sdcard_sdio_debugsop Manual
REVISION HISTORY¶
| Revision No. | Description |
Date |
|---|---|---|
| 1.0 | 02/21/2024 |
1. SD/SDIO Card Recognition Process Issues¶
| Process | Method | Exit Conditions | Next Step | Information to Provide to FAE |
|---|---|---|---|---|
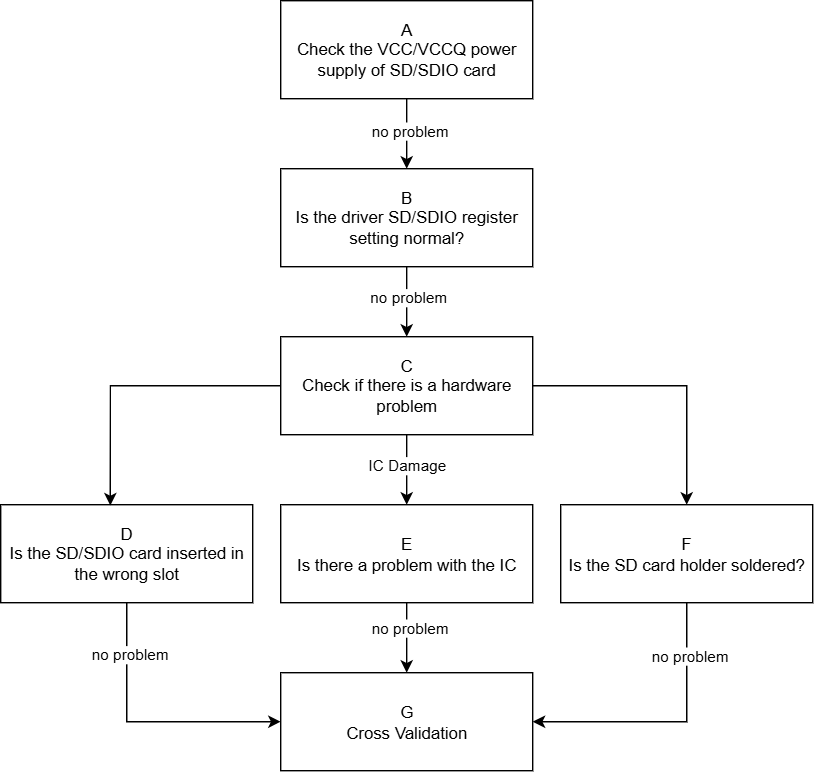
| A | 1. Use a multimeter to confirm whether the VCC voltage during the initialization phase of the SD card is 3.3V; confirm whether the VCCQ (IO) voltage complies with the specifications according to the SDIO device user manual, generally SDIO devices can support a range of 1.7V~3.6V, and the VCC voltage is determined based on the actual situation of the SDIO device, the manufacturer will provide a user manual. 2. Confirm that the CLK line is low level by default, and the CMD/data lines are high level. 3. Confirm whether the VCCQ voltage of the SD/SDIO is within the range of 1.8/3.3V. |
Exit Condition 1: 1. The VCC power supply of the SD card during the initialization phase is significantly different from 3.3V, or the VCC power supply of the SDIO card does not comply with the manual specifications. 2. Or the default state of the bus line is incorrect. 3. Or the VCCQ power supply of the SD/SDIO card is not within the effective range of 1.8/3.3V. > Power supply issue. Exit Condition 2: Power supply is normal. > No issue. |
Exit Condition 1: > Process ends. Exit Condition 2: > B |
Exit Condition 1: ==> Seek hardware assistance. |
| B | 1. Confirm whether the padmux configuration of the SD/SDIO corresponds to the development board, whether the pads conflict with other modes, confirmation method: cd kernel_path vim arch/arm/boot/dts/pcupid_xxxx-padmux.dtsi The SD/SDIO padmux mode will have the keywords 'SD_BOOT_MODE' or 'SDIO_MODE', and the corresponding GPIO pad needs to be confirmed for reuse with other modules. 2. Confirm whether the DTS related configuration of the SD/SDIO matches the currently used slot method: cd kernel_path vim arch/arm/boot/dts/pcupid.dtsi For the meaning of related configuration items, please refer to "SDMMC Usage Reference", focusing on: 2.1 no-sdio/no-sd/no-mmc, which type of device is connected, comment out the corresponding item, and configure the other two, for example: if connecting an SD card, comment out no-sd and configure no-sdio/no-mmc. |
Exit Condition 1: 1. The padmux is not correctly configured or there is a conflict with other modes. 2. The relevant configuration items of the SD/SDIO in the DTS do not match the currently used slot. > Configuration error issue. Exit Condition 2: Configuration is normal. > No issue. |
Exit Condition 1: > Process ends. Exit Condition 2: > C |
Exit Condition 1: ==> Seek hardware confirmation of the current padmux situation used by the development board, and then configure the correct padmux and DTS according to the actual situation. |
| C | 1. Confirm whether there is a hardware issue. 1.1. Scenario 1 - Wrong slot: When the development board has multiple slots, it should be connected according to the actual padmux. 1.2. Scenario 2 - IC pin output is unstable: Use a multimeter or oscilloscope to measure signals near the IC side and near the device side, there should be no signal instability. 1.3. Scenario 3 - SD card socket cold solder: If no issues are found in other conditions, you can first try the SD small socket in the same slot, if there are no issues, then try re-soldering the SD card socket. |
Exit Condition 1: 1. Confirm that the SD card is inserted in the wrong slot. > Insert into the correct slot. Exit Condition 2: IC pin output is unstable, leading to poor signal quality. > Replace with a new IC. Exit Condition 3: SD card socket cold solder, leading to poor signal quality. > Re-solder the SD card socket. Exit Condition 4: Hardware is normal. > No issue. |
Exit Condition 1: > Process ends. Exit Condition 2: > Process ends. Exit Condition 3: > Process ends. Exit Condition 4: > G |
Exit Condition 2: > Seek hardware assistance. Exit Condition 3: > Seek hardware assistance. |
| G | 1. Replace with a same specification SD/SDIO card and test again to see if it is recognized normally. 2. Replace the development board and test the same specification SD/SDIO card to see if it is recognized normally. 3. Test the same specification SD/SDIO card on other platforms to see if it is recognized normally. |
Exit Condition 1: After replacing with a same specification SD/SDIO card, it can be recognized normally. > SD/SDIO device issue. Exit Condition 2: After testing with a replaced development board, it can be recognized normally. > Development board issue. Exit Condition 3: After testing on other platforms, it can be recognized normally. ==> Driver issue. |
Exit Condition 1: > Process ends. Exit Condition 2: > Process ends. Exit Condition 3: ==> Process ends. |
Exit Condition 3: >1. Provide serial log. >2. Use LA or oscilloscope to capture the waveform of the entire initialization process. ==>3. In the Linux console, use the RIU command to dump the relevant bank information of the SDIO IP: 0x1413/0x1038/0x103C/0x103E |
2. SD/SDIO Communication Process Issues¶
| Process | Method | Exit Conditions | Next Step | Information to be Provided to FAE |
|---|---|---|---|---|
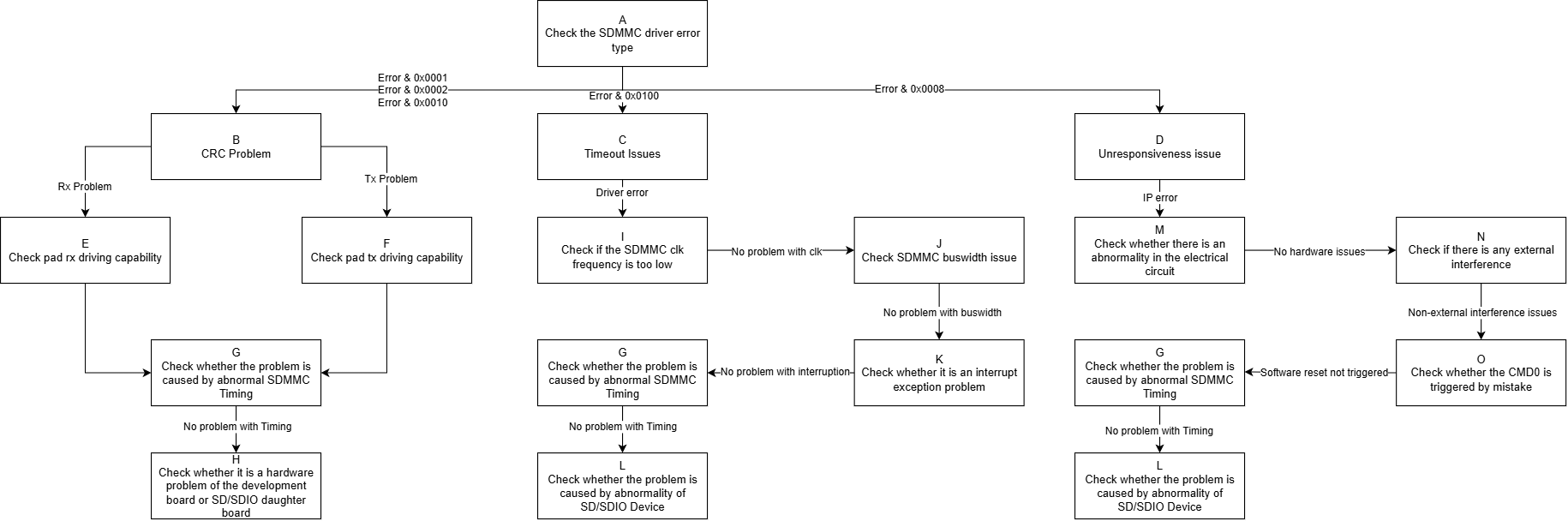
| A | When an error occurs, search the debug log based on the keyword "[sdmmc", mainly focusing on error numbers: 1.(E: 0x0001): read crc 2.(E: 0x0002): write crc 3.(E: 0x0010): cmd rsp crc 3.(E: 0x0100): driver reports timeout 4.(E: 0x0008): IP reports device no rsp |
Exit Condition 1: 1. cmd 12/13/17/18/23/24/25/52/53 and other read/write related commands report crc errors Exit Condition 2: 1. cmd 12/13/17/18/23/24/25/52/53 and other read/write related commands report timeout errors Exit Condition 3: 1. cmd 12/13/17/18/23/24/25/52/53 and other read/write related commands report device no response errors |
Exit Condition 1: >B Exit Condition 2: >C Exit Condition 3: ==>D |
|
| B | The essence of the crc issue is poor signal quality. You can select the best driving capability of the pad based on the type of crc error and adjust the driving (the range for GPIOE pads is 0-1, and for GPIOA pads is 0-3) | Exit Condition 1: 1. The type of crc error is rx crc, which means an error occurred during reading Exit Condition 2: 1. The type of crc error is tx crc, which means an error occurred during writing Exit Condition 3: 1. Other types of crc errors |
Exit Condition 1: >E Exit Condition 2: >F Exit Condition 3: ==>G |
|
| C | 1. When the driver reports a timeout issue during read/write operations, capture the waveform immediately to confirm whether there is a transmission performance issue. 2. If there is no issue with the waveform, determine whether the sdmmc MIE interrupt is reported or received normally. 3. Check whether there are any abnormalities in sdmmc timing. 4. If none of the above issues are present, consider whether the sd/sdio device is abnormal. |
Exit Condition 1: 1. The current working frequency is lower than expected based on the waveform Exit Condition 2: 1. The bus width does not match expectations Exit Condition 3: 1. The debug log shows that related events did not trigger normally when an error occurred Exit Condition 4: 1. Abnormal sdmmc timing Exit Condition 5: 1. The sd/sdio device causes the card to be busy |
Exit Condition 1: >I Exit Condition 2: >J Exit Condition 3: >K Exit Condition 4: >G Exit Condition 5: ==>L |
|
| D | 1. For the sdmmc IP reporting device no response issue, you can capture the waveform to confirm whether a response was not received after the cmd was sent. 2. Refer to this article "1: sd/sdio card identification process issues" to check whether the relevant configurations are correct. 3. Prioritize checking whether the hardware electrical path is normal and whether the operating environment has interference tests (such as electrostatic discharge, high and low temperature, etc.). 4. Search the debug log for the keyword "SAR1 SDMMC WARN trigger" to determine whether there is a case of power-off protection being falsely triggered. 5. Check whether there are any abnormalities in sdmmc timing. 6. If none of the above issues are present, consider whether the sd/sdio device is abnormal. |
Exit Condition 1: 1. Check that the configuration is correct, and the waveform shows that after the cmd is sent, no device response is received. Exit Condition 2: 1. Check for significant signal attenuation in the electrical path between the chip and the sd/sdio device sub-board. Exit Condition 3: 1. The operating environment is currently undergoing electrostatic discharge or high/low temperature stress testing. Exit Condition 4: 1. Search the log and find that sdmmc has triggered power-off protection without power-off. Exit Condition 5: 1. Abnormal sdmmc timing. Exit Condition 6: 1. The sd/sdio device causes a no response situation. Exit Condition 7: 1. The waveform shows that the device has responded, but the IP judges it as no response. |
Exit Condition 1: >Process Ends Exit Condition 2: 1. Please assist CAE in troubleshooting the issue. Exit Condition 3: >Process Ends Exit Condition 4: >Process Ends Exit Condition 5: >G Exit Condition 6: >L Exit Condition 7: >Process Ends |
Exit Condition 1: 1. Dump debug log and DTS configuration file. Exit Condition 3: Exit Condition 4: 1. Dump debug log. Exit Condition 7: 1. Expected CHIP design defect. |
| E | Adjust driving (the range for GPIOE pads is 0-1, and for GPIOA pads is 0-3). | Exit Condition 1: 1. After setting the data driving level according to the actual situation, it returns to normal. Exit Condition 2: 1. After trying all data driving levels, it still reports crc errors. |
Exit Condition 1: >Process Ends Exit Condition 2: >G |
|
| F | Adjust driving (the range for GPIOE pads is 0-1, and for GPIOA pads is 0-3). | Same as "E". | Same as "E". | |
| G | 1. Adjust driving (the range for GPIOE pads is 0-1, and for GPIOA pads is 0-3) to comprehensively adjust the driving capability of the clk/cmd line. 2. Adjust the clk phase; specific operations can be consulted with FAE. 3. Check whether the HW FAE supports adjusting the clock signal sampling mode according to the tmux table. 4. When using DMA in trans-mode, set reg_dma_rd_clk_stop to avoid data loss. 5. Use LA or an oscilloscope to capture the complete waveform during the problematic phase. |
Exit Condition 1: 1. After comprehensively adjusting the driving levels of the signal lines, it returns to normal. Exit Condition 2: 1. After adjusting the clk's four-phase or eight-phase, it returns to normal. Exit Condition 3: 1. After adjusting the clock signal sampling mode, it returns to normal. Exit Condition 4: 1. In the DMA mode transmission scenario, set offset:0xb bit7 to return to normal. Exit Condition 5: 1. If the above measures have no effect, the waveform differs from the normal waveform, such as insufficient rise time sampling lock time, cmd overlap, cmd minimum interval not met, etc. Exit Condition 6: 1. Confirm that the above settings are normal, and the waveform shows no abnormalities. |
Exit Condition 1: Exit Condition 2: Exit Condition 3: Exit Condition 4: >Process Ends Exit Condition 5: >Process Ends Exit Condition 6: ==>H/L |
Exit Condition 5: 1. Dump the complete debug log of the entire process, including logs from the start of sd/sdio init to the occurrence of the issue. 2. Capture the complete waveform of the abnormal scenario, preferably with a waveform of the normal scenario under the same conditions for comparison. 3. Use the riu command in the Linux console to dump the relevant bank information of the sdmmc IP: 0x1413/0x1038/0x103C/0x103E |
| H | 1. First refer to the cross-validation section of this article "1: sd/sdio card identification process issues". 2. In the default state (i.e., no data interaction), use a multimeter or oscilloscope to measure whether the electrical signals of the sd/sdio clk/cmd/data lines meet expectations. 3. In the case of communication triggering (i.e., data interaction), use a multimeter or oscilloscope to measure the electrical signals near the chip end and near the device end to see if there are significant signal differences. 4. Try to enhance driving capability from a hardware perspective by adding pull-up resistors and other means. |
Exit Condition 1: 1. After cross-validation, communication returns to normal. Exit Condition 2: 1. Under default conditions, the clk line is not low, and the cmd/data lines are not high. Exit Condition 3: 1. There are attenuation or other abnormal phenomena in the electrical signals between the IC end and the device end. Exit Condition 4: 1. After adjusting the electrical signal quality from the hardware side, communication returns to normal. Exit Condition 5: 1. No abnormalities in electrical signals, and hardware adjustments have no effect. |
Exit Condition 1: >Process Ends Exit Condition 2: 1. Check whether the padmux configuration is consistent with the current sd/sdio slot being used. 2. In Linux, use LA or an oscilloscope to manually pull up and down the sd/sdio pin GPIO to see if it meets expectations. Exit Condition 3: Exit Condition 4: Exit Condition 5: >Process Ends |
Exit Condition 3: 1. Seek hardware assistance. Exit Condition 5: 1. Synchronize hardware conditions to help FAE set up a reproduction environment. |
| I | 1. Clarify the version of the sd/sdio IP used in the current slot according to the manual. 1.1 sd/sdio 2.0 supports a maximum of 48MHz. 1.2 sd/sdio 3.0 supports a maximum of 200MHz. 2. Confirm whether it is already at the highest level within the frequency range allowed by the IP. 3. Read bank 0x1038 offset 0x43/bank 0x42 offset 0x24 to confirm whether clk is set successfully as expected. 4. Use the dd command or fio tool to test the rate and provide rate information to FAE for confirmation. |
Exit Condition 1: 1. Adjust clk to the highest level, and communication returns to normal. Exit Condition 2: 1. Adjusting clk has no effect or is already at the highest level. Exit Condition 3: 1. clk setting does not match the register reading value. |
Exit Condition 1: >Process Ends Exit Condition 2: >J Exit Condition 3: ==>Process Ends |
Exit Condition 3: 1. Dump 0x1038/0x1133 register information. 2. Provide DTS configuration file. 3. Provide debug log. |
| J | 1. According to the SPEC document, different speed modes have corresponding supported bus widths. 1.1 sd/sdio 2.0 can use 1bit/4bit Buswidth. 1.2 sd/sdio 3.0 can only use 4bit width. 2. Read bank 0x1413/0x42 offset 0xb[2:1] to confirm. |
Exit Condition 1: 1. Adjust bus width to the maximum width corresponding to the speed mode, and communication returns to normal. Exit Condition 2: 1. Adjusting bus width has no effect or is already at the maximum width for that speed mode. Exit Condition 3: 1. bus width setting does not match the register reading value. |
Exit Condition 1: >Process Ends Exit Condition 2: >K Exit Condition 3: ==>Process Ends |
Exit Condition 3: 1. Dump 0x1413/0x42 register information. 2. Provide DTS configuration file. 3. Provide debug log. |
| K | 1. Read bank 0x1413 offset 0x0[1:0] to determine whether the read/write complete event has been raised. 2. If the event has been triggered but the driver still reports a timeout, prioritize checking the CPU loading and the number of interrupt triggers. |
Exit Condition 1: 1. Within the driver timeout period, the event has not been raised. Exit Condition 2: 1. The event has been raised, and the CPU loading is high or there are many interrupt triggers. Exit Condition 3: 1. The event is raised normally, and there are no other abnormalities in the environment. |
Exit Condition 1: >Process Ends Exit Condition 2: Investigate which process is causing high CPU loading and try binding the sdmmc MIE interrupt handling to CPU1. Exit Condition 3: >G |
Exit Condition 1: 1. Attempt to reproduce on the public version to assist FAE in setting up the environment. |
| L | 1. Refer to the cross-validation and solder joint issues of the sd card socket in this article "1: sd/sdio card identification process issues". |
Exit Condition 1: 1. After cross-validation or re-soldering, communication returns to normal. Exit Condition 2: 1. Confirm that the sd/sdio device is normal. |
Exit Condition 1: >Replace the sd/sdio device. Exit Condition 2: >Process Ends |
Exit Condition 2: 1. Attempt to reproduce on the public version to assist FAE in setting up the environment. |
| M | 1. Use a multimeter or oscilloscope to measure the entire path from the chip to the sd/sdio sub-board, mainly observing whether there are significant differences in signals near the IC end and the sd/sdio sub-board end. | Exit Condition 1: 1. There is a significant attenuation phenomenon in the electrical signals near the IC end and the sd/sdio sub-board end. Exit Condition 2: 1. The electrical path is normal. |
Exit Condition 1: 1. Please assist CAE in troubleshooting. Exit Condition 2: ==>N |
|
| N | 1. Clarify with the customer whether there are external interferences in the operating environment, such as ongoing electrostatic discharge, high/low temperature stress testing. | Exit Condition 1: 1. Ongoing stress testing, with additional electrostatic discharge, high/low temperature, etc. Exit Condition 2: 1. No external interference, normal operating environment. |
Exit Condition 1: >Process Ends Exit Condition 2: >O |
Exit Condition 1: 1. Capture debug log and waveform. 2. Coordinate with hardware for troubleshooting. |
| O | 1. In a non-power-off operating environment, check whether the debug log contains the keyword "SAR1 SDMMC WARN trigger". 2. Check whether the filter includes "retry" and "reset" keywords related to the sdmmc driver. |
Exit Condition 1: 1. Check the debug log for emmc/sdmmc triggering power-off protection or retry operations. Exit Condition 2: 1. The environment has not been reset or falsely triggered power-off protection. |
Exit Condition 1: >Process Ends Exit Condition 2: >G |
Exit Condition 1: 1. If emmc falsely triggers power-off protection, consult HW FAE. 2. If the environment has been reset, capture the debug log. |
3. Issues Related to Data Transfer Process at the End of SD/SDIO Communication¶
| Process | Method | Exit Conditions | Next Step | Information to be Provided to SWRD |
|---|---|---|---|---|
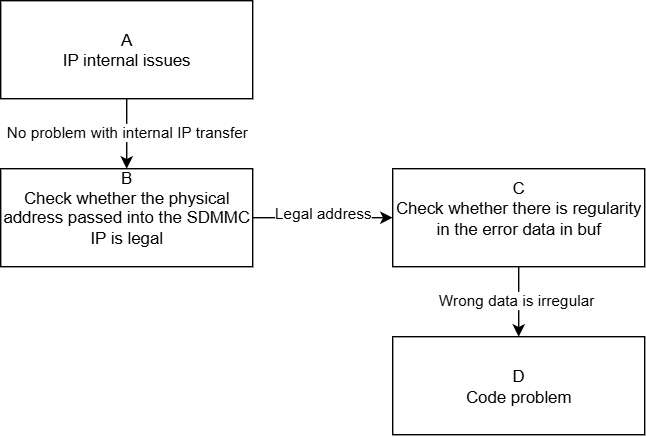
| A | 1. According to the sd/sdio host modes in the SPEC, the entire sd/sdio protocol system can be abstracted into host, bus, and device. 2. By confirming that the padmux settings are correct and correspond to the current operating environment, and that the LA/oscilloscope displays waveforms and timing are normal, but the dma_end event is always not received. 3. Combining the host mode can rule out host cmd sending, bus communication, and device abnormalities, considering that there is an issue with data transfer inside the host IP. |
Exit Condition 1: 1. FAE assists in interpreting the debug bus and provides it to RD for analysis. Exit Condition 2: 1. sdmmc IP is normal. |
Exit Condition 1: >Process Ends Exit Condition 2: >B |
|
| B | 1. Refer to the specification document to confirm the valid DRAM address space that can be used by the sdmmc IP, and then confirm whether the physical address offset passed to the sdmmc IP is valid, i.e., the address composed of bank 1413/42 offset 0x3/0x4. | Exit Condition 1: 1. The physical address offset passed to the sdmmc IP exceeds the valid range. Exit Condition 2: 1. The physical address offset passed to the sdmmc IP is valid and effective. |
Exit Condition 1: >Process Ends Exit Condition 2: >C |
Exit Condition 1: 1. Use the standard address space allocation interface provided by the system to request the buffer. |
| C | 1. Construct a test pattern to confirm whether there is a regularity in the difference between the source pattern and the pattern obtained from reading/writing. | Exit Condition 1: 1. The pattern errors are obviously regular, always occurring with the size of the sdmmc driver cache line. Exit Condition 2: 1. The pattern errors have no obvious regularity. |
Exit Condition 1: >Process Ends Exit Condition 2: >D |
Exit Condition 1: 1. Confirm whether the standard read/write interface of sdmmc is used; if not, further confirm whether the buffer is non-cache. 2. Assist FAE in setting up a reproduction environment. |
| D | The sdmmc driver read/write process is normal, but there is an issue with data transfer inside the IP. The following points are mainly considered: 1. Whether the dma burst length is set to 8, i.e., bank 1413/42 offset 0x2[5:4]. 2. Whether read/write operations do not consider cache operations or are handled incorrectly. 3. Data synchronization issues caused by modern CPU out-of-order execution. |
Exit Condition 1: 1. The dma burst length is not set to the maximum. Exit Condition 2: 1. In the dcache-on operating environment, the buffer read/write did not perform invalid and flush operations, leading to inconsistent data. Exit Condition 3: 1. Logic requiring synchronization calls did not perform memory barrier processing, leading to out-of-order execution. Exit Condition 4: 1. Other issues. |
Exit Condition 1: 1. Attempt to manually set the dma burst to the maximum value of 8. Exit Condition 2: 1. Attempt to perform flush operations during write operations and invalid operations after read operations. Exit Condition 3: Exit Condition 4: ==>Process Ends |
Exit Condition 3: Exit Condition 4: 1. Confirm the status of the customer's branch and patches applied. 2. Assist FAE in setting up a reproduction environment. |
| --- |
4. Issues Related to Hot Swapping of SD Cards¶
| Process | Method | Exit Conditions | Next Step | Information to Provide to FAE |
|---|---|---|---|---|
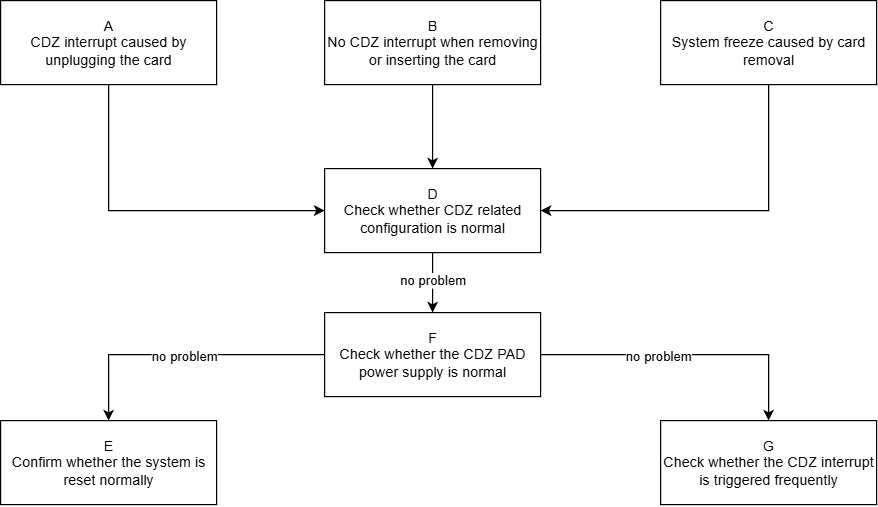
| A | 1. CDZ interrupt trigger principle: The result after xor(src, polarity), that is: 1.1. When the level of CDZ src is 0, the polarity level (0->1) will trigger an interrupt 1.2. When the level of CDZ src is 1, the polarity level (1->0) will trigger an interrupt 2. After system WDT reset or STR, there will be a CDZ interrupt that meets the trigger condition |
Exit Condition 1: 1. Confirm that the system is performing WDT reset or STR operation Exit Condition 2: 1. The system is running normally, without executing WDT reset or STR operation |
Exit Condition 1: >E Exit Condition 2: >D |
|
| B | 1. First, check whether the CDZ-related configuration items are correctly enabling the CDZ interrupt 2. If the configuration is fine, prioritize checking whether the SD card socket hardware is faulty and whether the CDZ pad power supply is normal 3. According to the CDZ trigger principle in A, check whether there are mismatches between src and polarity in the code |
Exit Condition 1: 1. CDZ-related configuration is not correctly configured Exit Condition 2: 1. SD card socket failure leads to abnormal CDZ pad power supply Exit Condition 3: Code logic issue |
Exit Condition 1: >D Exit Condition 2: >F Exit Condition 3: ==>Process End |
Exit Condition 3: 1. Provide SDK version information to FAE |
| C | 1. First confirm whether the system exception is caused by the CDZ interrupt itself or due to logic triggered by insertion/removal actions 2. Check whether there are any configuration errors in the CDZ-related configuration items |
Exit Condition 1: 1. CDZ-related configuration is not correctly configured Exit Condition 2: 1. Confirm that the CDZ interrupt itself is frequently triggered causing system stuttering Exit Condition 3: 1. Confirm that the logic after inserting/removing the card causes the system to freeze |
Exit Condition 1: >D Exit Condition 2: >G Exit Condition 3: ==>Process End |
Exit Condition 3: 1. Assist FAE in setting up a reproduction environment for troubleshooting |
| D | 1. Confirm whether the CDZ padmux configuration for SD/SDIO corresponds to the development board, and whether the pad conflicts with other modes. Confirmation method: cd kernel_path vim arch/arm/boot/dts/pcupid_xxxx-padmux.dtsi 2. Confirm whether the CDZ-related configuration for SD/SDIO is correct: cd kernel_path vim arch/arm/boot/dts/pcupid.dtsi Mainly check whether the 'fake-cdz' and 'rev-cdz' configuration items are correct; whether the 'cdz_slot0_irq' interrupt configuration is correct |
Exit Condition 1: 1. CDZ padmux is not correctly configured; 2. CDZ-related configuration items are incorrectly configured Exit Condition 2: 1. CDZ configuration is fine |
Exit Condition 1: 1. Correctly configure according to padmux and actual operating environment >Process End Exit Condition 2: >F |
|
| E | 1. When the SD card is not inserted, after WDT reset, the system will generate a CDZ interrupt that meets condition 1.2 in A 2. When the SD card is not inserted, if the system performs STR, during the resume phase it will also meet condition 1.2 in A and generate a CDZ interrupt |
Exit Condition 1: 1. Confirm that the system has triggered a reset operation Exit Condition 2: 1. The system is running normally, without triggering any related reset operations |
Exit Condition 1: 1. Seek help from FAE to provide a solution to mask this unexpected interrupt Exit Condition 2: ==>Process End |
Exit Condition 2: 1. Assist FAE in setting up a reproduction environment |
| F | 1. The CDZ pad is designed for hot-swapping of SD cards, the default state is a high-level state pulled up by an external 3.3V voltage. When the SD/SDIO card is inserted into the slot, the contact pin is grounded and becomes a low-level state 2. The CDZ interrupt is edge-triggered bidirectionally, with the insertion/removal of the card causing changes in the CDZ pad's level state, which will trigger the CDZ interrupt according to the principle in A 3. Under correct CDZ-related configuration, the LA or oscilloscope can be used to observe whether there are fluctuations in the CDZ pad level |
Exit Condition 1: 1. Observed that the fluctuation amplitude of the CDZ pad level is too large, reaching the CDZ trigger threshold; Exit Condition 2: 1. CDZ pad level is normal |
Exit Condition 1: 1. Seek hardware assistance for troubleshooting Exit Condition 2: ==>E/G |
|
| G | 1. When able to access the console: linux: cat /proc/interrupts |grep cdz rtos: echo cli intrstat > /proc/dualos/rtos Check the number of CDZ interrupt triggers 2. Use the tvtool tool to check the trigger situation of bank:0x1009 corresponding to the CDZ interrupt |
Exit Condition 1: 1. CDZ interrupt is triggered abnormally frequently, and after umask irq, the system returns to normal Exit Condition 2: 1. CDZ interrupt is normal, consistent with the number of insertions/removals |
Exit Condition 1: >Process End Exit Condition 2: >Process End |
Exit Condition 1: Exit Condition 2: 1. Assist FAE in setting up a reproduction environment |
5. Appendix¶
5.1 SDIO Device Initialization Process¶
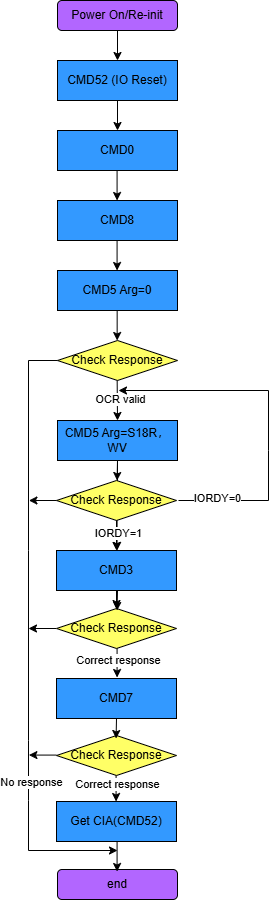

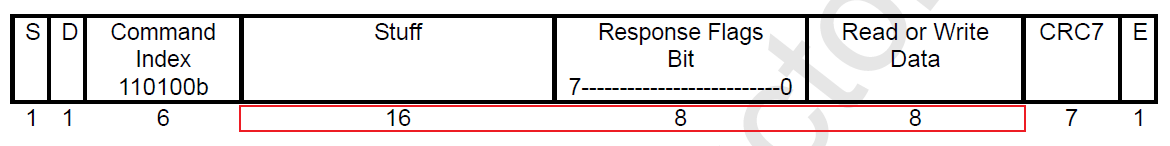
Regardless of the type of command, focus on the 32-bit content in the middle of the request and response commands.
>>>sdio soft reset: cmd52 read/write CCCR register completed
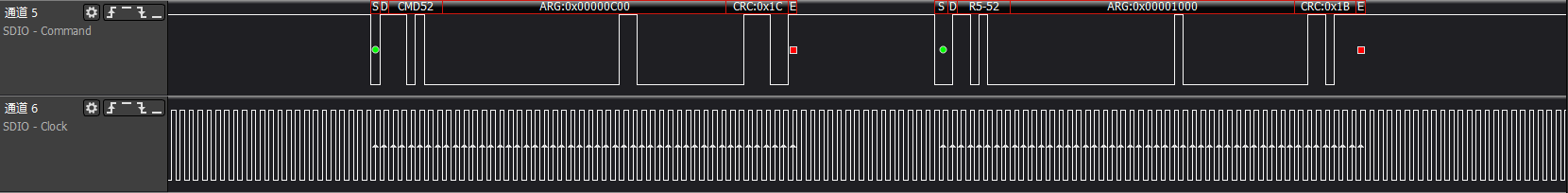
the first two cmd52 commands will complete normally, but cmd52 often reports 0x8 no rsp err ("details can be found in Chapter 2"). The root cause is that the SDIO device
has not completed the power-on initialization procedure. To solve this problem, it is generally done by configuring the 'pwr-off-delay' in the dtsi to more than 150ms.
>>>device go idle: Effective for SDIO cards with storage
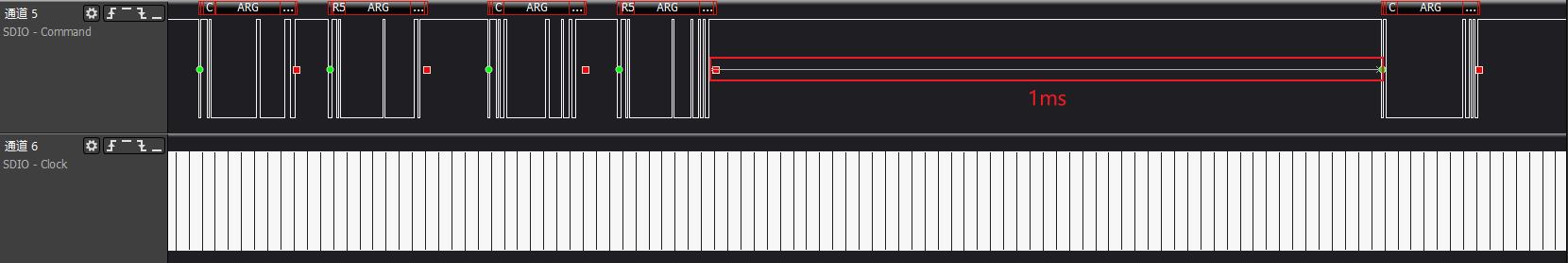
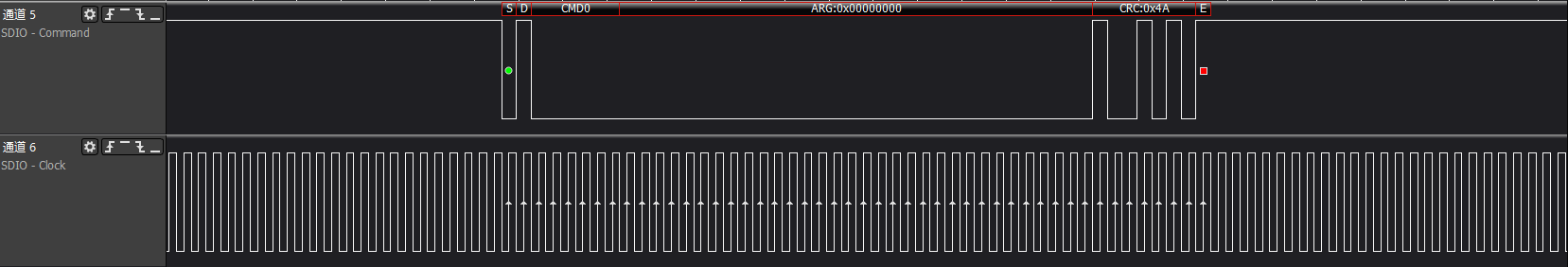
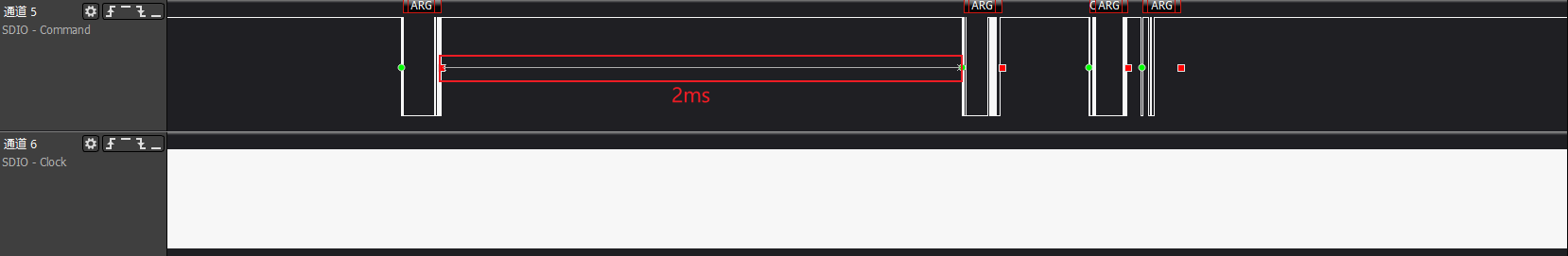
>>>check sd card: Effective for SDIO cards with storage
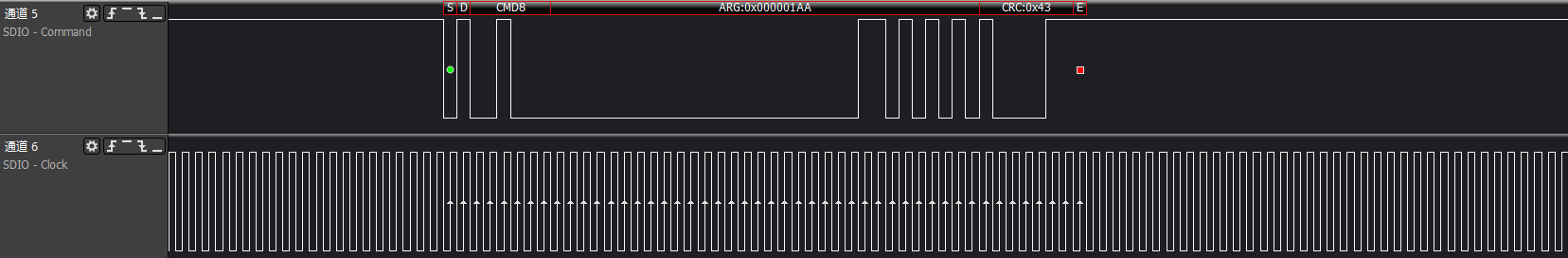
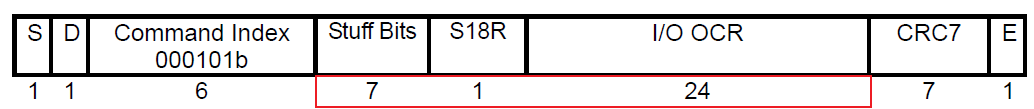
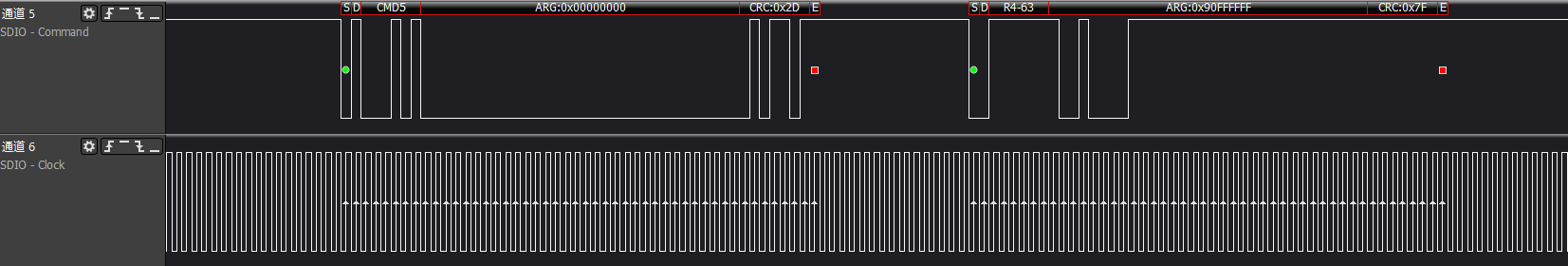
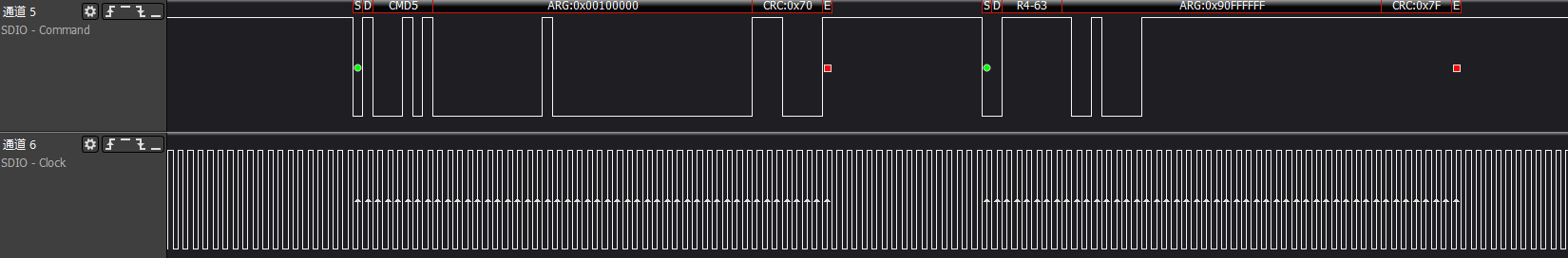
>>>cmd5: Get the operating voltage range supported by the SDIO card
some time to power on to ready, but if the cmd5 command fails, it means there is a real communication issue.
First ARG:0x00000000, mainly to get the voltage support range of the SDIO device
Second ARG:0x00100000, sends the voltage supported by the host side and triggers the device init action.
The host will test the response of cmd5, polling to check if ARG: bit31 is set to 1 (device ready).
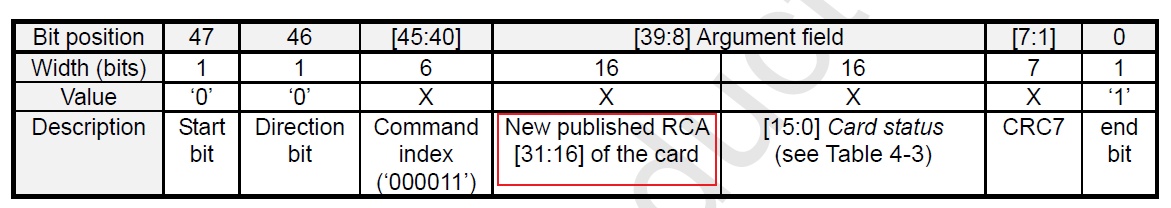
>>>cmd3/cmd7: Host gets the SDIO card RCA address and selects the card for operation based on the address
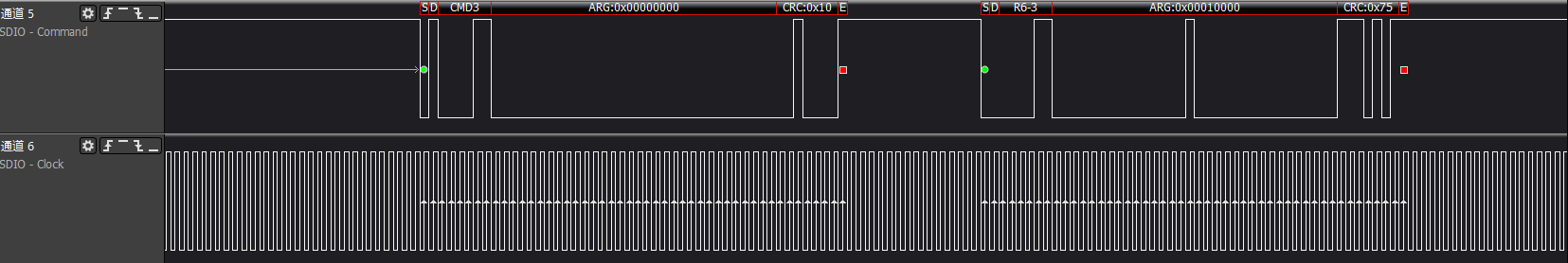
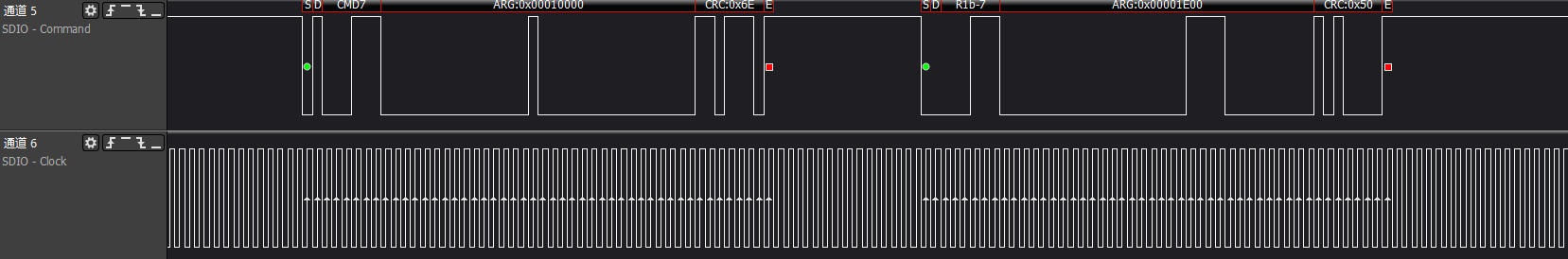
>>>Get CIA information: func0's CCCR/CIS information
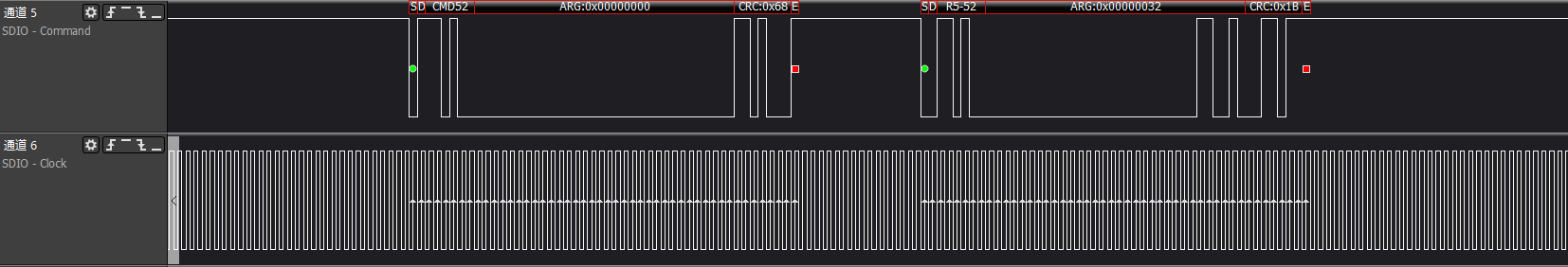
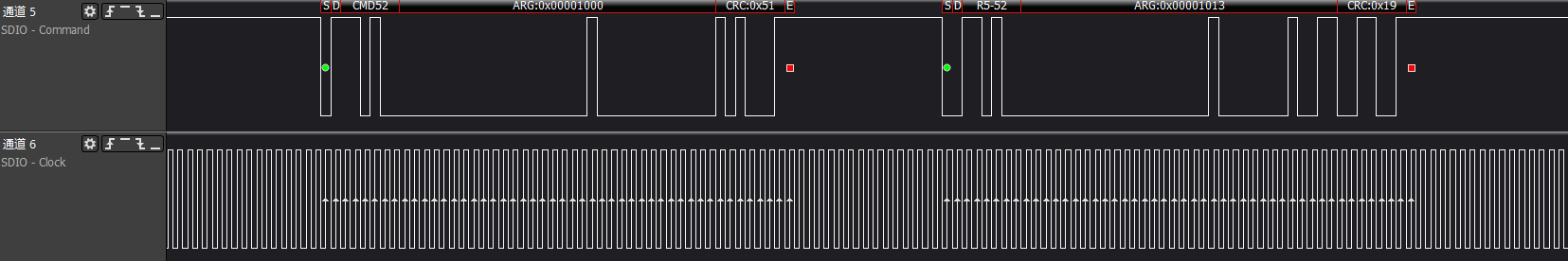
has func0, CCCR, and each FBR has 256 bytes; the init flow will acquire some key information from them.
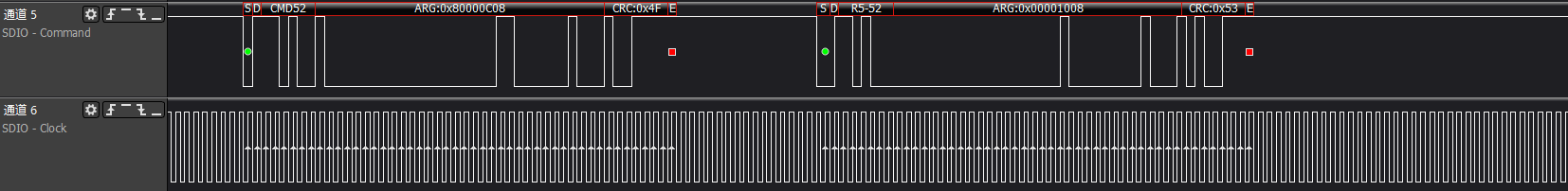
ARG:0x00000000, reads func0 (CCCR) at address 0x0, which is the CCCR/SDIO revision version information
ARG:0x00001000, reads func0 (CCCR) at address 0x8, which is the Card Capability information, response: 0x00001013 indicates that the device supports
1. do CMD52 while data transfer
2. do multi-block xfers
3. interrupt during 4-bit CMD53
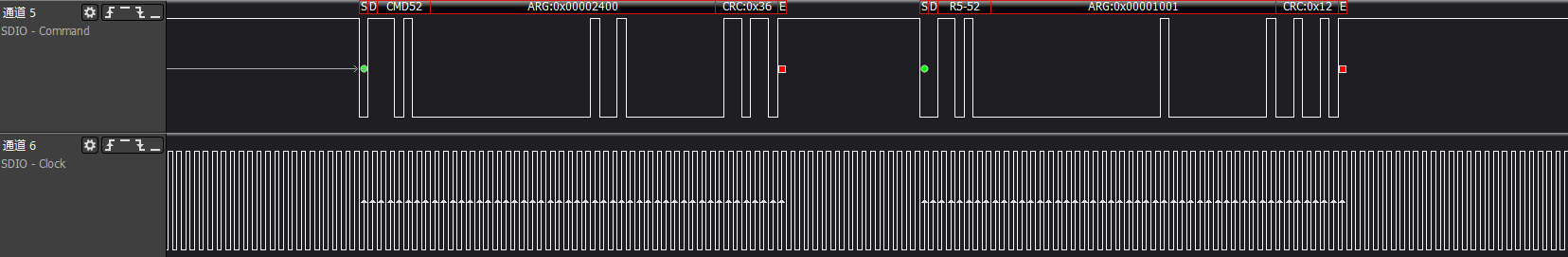
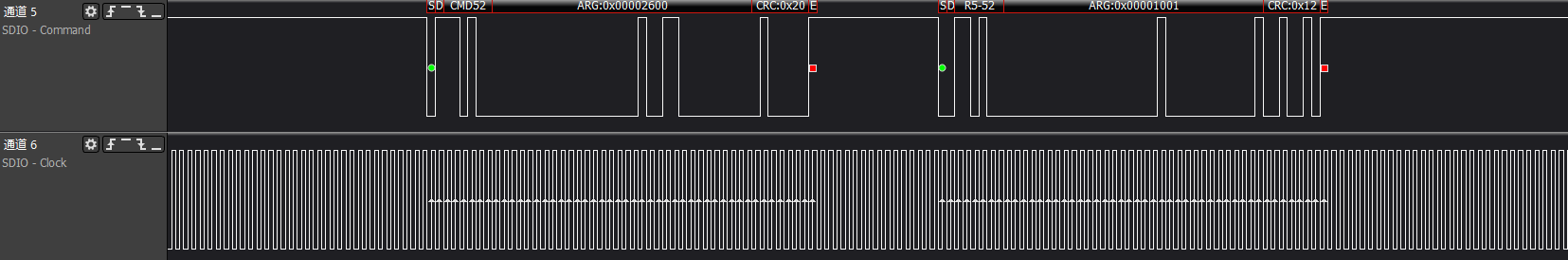
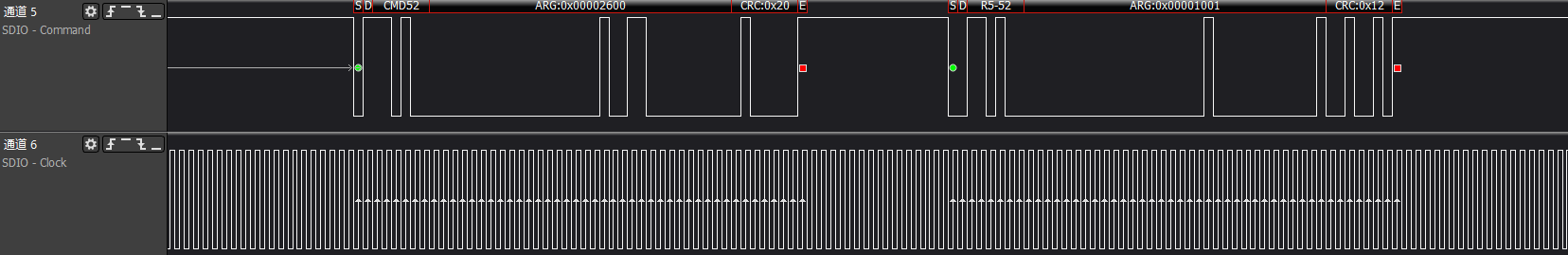
ARG:0x00002400, reads func0 (CCCR) at address 0x12, which is the power control information, response: 0x00001001 indicates that the device supports the host to perform power control
ARG:0x00002600, reads func0 (CCCR) at address 0x13, which is the bus speed select information, response: 0x00001001 indicates that the device supports High-Speed mode
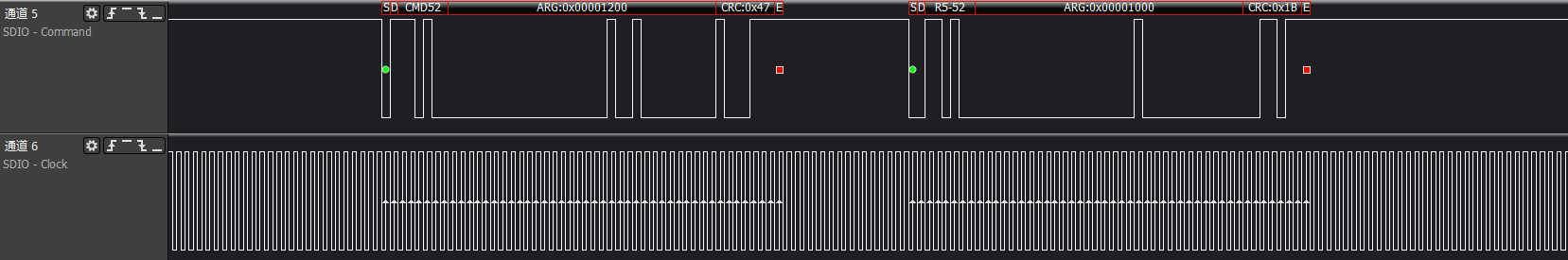
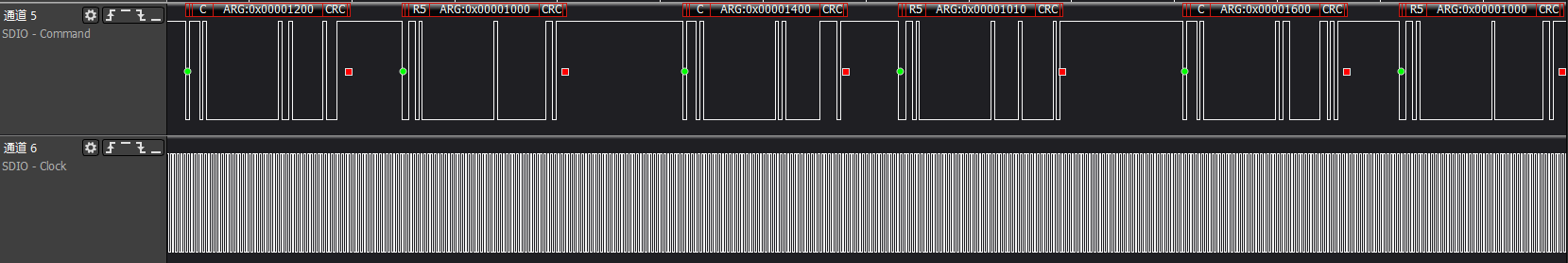
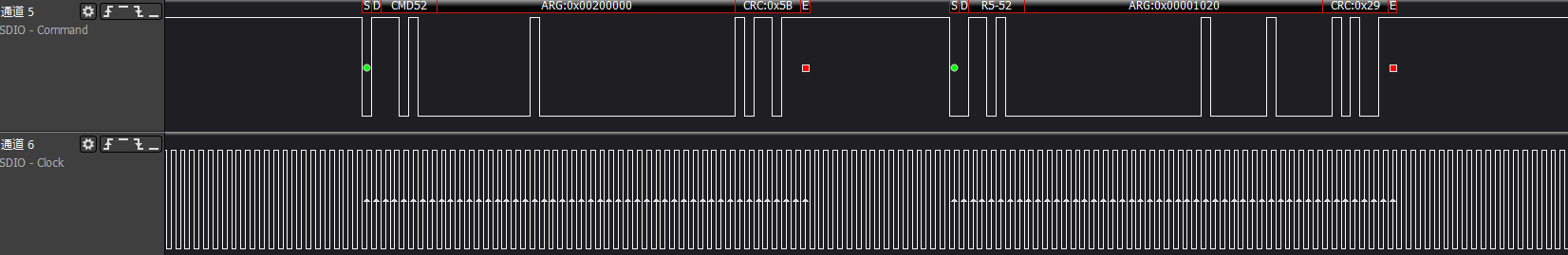
ARG:0x00001200/0x00001400/0x00001600 three commands to get func0 (CCCR) at addresses 0x9-0xb, which are the CIS pointer information to access CIS area information
ARG:0x00200000/.../0x00202000 a series of commands to read information from the Common CIS area
At this point, the host has obtained the basic information related to func0 of the card.
>>>bus speed/bus width: Switch rate and bit width
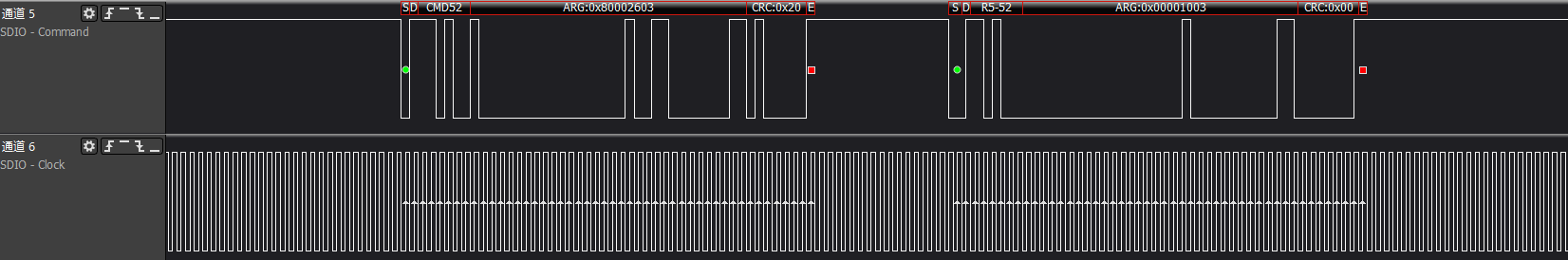
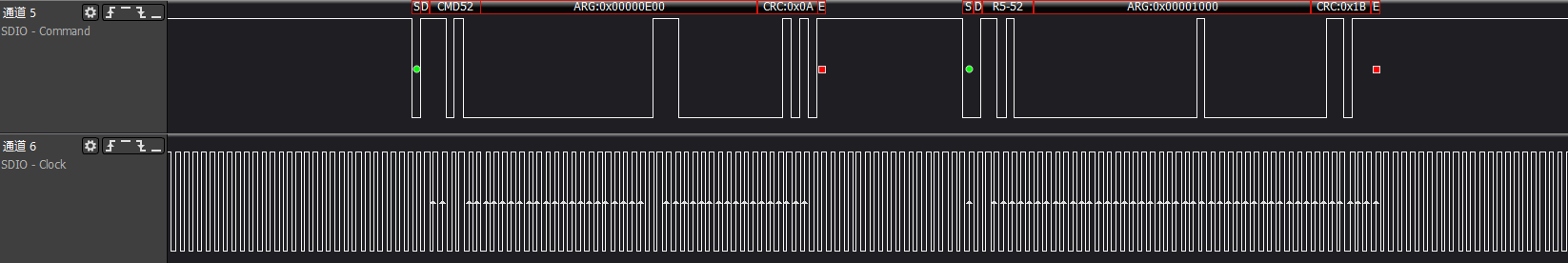
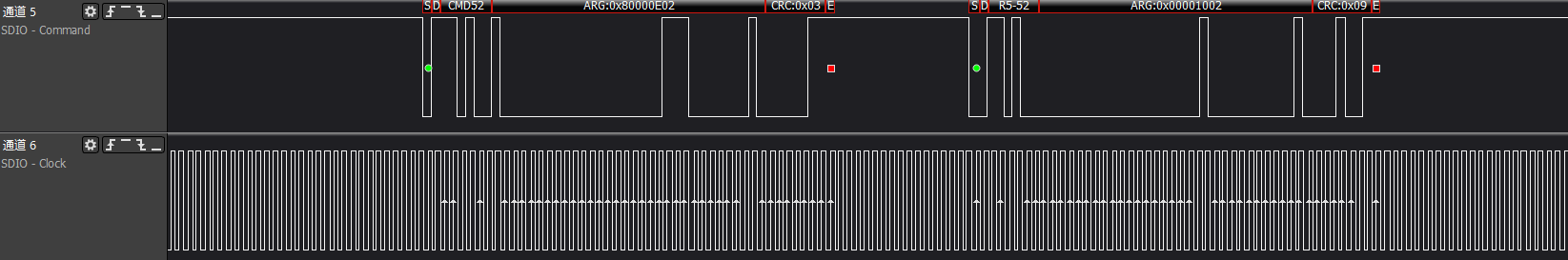
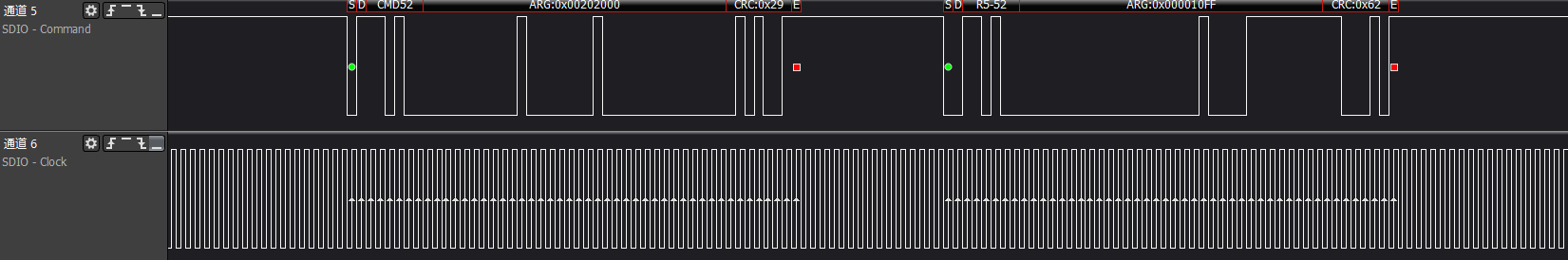
ARG:0x80002603, writes to func0 (CCCR) at address 0x13, enabling high-speed bus speed
ARG:0x00000E00, reads func0 (CCCR) at address 0x7, which is the bus interface control information
ARG:0x80000E02, writes to func0 (CCCR) at address 0x7, enabling 4-bit bus interface control
At this point, the SDIO card will switch to a 4-bit 48MHz working environment
>>>Get CIA information: func1's FBR/CIS information
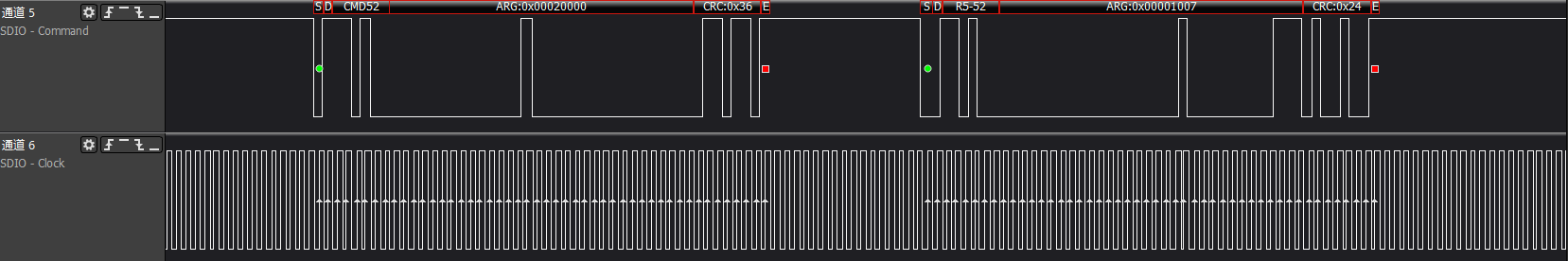
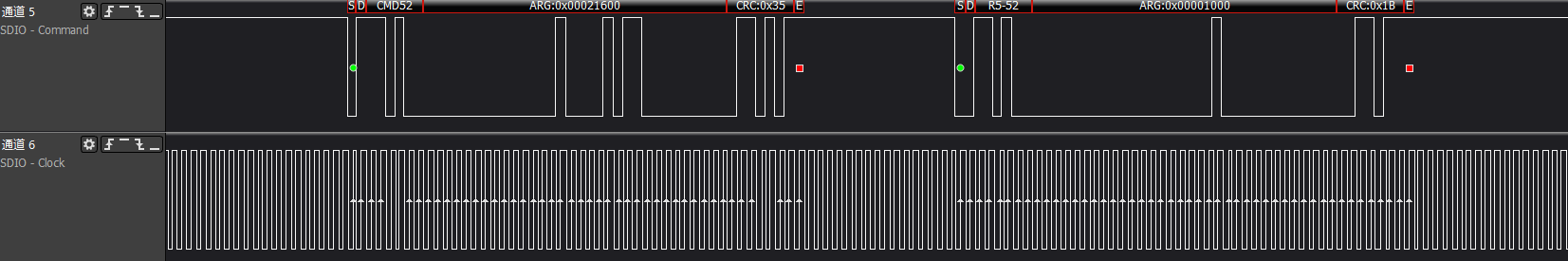
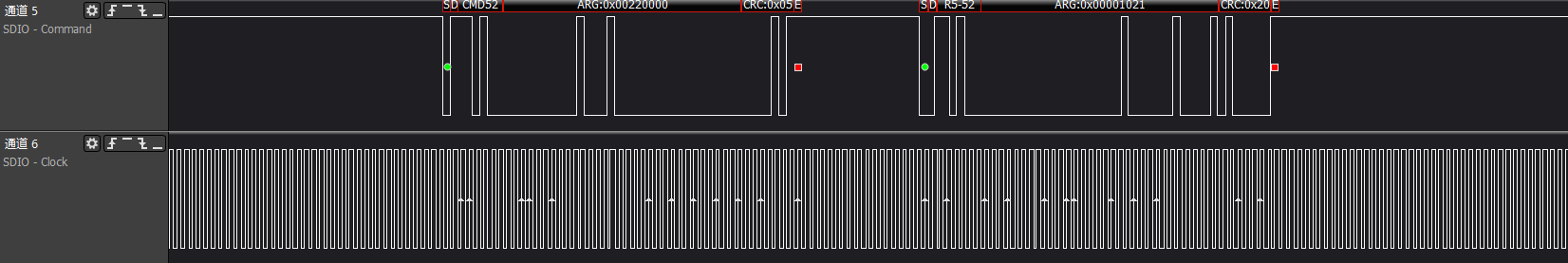
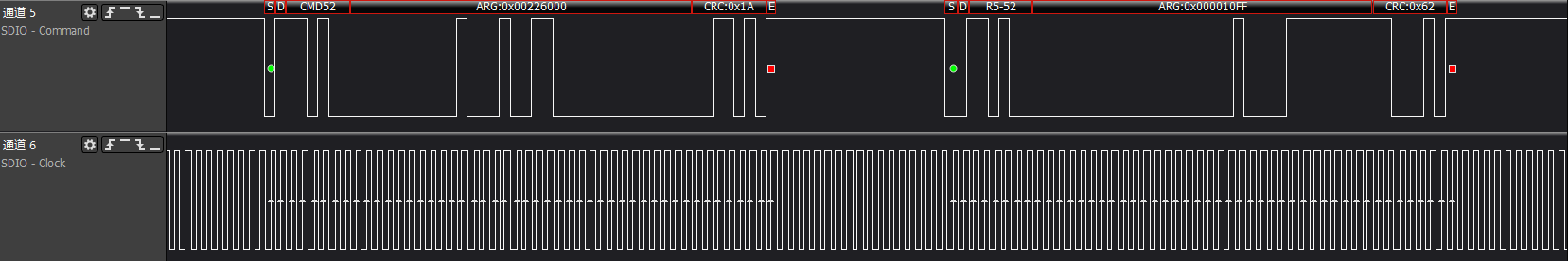
The reading of FBR/CIS information is completely consistent with the reading of the above func0's CCCR/CIS general information, only the func number in cmd52 changes to the corresponding func; generally, the SDIO card
will support func1 functionality
ARG:0x00020000, reads func1 at address 0x100, which is the func1 SDUI function interface code information
ARG:0x00021600, reads func1 at address 0x10b, which is the last item of func1's CIS pointer address
The description here is omitted for the cmd52 between 0x100-0x10b
ARG:0x00220000/.../0x00226000 a series of commands to read information from func1's CIS area
At this point, the core commands involved in the SDIO card initialization process are complete.
>>>SDIO card identification successful

5.2 SD Card Initialization Process¶
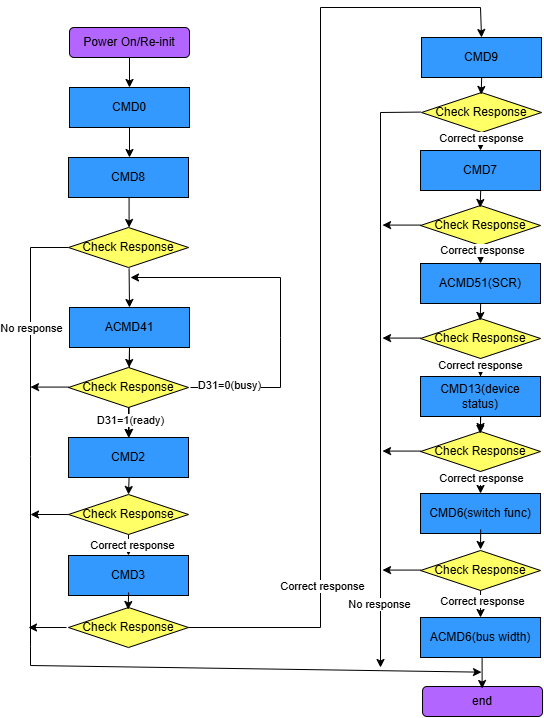
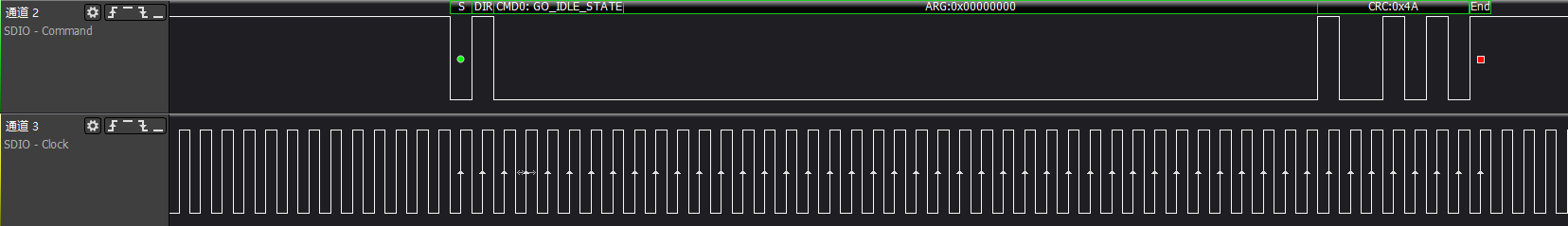
>>>sd go idle: cmd0 makes the card enter idle state
>>>host synchronize support voltage: Let the card confirm whether it supports the voltage list provided by the host
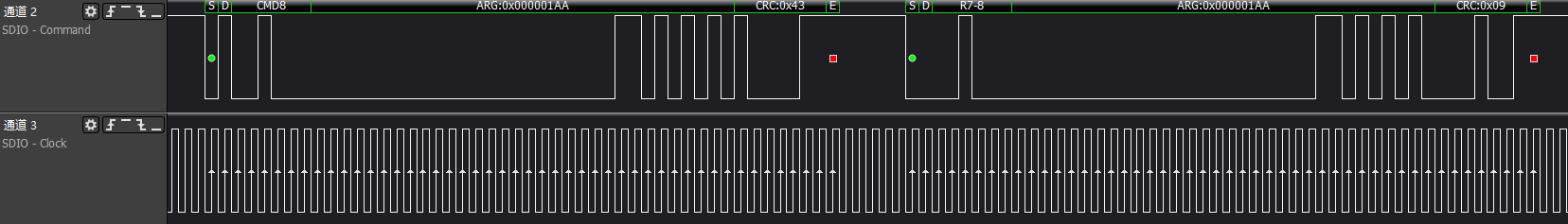
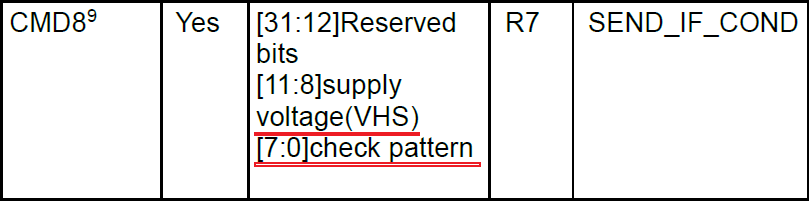
>>>Get OCR information: The first time does not care about the card's state
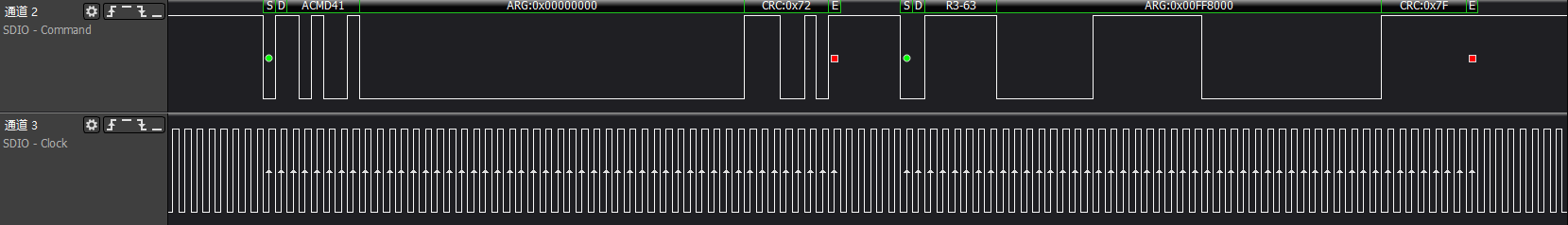
>>>sd go idle again: cmd0 makes the card enter idle state

>>>host synchronize updated support voltage: Let the card confirm whether it supports the voltage list provided by the host

>>>host synchronize capability set and confirm OCR information
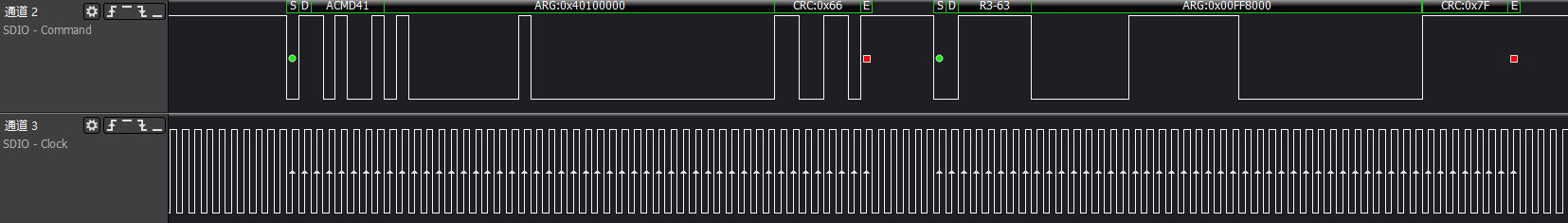
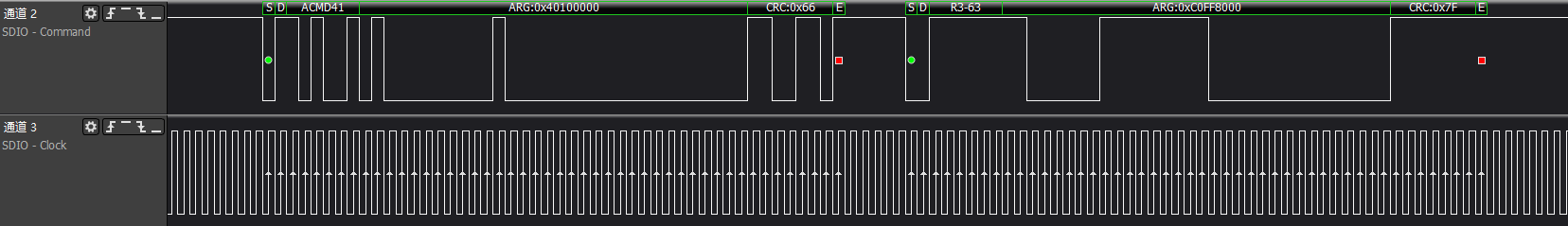
>>>host gets card CID information: Factory settings such as MID/OID and other identification information

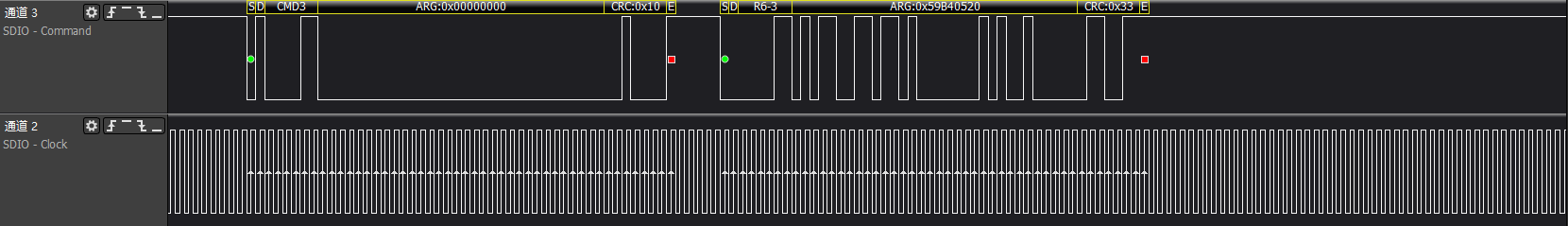
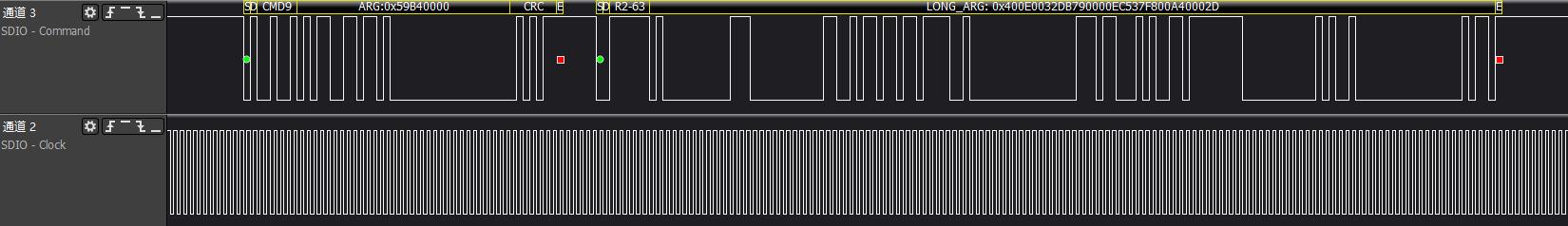
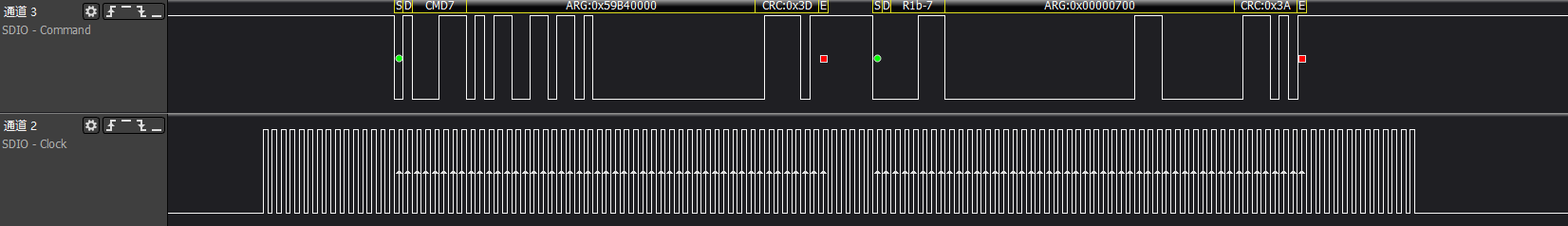
>>>cmd3/cmd9/cmd7: Host gets the SD card RCA address and retrieves CSD register information based on the address
>>>acmd51: Read SCR register information
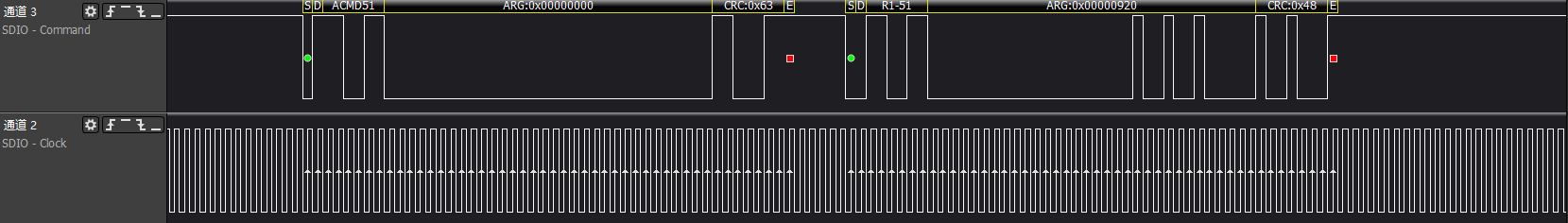
>>>acmd13: Get device status information, passing 512 bytes of register information via the data line
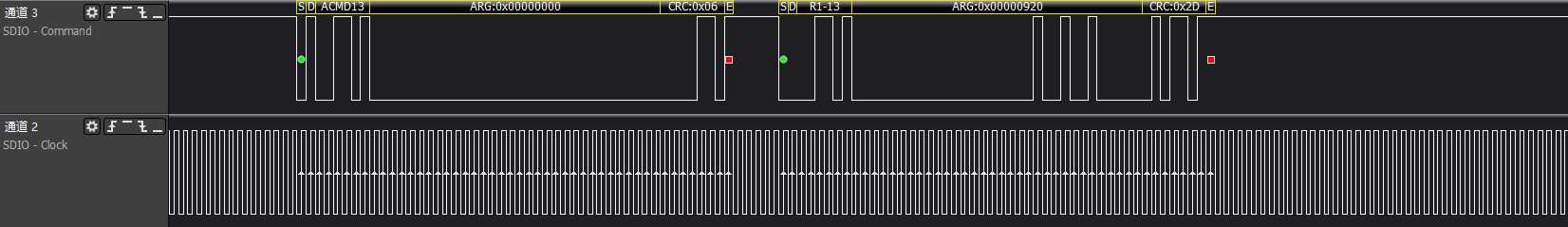
>>>host gets check func information and executes switch func information
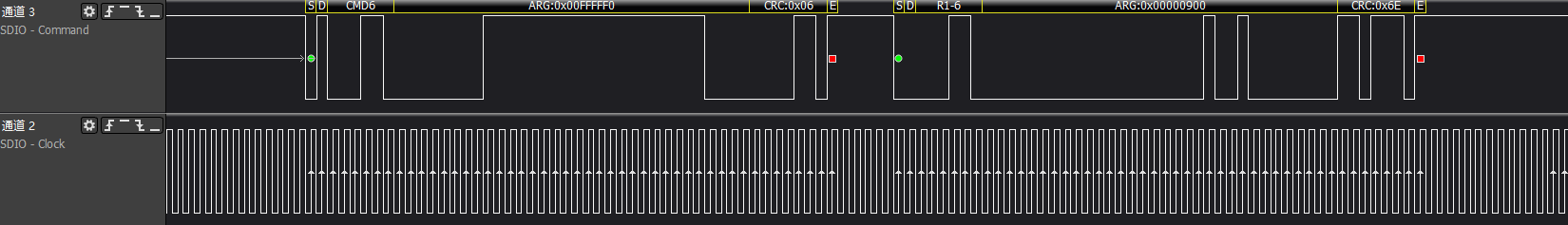
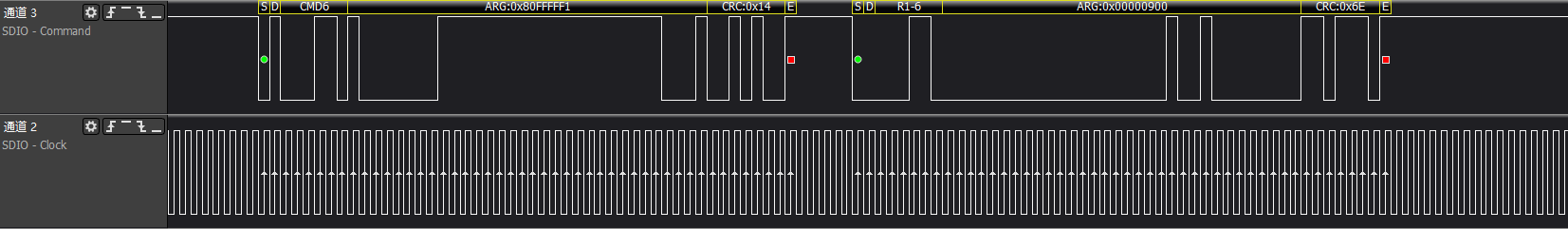
ARG:0x80FFFFF1, bit31 is 1, switch func operation, switch access mode func1 to high-speed
After this step, the SD clock will adjust to 48MHz
>>>acmd6: Adjust device bus width
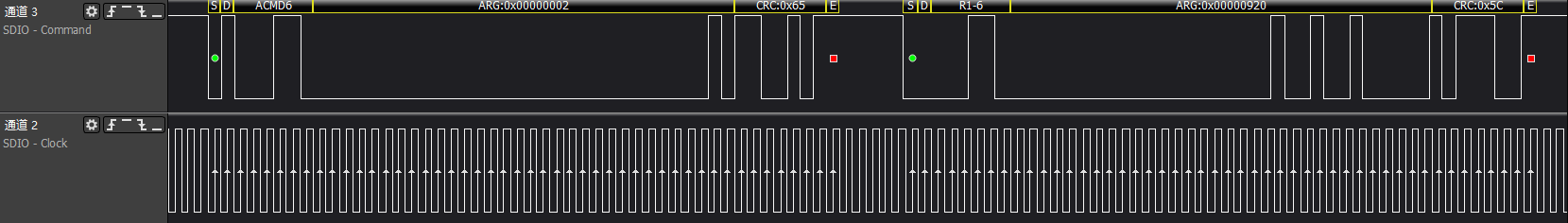
After this step, because the card device is generated, it will match with the card driver, generating a block device node
>>>SD card identification successful

5.3 Common Error Waveforms and Logs for SD/SDIO¶
>>>cmd no rsp
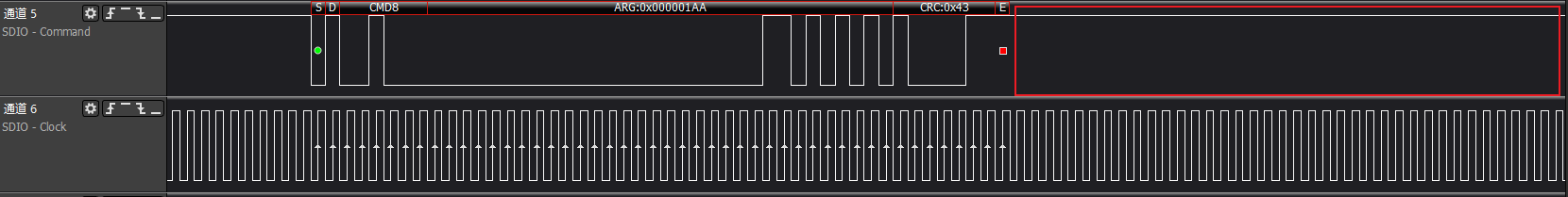

The driver will print SD_STS:0x0F08 error code
>>>cmd crc


The CRC for read commands is an internal IP check
The driver will print SD_STS:0x0F01 (read CRC)/SD_STS:0x0F02 (write CRC) error codes
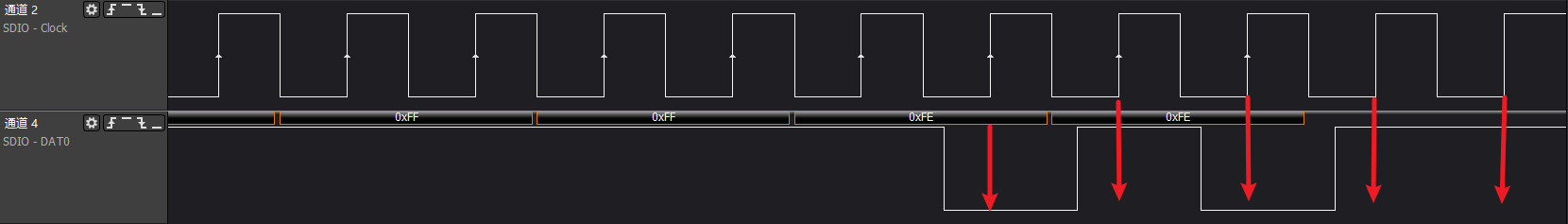
>>>cmd timeout

The driver will print (FAIL)= 0100 error code, indicating that the waiting time set by the driver has been reached, but the event has not been received, refer to "2. SD/SDIO Communication Process Issues"
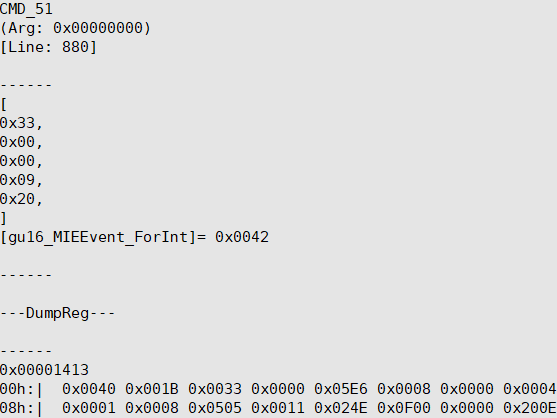
>>>cmd6 execution switch func error
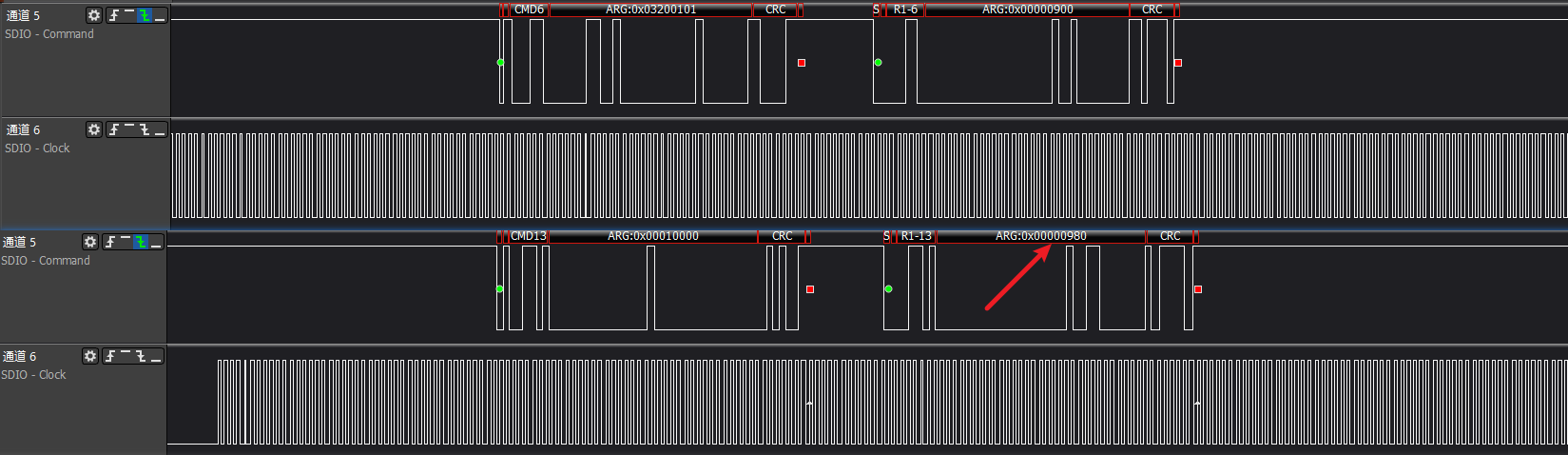
The image shows a switch error, with cmd13 response status displayed as '980', indicating a device switch error