MI IPU API
REVISION HISTORY¶
| Revision No. | Description |
Date |
|---|---|---|
| 3.0 | 07/23/2021 | |
| 08/25/2021 | ||
| 11/30/2021 | ||
| 12/21/2021 | ||
| 01/20/2022 | ||
| 02/25/2022 | ||
| 06/01/2022 | ||
| 06/13/2022 | ||
| 08/15/2022 | ||
| 05/25/2023 | ||
| 09/26/2023 | ||
| 07/25/2024 | ||
| 04/16/2025 |
1. OVERVIEW¶
1.1. Module Description¶
IPU is an intelligent process unit. It's used to accelerates the inferences of AI models under the MI IPU module.
Keyword description:
-
IPU
Intelligent process unit
-
Firmware
The program which drives the IPU HW
-
Tensor
Multi dimension data in the AI model
-
Input Tensor
Input Tensor of the AI model
-
Output Tensor
Output Tensor of the AI model
1.2. Basic Structure¶
MI IPU module supports multi AI models by channels. It Internally manages the acquisition and release of input and output Tensor while supporting external buffer as Input Tensor.
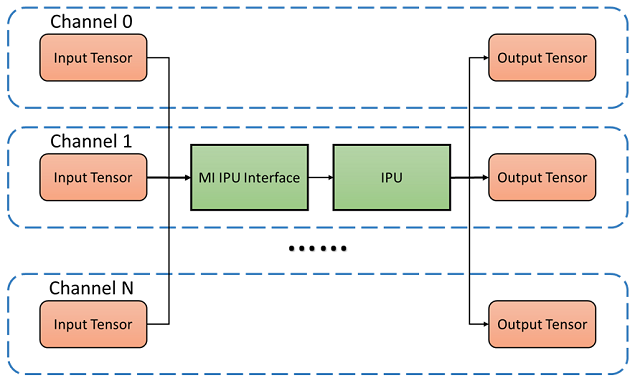
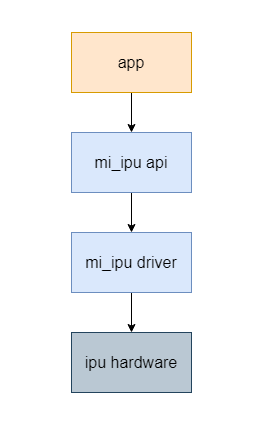
From the perspective of software development, applications invoke the IPU driver via the MI IPU API, which subsequently enables the IPU hardware to perform inference on AI models.
1.3. Module Function¶
MI IPU module supports the following features:
-
Support multi-thread and multi-process inference execution.
-
Support multiple channels.
-
Support both automatic buffer allocation and manual buffer allocation by users for models.
-
Support setting priority for IPU inference tasks.
-
Support single input or multiple inputs for each inference task.
1.4. Application Scenario¶
MI IPU module supports the following application scenarios:
-
Robotics : Applied in industrial or service robots to achieve environmental perception, path planning, and task execution.
-
Smart IPC/NVR : Applied in intelligent security devices, incorporating face recognition, behavior analysis, and anomaly detection to enhance monitoring effectiveness.
-
Conference Systems : Utilizes speech recognition and face recognition technologies to optimize meeting experiences.
1.5. Chip Difference¶
The chip described in this document is Pcupid. For MI IPU module, the differences between each generation of chips are listed in the following table.
| Pudding | Tiramisu | Muffin | Mochi | Maruko | Opera | Souffle | Ifado | Iford | Pcupid | Ibopper | Ifackel | Jaguar1 | Ifliegen | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Channel Number | 48 | 48 | 48 | 48 | 48 | 48 | 48 | 8 | 48 | 48 | 48 | 48 | 48 | 48 |
| Core Number | 1 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 2 |
Note:
- Core0 of Ifackel and Ifliegen IPU is used to run the AI ISP model, and core1 is used to run the common AI model.
- Both core0 and core1 of Muffin IPU are used to run common AI models.
1.6. Principle¶
Before invoking the MI IPU module for model inference, the user must first convert the original deep learning model into an offline model file compatible with the hardware using the IPU SDK toolchain. Subsequently, the offline model should be loaded on the board end by calling the MI IPU API to facilitate accelerated inference of the offline model.
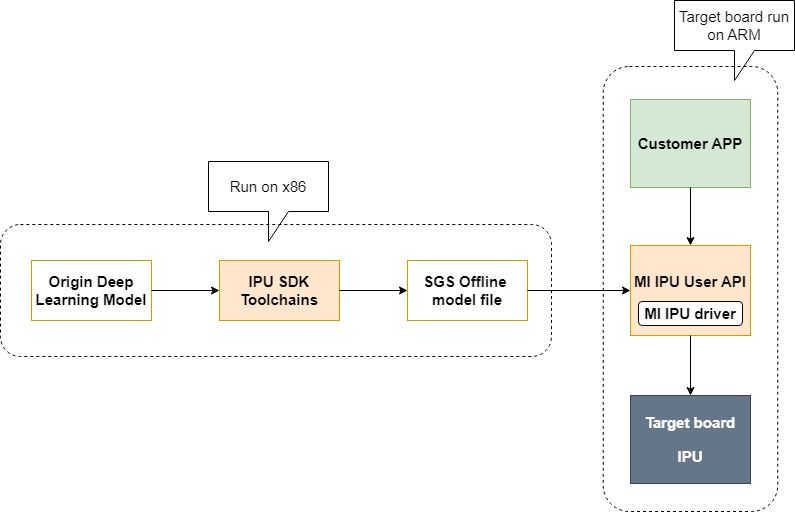
1.7. Interface Call¶
While executing model inference through MI IPU module, the sequence of interface call is usually as follows.
-
Parse model information to get variable buffer size
-
Create IPU device
-
Create IPU channel
-
Get input and output description of IPU channel
-
Get address of input buffers, and copy the input content to this buffer, and then flush the cache to ensure that the contents in the buffer are the same as those in the cache
-
Get address of output buffers
-
Perform model inference
-
Return the previously obtained input and output buffers to all buffers of the channel
-
Destroy IPU channel
-
Destroy IPU device

1.8. Example¶
1.8.1. dla_classify¶
dla_classify is applicable to the inference for classification model. At this time, the input format of the model is required to be BGR or RGB. During runtime, this demo first loads the offline model and drives the IPU to classify the input images. Finally, it prints the prediction results of the top 5 classifications and the corresponding confidence levels. The specific code can be referred to in
#include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> #include <unistd.h> #include <string.h> #include <sys/types.h> #include <sys/stat.h> #include <fcntl.h> #include <signal.h> #include <stdbool.h> #include <error.h> #include <errno.h> #include <pthread.h> #include <string.h> #include <fstream> #include <iostream> #include <string> #include <opencv2/core/core.hpp> #include <opencv2/highgui/highgui.hpp> #include <opencv2/imgproc/imgproc.hpp> #include <sys/time.h> #include <unistd.h> #include <sys/mman.h> #if 0 #include <openssl/aes.h> #include <openssl/evp.h> #include <openssl/rsa.h> #endif using namespace std; using std::cout; using std::endl; using std::ostringstream; using std::vector; using std::string; #include "mi_common_datatype.h" #include "mi_sys_datatype.h" #include "mi_ipu.h" #include "mi_sys.h" #define LABEL_IMAGE_FUNC_INFO(fmt, args...) do {printf("[Info ] [%-4d] [%10s] ", __LINE__, __func__); printf(fmt, ##args);} while(0) #define alignment_up(a,b) (((a)+(b-1))&(~(b-1))) struct PreProcessedData { char *pImagePath; int intResizeH; int intResizeW; int intResizeC; bool bNorm; float fmeanB; float fmeanG; float fmeanR; float std; bool bRGB; unsigned char * pdata; } ; struct NetInfo { MI_IPU_OfflineModelStaticInfo_t OfflineModelInfo; MI_IPU_SubNet_InputOutputDesc_t desc; }; #define LABEL_CLASS_COUNT (1200) #define LABEL_NAME_MAX_SIZE (60) MI_S32 IPUCreateDevice(char *pFirmwarePath,MI_U32 u32VarBufSize) { MI_S32 s32Ret = MI_SUCCESS; MI_IPU_DevAttr_t stDevAttr; memset(&stDevAttr, 0, sizeof(stDevAttr)); stDevAttr.u32MaxVariableBufSize = u32VarBufSize; s32Ret = MI_IPU_CreateDevice(&stDevAttr, NULL, pFirmwarePath, 0); return s32Ret; } static int H2SerializedReadFunc_1(void *dst_buf,int offset, int size, char *ctx) { // read data from buf return 0; } static int H2SerializedReadFunc_2(void *dst_buf,int offset, int size, char *ctx) { // read data from buf std::cout<<"read from call back function"<<std::endl; memcpy(dst_buf,ctx+offset,size); return 0; } MI_S32 IPUCreateChannel(MI_U32 *s32Channel, char *pModelImage) { MI_S32 s32Ret ; MI_SYS_GlobalPrivPoolConfig_t stGlobalPrivPoolConf; MI_IPUChnAttr_t stChnAttr; //create channel memset(&stChnAttr, 0, sizeof(stChnAttr)); stChnAttr.u32InputBufDepth = 2; stChnAttr.u32OutputBufDepth = 2; return MI_IPU_CreateCHN(s32Channel, &stChnAttr, NULL, pModelImage); } MI_S32 IPUCreateChannel_FromMemory(MI_U32 *s32Channel, char *pModelImage) { MI_S32 s32Ret ; MI_SYS_GlobalPrivPoolConfig_t stGlobalPrivPoolConf; MI_IPUChnAttr_t stChnAttr; //create channel memset(&stChnAttr, 0, sizeof(stChnAttr)); stChnAttr.u32InputBufDepth = 2; stChnAttr.u32OutputBufDepth = 2; return MI_IPU_CreateCHN(s32Channel, &stChnAttr, H2SerializedReadFunc_2, pModelImage); } MI_S32 IPUCreateChannel_FromEncryptFile(MI_U32 *s32Channel, char *pModelImage) { MI_S32 s32Ret ; MI_SYS_GlobalPrivPoolConfig_t stGlobalPrivPoolConf; MI_IPUChnAttr_t stChnAttr; //create channel memset(&stChnAttr, 0, sizeof(stChnAttr)); stChnAttr.u32InputBufDepth = 2; stChnAttr.u32OutputBufDepth = 2; return MI_IPU_CreateCHN(s32Channel, &stChnAttr, H2SerializedReadFunc_2, pModelImage); } MI_S32 IPUDestroyChannel(MI_U32 s32Channel) { MI_S32 s32Ret = MI_SUCCESS; s32Ret = MI_IPU_DestroyCHN(s32Channel); return s32Ret; } void GetImage( PreProcessedData *pstPreProcessedData) { string filename=(string)(pstPreProcessedData->pImagePath); cv::Mat sample; cv::Mat img = cv::imread(filename, -1); if (img.empty()) { std::cout << " error! image don't exist!" << std::endl; exit(1); } int num_channels_ = pstPreProcessedData->intResizeC; if (img.channels() == 3 && num_channels_ == 1) { cv::cvtColor(img, sample, cv::COLOR_BGR2GRAY); } else if (img.channels() == 4 && num_channels_ == 1) { cv::cvtColor(img, sample, cv::COLOR_BGRA2GRAY); } else if (img.channels() == 4 && num_channels_ == 3) { cv::cvtColor(img, sample, cv::COLOR_BGRA2BGR); } else if (img.channels() == 1 && num_channels_ == 3) { cv::cvtColor(img, sample, cv::COLOR_GRAY2BGR); } else { sample = img; } cv::Mat sample_float; if (num_channels_ == 3) sample.convertTo(sample_float, CV_32FC3); else sample.convertTo(sample_float, CV_32FC1); cv::Mat sample_norm = sample_float; if (pstPreProcessedData->bRGB) { cv::cvtColor(sample_float, sample_norm, cv::COLOR_BGR2RGB); } cv::Mat sample_resized; cv::Size inputSize = cv::Size(pstPreProcessedData->intResizeW, pstPreProcessedData->intResizeH); if (sample.size() != inputSize) { cout << "input size should be :" << pstPreProcessedData->intResizeC << " " << pstPreProcessedData->intResizeH << " " << pstPreProcessedData->intResizeW << endl; cout << "now input size is :" << img.channels() << " " << img.rows<<" " << img.cols << endl; cout << "img is going to resize!" << endl; cv::resize(sample_norm, sample_resized, inputSize); } else { sample_resized = sample_norm; } float *pfSrc = (float *)sample_resized.data; int imageSize = pstPreProcessedData->intResizeC*pstPreProcessedData->intResizeW*pstPreProcessedData->intResizeH; for(int i=0;i<imageSize;i++) { *(pstPreProcessedData->pdata+i) = (unsigned char)(round(*(pfSrc + i))); } } static MI_BOOL GetTopN(float aData[], int dataSize, int aResult[], int TopN) { int i, j, k; float data = 0; MI_BOOL bSkip = FALSE; for (i=0; i < TopN; i++) { data = -0.1f; for (j = 0; j < dataSize; j++) { if (aData[j] > data) { bSkip = FALSE; for (k = 0; k < i; k++) { if (aResult[k] == j) { bSkip = TRUE; } } if (bSkip == FALSE) { aResult[i] = j; data = aData[j]; } } } } return TRUE; } MI_U32 _MI_IPU_GetTensorUnitDataSize(MI_IPU_ELEMENT_FORMAT eElmFormat) { switch (eElmFormat) { case MI_IPU_FORMAT_INT16: return sizeof(short); case MI_IPU_FORMAT_INT32: return sizeof(int); case MI_IPU_FORMAT_INT8: return sizeof(char); case MI_IPU_FORMAT_FP32: return sizeof(float); case MI_IPU_FORMAT_UNKNOWN: default: return 1; } } MI_U32 IPU_CalcTensorSize(MI_IPU_TensorDesc_t* pstTensorDescs) { MI_U32 u32Size = 1; MI_U32 u32UnitSize = 1; u32UnitSize = _MI_IPU_GetTensorUnitDataSize(pstTensorDescs->eElmFormat); for (int i = 0; i < pstTensorDescs->u32TensorDim; i++) { u32Size *= pstTensorDescs->u32TensorShape[i]; } u32Size *= u32UnitSize; return u32Size; } static void IPU_PrintOutputXOR(MI_IPU_SubNet_InputOutputDesc_t* desc, MI_IPU_TensorVector_t OutputTensorVector) { MI_U32 u32InputNum = desc->u32InputTensorCount; MI_U32 u32OutputNum = desc->u32OutputTensorCount; volatile MI_U32 u32XORValue = 0; MI_U8 *pu8XORValue[4]= {(MI_U8 *)&u32XORValue,(MI_U8 *)&u32XORValue+1,(MI_U8 *)&u32XORValue+2,(MI_U8 *)&u32XORValue+3 }; MI_U32 u32Count = 0; for (MI_U32 idxOutputNum = 0; idxOutputNum < desc->u32OutputTensorCount; idxOutputNum++) { MI_U8 u8Data = 0; MI_U8 *pu8Data = (MI_U8 *)OutputTensorVector.astArrayTensors[idxOutputNum].ptTensorData[0]; for(int i = 0; i < IPU_CalcTensorSize(&(desc->astMI_OutputTensorDescs[idxOutputNum])); i++) { u8Data = *(pu8Data + i); *pu8XORValue[u32Count%4] ^= u8Data; u32Count++; } } printf("All outputs XOR = 0x%08x\n", u32XORValue); } int main(int argc,char *argv[]) { if ( argc < 5 ) { std::cout << "USAGE: " << argv[0] <<": <xxxsgsimg.img> " \ << "<picture> " << "<labels> "<< "<model intput_format:RGB or BGR>"<<std::endl; exit(0); } else { std::cout<<"model_img:"<<argv[1]<<std::endl; std::cout<<"picture:"<<argv[2]<<std::endl; std::cout<<"labels:"<<argv[3]<<std::endl; std::cout<<"model input_format:"<<argv[4]<<std::endl; } char * pFirmwarePath = NULL; char * pModelImgPath = argv[1]; char * pImagePath= argv[2]; char * pLabelPath =argv[3]; char * pRGB = argv[4]; char * pfps = NULL; char * ptime = NULL; int fps = -1; int duration = -1; if (argc == 7) { pfps = argv[5]; ptime = argv[6]; fps = atoi(pfps); duration = atoi(ptime); } MI_BOOL bRGB = FALSE; if(strncmp(pRGB,"RGB",sizeof("RGB"))!=0 && strncmp(pRGB,"BGR",sizeof("BGR"))!=0 && strncmp(pRGB,"RAWDATA",sizeof("RAWDATA"))!=0) { std::cout << "model intput_format error" <<std::endl; return -1; } static char label[LABEL_CLASS_COUNT][LABEL_NAME_MAX_SIZE]; MI_U32 u32ChannelID = 0; MI_S32 s32Ret; MI_IPU_TensorVector_t InputTensorVector; MI_IPU_TensorVector_t OutputTensorVector; auto net_info = std::make_shared<NetInfo>(); ifstream LabelFile; LabelFile.open(pLabelPath); int n=0; while(1) { LabelFile.getline(&label[n][0],60); if(LabelFile.eof()) break; n++; if(n>=LABEL_CLASS_COUNT) { cout<<"the labels have line:"<<n<<" ,it supass the available label array"<<std::endl; break; } } LabelFile.close(); MI_SYS_Init(0); //1.create device cout<<"get variable size from memory__"<<std::endl; char *pmem = NULL; int fd = 0; struct stat sb; fd = open(pModelImgPath, O_RDWR); if (fd < 0) { perror("open"); return -1; } memset(&sb, 0, sizeof(sb)); if (fstat(fd, &sb) < 0) { perror("fstat"); return -1; } pmem = (char *)mmap(NULL, sb.st_size, PROT_READ, MAP_SHARED, fd, 0); if (pmem == NULL) { perror("mmap"); return -1; } if (MI_SUCCESS != MI_IPU_GetOfflineModeStaticInfo(H2SerializedReadFunc_2, pmem, &net_info->OfflineModelInfo)) { cout<<"get model variable buffer size failed!"<<std::endl; return -1; } if(MI_SUCCESS !=IPUCreateDevice(pFirmwarePath,net_info->OfflineModelInfo.u32VariableBufferSize)) { cout<<"create ipu device failed!"<<std::endl; return -1; } //2.create channel /*case 0 create module from path*/ #if 0 if(MI_SUCCESS !=IPUCreateChannel(u32ChannelID,pModelImgPath)) { cout<<"create ipu channel failed!"<<std::endl; MI_IPU_DestroyDevice(); return -1; } #endif #if 1 /*case1 create channel from memory*/ cout<<"create channel from memory__"<<std::endl; if(MI_SUCCESS !=IPUCreateChannel_FromMemory(&u32ChannelID,pmem)) { cout<<"create ipu channel failed!"<<std::endl; MI_IPU_DestroyDevice(); return -1; } #endif //3.get input/output tensor s32Ret = MI_IPU_GetInOutTensorDesc(u32ChannelID, &net_info->desc); if (s32Ret == MI_SUCCESS) { for (int i = 0; i < net_info->desc.u32InputTensorCount; i++) { cout<<"input tensor["<<i<<"] name :"<<net_info->desc.astMI_InputTensorDescs[i].name<<endl; } for (int i = 0; i < net_info->desc.u32OutputTensorCount; i++) { cout<<"output tensor["<<i<<"] name :"<<net_info->desc.astMI_OutputTensorDescs[i].name<<endl; } } unsigned char *pu8ImageData = NULL; const char* dump_input_bin = getenv("DUMP_INPUT_BIN"); MI_IPU_GetInputTensors( u32ChannelID, &InputTensorVector); int datasize = 0; if(strncmp(pRGB,"RAWDATA",sizeof("RAWDATA"))==0) { FILE* stream; stream = fopen(pImagePath,"r"); fseek(stream, 0, SEEK_END); int length = ftell(stream); cout << "length==" << length<<endl; rewind(stream); if(length != net_info->desc.astMI_InputTensorDescs[0].s32AlignedBufSize) { cout<<"please check input bin size"<<endl; exit(0); } pu8ImageData = new unsigned char[length]; datasize = fread(pu8ImageData,sizeof(unsigned char),length,stream); cout << "size==" << datasize <<endl; fclose(stream); } else { int intResizeH = net_info->desc.astMI_InputTensorDescs[0].u32TensorShape[1]; int intResizeW = net_info->desc.astMI_InputTensorDescs[0].u32TensorShape[2]; int intResizeC = net_info->desc.astMI_InputTensorDescs[0].u32TensorShape[3]; pu8ImageData = new unsigned char[intResizeH*intResizeW*intResizeC]; PreProcessedData stProcessedData; stProcessedData.intResizeC = intResizeC; stProcessedData.intResizeH = intResizeH; stProcessedData.intResizeW = intResizeW; stProcessedData.pdata = pu8ImageData; stProcessedData.pImagePath = pImagePath; if(strncmp(pRGB,"RGB",sizeof("RGB"))==0) { bRGB = TRUE; } stProcessedData.bRGB = bRGB; GetImage(&stProcessedData); datasize=intResizeH*intResizeW*intResizeC; } memcpy(InputTensorVector.astArrayTensors[0].ptTensorData[0],pu8ImageData,datasize); MI_SYS_FlushInvCache(InputTensorVector.astArrayTensors[0].ptTensorData[0], datasize); MI_IPU_GetOutputTensors( u32ChannelID, &OutputTensorVector); if(dump_input_bin) { FILE* stream_input = fopen("inputtoinvoke.bin","w"); int input_size = fwrite(InputTensorVector.astArrayTensors[0].ptTensorData[0],sizeof(unsigned char),datasize,stream_input); fclose(stream_input); } //4.invoke int times = 32; if(fps!=-1) { times =duration*fps; } printf("the times is %d \n",times); struct timespec ts_start, ts_end; clock_gettime(CLOCK_MONOTONIC, &ts_start); for (int i=0;i<times;i++ ) { struct timespec ts_start_1; clock_gettime(CLOCK_MONOTONIC, &ts_start_1); if(MI_SUCCESS!=MI_IPU_Invoke(u32ChannelID, &InputTensorVector, &OutputTensorVector)) { cout<<"IPU invoke failed!!"<<endl; delete pu8ImageData; IPUDestroyChannel(u32ChannelID); MI_IPU_DestroyDevice(); return -1; } struct timespec ts_end_1; clock_gettime(CLOCK_MONOTONIC, &ts_end_1); int elasped_time_1 = (ts_end_1.tv_sec-ts_start_1.tv_sec)*1000000+(ts_end_1.tv_nsec-ts_start_1.tv_nsec)/1000; float durationInus = 0.0; if(fps!=-1) { durationInus = 1000000.0/fps; } if ((elasped_time_1<durationInus)&&(fps!=-1)) { usleep((int)(durationInus-elasped_time_1)); } } clock_gettime(CLOCK_MONOTONIC, &ts_end); int elasped_time = (ts_end.tv_sec-ts_start.tv_sec)*1000000+(ts_end.tv_nsec-ts_start.tv_nsec)/1000; cout<<"fps:"<<1000.0/(float(elasped_time)/1000/times)<<std::endl; // show result of classify IPU_PrintOutputXOR(&net_info->desc, OutputTensorVector); int s32TopN[5]; memset(s32TopN,0,sizeof(s32TopN)); int iDimCount = net_info->desc.astMI_OutputTensorDescs[0].u32TensorDim; int s32ClassCount = 1; for(int i=0;i<iDimCount;i++ ) { s32ClassCount *= net_info->desc.astMI_OutputTensorDescs[0].u32TensorShape[i]; } float *pfData = (float *)OutputTensorVector.astArrayTensors[0].ptTensorData[0]; cout<<"the class Count :"<<s32ClassCount<<std::endl; cout<<std::endl; cout<<std::endl; GetTopN(pfData, s32ClassCount, s32TopN, 5); for(int i=0;i<5;i++) { cout<<"order: "<<i+1<<" index: "<<s32TopN[i]<<" "<<pfData[s32TopN[i]]<<" "<<label[s32TopN[i]]<<endl; } //5. put intput tensor MI_IPU_PutInputTensors(u32ChannelID,&InputTensorVector); MI_IPU_PutOutputTensors(u32ChannelID,&OutputTensorVector); //6.destroy channel/device delete pu8ImageData; IPUDestroyChannel(u32ChannelID); MI_IPU_DestroyDevice(); return 0; }
1.8.2. dla_detect¶
dla_detect is used for the inference of the detection model. The input format of the detection model needs to be RGB or BGR. During runtime, this example first loads the offline model file and drives the IPU to perform inference detection on the input image, and finally outputs the image with the detection result box in the current directory. The specific code can be referred to in
1.8.3. dla_classifyNBatch¶
dla_classifyNBatch is also used for the inference of the classification model, and the requirements for the model and input are the same as those for dla_classify. The difference lies in that this example shows the arrangement of input and output memory when calling MI_IPU_Invoke2 and MI_IPU_Invoke2Custom, as well as the precautions such as the interfaces to be called and memory alignment when the user allocates memory by themselves. The specific code can be referred to in
1.8.4. dla_simulator¶
dla_simulator is used to perform model inference on the board side, and compare it with the running results of simulator.py provided by the IPU SDK toolchain on the PC side, thereby verifying the correctness of the model inference on the board side. The model applicable to this example must be the offline model converted by the IPU SDK toolchain. The model input and format are determined by the model itself. The specific code can be referred to in
1.8.5. dla_simulatorNBatch¶
dla_simulatorNBatch is also used for model inference on the board side, and its applicable models and input requirements are the same as those of dla_simulator. The difference lies in that in the dla_simulatorNBatch example, the MI_IPU_Invoke2 interface is called to support single inference of multiple inputs. The specific code can be referred to in
1.8.6. dla_show_img_info¶
dla_show_img_info is used to display the frame rate and bandwidth statistics of the offline model for inference on the board side. It can also dump IPU log to analyze the performance of each layer of the model. The input of this tool is any model transformed through the IPU SDK toolchain. The specific code can be referred to in
1.8.7. ipu_log¶
The ipu_log tool is used to dump IPU log when it is necessary to analyze the performance of each layer of the model. This tool is also integrated in dla_show_img_info. The specific code can be referred to in
1.8.8. ipu_utilization¶
The ipu_utilization tool is used to print the utilization rate of IPU. When the application calls the MI IPU interface to perform model inference, this tool can be run to monitor the utilization rate of IPU. The specific code can be referred to in
1.8.9. ipu_server¶
ipu_server is used to create the inference service of IPU and uses the python interface to perform model inference on the PC side. Firstly, users must run this tool and configure the port number on the board side. Then, users can use rpc_simulator.py provided by the IPU SDK toolchain to connect the IP of the board side and the configured port number. Any models can be inferred by this tool, and the running results are saved in the log/output in the current directory of the PC side. For more usage of rpc_simulator.py, please refer to the IPU SDK user documentation. The code of this tool can be referred to in
2. API REFERENCE¶
2.1. API List¶
| API Name | Function |
|---|---|
| MI_IPU_CreateDevice | Create an IPU device |
| MI_IPU_DestroyDevice | Destroy an IPU device |
| MI_IPU_CreateCHN | Create an IPU channel |
| MI_IPU_DestroyCHN | Destroy an IPU channel |
| MI_IPU_GetInOutTensorDesc | Get the input and output information of the network by specified channel |
| MI_IPU_GetInputTensors | Allocate specified channel for input Tensor Buffer |
| MI_IPU_PutInputTensors | Release specified channel for input Tensor Buffer |
| MI_IPU_GetOutputTensors | Allocate specified channel for output Tensor Buffer |
| MI_IPU_PutOutputTensors | Release specified channel for output Tensor Buffer |
| MI_IPU_Invoke | Execute AI network inference |
| MI_IPU_GetInputTensors2 | Get batch input Tensor Buffer from the specified channel |
| MI_IPU_PutInputTensors2 | Release the batch input Tensor Buffer of the specified channel |
| MI_IPU_GetOutputTensors2 | Get batch output Tensor Buffer from the specified channel |
| MI_IPU_PutOutputTensors2 | Release the batch output Tensor Buffer of the specified channel |
| MI_IPU_Invoke2 | Execute countless AI network inference |
| MI_IPU_Invoke2Custom | Execute one_buf batch AI network inference |
| MI_IPU_GetOfflineModeStaticInfo | Get variable buffer size and offline model file size of an offline model |
| MI_IPU_CancelInvoke | Cancel running invoke task |
| MI_IPU_CreateCHNWithUserMem | Create an IPU channel by MMA memory which was provided by user |
| MI_IPU_DestroyDeviceExt | Destroy an IPU device by parameter |
2.2. MI_IPU_CreateDevice¶
-
Function
Create an IPU device.
-
Definition
MI_S32 MI_IPU_CreateDevice(MI_IPU_DevAttr_t *pstIPUDevAttr, SerializedReadFunc pReadFunc, char *pReadCtx, MI_U32 FWSize);
-
Parameter
Parameters Description Input/Output pstIPUDevAttr IPU device attributes structure pointer Input pReadFunc User’s custom function pointer to read file (using default file reading function by MI IPU if set NULL) Input pReadCtx IPU firmware path (default is “config/dla/ipu_firmware.bin” by MI IPU if set NULL) Input FWSize IPU firmware file size (default is auto get file size if set 0) Input -
Return value
-
MI_SUCCESS: Successful
-
Others: Failed, see error code for details
-
-
Dependence
-
Head file: mi_ipu.h
-
Library: libmi_ipu.so
-
-
Example
MI_S32 s32Ret; stDevAttr.u32MaxVariableBufSize = BufSize; /* The maximum size of the memory used by Tensor in the model */ s32Ret = MI_IPU_CreateDevice(&stDevAttr, NULL, NULL, 0); if (s32Ret != MI_SUCCESS) { printf("fail to create ipu device\n"); return s32Ret; }
2.3. MI_IPU_DestroyDevice¶
-
Function
Destroy an IPU device.
-
Definition
MI_S32 MI_IPU_DestroyDevice(void);
-
Return value
-
MI_SUCCESS: Successful
-
Others: Failed, see error code for details
-
-
Dependence
-
Head file: mi_ipu.h
-
Library: libmi_ipu.so
-
-
Example
MI_IPU_DestroyDevice();
2.4. MI_IPU_CreateCHN¶
-
Function
Create an IPU channel.
-
Definition
MI_S32 MI_IPU_CreateCHN(MI_IPU_CHN *ptChnId,MI_IPUChnAttr_t *pstIPUChnAttr, SerializedReadFunc pReadFunc, char *pReadCtx);
-
Parameter
Parameters Description Input/Ouput ptChnId The point of created IPU channel ID Input pstIPUChnAttr IPU channel attributes structure pointer Input pReadFunc User’s custom function pointer to read file (using default file reading function by MI IPU if set NULL) Input pReadCtx AI Network file path or file memory address of OS Input -
Return value
-
MI_SUCCESS: Successful
-
Others: Failed, see error code for details
-
-
Dependence
-
Head file: mi_ipu.h
-
Library: libmi_ipu.so
-
-
Note
-
MI_IPUChnAttr_t.u32BatchMax is the maximum value of batch processing. If not needed, set this value to 1 or 0.
-
MI_IPUChnAttr.u32InputBufDepth is the number of pre allocated private input tensor buffer* u32BatchMax, such as 0 or 1 or 2 or 3. When set to 0, it represents the buffer allocated from external module. If the output buffers of previous MI modules can be directly used, it is better to set input_depth to zero for memory saving.
-
MI_IPUChnAttr_t. u32OutputBufDepth is the number of pre allocated private output tensor buffer* u32BatchMax, such as 0 or 1 or 2 or 3. When set to 0, it represents the buffer allocated from external module, such as the MI_RGN module.
-
If user creates channel with one_buf batch model, MI IPU won’t pre allocate input/output tensor buffers.
-
The maximum number of IPU channels is 48.
-
-
Example
MI_S32 s32Ret, buf_depth = 3, batch_max = 1; MI_IPU_CHN u32ChnId = 0; chnAttr.u32InputBufDepth = buf_depth; chnAttr.u32OutputBufDepth = buf_depth; chnAttr. u32BatchMax = batch_max; char pReadCtx[] = "caffe_mobilenet_v2.tflite_sgsimg.img"; s32Ret = MI_IPU_CreateCHN(&u32ChnId, &chnAttr, NULL, pReadCtx); if (s32Ret != MI_SUCCESS) { printf("fail to create ipu channel\n"); MI_IPU_DestroyDevice(); return s32Ret; }
2.5. MI_IPU_DestroyCHN¶
-
Function
Destroy an IPU channel.
-
Definition
MI_S32 MI_IPU_DestroyCHN(MI_IPU_CHN u32ChnId);
-
Parameter
Parameters Description Input/Output u32ChnId IPU channel ID Input -
Return value
-
MI_SUCCESS: Successful
-
Others: Failed, see error code for details
-
-
Dependence
-
Head file: mi_ipu.h
-
Library: libmi_ipu.so
-
-
Note
- The maximum number of IPU channels is 48.
-
Example
MI_IPU_DestroyCHN(u32ChnId);
2.6. MI_IPU_GetInOutTensorDesc¶
-
Function
Get the input and output information of the network by specified channel.
-
Definition
MI_S32 MI_IPU_GetInOutTensorDesc(MI_IPU_CHN u32ChnId,MI_IPU_SubNet_InputOutputDesc_t *pstDesc);
-
Parameter
Parameters Description Input/Output u32ChnId IPU channel ID Input pstDesc Network output description structure pointer Output -
Return value
-
MI_SUCCESS: Successful
-
Others: Failed, see error code for details
-
-
Dependence
-
Head file: mi_ipu.h
-
Library: libmi_ipu.so
-
-
Note
- The maximum number of IPU channels is 48.
-
Example
MI_IPU_SubNet_InputOutputDesc_t desc; s32Ret = MI_IPU_GetInOutTensorDesc(u32ChnId, &desc); if (s32Ret) { printf("fail to get network description\n"); MI_IPU_DestroyCHN(u32ChnId); MI_IPU_DestroyDevice(); return s32Ret; } else { int iNum = desc.astMI_InputTensorDescs[0].u32TensorShape[0]; int iResizeH = desc.astMI_InputTensorDescs[0].u32TensorShape[1]; int iResizeW = desc.astMI_InputTensorDescs[0].u32TensorShape[2]; int iResizeC = desc.astMI_InputTensorDescs[0].u32TensorShape[3]; unsigned char *pu8ImageData = new unsigned char[iNum*iResizeH*iResizeW*iResizeC]; ... }
2.7. MI_IPU_GetInputTensors¶
-
Function
Allocate specified channel for input Tensor Buffer.
-
Definition
MI_S32 MI_IPU_GetInputTensors(MI_IPU_CHN u32ChnId,MI_IPU_TensorVector_t *pstInputTensorVector);
-
Parameter
Parameters Description Input/Output u32ChnId IPU channel ID Input pstInputTensorVector Input IPU Tensor array structure pointer Input -
Return value
-
MI_SUCCESS: Successful
-
Others: Failed, see error code for details
-
-
Dependence
-
Head file: mi_ipu.h
-
Library: libmi_ipu.so
-
-
Note
There are two ways to input the buffer source of tensor:
1. Allocate buffer through MI_IPU_GetInputTensors;
2. Allocated buffer by other modules of MI.
-
Example
Allocate input tensor by MI_IPU_GetInputTensors:
MI_IPU_TensorVector_t inputV; MI_IPU_TensorVector_t OutputV; MI_U8 au8MaggiePic[3*224*224] ; cv::Mat img = cv::imread(filename, -1); cv::Size inputSize = cv::Size(224,224,3) cv ::Mat imgResize ; cv::resize(img, imgResize, inputSize); memcpy(au8MaggiePic, imgResize.data, sizeof(au8MaggiePic)); s32Ret = MI_IPU_GetInputTensors(u32ChnId, &inputV); if (s32Ret == MI_SUCCESS) { memcpy(inputV.astArrayTensors[0].ptTensorData[0], au8MaggiePic, sizeof(au8MaggiePic)); MI_SYS_FlushInvCache(inputV.astArrayTensors[0].ptTensorData[0], sizeof(au8MaggiePic)); } else { printf(“fail to get buffer, please try again”); } MI_IPU_GetOutputTensors( u32ChannelID, &OutputV); if(MI_SUCCESS!=MI_IPU_Invoke(u32ChannelID, & inputV, &OutputV)) { cout<<"IPU invoke failed!!"<<endl; MI_IPU_DestroyCHN(u32ChannelID); MI_IPU_DestroyDevice(); return -1; }Use external buffer as Input tensor:
MI_IPU_TensorVector_t inputVector, outputVector; inputVector.u32TensorCount = 1; if (stBufInfo.eBufType == E_MI_SYS_BUFDATA_RAW) { inputVector.astArrayTensors[0].phyTensorAddr[0] = stBufInfo.stRawData.phyAddr; inputVector.astArrayTensors[0].ptTensorData[0] = stBufInfo.stRawData.pVirAddr; } else if (stBufInfo.eBufType == E_MI_SYS_BUFDATA_FRAME) { inputVector.astArrayTensors[0].phyTensorAddr[0] = stBufInfo.stFrameData.phyAddr[0]; inputVector.astArrayTensors[0].ptTensorData[0] = stBufInfo.stFrameData.pVirAddr[0]; inputVector.astArrayTensors[0].phyTensorAddr[1] = stBufInfo.stFrameData.phyAddr[1]; inputVector.astArrayTensors[0].ptTensorData[1] = stBufInfo.stFrameData.pVirAddr[1]; } //prepare output vector s32Ret = MI_IPU_GetOutputTensors(FdaChn, &outputVector); s32Ret = MI_IPU_Invoke(FdaChn, &inputVector, &outputVector);
2.8. MI_IPU_PutInputTensors¶
-
Function
Release specified channel for input Tensor Buffer.
-
Definition
MI_S32 MI_IPU_PutInputTensors(MI_IPU_CHN u32ChnId,MI_IPU_TensorVector_t *pstInputTensorVector);
-
Parameter
Parameters Description Input/Output u32ChnId IPU channel ID Input pstInputTensorVector Input IPU Tensor array structure pointer Output -
Return value
-
MI_SUCCESS: Successful
-
Others: Failed, see error code for details
-
-
Dependence
-
Head file: mi_ipu.h
-
Library: libmi_ipu.so
-
2.9. MI_IPU_GetOutputTensors¶
-
Function
Allocate specified channel for output Tensor Buffer.
-
Definition
MI_S32 MI_IPU_GetOutputTensors(MI_IPU_CHN u32ChnId,MI_IPU_TensorVector_t *pstInputTensorVector);
-
Parameter
Parameters Description Input/Output u32ChnId IPU channel ID Input pstInputTensorVector Output IPU Tensor array structure pointer Output -
Return value
-
MI_SUCCESS: Successful
-
Others: Failed, see error code for details
-
-
Dependence
-
Head file: mi_ipu.h
-
Library: libmi_ipu.so
-
-
Example
MI_IPU_TensorVector_t outputV; s32Ret = MI_IPU_GetOutputTensors(u32ChnId, &outputV); if (s32Ret != MI_SUCCESS) { printf(“fail to get buffer, please try again”); }
2.10. MI_IPU_PutOutputTensors¶
-
Function
Release specified channel for output Tensor Buffer.
-
Definition
MI_S32 MI_IPU_PutOutputTensors(MI_IPU_CHN u32ChnId,MI_IPU_TensorVector_t *pstInputTensorVector);
-
Parameter
Parameters Description Input/Output u32ChnId IPU channel ID Input pstOutputTensorVector Output IPU Tensor array structure pointer Input -
Return value
-
MI_SUCCESS: Successful
-
Others: Failed, see error code for details
-
-
Dependence
-
Head file: mi_ipu.h
-
Library: libmi_ipu.so
-
2.11. MI_IPU_Invoke¶
-
Function
Execute AI network inference.
-
Definition
MI_S32 MI_IPU_Invoke(MI_IPU_CHN u32ChnId,MI_IPU_TensorVector_t *pstInputTensorVector,MI_IPU_TensorVector_t *pstOuputTensorVector);
-
Parameter
Parameters Description Input/Output u32ChnId IPU channel ID Input pstInputTensorVector Input IPU Tensor array structure pointer Input pstOuputTensorVector Output IPU Tensor array structure pointer Input -
Return value
-
MI_SUCCESS: Successful
-
Others: Failed, see error code for details
-
-
Dependence
-
Head file: mi_ipu.h
-
Library: libmi_ipu.so
-
-
Note
-
MI_IPU_Invoke is synchronous api.
-
The start physical address of each single input/output tensor must be 64 bytes aligned.
-
-
Example
s32Ret =MI_IPU_Invoke(u32ChnId, &inputV, &outputV); if (s32Ret == MI_SUCCESS) { // process output buffer data // ... }
2.12. MI_IPU_GetInputTensors2¶
-
Function
Get batch input Tensor Buffer from the specified channel.
-
Definition
MI_S32 MI_IPU_GetInputTensors2(MI_IPU_CHN u32ChnId, MI_IPU_BatchInvoke_param_t *pstInvokeParam);
-
Parameter
Parameters Description Input/Output u32ChnId IPU channel ID Input pstInvokeParam Batch parameter structure pointer Input -
Return value
-
MI_SUCCESS: Successful
-
Others: Failed, see error code for details
-
-
Dependence
-
Head file: mi_ipu.h
-
Library: libmi_ipu.so
-
-
Note
There are two ways to input the buffer source of tensor:
1. Allocate Buffer through MI_IPU_GetInputTensors2;
2. Allocated buffer by other modules of MI.
2.13. MI_IPU_PutInputTensors2¶
-
Function
Release the batch input Tensor Buffer of the specified channel.
-
Definition
MI_S32 MI_IPU_PutInputTensors2(MI_IPU_CHN u32ChnId, MI_IPU_BatchInvoke_param_t *pstInvokeParam);
-
Parameter
Parameters Description Input/Output u32ChnId IPU channel ID Input pstInvokeParam Batch parameter structure pointer Input -
Return value
-
MI_SUCCESS: Successful
-
Others: Failed, see error code for details
-
-
Dependence
-
Head file: mi_ipu.h
-
Library: libmi_ipu.so
-
2.14. MI_IPU_GetOutputTensors2¶
-
Function
Get batch output Tensor Buffer from the specified channel.
-
Definition
MI_S32 MI_IPU_GetOutputTensors2(MI_IPU_CHN u32ChnId, MI_IPU_BatchInvoke_param_t *pstInvokeParam);
-
Parameter
Parameters Description Input/Output u32ChnId IPU channel ID Input pstInvokeParam Batch parameter structure pointer Input -
Return value
-
MI_SUCCESS: Successful
-
Others: Failed, see error code for details
-
-
Dependence
-
Head file: mi_ipu.h
-
Library: libmi_ipu.so
-
2.15. MI_IPU_PutOutputTensors2¶
-
Function
Release the batch output Tensor Buffer of the specified channel.
-
Definition
MI_S32 MI_IPU_PutOutputTensors2(MI_IPU_CHN u32ChnId, MI_IPU_BatchInvoke_param_t *pstInvokeParam);
-
Parameter
Parameters Description Input/Output u32ChnId IPU channel ID Input pstInvokeParam Batch parameter structure pointer Input -
Return value
-
MI_SUCCESS: Successful
-
Others: Failed, see error code for details
-
-
Dependence
-
Head file: mi_ipu.h
-
Library: libmi_ipu.so
-
2.16. MI_IPU_Invoke2¶
-
Function
Execute n_buf batch AI network inference.
-
Definition
MI_S32 MI_IPU_Invoke2(MI_IPU_CHN u32ChnId, MI_IPU_BatchInvoke_param_t *pstInvokeParam, MI_IPU_RuntimeInfo_t *pstRuntimeInfo);
-
Parameter
Parameters Description Input/Output u32ChnId IPU channel ID Input pstInvokeParam Batch parameter structure pointer Input pstRuntimeInfo IPU operation information structure pointer Input -
Return value
-
MI_SUCCESS: Successful
-
Others: Failed, see error code for details
-
-
Dependence
-
Head file: mi_ipu.h
-
Library: libmi_ipu.so
-
-
Note
-
MI_IPU_Invoke2 is synchronous api.
-
MI_IPU_Invoke2 can only be used with n_buf mode model.
-
The start physical address of each single input/output tensor must be 64 bytes aligned.
-
The start physical address of variable tensor which is allocated by user must be 64 bytes aligned.
-
-
Example
MI_IPU_BatchInvoke_param_t stInvokeParam; MI_IPU_RuntimeInfo_t stRuntimeInfo; stInvokeParam.u32BatchN = 16; stInvokeParam.s32TaskPrio = 20; stInvokeParam.u32IpuAffinity = 0; // Called by ipu s32Ret = MI_IPU_GetInputTensors2(u32ChnId, &stInvokeParam); if (s32Ret != MI_SUCCESS) { printf(“Error: MI_IPU_GetInputTensors2 return %d\n”, s32Ret); return -1; } s32Ret = MI_IPU_GetOutputTensors2(u32ChnId, &stInvokeParam); if (s32Ret != MI_SUCCESS) { printf(“Error: MI_IPU_ GetOutputTensors2 return %d\n”, s32Ret); MI_IPU_PutInputTensors2(u32ChnId, &stInvokeParam); return -1; } s32Ret = MI_IPU_Invoke2(u32ChnId, &stInvokeParam, &stRuntimeInfo); if (s32Ret == MI_SUCCESS) { // process output buffer data // ... printf(“bw_total=%llu, bw_read=%llu, bw_read=%llu, iputime=%llu\n”, stRuntimeInfo.u64BandWidth, stRuntimeInfo.u64BandWidthRead, stRuntimeInfo.u64BandWidthWrite, stRuntimeInfo.u64IpuTime); }
2.17. MI_IPU_Invoke2Custom¶
-
Function
Execute one_buf batch AI network inference.
-
Definition
MI_S32 MI_IPU_Invoke2Custom(MI_IPU_CHN u32ChnId, MI_IPU_BatchInvoke_param_t *pstInvokeParam, MI_IPU_RuntimeInfo_t *pstRuntimeInfo);
-
Parameter
Parameters Description Input/Output u32ChnId IPU channel ID Input pstInvokeParam Batch parameter structure pointer Input pstRuntimeInfo IPU operation information structure pointer Input -
Return value
-
MI_SUCCESS: Successful
-
Others: Failed, see error code for details
-
-
Dependence
-
Head file: mi_ipu.h
-
Library: libmi_ipu.so
-
-
Note
-
MI_IPU_Invoke2 is synchronous api.
-
MI_IPU_Invoke2 can only be used with one_buf mode model.
-
The start physical address of each single input/output tensor must be 64 bytes aligned.
-
The start physical address of variable tensor which is allocated by user must be 64 bytes aligned.
-
-
Example
// input tensor number=1 output tensor number=1 MI_IPU_BatchInvoke_param_t stInvokeParam; MI_IPU_RuntimeInfo_t stRuntimeInfo; stInvokeParam.u32BatchN = 10; stInvokeParam.s32TaskPrio = 20; stInvokeParam.u32IpuAffinity = 0; //Called by ipu int s32InputSize, s32InputSizeOne; s32InputSizeOne = stDesc.astMI_InputTensorDescs[0].u32BufSize; s32InputSize = s32InputSizeOne * stInvokeParam.u32BatchN; int s32OutputSize, s32OutputSizeOne; s32OutputSizeOne = stDesc.astMI_OutputTensorDescs[0].u32BufSize; s32OutputSize = s32OutputSizeOne * stInvokeParam.u32BatchN; s32Ret = MI_SYS_MMA_Alloc(0, NULL, s32InputSize, &u64InputPhyAddr); if (s32Ret != MI_SUCCESS) { printf("fail to allocate input buffer\n"); return -1; } s32Ret = MI_SYS_Mmap(u64InputPhyAddr, s32InputSize, &pInputVirAddr, TRUE); if (s32Ret != MI_SUCCESS) { MI_SYS_MMA_Free(0, u64InputPhyAddr); printf("Error: fail to map input address, error=%d\n", s32Ret); return -1; } stInvokeParam.astArrayTensors[0].ptTensorData[0] = pInputVirAddr; stInvokeParam.astArrayTensors[0].phyTensorAddr[0] = u64InputPhyAddr; s32Ret = MI_SYS_MMA_Alloc(0, NULL, s32OutputSize, &u64OutputPhyAddr); if (s32Ret != MI_SUCCESS) { MI_SYS_Munmap(pInputVirAddr, s32InputSize); MI_SYS_MMA_Free(0, u64InputPhyAddr); printf("fail to allocate output buffer\n"); return -1; } s32Ret = MI_SYS_Mmap(u64OutputPhyAddr, s32OutputSize, &pOutputVirAddr, TRUE); if (s32Ret != MI_SUCCESS) { MI_SYS_Munmap(pInputVirAddr, s32InputSize); MI_SYS_MMA_Free(0, u64InputPhyAddr); MI_SYS_MMA_Free(0, u64OutputPhyAddr); printf("Error: fail to map output address, error=%d\n", s32Ret); return -1; } stInvokeParam.astArrayTensors[1].ptTensorData[0] = pOutputVirAddr; stInvokeParam.astArrayTensors[1].phyTensorAddr[0] = u64OutputPhyAddr; for (int i = 0; i < stInvokeParam.u32BatchN; i++) { memcpy(pInputVirAddr+i*s32InputSizeOne; pInputBuf[i], s32InputSizeOne); } MI_SYS_FlushInvCache(pInputVirAddr, s32InputSize); s32Ret = MI_IPU_Invoke2Custom(channel, &stInvokeParam, NULL); if (s32Ret != MI_SUCCESS) { printf("fail to invoke\n"); MI_SYS_Munmap(pInputVirAddr, s32InputSize); MI_SYS_MMA_Free(0, u64InputPhyAddr); MI_SYS_Munmap(pOutputVirAddr, s32OutputSize); MI_SYS_MMA_Free(0, u64OutputPhyAddr); return -1; } else { // process output data for (int i = 0; i < stInvokeParam.u32BatchN; i++) { // pOutputVirAddr+i*s32OutputSizeOne } }
2.18. MI_IPU_GetOfflineModeStaticInfo¶
-
Function
Get variable buffer size and offline model file size of an offline model.
-
Definition
MI_S32 MI_IPU_GetOfflineModeStaticInfo(SerializedReadFunc pReadFunc, char *pReadCtx, MI_IPU_OfflineModelStaticInfo_t *pStaticInfo);
-
Parameter
Parameters Description Input/Output pReadFunc User’s custom function pointer to read file (using default file reading function by MI IPU if set NULL) Input pReadCtx Offline model file path Input pStaticInfo Offline model static information structure pointer Input -
Return value
-
MI_SUCCESS: Successful
-
Others: Failed, see error code for details
-
-
Dependence
-
Head file: mi_ipu.h
-
Library: libmi_ipu.so
-
-
Example
MI_IPU_OfflineModelStaticInfo_t staticInfo; s32Ret = MI_IPU_GetOfflineModeStaticInfo(NULL, pModelImgPath, &staticInfo); if (s32Ret == MI_SUCCESS) { printf("variable buffer size: %u bytes\n%s size: %u bytes\n", staticInfo.u32VariableBufferSize, pModelImgPath, staticInfo.u32OfflineModelSize); }
2.19. MI_IPU_CancelInvoke¶
-
Function
Cancel running invoke task
-
Definition
MI_S32 MI_IPU_CancelInvoke(MI_U32 u32ThreadId, MI_IPU_CHN u32ChnId);
-
Parameter
Parameters Description Input/Output u32ThreadId The thread ID of cancelled invoke task Input u32ChnId The channel ID of cancelled invoke task Input -
Return value
- MI_SUCCESS: Successful
- Others: Failed, see error code for details
-
Dependence
- Head file: mi_ipu.h
- Library: libmi_ipu.so
-
Note
- MI_IPU_CancelInvoke can only cancel invoke task which belongs to this process.
-
Example
Thread-0: s32Ret =MI_IPU_Invoke(u32ChnId, &inputV, &outputV); OR s32Ret = MI_IPU_Invoke2(u32ChnId, &stInvokeParam, &stRuntimeInfo); OR s32Ret = MI_IPU_Invoke2Custom(channel, &stInvokeParam, NULL); if (s32Ret == E_IPU_ERR_INVOKE_CANCELED) { printf("invoke has been canceled\n"); } Thread-1: s32Ret = MI_IPU_CancelInvoke(u32ThreadId, u32ChnId); if (s32Ret == MI_SUCCESS) { printf("succeed to cancel invoke task, thread id=%u, channel id=%u\n", u32ThreadId, u32ChnId); } else if (s32Ret == E_IPU_ERR_NOT_FOUND) { printf("do not find invoke task belongs to thread id=%u, channel id=%u\n", u32ThreadId, u32ChnId); } else if (s32Ret == E_IPU_ERR_NOT_SUPPORT) { printf("do not support cancel invoke on this platform\n"); } else { printf("unexpected error=%d\n", s32Ret); }
2.20. MI_IPU_CreateCHNWithUserMem¶
-
Function
Create an IPU channel by MMA memory which was provided by user.
-
Definition
MI_S32 MI_IPU_CreateCHNWithUserMem(MI_IPU_CHN *ptChnId, MI_IPUChnAttr_t *pstChnAttr, MI_PHY u64ModelPA);
-
Parameter
Parameters Description Input/Output ptChnId The pointer of created IPU channel ID Output pstIPUChnAttr IPU channel attributes structure pointer Input u64ModelPA AI Network file MMA memory address Input -
Return value
-
MI_SUCCESS: Successful
-
Others: Failed, see error code for details
-
-
Dependence
-
Head file: mi_ipu.h
-
Library: libmi_ipu.so
-
-
Note
- MI_IPUChnAttr_t.u32BatchMax is the maximum value of batch processing. If not needed, set this value to 1 or 0.
- MI_IPUChnAttr.u32InputBufDepth is the number of pre allocated private input tensor buffer* u32BatchMax, such as 0 or 1 or 2 or 3. When set to 0, it represents the buffer allocated from external module. If the output buffers of previous MI modules can be directly used, it is better to set input_depth to zero for memory saving.
- MI_IPUChnAttr_t. u32OutputBufDepth is the number of pre allocated private output tensor buffer* u32BatchMax, such as 0 or 1 or 2 or 3. When set to 0, it represents the buffer allocated from external module, such as the MI_RGN module.
- If user creates channel with one_buf batch model, MI IPU won’t pre allocate input/output tensor buffers.
- The maximum number of IPU channels is 48.
- U64ModelPA can only be released after calling MI_IPU_DestroyCHN
-
Example
MI_S32 s32Ret, buf_depth = 3, batch_max = 1; MI_IPU_CHN u32ChnId = 0; MI_IPUChnAttr_t chnAttr; MI_S32 fd, s32ModelSize; MI_U64 u64ModelPA = 0; void *pmem = NULL; void *pModelVA = NULL; char *pModelPath = "caffe_mobilenet_v2.tflite_sgsimg.img"; chnAttr.u32InputBufDepth = buf_depth; chnAttr.u32OutputBufDepth = buf_depth; chnAttr.u32BatchMax = batch_max; fd = open(pModelPath, O_RDONLY); if (fd < 0) { perror("Fail to open model!\n"); return -1; } s32ModelSize = lseek(fd, 0, SEEK_END); pmem = mmap(NULL, s32ModelSize, PROT_READ, MAP_SHARED, fd, 0); if (pmem == MAP_FAILED) { perror("mmap"); close(fd); return -1; } s32Ret = MI_SYS_MMA_Alloc(0, NULL, s32ModelSize, &u64ModelPA); if (s32Ret != MI_SUCCESS) { printf("fail to allocate model buf!\n"); munmap(pmem, s32ModelSize); close(fd); return s32Ret; } s32Ret = MI_SYS_Mmap(u64ModelPA, s32ModelSize, &pModelVA, TRUE); if (s32Ret != MI_SUCCESS) { printf("fail to mmap"); MI_SYS_MMA_Free(0, u64PhyAddr); munmap(pmem, s32ModelSize); close(fd); return s32Ret; } memcpy(pModelVA, pmem, s32ModelSize); MI_SYS_FlushInvCache(pModelVA, s32ModelSize); s32Ret = MI_IPU_CreateCHNWithUserMem(&u32ChnId, &chnAttr, u64ModelPA); if (s32Ret != MI_SUCCESS) { printf("fail to create ipu channel\n"); MI_SYS_Munmap(pModelVA, s32ModelSize); MI_SYS_MMA_Free(0, u64PhyAddr); munmap(pmem, s32ModelSize); close(fd); return s32Ret; }
2.21. MI_IPU_DestroyDeviceExt¶
-
Function
Destroy an IPU device by parameter.
-
Definition
MI_S32 MI_IPU_DestroyDeviceExt(MI_IPU_DevAttr_t *pstIPUDevAttr);
-
Return value
-
MI_SUCCESS: Successful
-
Others: Failed, see error code for details
-
-
Dependence
-
Head file: mi_ipu.h
-
Library: libmi_ipu.so
-
-
Example
MI_S32 s32Ret; MI_IPU_DevAttr_t stDevAttr; stDevAttr.u32MaxVariableBufSize = BufSize; /* The maximum size of the memory used by Tensor in the model */ stDevAttr.u32VariableGroup = 0; stDevAttr.u32CoreMask = IPU_DEV_0; s32Ret = MI_IPU_CreateDevice(&stDevAttr, NULL, NULL, 0); if (s32Ret != MI_SUCCESS) { printf("fail to create ipu device\n"); return s32Ret; } ... MI_IPU_DestroyDeviceExt(&stDevAttr);
3. DATA TYPE¶
3.1. Data Type List¶
The table below lists the releated data type definition:
| Data Type | Definition |
|---|---|
| SerializedReadFunc | Used for customized file reading mode with customized AI network storage format supported |
| MI_IPU_ELEMENT_FORMAT | Define enumeration type of IPU input data |
| MI_IPU_BatchMode_e | Define enumeration type of IPU batch buffer mode |
| MI_IPU_LayoutType_e | Define enumeration type of tensor layout |
| MI_IPU_IpuWorkMode_e | Define enumeration type of IPU work mode |
| MI_IPU_TensorDesc_t | Define IPU Tensor shape structure |
| MI_IPU_SubNet_InputOutputDesc_t | Define IPU subnet input/output description structure |
| MI_IPU_Tensor_t | Define IPU Tensor address structure |
| MI_IPU_TensorVector_t | Define IPU Tensor array structure |
| MI_IPU_DevAttr_t | Define IPU device attributes structure |
| MI_IPU_ChnAttr_t | Define IPU channel attributes structure |
| MI_IPU_BatchInvoke_param_t | Define the batch parameter structure |
| MI_IPU_RuntimeInfo_t | Define the IPU operation information structure |
| MI_IPU_OfflineModelStaticInfo_t | Define IPU offline model static information structure |
3.2. SerializedReadFunc¶
-
Description
Used for customized file reading mode with customized AI network storage format supported.
-
Definition
typedef int (*SerializedReadFunc)(void *dst_buf,int offset, int size, char *ctx);
-
Members
Name Description dst_buf The address of data offset The offset from the beginning of file size Reading size ctx File path
3.3. MI_IPU_ELEMENT_FORMAT¶
-
Description
Enumeration type of IPU input data.
-
Definition
typedef enum { MI_IPU_FORMAT_U8, MI_IPU_FORMAT_NV12, MI_IPU_FORMAT_INT16, MI_IPU_FORMAT_INT32, MI_IPU_FORMAT_INT8, MI_IPU_FORMAT_FP32, MI_IPU_FORMAT_UNKNOWN, MI_IPU_FORMAT_ARGB8888, MI_IPU_FORMAT_ABGR8888, MI_IPU_FORMAT_GRAY, MI_IPU_FORMAT_COMPLEX64, } MI_IPU_ELEMENT_FORMAT; -
Members
Name Description MI_IPU_FORMAT_U8 UINT8 format MI_IPU_FORMAT_NV12 NV12 format, such as YUV MI_IPU_FORMAT_INT16 INT16 format MI_IPU_FORMAT_INT32 INT32 format MI_IPU_FORMAT_INT8 INT8 format MI_IPU_FORMAT_FP32 FLOAT format MI_IPU_FORMAT_UNKNOWN Unknown MI_IPU_FORMAT_ARGB8888 ARGB8888 format MI_IPU_FORMAT_ABGR8888 ABGR8888 format MI_IPU_FORMAT_GRAY GRAY format MI_IPU_FORMAT_COMPLEX64 COMPLEX64 format -
Note
-
ARGB/RGB/BGR Tensor belongs to MI_IPU_FORMAT_U8 format.
-
Only Input Tensor supports MI_IPU_FORMAT_NV12 format.
-
Only Output Tensor supports MI_IPU_FORMAT_FP32 format.
-
3.4. MI_IPU_BatchMode_e¶
-
Description
Define enumeration type of IPU batch buffer mode.
-
Definition
typedef enum { E_IPU_BATCH_N_BUF_MODE = 0, E_IPU_BATCH_ONE_BUF_MODE, } MI_IPU_BatchMode_e; -
Members
Name Description E_IPU_BATCH_N_BUF_MODE Model’s batch buffer mode is n_buf mode E_IPU_BATCH_ONE_BUF_MODE Model’s batch buffer mode is one_buf mode -
Related data type and interface
3.5. MI_IPU_LayoutType_e¶
-
Description
Define enumeration type of tensor layout.
-
Definition
typedef enum { E_IPU_LAYOUT_TYPE_NHWC = 0, E_IPU_LAYOUT_TYPE_NCHW, } MI_IPU_LayoutType_e; -
Members
Name Description E_IPU_LAYOUT_TYPE_NHWC This tensor’s layout is NHWC E_IPU_LAYOUT_TYPE_NCHW This tensor’s layout is NCHW -
Related data type and interface
3.6. MI_IPU_IpuWorkMode_e¶
-
Description
Define enumeration type of IPU work mode.
-
Definition
typedef enum { E_IPU_IPU_WORK_MODE_SINGLECORE = 0, E_IPU_IPU_WORK_MODE_MULTICORE, } MI_IPU_IpuWorkMode_e; -
Members
Name Description E_IPU_IPU_WORK_MODE_SINGLECORE The model is single-core model E_IPU_IPU_WORK_MODE_MULTICORE The model is multi-core model -
Related data type and interface
3.7. MI_IPU_TensorDesc_t¶
-
Description
IPU Tensor description structure.
-
Definition
typedef struct MI_IPU_TensorDesc_s { MI_U32 u32TensorDim; MI_IPU_ELEMENT_FORMAT eElmFormat; MI_U32 u32TensorShape[MI_IPU_MAX_TENSOR_DIM]; MI_S8 name[MAX_TENSOR_NAME_LEN]; MI_U32 u32InnerMostStride; MI_FLOAT fScalar; MI_S64 s64ZeroPoint; MI_S32 s32AlignedBufSize; MI_U32 u32BufSize; MI_U32 u32InputWidthAlignment; MI_U32 u32InputHeightAlignment; MI_IPU_LayoutType_e eLayoutType; MI_U32 au32Reserve[4]; // reserved } MI_IPU_TensorDesc_t; -
Members
Name Description u32TensorDim Tensor dimension eElmFormat Tensor data format u32TensorShape Tensor shape array name Tensor name u32InnerMostStride Tensor inner most dimension’s length (unit byte) fScalar Tensor quantization coefficient s64ZeroPoint Tensor quantization offset s32AlignedBufSize Tensor buffer aligned size u32BufSize Tensor buffer size u32InputWidthAlignment Input tensor aligned size on horizontal direction u32InputHeightAlignment Input tensor aligned size on vertical direction eLayoutType Tensor layout type au32Reserve Reserved -
Note
-
The maximum dimension is 10. The following macro definitions are recommended:
#define MI_IPU_MAX_TENSOR_DIM (10)
-
Input data must align to u32InputWidthAlignment and u32InputHeightAlignment, otherwise the result may be incorrect.
-
Alignment rules
input_formats rule RGB/BGR No alignment rule RGBA/BGRA W = ALIGN_UP(W * 4, input_width_alignment) / 4
input_width_alignment default is 1YUV_NV12 H = ALIGN_UP(H, input_height_alignment)
input_height_alignment default is 2
W = ALIGN_UP(W, input_width_alignment)
input_width_alignment default is 2GRAY H = ALIGN_UP(H, input_height_alignment)
input_height_alignment default is 1
W = ALIGN_UP(W, input_width_alignment)
input_width_alignment default is 1RAWDATA_F32_NHWC No alignment rule RAWDATA_S16_NHWC No alignment rule
-
3.8. MI_IPU_SubNet_InputOutputDesc_t¶
-
Description
IPU subnet input/output description structure.
-
Definition
typedef struct MI_IPU_SubNet_InputOutputDesc_s { MI_U32 u32InputTensorCount; MI_U32 u32OutputTensorCount; MI_IPU_TensorDesc_t astMI_InputTensorDescs[MI_IPU_MAX_INPUT_TENSOR_CNT]; MI_IPU_TensorDesc_t astMI_OutputTensorDescs[MI_IPU_MAX_OUTPUT_TENSOR_CNT]; } MI_IPU_SubNet_InputOutputDesc_t; -
Members
Name Description u32InputTensorCount Number of input tensor u32OutputTensorCount Number of output tensor astMI_InputTensorDescs Input Tensor shape structure array astMI_OutputTensorDescs Output Tensor shape structure array
3.9. MI_IPU_Tensor_t¶
-
Description
IPU Tensor address structure.
-
Definition
typedef struct MI_IPU_Tensor_s { void *ptTensorData[2]; MI_PHY phyTensorAddr[2];//notice that this is miu bus addr,not cpu bus addr. } MI_IPU_Tensor_t; -
Members
Name Description ptTensorData The virtual address of Tensor buffer phyTensorAddr The physical address of Tensor buffer
3.10. MI_IPU_TensorVector_t¶
-
Description
IPU Tensor array structure.
-
Definition
typedef struct MI_IPU_TensorVector_s { MI_U32 u32TensorCount; MI_IPU_Tensor_t astArrayTensors[MI_IPU_MAX_TENSOR_CNT]; } MI_IPU_TensorVector_t; -
Members
Name Description u32TensorCount The number of Tensor astArrayTensors Address information of each Tensor
3.11. MI_IPU_DevAttr_t¶
-
Description
IPU device attributes structure.
-
Definition
typedef struct MI_IPU_DevAttr_s { MI_U32 u32MaxVariableBufSize; MI_U32 u32YUV420_W_Pitch_Alignment; // unused MI_U32 u32YUV420_H_Pitch_Alignment; // unused MI_U32 u32XRGB_W_Pitch_Alignment; // unused MI_U32 u32VariableGroup; // variable group ID MI_U32 u32CoreMask; // ipu core mask MI_U32 au32Reserve[6]; // reserve } MI_IPU_DevAttr_t; -
Members
Name Description u32MaxVariableBufSize Maximum memory cost of IPU u32YUV420_W_Pitch_Alignment Unused u32YUV420_H_Pitch_Alignment Unused u32XRGB_W_Pitch_Alignment Unused u32VariableGroup Variable memory group ID u32CoreMask IPU core mask au32Reserve Reserved
3.12. MI_IPU_ChnAttr_t¶
-
Description
IPU channel attributes structure.
-
Definition
typedef struct MI_IPU_ChnAttr_s { MI_U32 u32SubNetId; MI_U32 u32OutputBufDepth; MI_U32 u32InputBufDepth; MI_U32 u32BatchMax; MI_U32 au32Reserve[8]; // reserved } MI_IPUChnAttr_t; -
Members
Name Description u32SubNetId Subnetwork ID u32OutputBufDepth The depth of output tensor buffer u32InputBufDepth The depth of input tensor buffer u32BatchMax Maximum batch size au32Reserve Reserved -
Note
Maximum depth of IPU input/output buffer is 3. The following macro definitions are recommended:
#define MAX_IPU_INPUT_OUTPUT_BUF_DEPTH (3)
3.13. MI_IPU_BatchInvoke_param_t¶
-
Description
Define the batch parameter structure.
-
Definition
typedef struct MI_IPU_BatchInvoke_param_s { MI_PHY u64VarBufPhyAddr; MI_U32 u32VarBufSize; MI_U32 u32BatchN; MI_S32 s32TaskPrio; MI_U32 u32IpuAffinity; MI_IPU_Tensor_t astArrayTensors[MI_IPU_MAX_BATCH_TENSOR_CNT]; MI_U32 au32Reserve[8]; // reserved } MI_IPU_BatchInvoke_param_t; -
Members
Name Description u64VarBufPhyAddr Variable buffer physical address allocated by user u32VarBufSize Variable buffer size allocated by user u32BatchN Number of batches s32TaskPrio Task priority u32IpuAffinity Binding ipu core astArrayTensors Batch process all input and output tensor buffer addresses au32Reserve Reserved -
Note
-
The astArrayTensors array stores all input and output tensor buffer addresses of batch processing. The rule is to store all input tensor buffer addresses in turn, and then store all output tensor buffer addresses.
-
The start physical address of each single input/output tensor must be 64 bytes aligned.
-
The start physical address of variable tensor which is allocated by user must be 64 bytes aligned.
-
3.14. MI_IPU_RuntimeInfo_t¶
-
Description
Define the IPU operation information structure.
-
Definition
typedef struct MI_IPU_RuntimeInfo_s { MI_U64 u64BandWidth; MI_U64 u64IpuTime; MI_U64 u64BandWidthRead; MI_U64 u64BandWidthWrite; MI_U32 au32Reserve[8]; // reserved } MI_IPU_RuntimeInfo_t; -
Members
Name Description u64BandWidth Total bandwidth (bytes) u64IpuTime IPU processing time (us) u64BandWidthRead Bandwidth of reading (bytes) u64BandWidthWrite Bandwidth of writing (bytes) au32Reserve Reserved
3.15. MI_IPU_OfflineModelStaticInfo_t¶
-
Description
Define IPU offline model static information structure.
-
Definition
typedef struct MI_IPU_OfflineModelStaticInfo_s { MI_U32 u32VariableBufferSize; MI_U32 u32OfflineModelSize; MI_IPU_BatchMode_e eBatchMode; MI_U32 u32TotalBatchNumTypes; MI_U32 au32BatchNumTypes[MI_IPU_MAX_BATCH_TYPE_NUM]; MI_IPU_IpuWorkMode_e eIpuWorkMode; MI_U32 au32Reserve[8]; // reserved } MI_IPU_OfflineModelStaticInfo_t; -
Members
Name Description u32VariableBufferSize Variable buffer size for running the offline model u32OfflineModelSize Offline model file size eBatchMode Offline model batch buffer mode u32TotalBatchNumTypes The number of batchNum types that this model supports au32BatchNumTypes n_buf mode: The max batch number that this model supports and the biggest number of all the batches suggested in this model
one_buf mode: All batchNum types that this model supportseIpuWorkMode Offline model work mode au32Reserve Reserved -
Note
-
If the model’s eBatchMode is E_IPU_BATCH_N_BUF_MODE:
u32TotalBatchNumTypes will return 2.
au32BatchNumTypes[0] will return the max batch number that this model supports when running on board.
au32BatchNumTypes[1] will return the biggest number of all the batches suggested in this model. (The batchNum suggested shall be a number or several numbers of the form 2n where n>=0. When au32BatchNumTypes[1] = 2n, which means the batchNums suggested of this model are 20, 21, ..., 2(n-1), 2n)
Ex:
au32BatchNumTypes[0] returns 128, which means this model can support 1~128 batches.
au32BatchNumTypes[1] returns 8, which means the batch numbers suggested in this model are 1, 2, 4, 8.
-
If the model’s eBatchMode is E_IPU_BATCH_ONE_BUF_MODE:
u32TotalBatchNumTypes will return the number of batchNum types that this model supports.
au32BatchNumTypes[0] ~ au32BatchNumTypes[u32TotalBatchNumTypes - 1] will return all batchNum types that this model supports.
Ex:
u32TotalBatchNumTypes==3
au32BatchNumTypes[0]==10
au32BatchNumTypes[1]==20
au32BatchNumTypes[2]==30
which means this model can support 10 batches, 20 batches and 30 batches.
-
4. ERROR CODE¶
| Error Code | Definition | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | MI_SUCCESS | Success |
| 1 | E_IPU_ERR_INVALID_CHNID | Invlalid channel ID |
| 2 | E_IPU_ERR_CHNID_EXIST | Channel already exists |
| 3 | E_IPU_ERR_CHNID_UNEXIST | Channel does not exist |
| 4 | E_IPU_ERR_NOMEM | Failure caused by malloc memory |
| 5 | E_IPU_ERR_NOBUF | Failure caused by malloc buffer |
| 6 | E_IPU_ERR_BADADDR | Bad address, buffer address is not gotten from IPU buffer allocator |
| 7 | E_IPU_ERR_SYS_TIMEOUT | System timeout |
| 8 | E_IPU_ERR_FILE_OPERATION | File cannot be opened or read or written |
| 9 | E_IPU_ERR_ILLEGAL_TENSOR_BUFFER_SIZE | Tensor buffer size does not meet the requirement, usually less than the requirement |
| 10 | E_IPU_ERR_ILLEGAL_BUFFER_DEPTH | Input or output buffer depth quantum exceeds maximum number |
| 11 | E_IPU_ERR_ILLEGAL_INPUT_OUTPUT_DESC | Network description is illegal, usually input or output buffer quantum is wrong |
| 12 | E_IPU_ERR_ILLEGAL_INPUT_OUTPUT_PARAM | Uer's input or output buffer quantum does not match network description |
| 13 | E_IPU_ERR_MAP | Address mapping error |
| 14 | E_IPU_ERR_INIT_FIRMWARE | Fail to initialize IPU firmware |
| 15 | E_IPU_ERR_CREATE_CHANNEL | Fail to create channel |
| 16 | E_IPU_ERR_DESTROY_CHANNEL | Fail to destroy channel |
| 17 | E_IPU_ERR_INVOKE | Fail to invoke |
| 18 | E_IPU_ERR_SET_MALLOC_REGION | Fail to set malloc region for freertos |
| 19 | E_IPU_ERR_SET_IPU_PARAMETER | Fail to set IPU parameter |
| 20 | E_IPU_ERR_INVALID_PITCH_ALIGNMENT | Invalid pitch alignment |
| 21 | E_IPU_ERR_NO_CREATED_IPU_DEVICE | There is no created IPU device |
| 22 | E_IPU_ERR_GET_IPU_VERSION | Fail to get IPU version from IPU firmware |
| 23 | E_IPU_ERR_MISMATCH_IPU_HEAD_FILE | IPU head files version not matched |
| 24 | E_IPU_ERR_NO_SUPPORT_REQ | IPU firmware does not support this request |
| 25 | E_IPU_ERR_FAILED | Unexpected error |
| 26 | E_IPU_ERR_SEND_REQUEST | Fail to send request to IPU |
| 27 | E_IPU_ERR_GET_FIRMWARE_INFO | Fail to get IPU firmware information |
| 28 | E_IPU_ERR_INVALID_IPUCORE_BOOTING_PARAM | Invalid IPU cores booting parameters |
| 29 | E_IPU_ERR_INVALID_IPUCORE_SHUTDOWNING_PARAM | Invalid IPU cores shutdowning parameters |
| 30 | E_IPU_ERR_NO_MULTICORE_ENV | Multicore mode needs all ipu cores being alive |
| 31 | E_IPU_ERR_INVALID_TASK_PRIORITY | Invalid ipu task priority |
| 32 | E_IPU_ERR_DEV_SHUTDOWN | Ipu core has been shutdown |
| 33 | E_IPU_ERR_DEV_FAIL_RESET | Fail to reset ipu |
| 34 | E_IPU_ERR_DEV_FAIL_SHUTDOWN | Fail to shutdown ipu |
| 35 | E_IPU_ERR_NO_AVAILABLE_DEV | No available ipu dev |
| 36 | E_IPU_ERR_RESET_OFF | Reset function is off |
| 37 | E_IPU_ERR_INVALID_BATCH_NUM | batch number error |
| 38 | E_IPU_ERR_BATCH_TYPE | batch type error |
| 39 | E_IPU_ERR_BATCH_MODE | batch mode error |
| 40 | E_IPU_ERR_NO_AVAILABLE_BATCH_MODE | do not find available batch mode |
| 41 | E_IPU_ERR_IPU_HANG | invoke was dropped due to ipu hang |
| 42 | E_IPU_ERR_NO_RESET_DEV | no reset ipu dev |
| 43 | E_IPU_ERR_NO_BATCH_PARAM | no batch parameter |
| 44 | E_IPU_ERR_INVALID_MODEL_BUFFER | invalid user model buffer physical address or size |
| 45 | E_IPU_ERR_INVALID_VARIABLE_BUFFER | invalid variable buffer physical address or size |
| 46 | E_IPU_ERR_NOT_ASSIGN_CORE | not assign ipu core when use user's variable buffer |
| 47 | E_IPU_ERR_SWDISP_NOT_REGISTER | model has unsupported swdisp function |
| 48 | E_IPU_ERR_SWDISP_NOT_FIND_TASKID | not find swdisp task id |
| 49 | E_IPU_ERR_SWDISP_INVALID_PARAM | invalid swdisp parameter |
| 50 | E_IPU_ERR_SWDISP_UNEXPECTED | unexpected swdisp error |
| 51 | E_IPU_ERR_SWDISP_UNKNOWN | unknown swdisp error |
| 52 | E_IPU_ERR_BAD_PHY_ADDR_ALIGNMENT | ipu buffer physical addr not aligned |
| 53 | E_IPU_ERR_MISMATCH_INVOKE_FUNC | n_buf/one_buf batch model should use MI_IPU_Invoke2/MI_IPU_Invoke2Custom |
| 54 | E_IPU_ERR_MISMATCH_MODEL | other platform's model |
| 55 | E_IPU_ERR_INVOKE_CANCELED | invoke has been canceled |
| 56 | E_IPU_ERR_INVOKE_CANCEL_FAIL | fail to cancel invoke |
| 57 | E_IPU_ERR_NOT_SUPPORT_CANCELINVOKE | do not support cancel invoke |
| 58 | E_IPU_ERR_PERMISSION_DENIED | permission denied |
| 59 | E_IPU_ERR_INVOKE_INTERRUPT | invoke task was interrupted (maybe on suspend), please try again |
| 256 | E_IPU_ERR_NO_AVAILABLE_CHNID | There is no available channel |
5. PROCFS INTRODUCTION¶
5.1. Summary¶
The main ways to debug IPU through the console is procfs.
-
IPU Procfs creates the node
proc/mi_modules/mi_ipu/mi_ipu0when opening the device (mi_dev), and deletes the node when closing the device. -
IPU Procfs creates the node
proc/mi_modules/mi_ipu/debug_hal/xxxwhen insmod ko.
5.2. How to cat MMA info¶
# cat /proc/mi_modules/mi_sys/mi_sys0
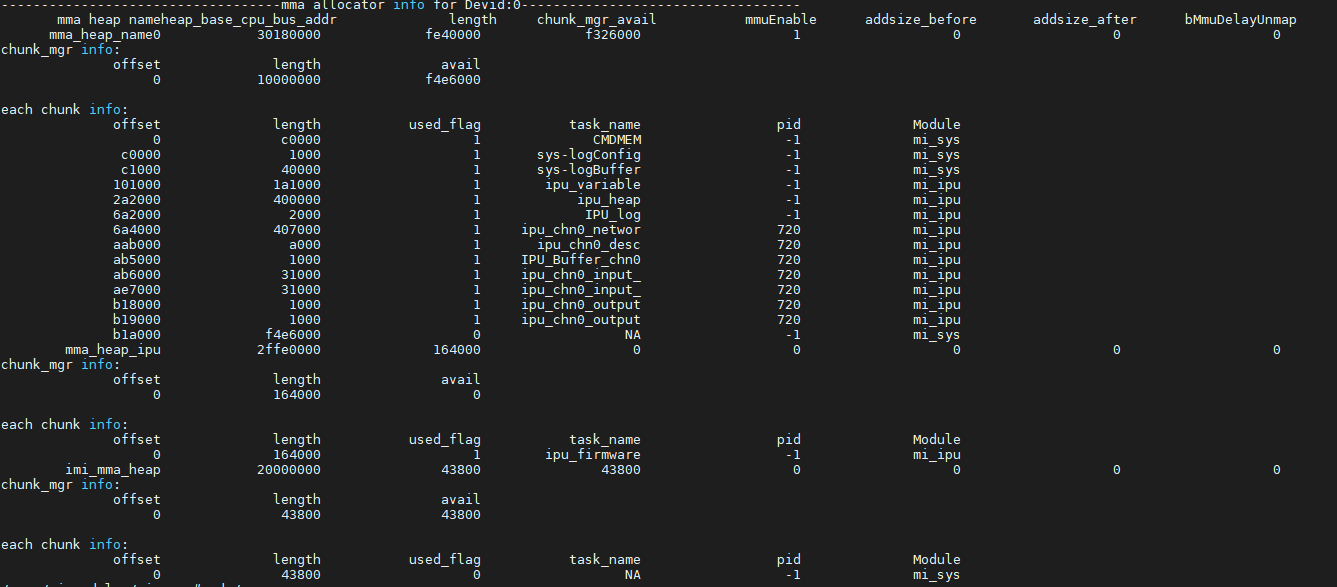
You can see the usage of all MMAs.
# cat /proc/mi_modules/mi_ipu/mi_ipu0
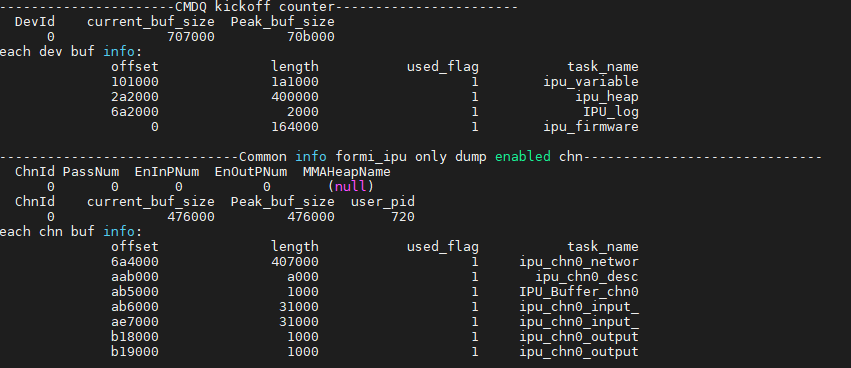
You can see how the IPU device and each channel use MMA.
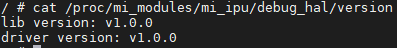
5.3. Cat IPU version info¶
# cat /proc/mi_modules/mi_ipu/debug_hal/version
5.4. Cat IPU clock info¶
# cat /proc/mi_modules/mi_ipu/debug_hal/freq
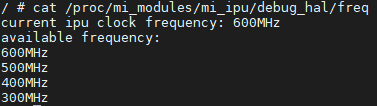
5.5. Adjust IPU clock¶
# echo xxx > /proc/mi_modules/mi_ipu/debug_hal/freq *(XXX must be available frequency)*
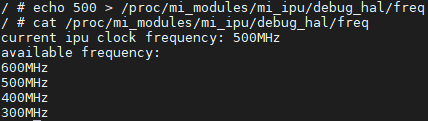
5.6. Switch auto reset function¶
The Auto reset function can reset the IPU after no response from the IPU and continue unfinished tasks.
Turn on auto reset function: echo on > /proc/mi_modules/mi_ipu/debug_hal/auto_reset
Ture off auto reset function: echo off > /proc/mi_modules/mi_ipu/debug_hal/auto_reset
In the early testing stage, it is recommended to turn off the auto reset function to clarify the reason why the IPU is not responding.
5.7. Get IPU log¶
# echo “ctrl_size=0x800000 corectrl_size=0x800000 ctrl=0xffffff corectrl=0x1fff” > /proc/mi_modules/mi_ipu/debug_hal/ipu_log
ctrl_size and corectrl_size are the buffer sizes allocated for ctrl log and corectrl log, ctrl and corectrl are the configuration of ctrl log and corectrl log.