptsinterval: pts interval max value |
| Example | echo ptsth 0 0 30000 40000 > /proc/mi_modules/mi_isp/mi_isp0 // Values with PTS interval less than 30ms and more than 40ms in channel0 port0 are printed out |
| Function | Enable port or not |
|---|---|
| Command | echo enableport [chnid, portid, bEn] > /proc/mi_modules/mi_isp/mi_isp0 |
| Parameter Description |
Chnid: channel id Portid: port id bEn: 1/0 |
| Example | echo enableport 0 0 1 > /proc/mi_modules/mi_isp/mi_isp0 |
| Function | Set output port parameters |
|---|---|
| Command | echo outputparam pixel [chnid, portid pixelmode] > /proc/mi_modules/mi _isp/mi_isp0 echo outputparam compress [chnid, portid compressmode] > /proc/mi_modules/mi_isp/mi_isp0 echo outputparam crop [chnid, portid cropX cropY cropW cropH] > /proc/mi_modules/mi_isp/mi_isp0 echo outputparam all [chnid, portid pixelmode compressmode cropX cropY cropW cropH] > /proc/mi_modules/mi_isp/mi_isp0 |
| Parameter Description |
Chnid: channel id Portid: port id Pixelmode: output pixel format Compressmode: output compress mode cropX: output crop X cropY: output crop Y cropW: output crop width cropH: output crop height |
| Example | echo outputparam pixel 0 1 11 > /proc/mi_modules/mi_isp/mi_isp0 echo outputparam compress 0 1 5 > /proc/mi_modules/mi_isp/mi_isp0 echo outputparam crop 0 1 0 0 1920 1080 > /proc/mi_modules/mi_isp/mi_isp0 echo outputparam all 0 1 11 5 0 0 1920 1080 > /proc/mi_modules/mi_isp/mi_isp0 |
| Function | Set to always send the same picture |
|---|---|
| Command | echo sendoneframe [chnid, bEn] > /proc/mi_modules/mi_isp/mi_isp0 |
| Parameter Description |
Chnid: channel id bEn: 1/0 |
| Example | echo sendoneframe 0 1 > /proc/mi_modules/mi_isp/mi_isp0 |
| Function | Set 3dnr level |
|---|---|
| Command | echo dnrlevel [chnid, level] > /proc/mi_modules/mi_isp/mi_isp0 |
| Parameter Description |
Chnid: channel id level: 3dnr level, please refer to MI_ISP_3DNR_Level_e |
| Example | echo dnrlevel 0 1 > /proc/mi_modules/mi_isp/mi_isp0 |
| Function | Reset ISP entire hardware |
|---|---|
| Command | echo resethw > /proc/mi_modules/mi_isp/mi_isp0 |
| Parameter Description |
none |
| Example | echo resethw > /proc/mi_modules/mi_isp/mi_isp0 |
| Function | Set output CRC check |
|---|---|
| Command | echo crcmode [chnid, bEn] > /proc/mi_modules/mi_isp/mi_isp0 |
| Parameter Description |
Chnid: channel id bEn: 1/0 |
| Example | echo crcmode 0 1 > /proc/mi_modules/mi_isp/mi_isp0 |
| Function | Set datagen |
|---|---|
| Command | echo datagen [chnid, bEn] > /proc/mi_modules/mi_isp/mi_isp0 |
| Parameter Description |
Chnid: channel id bEn: 1/0 |
| Example | echo datagen 0 1 > /proc/mi_modules/mi_isp/mi_isp0 |
| Function | Set the command fetching information executed after cmdq timeout |
|---|---|
| Command | echo cmdqtimeout [bEn, keyword, cmdline, path] > /proc/mi_modules/mi_isp/mi_isp0 |
| Parameter Description |
bEn: 1/0 keyword: Executed commands cmdline: Executed string path: Information saving path |
| Example | echo 1 cat /proc/mi_modules/mi_isp/mi_isp0 /mnt/cmdqerr.txt > /proc/mi_modules/mi_isp/mi_isp0 |
6. MODPARAM.JSON INTRODUCTION¶
6.1. The json file content¶
{
"E_MI_MODULE_ID_ISP" :
{
"u32DefaultDropNum": 10,
"s32ForceOverlap": -1,
"s32RotExtraBuf": -1,
"s32BufLayout": -1,
"bDefaultDropFifoBuffer": true,
"bFlushBuffer": true,
"s32ModuleTotalPlanenum": -1,
"u32threadPriorityArray": [98],
"u64PmTimeoutLatencyNS": [1000000000],
"au8ChnMaxEnqTasks": [0,0,2],
"bEnableSuspendWaitDone": true,
"u32DevDbgLv": [0,0],
"u32ChnDbgLv": [0,0,0,0],
"isp_clk" : 288000000,
"rootPath": "/config/iqfile"
}
}
The modparam.json file is typically located in the /config directory, but its path can also be specified when loading mi_common.ko, for example:insmod /config/modules/5.10/mi_common.ko g_modParamPath=/config/modparam.json.This file is loaded during the mi_isp insmod phase.
6.2. ISP common paramaters and paramater description¶
| Parameters | Default | Support chip | Customer configuration | Function |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| u32DefaultDropNum | 10 | Maruko, Opera, Souffle, Pcupid and later chip | N | Set isp default drop frame num, range [0-U32MAX] |
| s32ForceOverlap | -1 | Maruko, Opera, Souffle, Pcupid and later chip | N | Set isp force overlap value, -1: Use internal calculation,or 0, 128, 256, ... |
| s32RotExtraBuf | -1 | Maruko, Opera, Souffle, Pcupid and later chip | N | Set whether isp rot use extra buffer, 0: not use, 1: use, -1: use internal calculation |
| s32BufLayout | -1 | Maruko, Opera, Souffle, Pcupid and later chip | N | Set isp buffer layout, -1: Use internal calculation, 0: normal frame, 1: split left and right, 2: split top and bottom, 3: multi plane |
| bDefaultDropFifoBuffer | true | Maruko, Opera, Souffle, Pcupid and later chip | Y | Set whether isp drop fifo buffer by default, false: disable, true: enable |
| bFlushBuffer | true | Maruko, Opera, Souffle, Pcupid and later chip | Y | Set whether isp flush buffer, false: disable, true: enable |
| s32ModuleTotalPlanenum | -1 | Maruko, Opera, Souffle, Pcupid and later chip | N | Set isp total Plane number, -1: Use internal calculation,range [0-U32MAX] |
| u32threadPriorityArray | [98] | Maruko, Opera, Souffle, Pcupid and later chip | N | Set isp dev work thread priority, range [0-U32MAX], set the priority of each dev in order |
| u64PmTimeoutLatencyNS | [1000000000] | Maruko, Opera, Souffle, Pcupid and later chip | N | Set isp dev max pm timeout,[0-U64MAX], set the max pm timeout of each dev in order |
| au8ChnMaxEnqTasks | [0,0,2] | Maruko, Opera, Souffle, Pcupid and later chip | N | Set isp dev channel max enque task num. This parameter is grouped into 3, each group of parameters is dev, channel, taskNum [0-U8MAX] |
| bEnableSuspendWaitDone | true | Maruko, Opera, Souffle, Pcupid and later chip | N | Set isp waits for tasks to complete before entering suspend,false: disable, true: enable |
| u32DevDbgLv | [0,0] | Maruko, Opera, Souffle, Pcupid and later chip | N | set isp dev debug level. This parameter is grouped into 2, each group of parameters is dev, dbglv [0-U32MAX] |
| u32ChnDbgLv | [0,0,0,0] | Maruko, Opera, Souffle, Pcupid and later chip | N | Set isp dev channel debug level. This parameter is grouped into 4, each group of parameters is dev, channel, passid, dbglv[0-U32MAX] |
| isp_clk | 0 | Maruko, Opera, Souffle, Pcupid and later chip | N | Set isp clock, [0-U32MAX],0: Use the value configured by dts |
| rootPath | "" | Maruko, Opera, Souffle, Pcupid and later chip | N | Set isp root path of iqfile,empty string means use the default value:/config/iqfile in pure linux,/misc in dualos |