wpa_supplicant & iwlist Porting and User Guide
1. Porting¶
wpa_supplicant is an open source software for wireless network connection management. It is used for authentication and encrypted communication with wireless access points. It can run in Linux systems and supports a variety of wireless network cards and drivers. The wpa_supplicant tool includes two programs, wpa_supplicant and wpa_cli. The wpa_supplicant program runs in the background as a server to serve the requests of the wpa_cli client, thereby realizing the configuration connection of WiFi.
iwlist is a command line tool used to view wireless network information. It is used to obtain and display information related to wireless network cards.
- OpenSSL: 1.1.1i
- libnl: 3.5.0
- wpa_supplicant: 2.9
- wireless_tool: 29
1.1. Traditional method¶
1.1.1. OpenSSL cross-compilation¶
OpenSSL is an open source software library that provides a set of cryptographic functions and tools for secure communications. It is widely used in the implementation of security protocols, the establishment of encrypted communications, and the management of digital certificates.
1.1.1.1. Source code download
Version: 1.1.1i
1.1.1.2. Cross-compilation
After the resource package is downloaded, unzip it and enter the opensl-1.1.1i directory. Execute the Configure configuration file to configure the compilation tool chain and specify the corresponding installation path, as follows:
tar -zxvf openssl-1.1.1i.tar.gz cd openssl-1.1.1i/ export PATH=/tools/toolchain/gcc-10.2.1-20210303-sigmastar-glibc-x86_64_aarch64-linux-gnu/bin:$PATH ; export ARCH=arm64 ; export CROSS_COMPILE=aarch64-linux-gnu- ./Configure --prefix=$PWD/install linux-aarch64 make clean -j8 make -j8 make install
Note that the export command in the above example steps specifies the compilation chain address. In actual operation, please declare it according to the actual compilation chain path. After executing the above steps, you will find the generated header files and library files in the openssl-1.1.1i/install/ path.
1.1.2. libnl cross-compilation¶
libnl is a C library for handling Netlink protocol communications with the Linux kernel. It simplifies the process of communicating with the kernel, hides the details of the underlying Netlink protocol, and enables developers to write network-related applications more conveniently.
1.1.2.1. Source code download
Version: 3.5.0
1.1.2.2. Cross-compilation
After the resource package is downloaded, unzip it and enter the directory, and execute the configure file to configure the installation directory, as follows:
tar -zxvf libnl-3.5.0.tar.gz cd libnl-3.5.0/ export PATH= /tools/toolchain/gcc-10.2.1-20210303-sigmastar-glibc-x86_64_aarch64-linux-gnu/bin: $PATH ; export ARCH= arm64 ; export CROSS_COMPILE= aarch64-linux-gnu- ./configure --host=aarch64-linux-gnu --prefix=$PWD/install/ make clean -j8 make -j8 make install
Note that the export command in the above example steps specifies the compilation chain address. In actual operation, please declare it according to the actual compilation chain path. After executing the above steps, you will find the generated header files and library files in the libnl-3.5.0//install/ path.
1.1.3. wpa_supplicant cross-compilation¶
1.1.3.1. Source code download
wpa_supplicant download address
Version: 2.9
1.1.3.2. Cross-compilation
After the resource package is downloaded, unzip it and enter the directory, and execute the configure file to configure the compilation options as follows:
tar -zxvf wpa_supplicant-2.9.tar.gz
cd wpa_supplicant-2.9/wpa_supplicant/
cp defconfig .config
Modify .config file:
+CC=/tools/toolchain/gcc-10.2.1-20210303-sigmastar-glibc-x86_64_aarch64-linux-gnu/bin/aarch64-linux-gnu-gcc +CFLAGS += -I../../openssl-1.1.1i/install/include/ +LIBS += -L../../openssl-1.1.1i/install/lib/ -lssl -lcrypto +CFLAGS += -I../../libnl-3.5.0/install/include/ +LIBS += -L../../libnl-3.5.0/install/lib/ ... -CONFIG_CTRL_IFACE_DBUS_NEW=y +#CONFIG_CTRL_IFACE_DBUS_NEW=y
Execute the following command to cross compile:
export PKG_CONFIG_PATH= /home/veahow.chen/opensource/libnl-3.5.0/install/lib/pkgconfig: $PKG_CONFIG_PATH export PATH= /tools/toolchain/gcc-10.2.1-20210303-sigmastar-glibc-x86_64_aarch64-linux-gnu/bin: $PATH ; export ARCH= arm64 ; export CROSS_COMPILE= aarch64-linux-gnu- ./configure --host=aarch64-linux-gnu --with-libs --with-zlib=$PWD/../zlib-1.2.12/ --with-ssl-dir=$PWD/../openssl-1.1.1i/ --exec-prefix=/customer/ssh --prefix=$PWD/install --disable-etc-default-login --disable-strip CC=aarch64-linux-gnu-gcc AR=aarch64-linux-gnu-ar make clean -j8 make -j8
Finally, the programs wpa_supplicant and wpa_cli will be generated. The original generated programs are large in size and can be trimmed using the following command:
aarch64-linux-gnu-strip wpa_supplicant --strip-unneeded aarch64-linux-gnu-strip wpa_cli --strip-unneeded
The program depends on libnl-3.so.200 and libnl-genl-3.so.200.
1.1.4. iwlist cross-compilation¶
1.1.4.1. Source code download
Version: 29
1.1.4.2. Cross-compilation
After the resource package is downloaded, unzip it and enter the directory:
tar -zxvf wireless_tools.29.tar.gz
cd wireless_tools.29/
Modify the Makefile:
ifndef PREFIX -PREFIX=/usr/local +PREFIX=./install endif ... -CC=gcc +CC = aarch64-linux-gnu-gcc -AR=ar +AR = aarch64-linux-gnu-ar -RANLIB=ranlib +RANLIB = aarch64-linux-gnu-ranlib
Execute cross-compilation instructions:
export PATH= /tools/toolchain/gcc-10.2.1-20210303-sigmastar-glibc-x86_64_aarch64-linux-gnu/bin: $PATH ; export ARCH= arm64 ; export CROSS_COMPILE= aarch64-linux-gnu- make clean -j8 make -j8 make install
Finally, the program iwlist will be generated, which depends on libiw.so.29.
1.2. Based on Buildroot¶
wpa_supplicant and iwlist belong to the wpa_supplicant and wireless_tools packages, versions 2.9 and 30 respectively. You can compile and build them directly by following the steps below:
export PATH= /tools/toolchain/gcc-10.2.1-20210303-sigmastar-glibc-x86_64_aarch64-linux-gnu/bin: $PATH ; export ARCH= arm64 ; export CROSS_COMPILE= aarch64-linux-gnu- cd 3 rdparty/buildroot-masters make wpa_supplicant make wireless_tools
The wpa_supplicant built in this way depends on the dynamic libraries libnl-3.so.200 and libnl-genl-3.so.200, which are in the 3rdparty/buildroot-master/output/target/usr/lib/ folder; The iwlist built in this way is integrated into 3rdparty/buildroot-master/output/target/sbin/.
2. Environment Setup¶
2.1. Copy Files¶
Copy the relevant files and libraries to the bin and lib directories of project/release/chip/pcupid/dispcam/common/glibc/10.2.1/release/wifi/ and add executable permissions using the chmod +x command.
2.2. Package image¶
Executing make image_install under project will package rz and sz into project/image/output/customer/wifi.
3. Test verification¶
After confirming that a WiFi driver has been successfully loaded on the board, enter ifconfig wlan0 up to enable the WiFi network card for testing.
3.1. Use of wpa_supplicant¶
Run wpa_supplicant. The wpa_supplicant program is the server of wpa_cli and must be started before it can be accessed by wpa_cli.
The manual for wpa_supplicant states:
wpa_supplicant usage: wpa_supplicant [-BddhKLqqtvW] [-P<pid file>] [-g<global ctrl>] \ [-G <group>] \ -i<ifname> -c<config file> [-C<ctrl>] [-D<driver>] [-p<driver_param>] \ [-b<br_ifname>] [-e<entropy file>] \ [-o<override driver>] [-O<override ctrl>] \ [-N -i<ifname> -c<conf> [-C<ctrl>] [-D<driver>] \ [-p<driver_param>] [-b<br_ifname>] [-I<config file>] ...] drivers: nl80211 = Linux nl80211/cfg80211 wext = Linux wireless extensions (generic) wired = Wired Ethernet driver options: -b = optional bridge interface name -B = run daemon in the background -c = Configuration file -C = ctrl_interface parameter (only used if -c is not) -d = increase debugging verbosity (-dd even more) -D = driver name (can be multiple drivers: nl80211,wext) -e = entropy file -g = global ctrl_interface -G = global ctrl_interface group -h = show this help text -i = interface name -I = additional configuration file -K = include keys (passwords, etc.) in debug output -L = show license (BSD) -N = start describing new interface -o = override driver parameter for new interfaces -O = override ctrl_interface parameter for new interfaces -p = driver parameters -P = PID file -q = decrease debugging verbosity (-qq even less) -t = include timestamp in debug messages -v = show version -W = wait for a control interface monitor before starting
Please refer to the following commands:
wpa_supplicant -D nl80211 -i wlan0 -c /etc/wpa_supplicant.conf -B
-
-D nl80211: The driver type name is nl80211
-
-i wlan0: The network interface name is wlan0
-
-c /etc/wpa_supplicant.conf: The configuration file is wpa_supplicant.conf
-
-B: Run the daemon process wpa_supplicant in the background
The simple wpa_supplicant.conf is as follows, to test whether the board can connect to the wireless network named 10086 opened through the mobile phone hotspot:
ctrl_interface=/customer/wpa_supplicant
ap_scan=1
network={
ssid="10086"
psk="123654789"
}
Here is an example:

After successfully connecting to WiFi, enter udhcpc -i wlan0 -s /customer/udhcpc.script to dynamically obtain the IP address and view the information through ifconfig wlan0 .
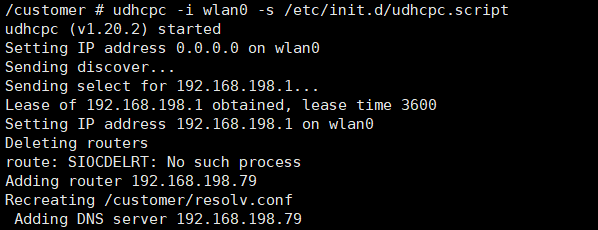
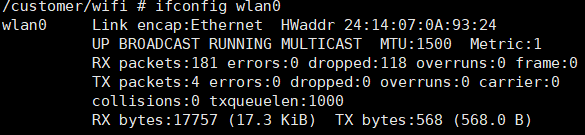
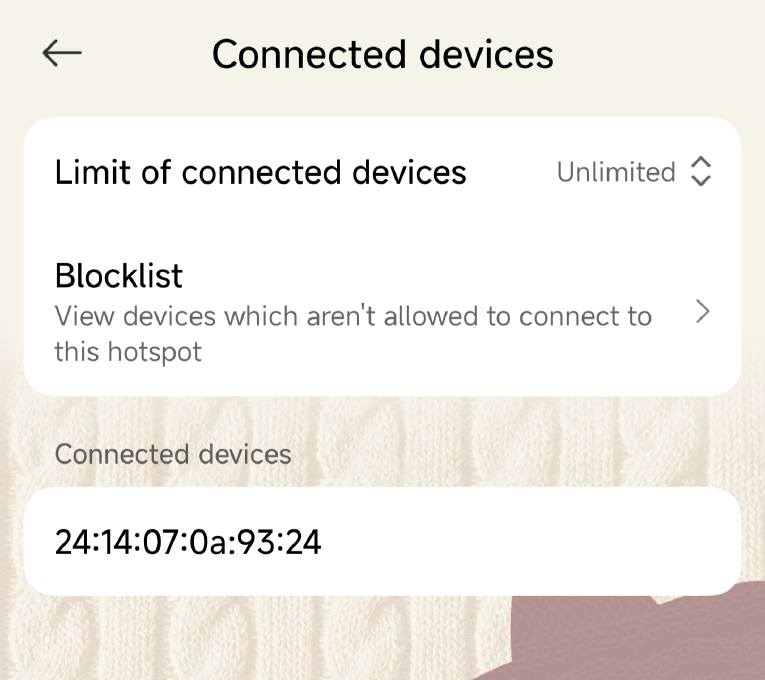
At the same time, the connected devices can also be seen normally on the mobile hotspot:
3.2. Use of wpa_cli¶
wpa_supplicant is already running as a server. Now start the wpa_cli client and perform network configuration operations through the wpa_cli client.
There are two ways to use wpa_cli. One is to enter the wpa_cli console interactive interface.
Example:
wpa_cli -p/data/system/wpa_supplicant -iwlan0
-p /data/system/wpa_supplicant is the ctrl_interface specified in wpa_supplicant.conf
-iwlan0 is the interface specified when wpa_supplicant is running
The other is to enter the complete command directly through the serial terminal without entering the console interactive interface. This article will introduce the WiFi configuration in this way.
Example:
wpa_cli -p/data/system/wpa_supplicant -iwlan0 help
Below we will introduce the use of wpa_cli from the common process of using WiFi. All command usage instructions can be viewed through the "wpa_cli -i wlan0 help" command.
3.2.1. Scan nearby WiFi hotspots¶
Start Scan:
wpa_cli -p/data/system/wpa_supplicant -iwlan0 scan
Note:
The scan process takes a certain amount of time. During the scan process, wpa_supplicant will be in a busy state. Sending the scan again will fail.
View scan results:
wpa_cli -p/data/system/wpa_supplicant -iwlan0 scan_results
Note:
scan_results prints out a list of available WiFi hotspots, including the ssid (name), bssid (mac address), signal level (signal strength, in dBm), flags (encryption type), etc.
It can be found that if there are multiple hotspots around, the printed WiFi list has one line of information for each hotspot, but the order of hotspots is not strictly arranged from large to small according to signal strength (negative value). Moreover, if you open a new WiFi hotspot, scan again, and then print the results with scan_results, you will find that the newly opened WiFi hotspot, although with a strong signal, is also ranked very far back in the list.
Therefore, if you want to sort the WiFi hotspots from high to low according to signal strength, you need to obtain the WiFi list and then sort them in descending order according to signal strength, so that the WiFi with strong signal is in front.
3.2.2. Connect to WiFi hotspot¶
Add a network id:
The add_network command will return a network id, and then the WiFi hotspot will be configured based on this network ID.
wpa_cli -i wlan0 add_network
Configure the name of the WiFi hotspot ssid:
wpa_cli -i wlan0 set_network <network number> ssid '"<WiFi name>"'
Example:
wpa_cli -i wlan0 set_network 0 ssid '"honor"'
Configure the WiFi hotspot password psk:
wpa_cli -i wlan0 set_network <network number> psk '"<password>"'
Example:
wpa_cli -i wlan0 set_network 0 psk '"12345678"'
View network list:
wpa_cli -i wlan0 list_network
Select Network:
Using the list_network command will print all successfully added WiFi hotspots. If there are multiple WiFi hotspots, you can use the select_network command to choose which hotspot to use, so that you can switch WiFi hotspots.
wpa_cli -i wlan0 select_network <network number>
Example:
wpa_cli -i wlan0 select_network 0
Note:
At this time, AP is only connected successfully, but IP and DNS are not obtained. You can use the udhcpc command to dynamically obtain IP.
Example:
udhcpc -q -i wlan0 -s /etc/init.d/udhcpc.script
3.2.3. View WiFi status information¶
wpa_cli -i wlan0 status
Use the status command to view the current wifi information, including bssid, ssid, IP, etc.
Note: Checking that the WiFi is connected through the status command does not guarantee access to the external network. You also need to check whether the IP and DNS have been obtained.
3.2.4. Save WiFi hotspot information¶
wpa_cli -i wlan0 save_config
Save the WiFi hotspot information to the configuration file /etc/wpa_supplicant.conf.
3.2.5. Stop using WiFi hotspot¶
wpa_cli -i wlan0 disable_network <network number>
At this time, it is still connected to the WiFi hotspot, but the WiFi is not activated.
Example:
wpa_cli -i wlan0 disable_network 0
3.2.6. Enable WiFi hotspot¶
wpa_cli -i wlan0 enable_network network number
Enable the corresponding WiFi hotspot according to the network number.
Example:
wpa_cli -i wlan0 enable_network 0
3.2.7. Disconnect from WiFi hotspot¶
wpa_cli -i wlan0 disconnect
3.2.8. Reconnect to WiFi hotspot¶
After disconnecting from WiFi, you can use reconnect to reconnect to the originally disconnected network.
wpa_cli -i wlan0 reconnect
3.2.9. Delete WiFi hotspot¶
After deleting the hotspot, it will be removed from list_network, that is, the previous network number cannot be deleted to configure the WiFi hotspot.
wpa_cli -i wlan0 disconnect
3.3. Use of iwlist¶
Use the iwlist scanning command to search for available wireless hotspots.