Bootlogo User Guide
1. Overview¶
The bootlogo is the screen displayed when booting. It can be displayed on various LCD screens, including TTL, BT656, SRGB, and can also be displayed on MIPI screens.
This article will introduce how to configure and use bootlogo.

2. Compile configuration options¶
cd boot make menuconfig
2.1 open bootlogo¶
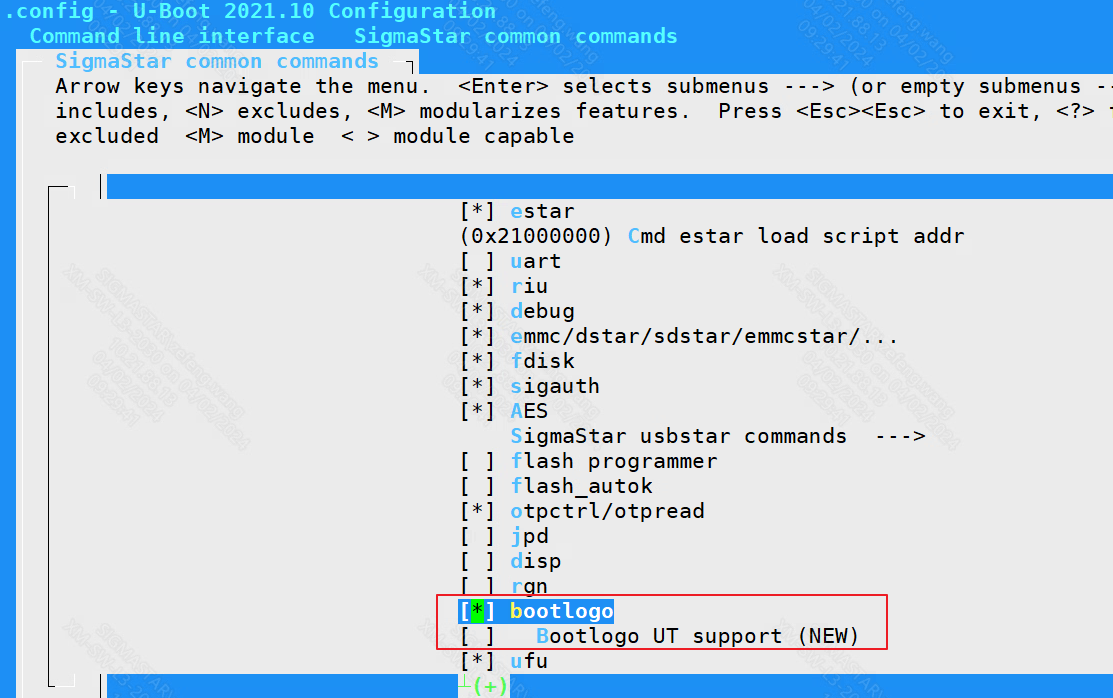
Command line interface ---> SigmaStar common commands ---> bootlogo
2.2 partition select¶
ARM architecture ----> SigmaStar arch features support
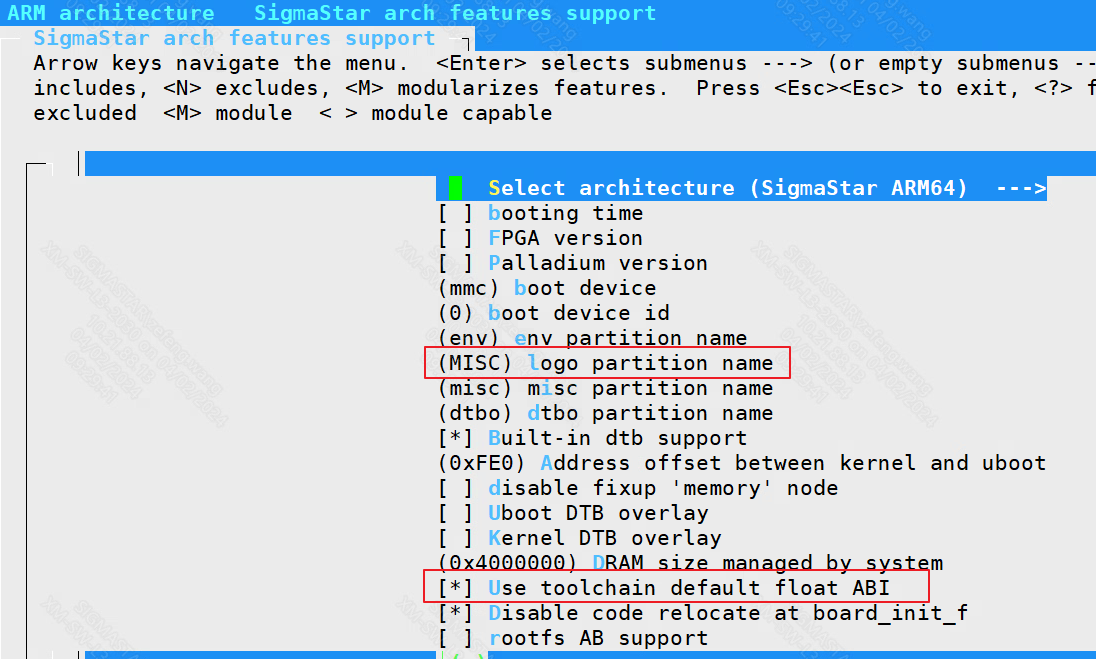
logo partition name: This partition stores images, screen parameters (config.json) and logo_configuration.json.
2.3 open drivers¶
2.3.1 pwm¶
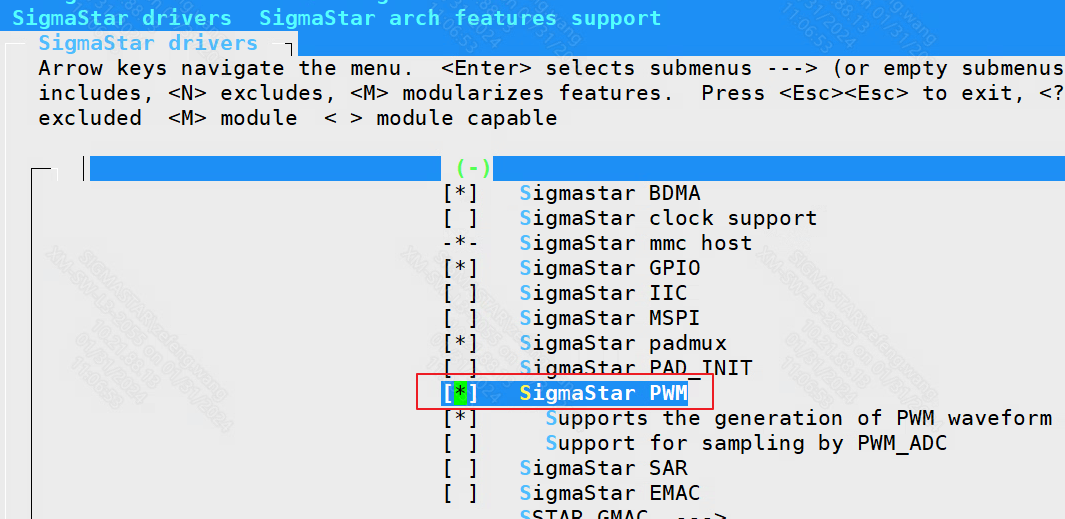
If the backlight needs to be controlled by PWM, then the PWM driver needs to be turned on.
SigmaStar drivers ----> SigmaStar PWM
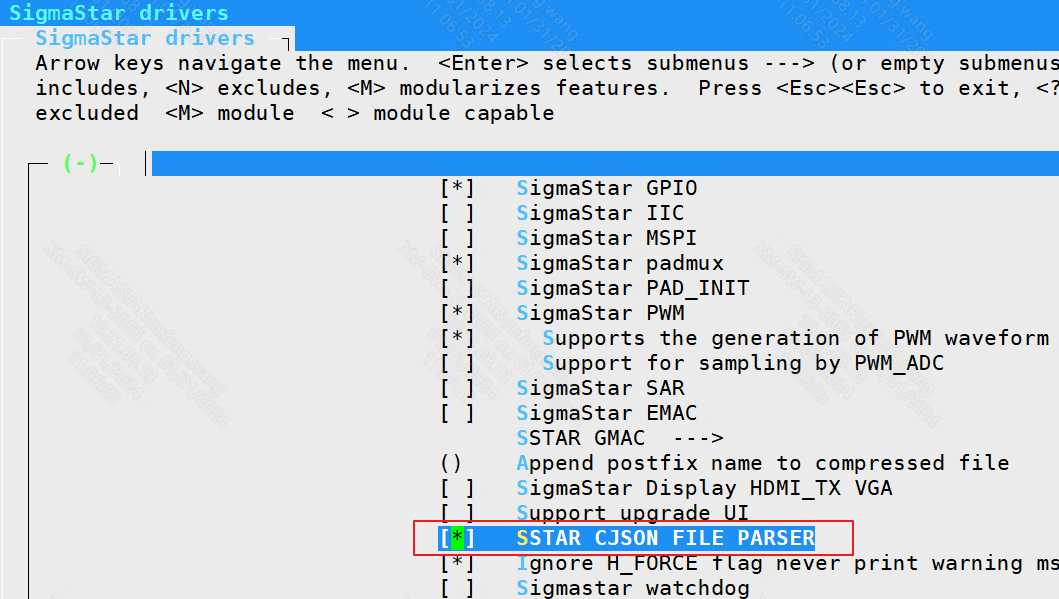
2.3.2 cjson parser¶
SigmaStar drivers ----> Sigmastar CJSON FILE PARSER
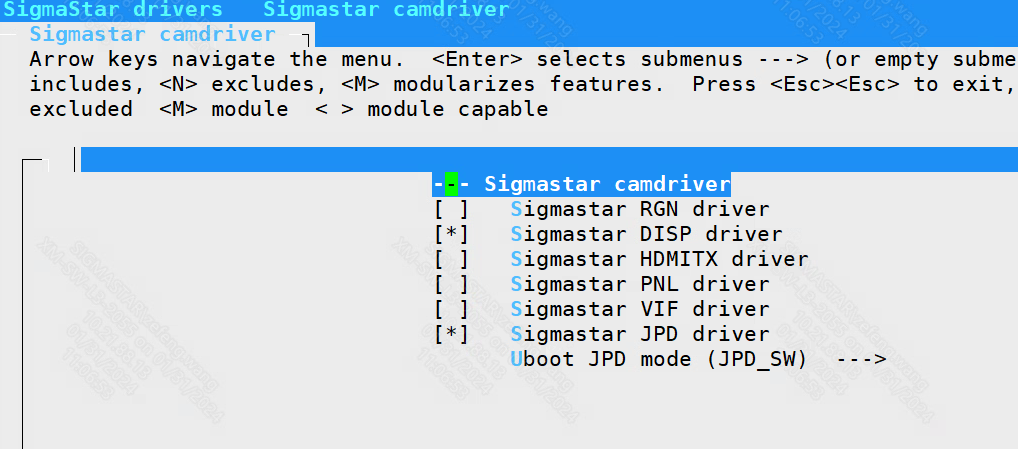
2.3.3 open camdriver module¶
SigmaStar drivers ----> Sigmastar camdriver ----> Sigmastar DISP driver SigmaStar drivers ----> Sigmastar camdriver ----> Sigmastar JPD driver
If you use gop display, you need to turn on
SigmaStar drivers ----> Sigmastar camdriver ----> Sigmastar RGN driver
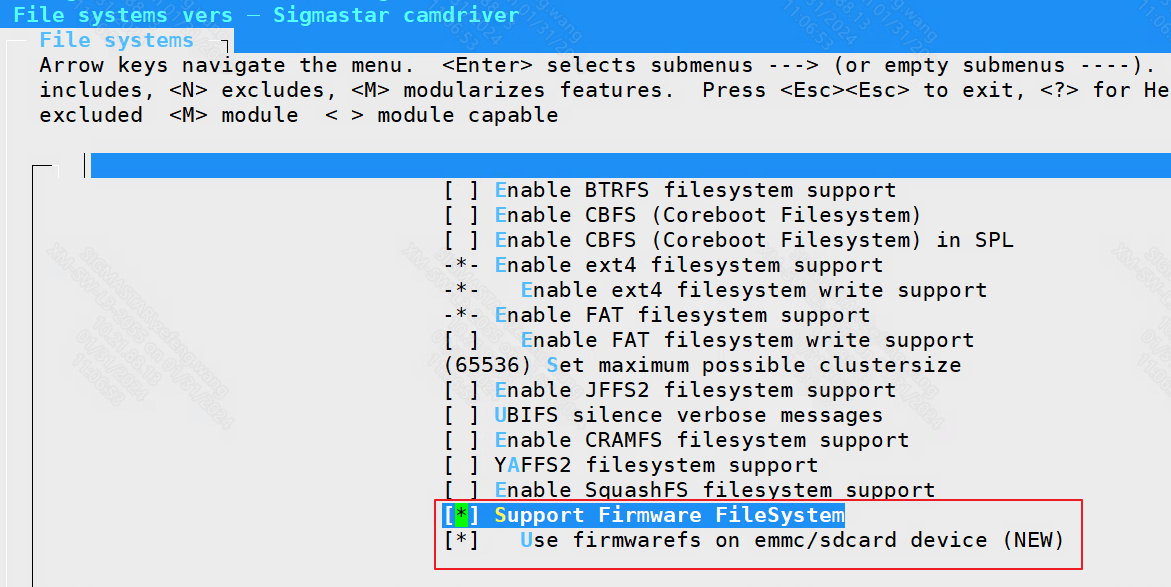
2.4 file systems¶
File systems ----> Support Firmware FileSystem
If the storage medium uses emmc, you need to select Use firmwarefs on emmc/sdcard device, otherwise it cannot be selected.
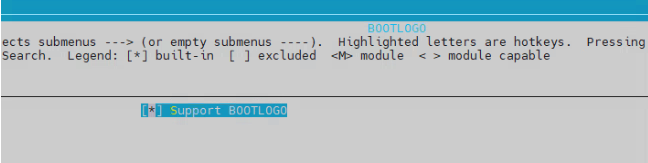
2.5 Open bootlogo requires files¶
cd project make menuconfig
Misc options ----> BOOTLOGO ----> Support BOOTLOGO
3. logo reserved buffer¶
This buffer is used for bootlogo display. If the kernel does not operate or release this address, it will remain displayed.
project/configs/verify/defconfigs/$(project_defconfig)
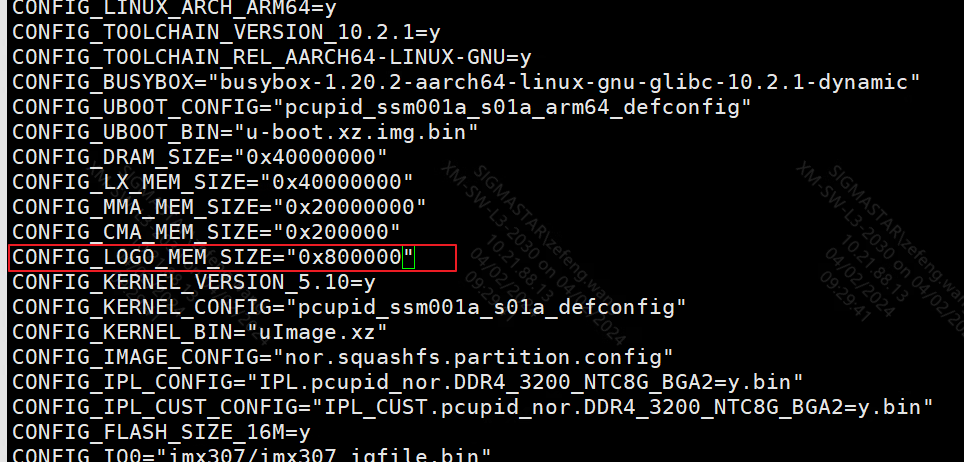
"CONFIG_LOGO_MEM_SIZE": The address configuration size where the logo is displayed.
After the above settings are completed, you can view the corresponding uboot environment variables on the board after burning. As shown in the figure below:
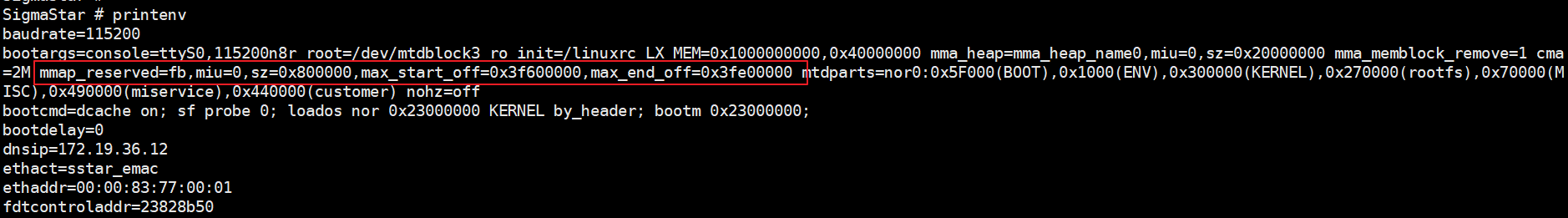
4. padmux¶
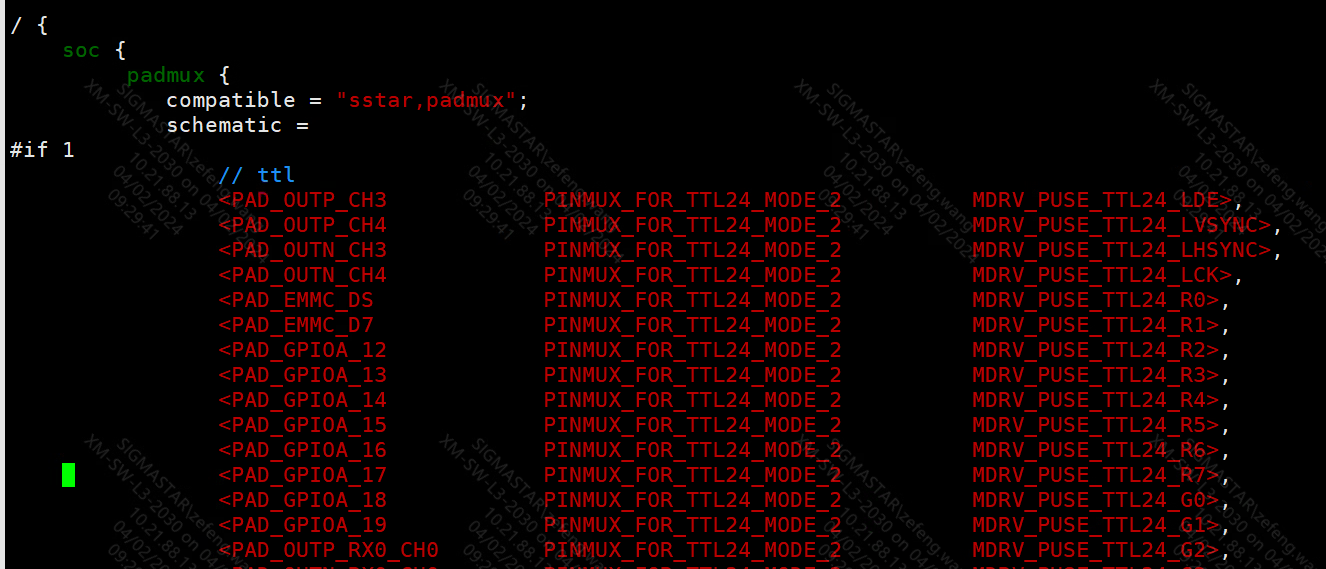
The screen needs to set padmux
boot/arch/arm/dts/$(boardname)-padmux.dtsi
For example, if you need to click on the TTL screen, you only need to change #if 0 to #if 1, as shown in the figure below
5. Logo storage location¶
project/board/ini/misc/$(logo_name)
If you want to put the pictures into the misc partition by default, you can modify the following location:
project/image/packaging/common/misc.mk
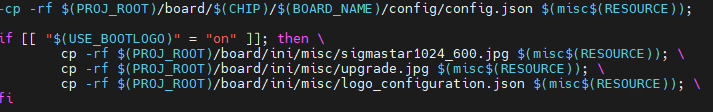
You can also copy the image to the misc partition after the board starts.
6. Bootlogo screen parameter configuration¶
Related file paths:
project/board/$(chip)/$(boardname)/config/config_disp.json project/board/ini/misc/logo_configuration.json
config_disp.json stores screen parameters, and logo_configuration.json specifies screen parameters, screen type, etc.
logo_configuration.json mainly includes the following parameters:
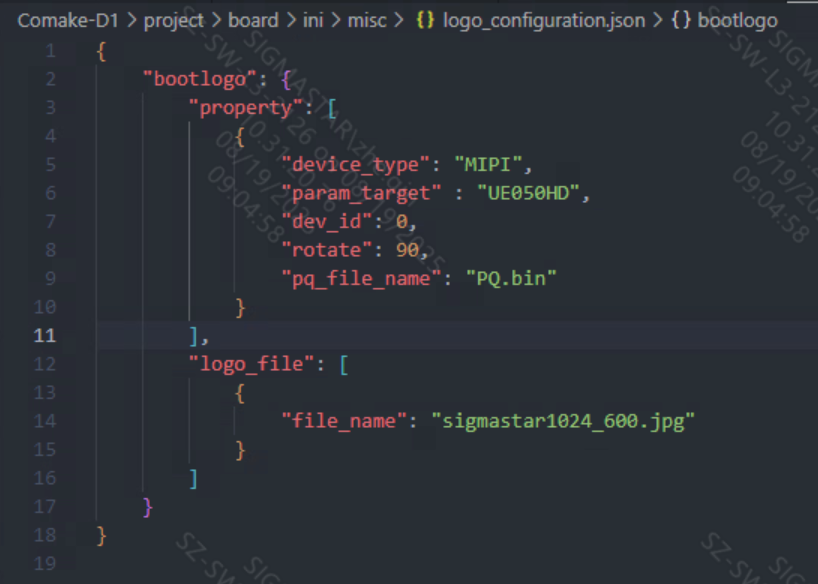
| Parameters | Description |
|---|---|
| device_type | Screen type TTL/MIPI/BT656/SRGB/MCU/MCU_NOFLM |
| param_target | Screen parameter name |
| dev_id | device id |
| rotate | Rotation parameters 0: 0° 90: 90° 180: 180° 270: 270° |
| file_name | logo image name |
Bootlogo will find the corresponding screen parameters in the config_disp.json file according to param_target and parse them.
The order of logo_file child nodes corresponds to the order of logo ids, with the first child node corresponding to logo id 0.
Note
The configuration file for Comake PI D1 does not include the following backlight control section. The backlight control pin for the MIPI screen of Comake D1 is PAD_PM_PWM0_OUT.
config_disp.json can set the backlight related parameters, as shown below
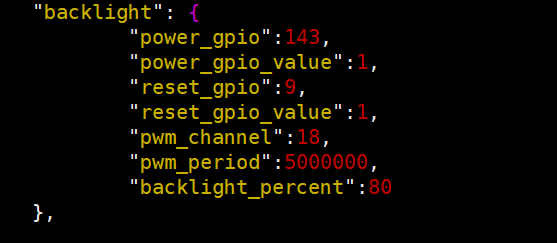
| Parameters | Description |
|---|---|
| power_gpio | gpio id of the power pin |
| power_gpio_value | power pin level 0: gpio active low 1: gpio active high |
| power_gpio_delay | power pin delay time,the unit is ms |
| reset_gpio | gpio id of reset pin |
| reset_gpio_value | reset pin level 0: gpio active low 1: gpio active high |
| reset_gpio_delay | reset pin delay time,the unit is ms |
| backlight_gpio | gpio id of backlight pin |
| backlight_gpio_value | backlight pin level 0: gpio active low 1: gpio active high |
| backlight_gpio_delay | backlight pin delay time,the unit is ms |
| pwm_channel | The channel of pwm |
| pwm_period | pwm period, the unit is ns |
| backlight_percent | Backlight brightness percentage |
Note: backlight gpio is reserved for the backlight that does not require pwm control. The backlight can be enabled by pulling the gpio pin.
If pwm is used to configure the backlight, in addition to configuring pwm_channel, pwm_period, and backlight_percent, the pwn padmux of uboot also needs to be configured. pwm config must be enabled: pwm config.
For the query method of pwm channel, please refer to pwm doc.
If there are special power-on and power-off timing sequences, please refer to the screen parameters for description in Section 4.2.
7. Introduction to bootlogo command¶
bootlogo [logo_id] [aspect ratio] [x] [y] [device_id] logo_id : image id. default is 0 aspect_ratio: 0: zoom, 1: center, 2: usr. default is 0 x : show horizontal start. it's valid when aspect_ratio is 2. default is 0 y : show vertical start. it's valid when aspect_ratio is 2. default is 0 device_id: device ID. default is 0 Example: bootlogo // No parameters, all default parameters are 0 bootlogo 1 // Select the second logo to display, other parameters default to 0 bootlogo 0 1 // Select the first logo, and center the image bootlogo 0 2 1 1 // Select the first logo, and start displaying the image from (1, 1) bootlogo 0 0 0 0 0 // device id is 0
Note: The aspect ratio function requires the size of the input image to be smaller than the size of the screen output in order to work properly. This chip has only one device, and device_id can only be filled with 0.
8. Upgrade screen command introduction¶
8.1 Upgrade screen command¶
Note: Upgrading the screen display requires enabling GOP configuration. To enable configuration, please refer to open gop
disp_ui_update [percentage/success/fail] [device_id] percentage: percentage. range [0, 100] device_id: device ID. default is 0 Example: disp_ui_update 10 // The progress bar is 10% disp_ui_update success // Upgrade successful disp_ui_update fail // Upgrade failed
8.2 Separate commands for drawing UI¶
disp_ui bar [percentage] [bar_color] [text_color] [bg_color] [device_id] bar : draw progress bar percentage: percentage. range [0, 100] bar_color: show bar color. fmt is rgb(bit[23, 0]). default is green text_color: show text color. default is white bg_color : show bar background. default is blue device_id: device ID. default is 0 Example: disp_ui bar 10 // The progress bar is 10% disp_ui bar 10 0xff00 // 10% progress bar color is green disp_ui bar 10 0xff00 0xffffff // 10% of the progress bar is green, and 10% of the characters are white disp_ui bar 10 0xff00 0xffffff 0xffffff // The background color of the progress bar is white, the color of the 10% progress bar is green, and the color of the 10% text is white disp_ui bar 10 0xff00 0xffffff 0xffffff 0 // device id is 0
disp_ui msg [text] [x] [y] [text_color] [bg_color] [device_id] msg : draw characters text : ascii text. default is blank x : show text horizontal start. default is 0 y : show text vertical start. default is 0 text_color: show text color. default is white bg_color : show bar background. default is blue device_id: device ID. default is 0 Example: disp_ui msg update \\ Draw the character "update", starting from (0, 0) by default disp_ui msg update 1 1 \\ Start drawing the character "update" from (1, 1) disp_ui msg update 1 1 0xffffff \\ Character color is white disp_ui msg update 1 1 0x0 0xffffff \\ Character color black, background color white disp_ui msg update 1 1 0x0 0xffffff 0 \\ device id is 0
disp_ui blank [x] [y] [w] [h] [BlankColor] [device_id] blank : erase x : erase horizontal start. default is 0 y : erase vertical start. default is 0 w : erase the length. default is 0 h : erase the width. default is 0 BlankColor: erase the color. default is blue device_id: device ID. default is 0 Example: disp_ui blank 1 1 10 10 \\ Erase the area with a width and height of 10 at the starting point (1, 1), and the color is blue disp_ui blank 1 1 10 10 0xffffff \\ The erase color is black disp_ui blank 1 1 10 10 0xffffff 0 \\ device id is 0