USB USER GUIDE
REVISION HISTORY¶
| Revision No. | Description |
Date |
|---|---|---|
| 1.0 | 09/06/2024 | |
| 1.1 | 04/18/2025 |
1. OVERVIEW¶
USB(Universal Serial Bus) is a widely used interface standard, mainly used to connect computers with external devices, achieve data transmission and device power supply
2. KEYWORD DESCRIPTION¶
-
Device
External hardware, such as USB drives, keyboards, mobile devices, etc., that connects computers or other devices through a USB interface to achieve data transfer, power supply, or expansion functions
-
Host
USB Host is the main control terminal that controls the USB bus and manages connected devices (such as computers and mobile phones). It is responsible for power supply, data transmission coordination, and driver loading, enabling external devices (such as USB drives and mice) to work properly
3. FUNCTION DESCRIPTION¶
-
Supports 2 USB ports
-
Each USB port supports host mode and device mode
-
USB device EP resources
EP0 EP1 EP2 EP3 EP4 EP5 EP6 64 2048 1024 64 512 128 128
4. Uboot usage introduction¶
4.1. ufu usage¶
To enable CMD_SSTAR-UFU in uboot config, if you need to compile an upgraded uboot with empty chips, you also need to additionally enable CONFIG_SSTAR_AUTOBOOT_RUN_UFU_ALWAYS
Usage: Enter ufu under uboot to enter ufu upgrade mode and wait for the PC tool to start the upgrade
4.2. usbstar usage¶
The uboot configuration needs to enable CMD_SSTAR_SUSBSTAR
Usage: Execute ./image/makefiletools/script/make_usb_upgrade_sigmastar.sh in project directory,put the generated bin into a Fat32 USB flash drive and connect it to the USB HOST port, Enter usbstar under uboot to start upgrading
5. Introduction to kernel usage¶
5.1. LINUX CONFIGURATION USING USB DEVICE¶
5.1.1. Kernel Config Configuration¶
The device configuration method mainly involves enabling UDC configuration (udc-msx250x.ko) and some gadget configurations. (depending on which function is needed)
Enable the Gadget core layer and UDC configuration. (Generate usb-common.ko, udc-core.ko, udc-msb250x.ko)
[*]USB support --->
[M]USB Gadget Support --->
USB Peripheral Controller --->
[M]Sstar USB 2.0 Device Controller
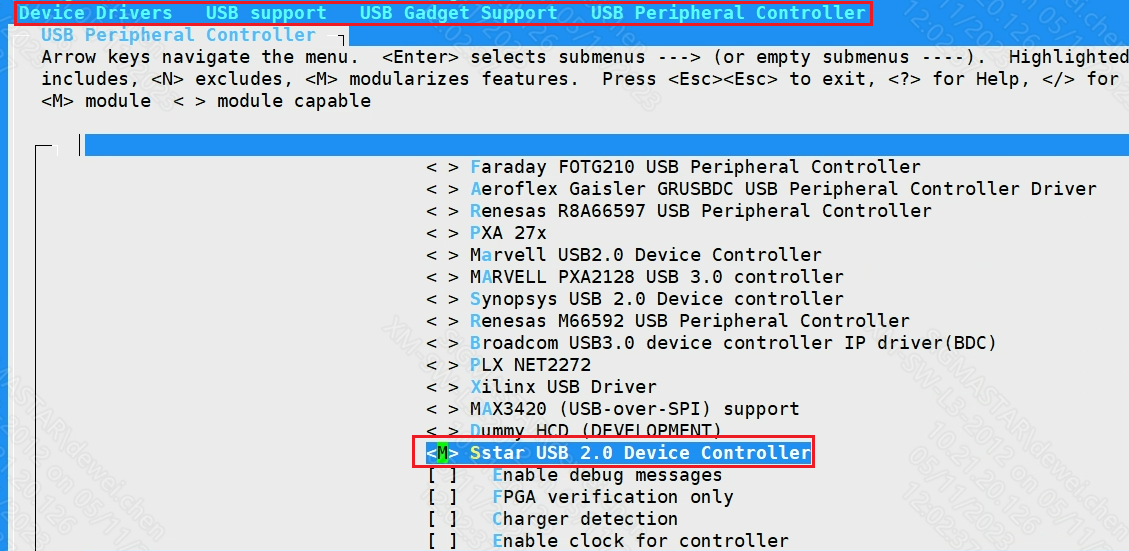
Use the configfs script to enable gadget configuration. The red arrow points to the specific device function to be configured. (generate libcomposite.ko, and the ko of the specific function (usb_f_xxx.ko))
[*]USB support --->
[M]USB Gadget Support --->
[M]USB functions configurable through configfs
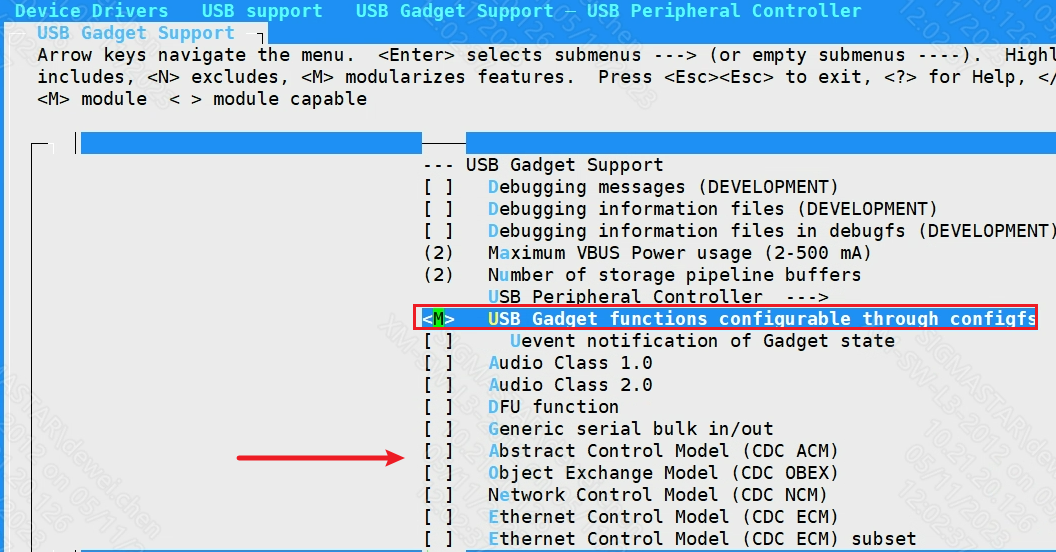
Alternatively, it can configure the gadget by loading the corresponding g_xxx.ko in leagacy way:
[*]USB support --->
[M]USB Gadget Support --->
USB Gadget precomposed configurations
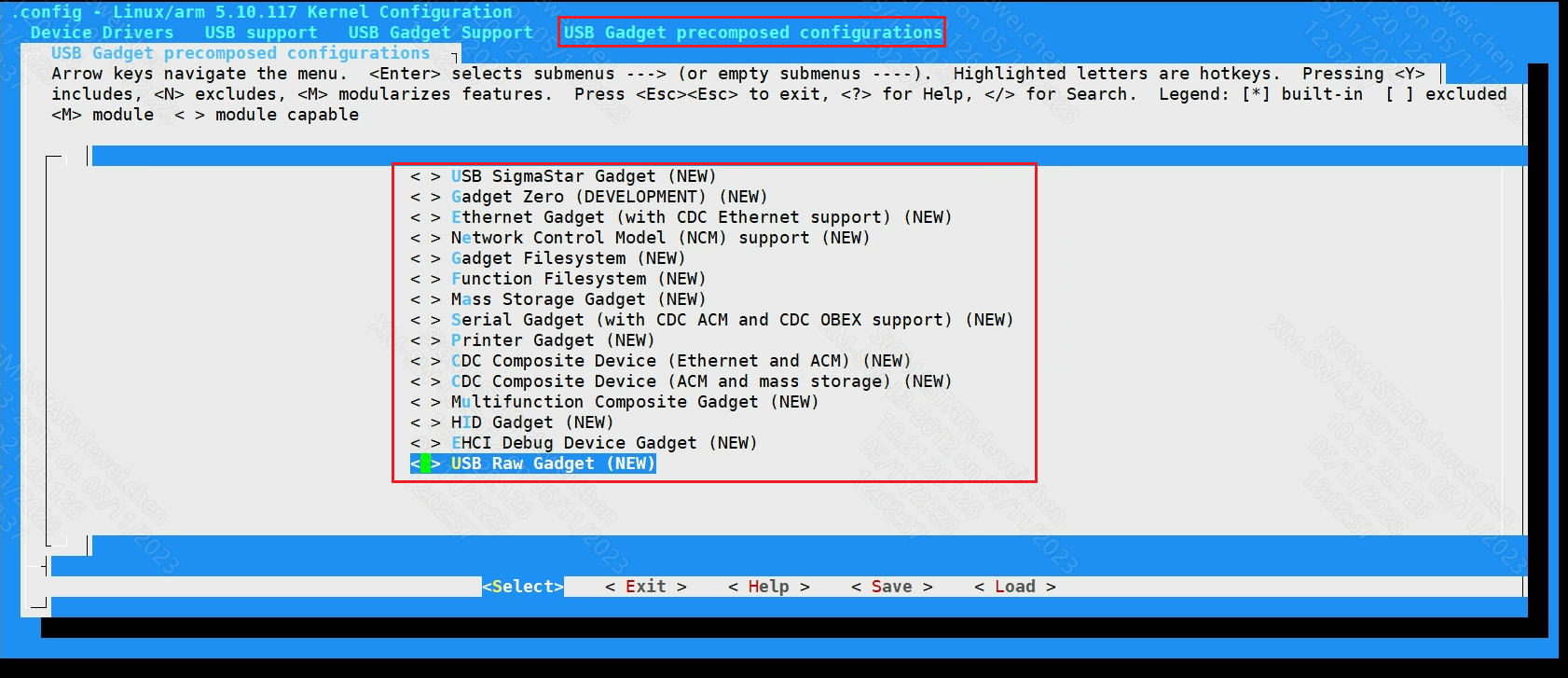
For example, adb needs to open the following configuration. (generate usb_f_fs.ko):
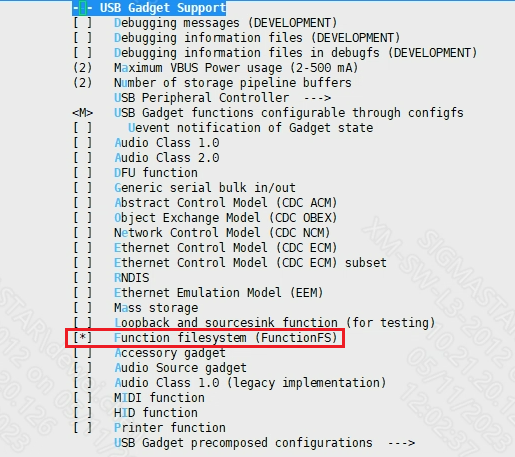
5.1.2. DTS Configuration¶
The corresponding nodes in pcupid.dtsi are as follows, msb250x-udc-p0 and msb25x-udc-p1 correspond to P0 and P1 respectively, and the default status is okay and disabled respectively.
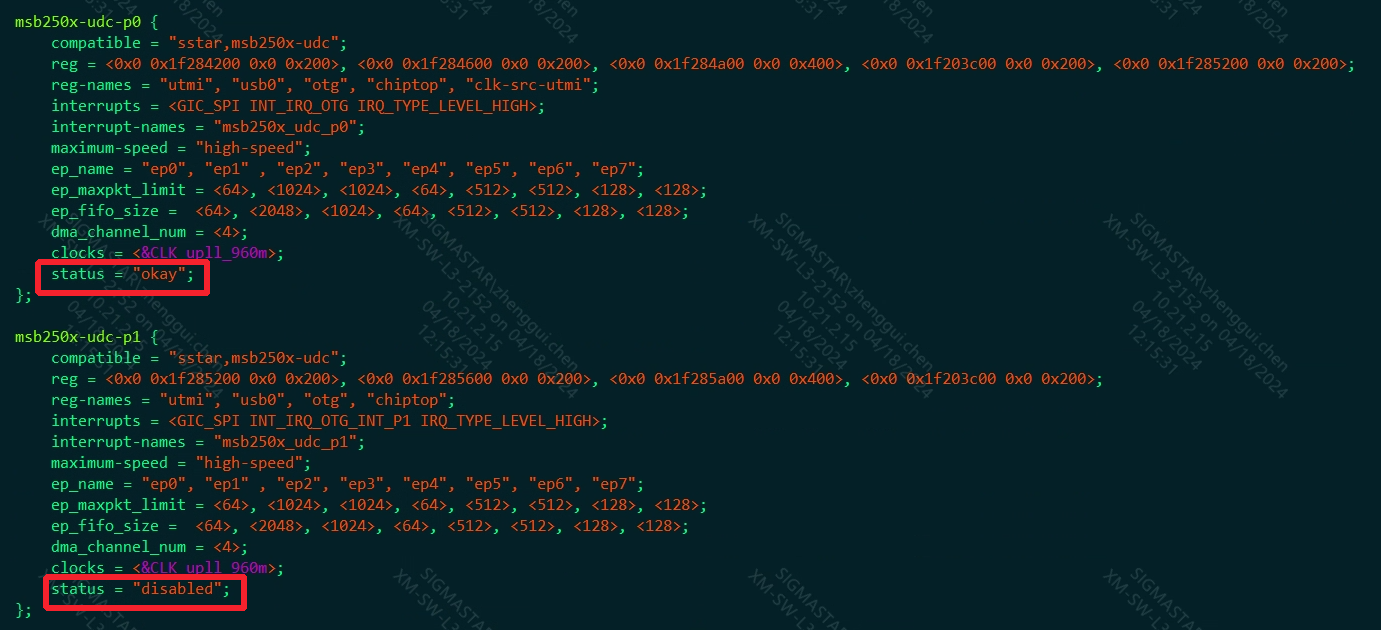
| Parameter | Description | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| reg | register base addr | Hardware fixed address, cannot be modified |
| reg-names | register names | The driver retrieves the reg based on its name and cannot be modified |
| interrupts | interrupt num | determined by hardware |
| interrupt-names | interrupt names | Driver retrieves interrupts based on name |
| maximum-speed | max speed | support high-speed and full-speed |
| ep_name | endpoint name | Driver retrieves the number of EP based on their names |
| ep_maxpkt_limit | endpoint max packet limit | Hardware fixed value |
| ep_fifo_size | endpoint fifo size | Hardware fixed value |
| dma_channel_num | dma channel num | Hardware fixed value |
| clocks | clocks configuration | Hardware fixed value |
5.1.3. Ko Loading¶
Load ko in the following order:
#usb2.0 device normal ko usb-common.ko udc-core.ko udc-msb250x.ko libcomposite.ko #device function ko for example, adb need to load usb_f_fs.ko #if using leagacy configuration, need to load g_xxx.ko
5.2 LINUX CONFIGURATION USING USB HOST¶
Both 2 USB ports of Pcupid support being configured as USB hosts.
5.2.1 Kernel Config Configuration¶
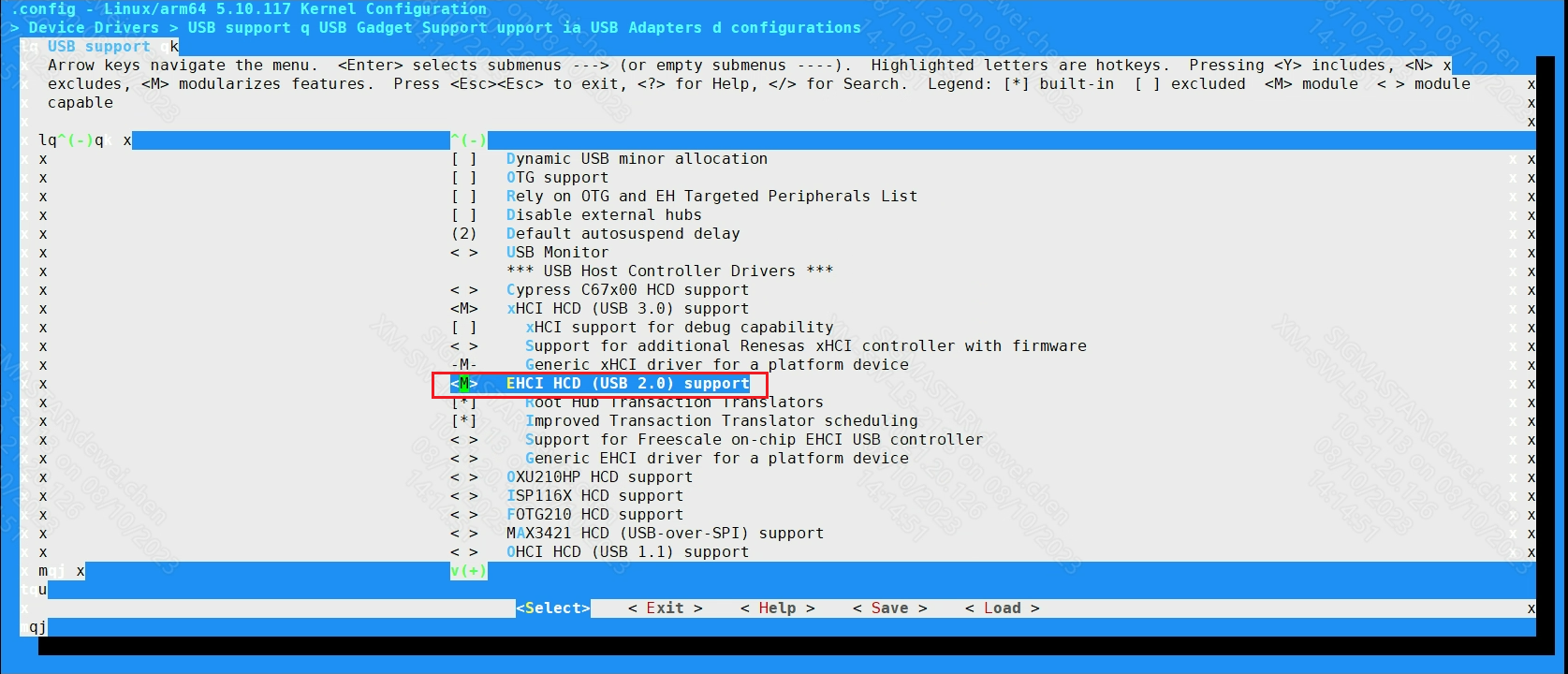
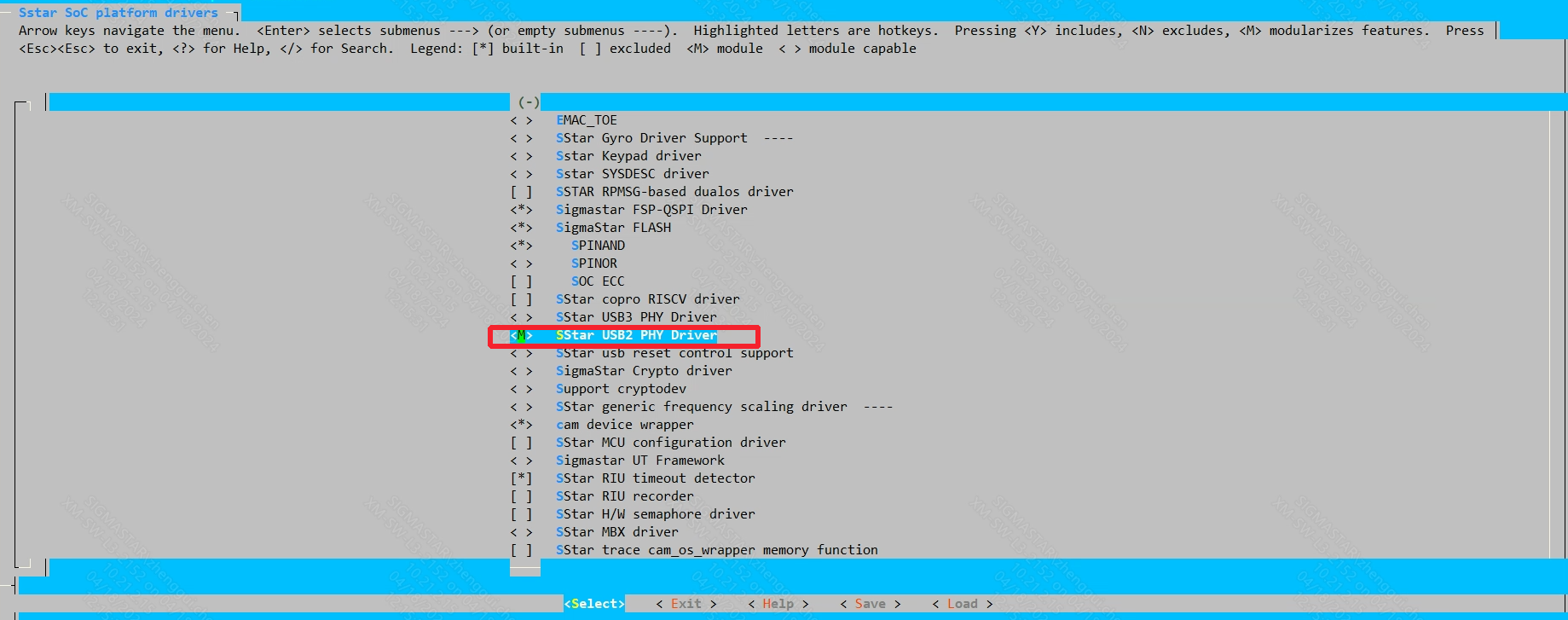
Kernel config open the following configuration:
COFNIG_USB_EHCI_HCD: (generate ehci-hcd.ko)
CONFIG_SSTAR_USB2_PHY: (generate sstar-usb2-phy.ko)
5.2.2. DTS Configuration¶
The corresponding nodes of pcupid.dtsi are as follows. When USB2.0 is configured as host, the status of sstar_ehci0/sstar_ehci1 nodes needs to be set to okay. Currently, ehci0/ehci1 is disabled/okay by default.
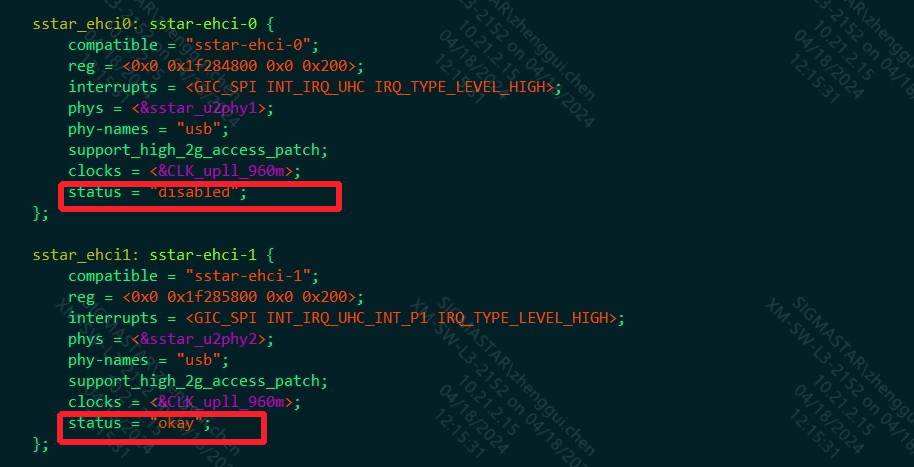
| Paramater | Description | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| reg | register base address | hardware fixed address |
| interrupts | interrupt num | Fixed Interrupt |
| phys | phy nodes | The referenced phy node |
| phy-names | phy name | Drive to obtain phy nodes based on this |
| clocks | clock configuration | Clock source |
5.2.3. Ko Loading¶
Load ko in the following order:
#usb2.0 host normal ko usb-common.ko usbcore.ko sstar-usb2-phy.ko ehci-hcd.ko
5.2.4. USB2.0 Port0 OTG Usage Reference¶
First, both host and device need to be enabled in dts.
P0 port: msb250x-udc-p0 and sstar_ehci0.
P1 port: msb250x-udc-p1 and sstar_ehci1.
If both host and device drivers are loaded, they will be configured as device by default according to the loading order. You can switch host or device through scripts. Script path: Alkaid\project\release\chip\pcupid\dispcam\common\glibc\10.2.1\debug\bin\debug\usb_otg.sh. Board rootfs path: /customer/usb_otg.sh.
#USB2.0 P0 will be switched to device /customer/usb_otg.sh 0 device #USB2.0 P0 will be switched to host /customer/usb_otg.sh 0 host #USB2.0 P1 will be switched to device /customer/usb_otg.sh 1 device #USB2.0 P1 will be switched to host /customer/usb_otg.sh 1 host
5.3. UVC DEVICE CONFIGURATION¶
First, please refer to Linux configuration using USB device
5.3.1. Kernel Config Configuration¶
Enable UVC device function configuration (generate ko: libcomposite.ko, usb_f_uvc.ko, g_sstar_gadget.ko)
Device Drivers --->
[*]USB support --->
[M]USB Gadget Support --->
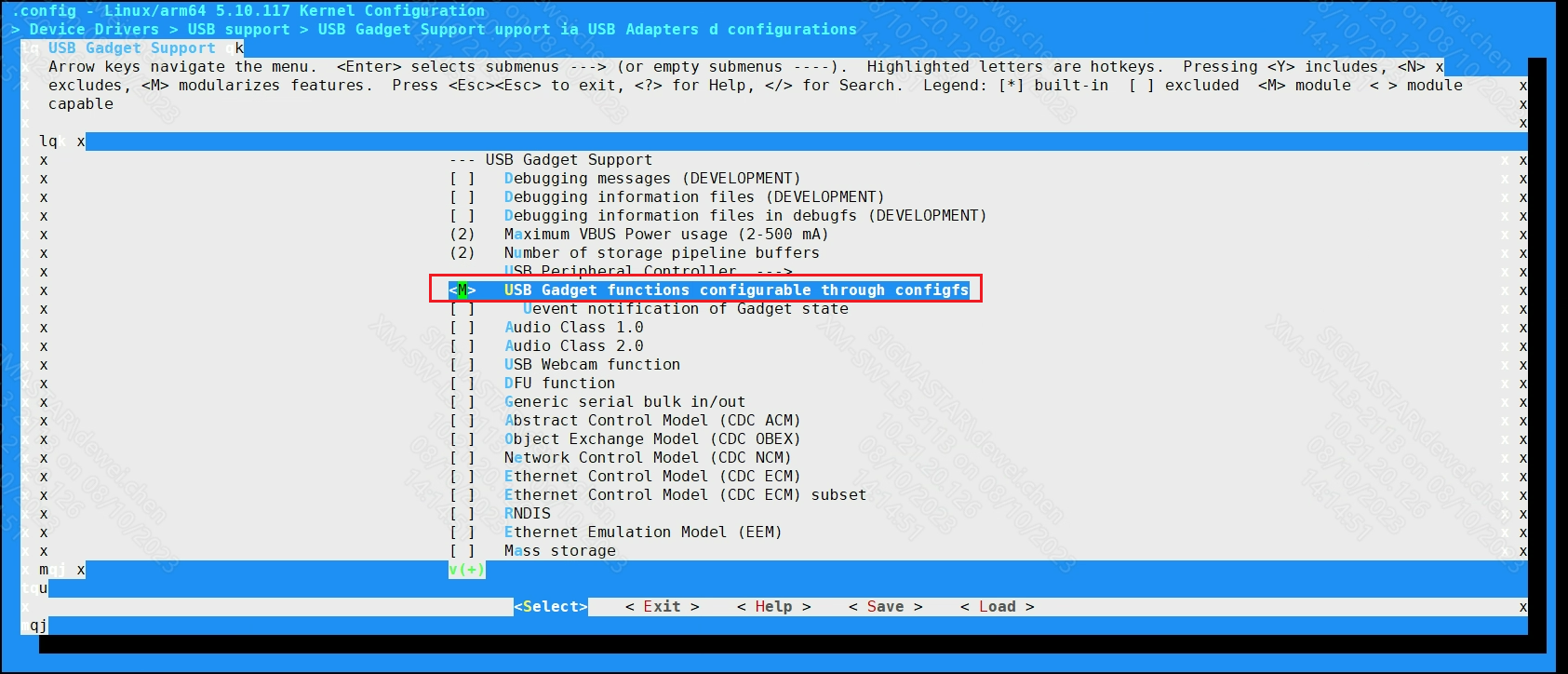
[M]USB functions configurable through configfs
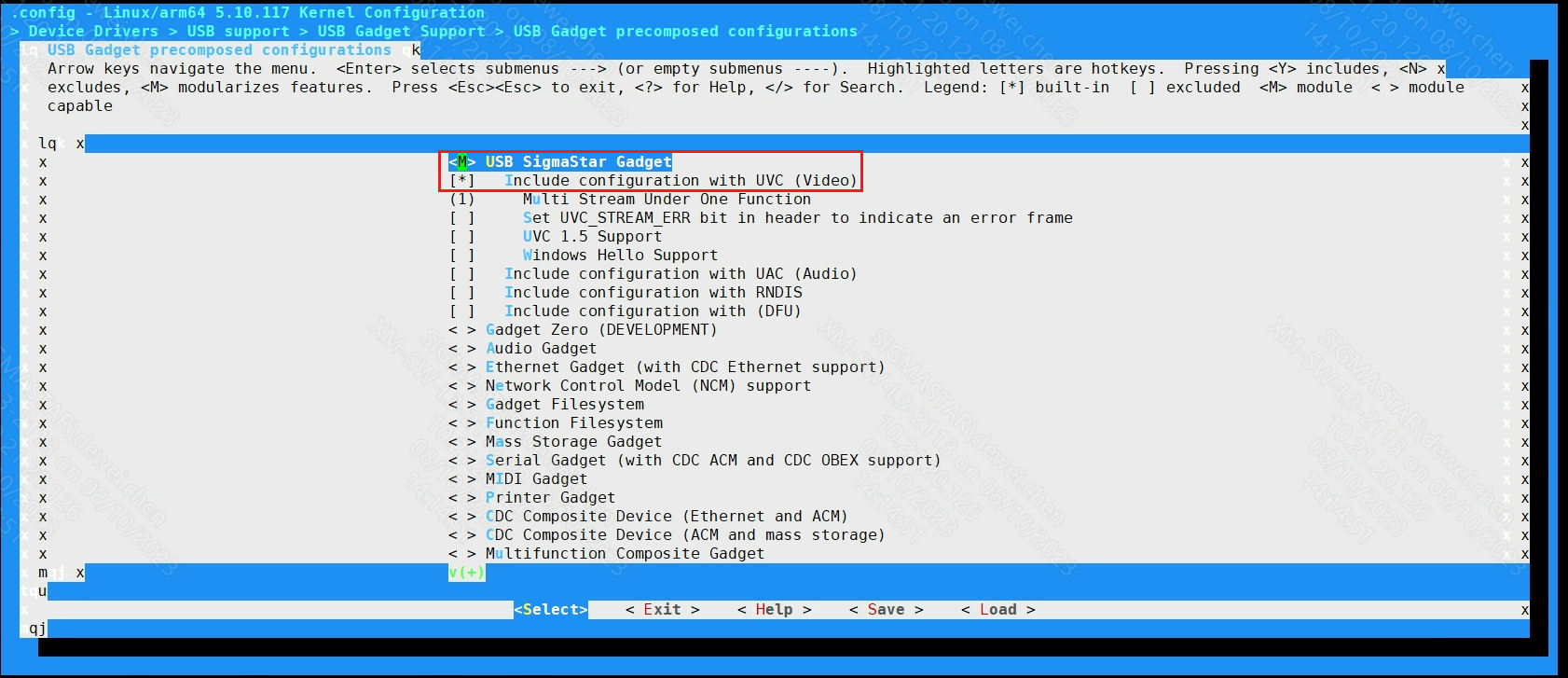
USB Gadget precomposed configurations --->
[M]USB SigmaStar Gadget
[*]Include configuration with UVC (Video)
Enable Multimedia configuration (generate ko: mc.ko, videodev.ko, videobuf2-common.ko, videobuf2-v4l2.ko, videobuf2-memops.ko, videobuf2-vmalloc.ko, videobuf2-dma-sg.ko, uvcvideo.ko)
Device Drivers --->
[*]Multimedia support --->
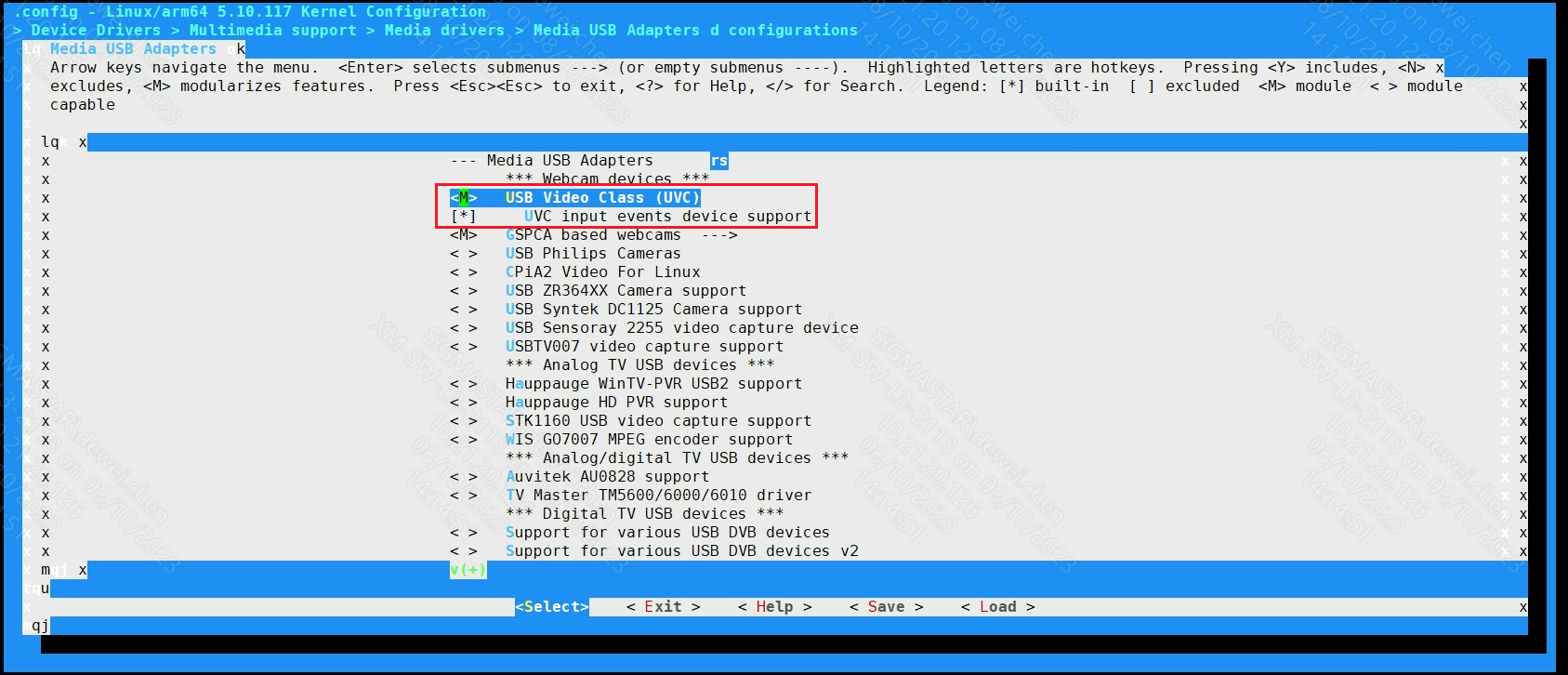
Media drivers --->
[*]Media USB Adapters --->
[M]USB Vide Class (UVC)
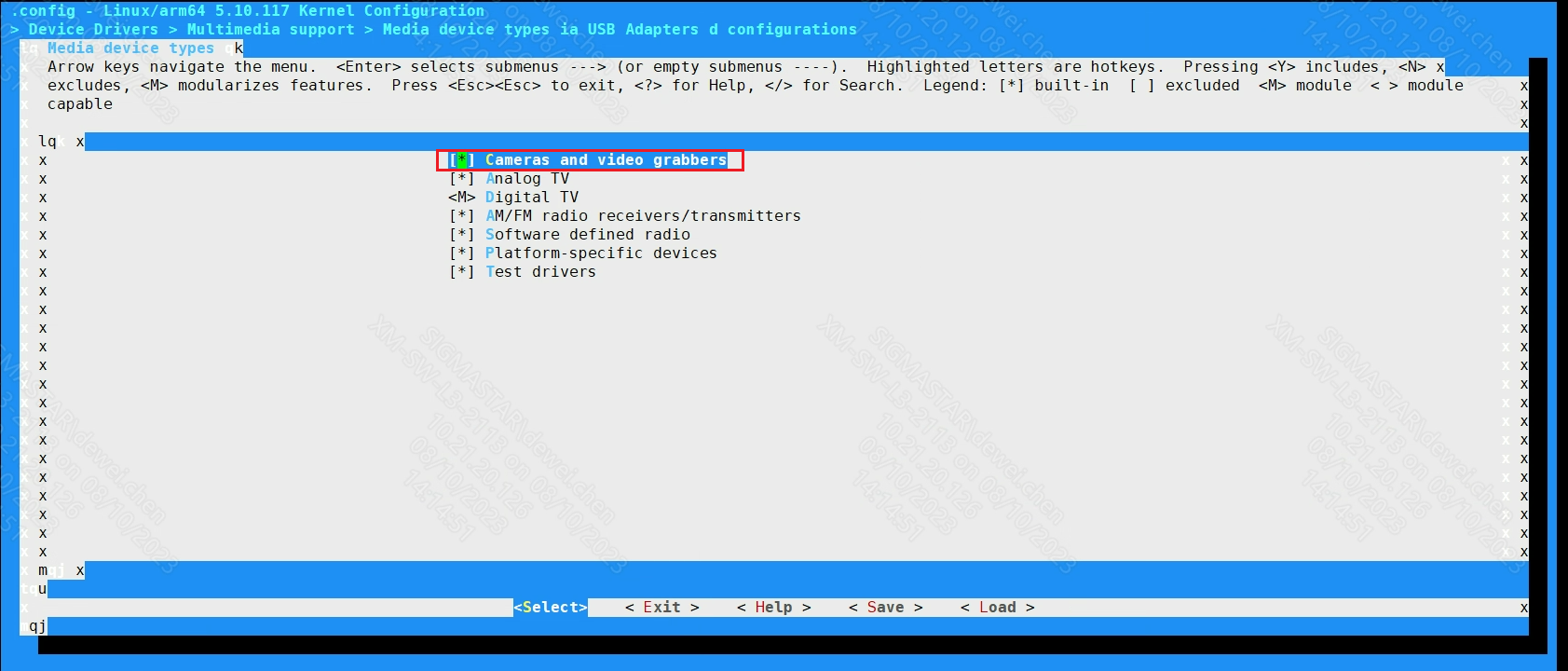
Media device types --->
[*]Cameras and video grabbers
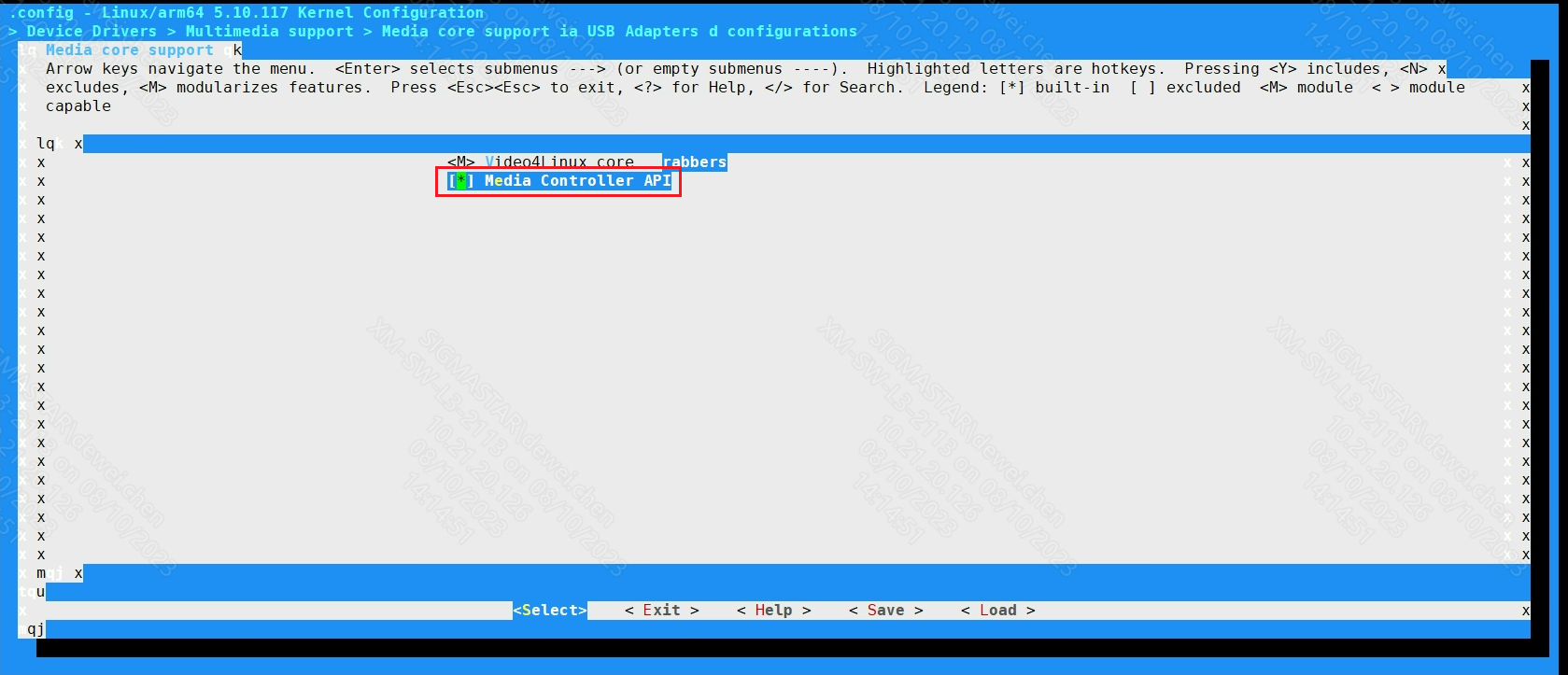
Media core support --->
[*]Media Controller API
5.3.2. Ko Loading¶
Load ko in the following order:
#multimedia ko mc.ko videodev.ko videobuf2-common.ko videobuf2-v4l2.ko videobuf2-memops.ko videobuf2-vmalloc.ko videobuf2-dma-sg.ko uvcvideo.ko #uvc device ko udc-core.ko libcomposite.ko usb_f_uvc.ko udc-msb250x.ko g_sstar_gadget.ko
After ko is loaded successfully, the /dev/video0 node will be generated. Connect the USB device port of the board to the PC with a USB cable. Run the UVC demo and use a player such as PotPlayer to open the camera device, the UVC Camera device will appear.
5.4. UVC HOST CONFIGURATION¶
First, please refer to Linux configuration using USB Host
5.4.1. Kernel Config Configuration¶
Enable Multimedia configuration (generate ko: mc.ko, videodev.ko, videobuf2-common.ko, videobuf2-v4l2.ko, videobuf2-memops.ko, videobuf2-vmalloc.ko, videobuf2-dma-sg.ko, uvcvideo.ko)
Device Drivers --->
[*]Multimedia support --->
Media drivers --->
[*]Media USB Adapters --->
[M]USB Vide Class (UVC)
Media device types --->
[*]Cameras and video grabbers
Media core support --->
[*]Media Controller API



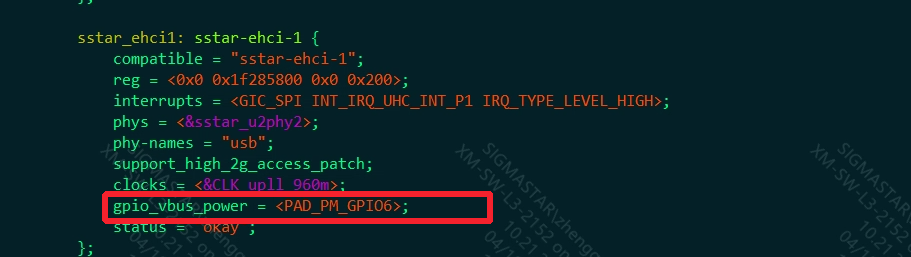
5.4.2. VBUS CONTROL¶
At present, uboot and kernel already contain the relevant logic of Vbus to pull gpio. It is necessary to add vbus control information in dts. The following figure adds the vbus GPIO information of P1.
5.4.3. Ko Loading¶
#multimedia ko mc.ko videodev.ko videobuf2-common.ko videobuf2-v4l2.ko videobuf2-memops.ko videobuf2-vmalloc.ko videobuf2-dma-sg.ko uvcvideo.ko #usb2.0 host ko sstar-usb2-phy.ko ehci-hcd.ko
After ko is loaded successfully, the USB host port of the board is connected to the uvc device with a USB cable, and the /dev/videoX node can be seen.
6. FAQ¶
Q1:Unable to recognize USB host connected device under kernel
-
Check if the VBUS power supply has been pulled up
-
Check if the
statusof DTS ehci node isOK -
Check if the kernel config is configured
Q2:High speed devices recognized as full speed in the kernel
- Check if the upper level of the device is connected to the full speed hub
Q3:U-disk upgrade failed under uboot
-
Check if the VBUS power supply has been pulled up
-
Check if the
statusof DTS ehci node isOK -
Check if the USB drive is in FAT32 format
Q4:USB empty chip upgrade failed
-
Check if it is in an empty upgrade state, the serial port will print a log(Start USB Mode) for the empty upgrade state
-
Check if the packaged USB image matches the board