MI GFX API
REVISION HISTORY¶
| Revision No. | Description |
Date |
|---|---|---|
| 3.0 | 11/30/2020 | |
| 08/25/2021 | ||
| 3.1 | 03/20/2022 | |
| 3.2 | 05/06/2022 | |
| 04/16/2025 |
1. Overview¶
1.1. Module Description¶
GFX (Graphic Engine) hardware provides fast graphics rendering function, mainly including rectangles drawing, straight lines drawing,and bitmap moving which supports scaling, rotation, mirror flipping, format conversion, alpha blending and overlay, Color Key and etc.).
Keyword Description
-
Fence
The state in which a GFX operation needs to wait blocks the wait, but there is also an internal timeout mechanism to prevent latencies.
-
Colorkey
Key colors, such as removing a color from the bitmap when moving, can be set to key colors.
-
Pitch
The number of bytes per row of pixels,(pixel bits /8) * Width. It also corresponds to the commonly used Stride and LineLength.
1.2. Basic Structure¶
GFX only requires the output buffer when drawing rectangles and lines, in which case it will directly render onto the output buffer. When GFX performs bitmap movement, both an input buffer and an output buffer are required, and GFX computes the output by processing the input buffer and output buffer based on the parameters before writing to the output buffer.
1.3. Function introduction¶
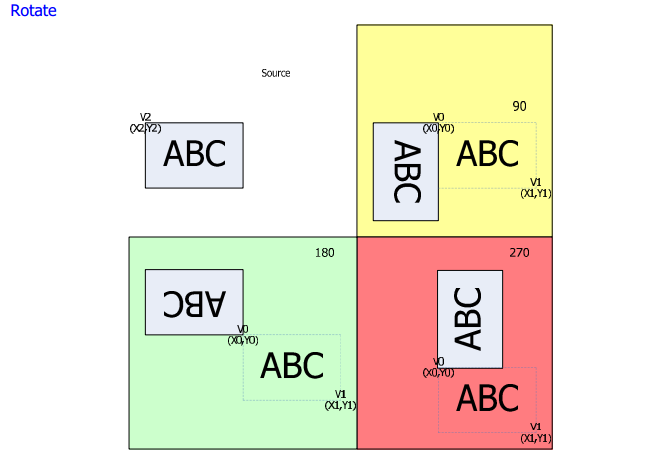
Rotate:The hardware supports 90/180/270 degree rotation.
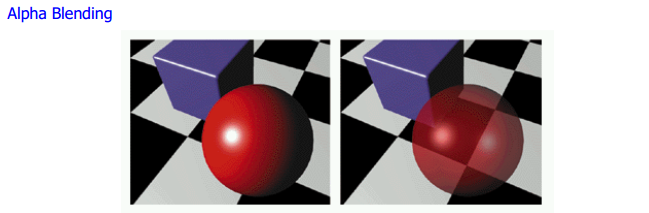
Alpha blending overlay: Supports normal 2D Alpha operation.
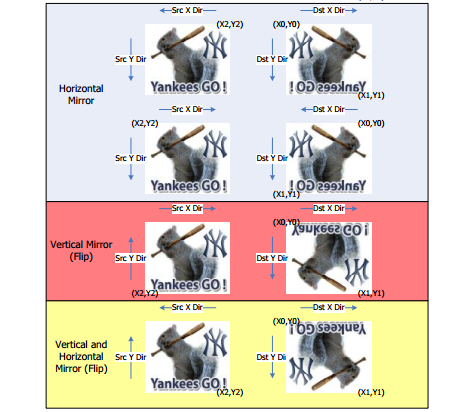
Mirror: Support H mirror, V mirror and HV mirror.
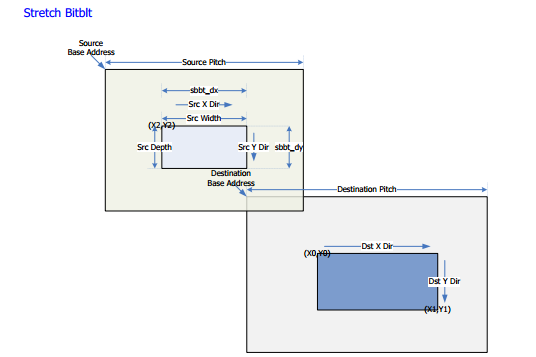
Zooming: Supports zooming at Bitblit.
Bitblit supports two interpolation algorithms: proximity interpolation and bilinear interpolation. It should be noted that when the image is enlarged, bilinear interpolation may produce new colors in order to make the image excessively smoother, while proximity interpolation will not produce new colors, but the blocky effect of the image will be more pronounced. Select the interpolation algorithm based on the actual scenario.
When using bilinear interpolation to scale, it involves the concept of geometric center shift of the image. The following figure is an example when a 5x5 image (figure (1)) needs to be shrunk to a 3x3 image (figure (2)). When the offset is not set, the pixel correspondence between the scaled image and the original image will be left overall as shown in Figure (3), while figure (4) shows the corresponding relation with the geometric center offset of the image.
Image geometric center:
SrcX = (dstX + coeff)* (srcWidth/dstWidth) - coeff SrcY = (dstY + coeff) * (srcHeight/dstHeight)- coeff
1.4. Application Scenarios¶
GFX is commonly used in the following scenarios:
-
To interface with UI engines (such as lvgl, dfb, flythings, etc.) to accelerate drawing.
-
To utilize GFX's bitmap transfer to replace BDMA for memory copying, commonly seen in copying UI buffers to frame buffers.
-
To use the Y component in formats such as ARGB4444 and ARGB1555 with 16 bits per pixel, and the UV components in I8 format, rotating the Y and UY components respectively to achieve rotation of the YUV420SP buffer.
1.5. Chip Difference Description¶
Currently, Taiyaki, Takoyaki, Tiramisu, Ikayaki, Muffin, Mochi, Jaguar1, and iBopper series chips support GFX. Only iBopper series chips do not support rotate.
1.6. Example introduction¶
If you wish to use GFX for drawing rectangles, drawing lines, and moving bitmaps, you may refer to the following process.
If you want to use GFX to handle video data output from other modules, please refer to the following process.
1.6.1. Create and destroy devices¶
1. MI_S32 s32Ret = 0;
2. #define DEFAULT_GFX_DEV_ID (0)
3. #define DEFAULT_SOC_ID (0)
4.
4. MI_SYS_Init(DEFAULT_SOC_ID);
5. /* open GFX device*/
6. s32Ret = MI_GFX_Open(DEFAULT_GFX_DEV_ID);
7. if (MI_SUCCESS != s32Ret)
8. {
9. return -1;
10. }
11. /* close GFX device*/
12. MI_GFX_Close(DEFAULT_GFX_DEV_ID);
13. MI_SYS_Exit(DEFAULT_SOC_ID);
1.6.2. Draw a rectangle¶
1. #define DEFAULT_GFX_DEV_ID (0)
2. #define DEFAULT_SOC_ID (0)
3. FILE *fp = NULL;
4. MI_PHY phyAddr;
5. void *pVirAddr = NULL;
6. MI_GFX_Surface_t stDst;
7. MI_GFX_Rect_t stDstRect;
8. MI_U32 u32ColorVal = 0xffff0000;
9. MI_U16 u16TargetFence;
10.
10. fp = fopen(SRC_FILE_NAME, "wb");
12.
11. ExecFunc(MI_SYS_Init(DEFAULT_SOC_ID), MI_SUCCESS);
12. ExecFunc(MI_SYS_MMA_Alloc("mma_heap_name0", SRC_WIDTH*SRC_HEIGHT*2, &phyAddr), MI_SUCCESS);
13. ExecFunc(MI_SYS_Mmap(phyAddr, SRC_WIDTH*SRC_HEIGHT*2, &pVirAddr , FALSE), MI_SUCCESS);
14. memset(pVirAddr, 0x22, SRC_WIDTH*SRC_HEIGHT*2);
17.
15. ExecFunc(MI_GFX_Open(DEFAULT_GFX_DEV_ID), MI_SUCCESS);
19.
16. //fillrect
17. memset(&stDst, 0x0 , sizeof(stDst));
18. stDst.eColorFmt = E_MI_GFX_FMT_ARGB1555;
19. stDst.u32Width = SRC_WIDTH;
20. stDst.u32Height = SRC_HEIGHT;
21. stDst.u32Stride = SRC_WIDTH * 2;
22. stDst.phyAddr = phyAddr;
27.
23. memset(&stDstRect, 0x0, sizeof(stDstRect));
24. stDstRect.s32Xpos = 100;
25. stDstRect.s32Ypos = 100;
26. stDstRect.u32Width = 100;
27. stDstRect.u32Height = 100;
28. ExecFunc(MI_GFX_QuickFill(DEFAULT_GFX_DEV_ID, &stDst, &stDstRect, u32ColorVal, &u16TargetFence), MI_SUCCESS);
29. ExecFunc(MI_GFX_WaitAllDone(DEFAULT_GFX_DEV_ID, FALSE, u16TargetFence), MI_SUCCESS);
30. if (NULL != fp)
31. {
32. fwrite(pVirAddr, 1, SRC_WIDTH*SRC_HEIGHT*2, fp);
33. fclose(fp);
34. fp = NULL;
35. }
36. ExecFunc(MI_SYS_Munmap(pVirAddr, SRC_WIDTH*SRC_HEIGHT*2), MI_SUCCESS);
37. ExecFunc(MI_SYS_MMA_Free(phyAddr), MI_SUCCESS);
43.
38. ExecFunc(MI_GFX_Close(DEFAULT_GFX_DEV_ID), MI_SUCCESS);
39. ExecFunc(MI_SYS_Exit(DEFAULT_SOC_ID), MI_SUCCESS);
1.6.3. Bitmap Migration¶
1. #define DEFAULT_GFX_DEV_ID (0)
2. #define DEFAULT_SOC_ID (0)
3.
3. FILE *fp = NULL;
4. FILE *dstfp = NULL;
5. MI_PHY phyAddr, phyAddr2;
6. void *pVirAddr = NULL, *pVirAddr2 = NULL;
7. MI_GFX_Surface_t stSrc, stDst;
8. MI_GFX_Rect_t stSrcRect, stDstRect;
9. MI_U16 u16TargetFence;
10. MI_GFX_Opt_t stOpt = {};
12.
11. fp = fopen(SRC_FILE_NAME, "wb");
12. dstfp = fopen(DST_FILE_NAME, "wb");
15.
13. ExecFunc(MI_SYS_Init(DEFAULT_SOC_ID), MI_SUCCESS);
14. ExecFunc(MI_SYS_MMA_Alloc("mma_heap_name0", SRC_WIDTH*SRC_HEIGHT*2, &phyAddr), MI_SUCCESS);
15. ExecFunc(MI_SYS_MMA_Alloc("mma_heap_name0", DST_WIDTH*360*2, &phyAddr2), MI_SUCCESS);
19.
16. //MI_U32 phySrcAddr, phyDstAddr;
17. ExecFunc(MI_GFX_Open(DEFAULT_GFX_DEV_ID), MI_SUCCESS);
18. ExecFunc(MI_SYS_Mmap(phyAddr, SRC_WIDTH*SRC_HEIGHT*2, &pVirAddr , FALSE), MI_SUCCESS);
19. memset(pVirAddr, 0x22, SRC_WIDTH*SRC_HEIGHT*2);
24.
20. ExecFunc(MI_SYS_Mmap(phyAddr2, DST_WIDTH*DST_HEIGHT*2, &pVirAddr2 , FALSE), MI_SUCCESS);
21. memset(pVirAddr2, 0x0F, DST_WIDTH*DST_HEIGHT*2);
27.
22. //bitblit
23. memset(&stSrc, 0x0, sizeof(stSrc));
24. stSrc.eColorFmt = E_MI_GFX_FMT_ARGB1555;
25. stSrc.u32Width = SRC_WIDTH;
26. stSrc.u32Height = SRC_HEIGHT;
27. stSrc.u32Stride = SRC_WIDTH * 2;
28. stSrc.phyAddr = phyAddr;
35.
29. memset(&stSrcRect, 0x0, sizeof(stSrcRect));
30. stSrcRect.s32Xpos = 100;
31. stSrcRect.s32Ypos = 100;
32. stSrcRect.u32Width = 300;
33. stSrcRect.u32Height = 300;
41.
34. memset(&stDst, 0x0, sizeof(stDst));
35. stDst.eColorFmt = E_MI_GFX_FMT_ARGB1555;
36. stDst.u32Width = DST_WIDTH;
37. stDst.u32Height = DST_HEIGHT;
38. stDst.u32Stride = DST_WIDTH * 2;
39. stDst.phyAddr = phyAddr2;
48.
40. memset(&stDstRect, 0x0, sizeof(stDstRect));
41. stDstRect.s32Xpos = 200;
42. stDstRect.s32Ypos = 100;
43. stDstRect.u32Width = 200;
44. stDstRect.u32Height = 100;
54.
45. stOpt.stClipRect = stDstRect;
46. stOpt.eSrcDfbBldOp = E_MI_GFX_DFB_BLD_ONE;
47. stOpt.eDstDfbBldOp = E_MI_GFX_DFB_BLD_ZERO;
58.
48. ExecFunc(MI_GFX_BitBlit(DEFAULT_GFX_DEV_ID, &stSrc, &stSrcRect, &stDst, &stDstRect, &stOpt, &u16TargetFence), MI_SUCCESS);
49. ExecFunc(MI_GFX_WaitAllDone(DEFAULT_GFX_DEV_ID, FALSE, u16TargetFence), MI_SUCCESS);
50. if (NULL != dstfp)
51. {
52. fwrite(pVirAddr2, 1, DST_WIDTH*DST_HEIGHT*2, dstfp);
53. fclose(dstfp);
54. dstfp = NULL;
55. }
67.
56. ExecFunc(MI_SYS_Munmap(pVirAddr, SRC_WIDTH*SRC_HEIGHT*2), MI_SUCCESS);
57. ExecFunc(MI_SYS_MMA_Free(phyAddr), MI_SUCCESS);
70.
58. ExecFunc(MI_SYS_Munmap(pVirAddr2, DST_WIDTH*DST_HEIGHT*2), MI_SUCCESS);
59. ExecFunc(MI_SYS_MMA_Free(phyAddr2), MI_SUCCESS);
73.
60. ExecFunc(MI_GFX_Close(DEFAULT_GFX_DEV_ID), MI_SUCCESS);
61. ExecFunc(MI_SYS_Exit(DEFAULT_SOC_ID), MI_SUCCESS);
1.6.4. Configuration Color Palette¶
1. #define DEFAULT_GFX_DEV_ID (0) 2. MI_GFX_Palette_t myPal; 3. MI_GFX_PaletteEntry_t index_0; 4. MI_GFX_PaletteEntry_t index_1; 5. index_0.RGB.u8A = 0x40; 6. index_0.RGB.u8R = 0xFF; 7. index_0.RGB.u8G = 0; 8. index_0.RGB.u8B = 0; 9. index_1.RGB.u8A = 0x40; 10. index_1.RGB.u8R = 0; 11. index_1.RGB.u8G = 0xFF; 12. index_1.RGB.u8B = 0; 13. 13. myPal.aunPalette[0] = index_0; 14. myPal.aunPalette[1] = index_1; 15. myPal.u16PalStart = 0 16. myPal.u16PalEnd = 1; 17. MI_GFX_SetPalette(DEFAULT_GFX_DEV_ID, E_MI_GFX_FMT_I8, &myPal);
1.6.5. Draw a straight line.¶
1. #define DEFAULT_GFX_DEV_ID (0)
2. #define DEFAULT_SOC_ID (0)
3.
3. FILE *fp = NULL;
4. MI_GFX_Surface_t stDst;
5. MI_GFX_Line_t stLine;
6. MI_U16 u16TargetFence;
7. MI_PHY phyAddr;
8. void *VirAddr;
10.
9. ExecFunc(MI_SYS_Init(DEFAULT_SOC_ID), MI_SUCCESS);
10. fp = fopen(SRC_FILE_NAME, "wb");
11. ExecFunc(MI_SYS_MMA_Alloc("mma_heap_name0", SRC_WIDTH*SRC_HEIGHT*2, &phyAddr), MI_SUCCESS);
14.
12. //MI_U32 phySrcAddr, phyDstAddr;
13. ExecFunc(MI_GFX_Open(DEFAULT_SOC_ID), MI_SUCCESS);
14. ExecFunc(MI_SYS_Mmap(phyAddr, SRC_WIDTH*SRC_HEIGHT*2, &pVirAddr , FALSE), MI_SUCCESS);
15. memset(pVirAddr, 0x22, SRC_WIDTH*SRC_HEIGHT*2);
19.
16. //draw line
17. memset(&stDst, 0x0, sizeof(stDst));
18. stDst.eColorFmt = E_MI_GFX_FMT_ARGB1555;
19. stDst.u32Width = SRC_WIDTH;
20. stDst.u32Height = SRC_HEIGHT;
21. stDst.u32Stride = SRC_WIDTH * 2;
22. stDst.phyAddr = phyAddr;
27.
23. memset(&stLine, 0x0, sizeof(stLine));
24. stLine.stPointFrom.s16x = 0;
25. stLine.stPointFrom.s16y = 0;
26. stLine.stPointTo.s16x = 100;
27. stLine.stPointTo.s16y = 100;
28. stLine.u16Width = 1;
29. stLine.bColorGradient = TRUE;
30. stLine.bColorFrom = 0xffff0000;
31. stLine.bColorTo = 0xffff00ff;
37.
32. ExecFunc(MI_GFX_DrawLine(DEFAULT_SOC_ID, &stDst, &stLine, &u16TargetFence), MI_SUCCESS);
33. ExecFunc(MI_GFX_WaitAllDone(DEFAULT_SOC_ID, FALSE, u16TargetFence), MI_SUCCESS);
34. if (NULL != fp)
35. {
36. fwrite(pVirAddr, 1, SRC_WIDTH*SRC_HEIGHT*2, fp);
37. fclose(fp);
38. fp = NULL;
39. }
40. ExecFunc(MI_SYS_Munmap(pVirAddr, SRC_WIDTH*SRC_HEIGHT*2), MI_SUCCESS);
41. ExecFunc(MI_SYS_MMA_Free(phyAddr), MI_SUCCESS);
48.
42. ExecFunc(MI_GFX_Close(DEFAULT_SOC_ID), MI_SUCCESS);
43. ExecFunc(MI_SYS_Exit(DEFAULT_SOC_ID), MI_SUCCESS);
2. API LIST¶
The MI GFX module provides the following APIs:
| API Name | Function |
|---|---|
| MI_GFX_Open | Open GFX device |
| MI_GFX_Close | Close GFX device |
| MI_GFX_WaitAllDone | Wait for one/all GFX tasks to complete |
| MI_GFX_QuickFill | Add quick fill operation to the task |
| MI_GFX_GetARGB8888To1555AlphaThreshold | Get alpha threshold value of ARGB8888 convert to ARGB1555 |
| MI_GFX_SetARGB8888To1555AlphaThreshold | Set alpha threshold value of ARGB8888 convert to ARGB1555 |
| MI_GFX_Bitblit | Add a raster bitmap to the task to perform move operations with additional functions |
| MI_GFX_SetPalette | Set palette for Index Color format |
| MI_GFX_CreateDev | Initialize GFX device |
| MI_GFX_DestroyDev | De-initialize GFX device |
| MI_GFX_GetARGB1555To8888AlphaValue | Get alpha value of ARGB1555 convert to ARGB8888 |
| MI_GFX_SetARGB1555To8888AlphaValue | Set alpha value of ARGB1555 convert to ARGB8888 |
| MI_GFX_GetInitialScalingCoeff | Get initial scaling coefficient |
| MI_GFX_SetInitialScalingCoeff | Set initial scaling coefficient |
| MI_GFX_DrawLine | Add line drawing operations to the task |
2.1. MI_GFX_Open¶
-
Function
Call this interface to open GFX device and initialize hardware system
-
Syntax
MI_ S32 MI_GFX_Open(MI_GFX_DEV GfxDevId);
-
Parameter
Parameter Name Description Input/Output GfxDevId GFX device id Input -
Return Value
-
Zero: Successful
-
Non-zero: Failed, see error code for details
-
-
Requirement
-
Header: mi_gfx.h, mi_gfx_datatype.h
-
Library: libmi_gfx.a / libmi_gfx.so
-
-
Note
-
Before performing any GFX related operations, call this interface and make sure GFX device is opened.
-
Calling this interface after the GFX device has been initialized will return a “module initialized” message.
-
-
Example
- Please refer to the sample code
2.2. MI_GFX_Close¶
-
Function
Call this interface to close GFX device
-
Syntax
MI_S32 MI_GFX_Close(MI_GFX_DEV GfxDevId);
-
Parameter
Parameter Name Description Input/Output GfxDevId GFX device id Input -
Return Value
-
Zero: Successful
-
Non-zero: Failed, see error code for details
-
-
Requirement
-
Header: mi_gfx.h, mi_gfx_datatype.h
-
Library: libmi_gfx.a / libmi_gfx.so
-
-
Note
Times of calling MI_GFX_Open and MI_GFX_Close must be consistent. Repeated calling is allowed. When the times of Open is Same as Close, the GFX API will no longer be able to be called.
2.3. MI_GFX_WaitAllDone¶
-
Function
Call this interface to wait for completion of all or specified GFX tasks.
-
Syntax
MI_S32 MI_GFX_WaitAllDone(MI_GFX_DEV GfxDevId, MI_BOOL bWaitAllDone, MI_U16 u16TargetFence);
-
Parameter
Parameter Name Description Input/Output GfxDevId GFX device id Input bWaitAllDone Wait until all GFX tasks are completed Input u16TargetFence Wait until specified fence is reached. This parameter takes effect only when bWaitAllDone is FALSE. Input -
Return Value
-
Zero: Successful
-
Non-zero: Failed, see error code for details
-
-
Requirement
-
Header: mi_gfx.h, mi_gfx_datatype.h
-
Library: libmi_gfx.a / libmi_gfx.so
-
-
Note
This interface is a blocking interface which will block operations until all the GFX tasks are completed.
2.4. MI_GFX_QuickFill¶
-
Function
Fill in the color of u32ColorVal to the target area pstDstRect in the target bitmap pstDst to realize the function of color filling.
-
Syntax
MI_S32 MI_GFX_QuickFill(MI_GFX_DEV GfxDevId, MI_GFX_Surface_t *pstDst, MI_GFX_Rect_t *pstDstRect, MI_U32 u32ColorVal, MI_U16 *pu16Fence);
-
Parameter
Parameter Name Description Input/Output GfxDevId GFX device id Input pstDst Destination bitmap Input pstDstRect Operating area in destination bitmap Input u32ColorVal Color fill value Input pu16Fence Returned fence pointer Output -
Return Value
-
Zero: Successful
-
Non-zero: Failed, see error code for details
-
-
Requirement
-
Header: mi_gfx.h, mi_gfx_datatype.h
-
Library: libmi_gfx.a / libmi_gfx.so
-
-
Note
-
Before calling this interface, make sure to call MI_GFX_Open to open the GFX device.
-
The target bitmap operation area cannot exceed the size of the target bitmap.
-
If the pixel format of the target bitmap is RGB or ARGB, u32ColorVal from high to low is A8: R8: G8: B8. If the pixel format of the target bitmap is YUYV422, A8 is invalid, and R corresponds to Y, G Corresponds to U, B corresponds to V.
-
-
Example
- Please refer to the sample code.
2.5. MI_GFX_GetARGB8888To1555AlphaThreshold¶
-
Function
Get alpha threshold value.
When the source bitmap and the target bitmap do bitblit operations, they are converted into an intermediate bitmap with a fixed pixel format according to the pixel format of the target bitmap (if the target bitmap is in RGB color space, it is converted to ARGB8888; if the target bitmap is in YUV color space, it is converted to AYUV8888), and then the operation result of the intermediate bitmap is output to the target bitmap. When the target image pixel format is ARGB1555/RGBA5551/ABGR1555/BGRA5551 and the intermediate bitmap pixel format is ARGB8888, if the alpha value of a pixel after the intermediate bitmap operation is less than this threshold, the alpha bit of the pixel output to the target bitmap is 0; if it is greater than or equal to this threshold, the alpha bit of the pixel is 1.
-
Syntax
MI_S32 MI_GFX_GetARGB8888To1555AlphaThreshold(MI_GFX_DEV GfxDevId, MI_U8 *pu8ThresholdValue);
-
Parameter
Parameter Name Description Input/Output GfxDevId GFX device id Input pu8ThresholdValue Pointer to alpha threshold value Output -
Return Value
-
Zero: Successful
-
Non-zero: Failed, see error code for details
-
-
Requirement
-
Header: mi_gfx.h, mi_gfx_datatype.h
-
Library: libmi_gfx.a / libmi_gfx.so
-
2.6. MI_GFX_SetARGB8888To1555AlphaThreshold¶
-
Function
Set alpha threshold value.
When the source bitmap and the target bitmap do bitblit operations, they are converted into an intermediate bitmap with a fixed pixel format according to the pixel format of the target bitmap (if the target bitmap is in RGB color space, it is converted to ARGB8888; if the target bitmap is in YUV color space, it is converted to AYUV8888), and then the operation result of the intermediate bitmap is output to the target bitmap. When the target image pixel format is ARGB1555/RGBA5551/ABGR1555/BGRA5551 and the intermediate bitmap pixel format is ARGB8888, if the alpha value of a pixel after the intermediate bitmap operation is less than this threshold, the alpha bit of the pixel output to the target bitmap is 0; if it is greater than or equal to this threshold, the alpha bit of the pixel is 1.
-
Syntax
MI_S32 MI_GFX_SetARGB8888To1555AlphaThreshold(MI_GFX_DEV GfxDevId, MI_U8 u8ThresholdValue);
-
Parameter
Parameter Name Description Input/Output GfxDevId GFX device id Input u8ThresholdValue Alpha threshold value Input -
Return Value
-
Zero: Successful
-
Non-zero: Failed, see error code for details
-
-
Requirement
-
Header: mi_gfx.h, mi_gfx_datatype.h
-
Library: libmi_gfx.a / libmi_gfx.so
-
2.7. MI_GFX_BitBlit¶
-
Function
Operate the specified area (pstSrcRect, pstDstRect) of the source bitmap (pstSrc) and the target bitmap (pstDst), and copy the calculated bitmap to the specified area (pstDstRect) of the target bitmap (pstDst).
-
Syntax
MI_S32 MI_GFX_BitBlit(MI_GFX_DEV GfxDevId, MI_GFX_Surface_t *pstSrc, MI_GFX_Rect_t *pstSrcRect, MI_GFX_Surface_t *pstDst, MI_GFX_Rect_t *pstDstRect, MI_GFX_Opt_t *pstOpt, MI_U16 *pu16Fence);
-
Parameter
Parameter Name Description Input/Output GfxDevId GFX device id Input pstSrc Source bitmap Input pstSrcRect Source bitmap operation region Input pstDst Destination bitmap Input pstDstRect Destination bitmap operation region Input pstOpt Operating parameter setting structure Input pu16Fence Pointer to the returned fence Output -
Return Value
-
Zero: Successful
-
Non-zero: Failed, see error code for details
-
-
Requirement
-
Header: mi_gfx.h, mi_gfx_datatype.h
-
Library: libmi_gfx.a / libmi_gfx.so
-
-
Note
-
Before calling this interface, make sure to call MI_GFX_Open to open the GFX device.
-
When the size of the source bitmap operation area is inconsistent with the target bitmap operation area, the source area is scaled according to the target area ratio, and then the operation is performed with the target area.
-
If the clip operation is an in-area clip, the cut area must have a common intersection with the operation area, otherwise an error will be returned.
-
The MI_GFX_Opt_t structure stores the configuration information of the GFX calculation function, such as: whether to use the colorkey and the configuration value of the colorkey; whether to perform clip operation and specify the clip area; whether to mirror or perform alpha blending, etc. The above operations can be enabled at same time.
-
-
Example
- Please refer to the sample code
2.8. MI_GFX_SetPalette¶
-
Function
Set Palette for Index Color (I8).
-
Syntax
MI_S32 MI_GFX_SetPalette(MI_GFX_DEV GfxDevId, MI_GFX_ColorFmt_e eColorFmt, MI_GFX_Palette_t *pstPalette);
-
Parameter
Parameter Name Description Input/Output GfxDevId GFX device id Input eColorFmt Specific Index Color format: MI_GFX_ColorFmt_e Input pstPalette Data array of corresponding Index Color Input -
Return Value
-
Zero: Successful
-
Non-zero: Failed, see error code for details
-
-
Requirement
-
Header: mi_gfx.h, mi_gfx_datatype.h
-
Library: libmi_gfx.a / libmi_gfx.so
-
-
Note
-
Before calling this interface, make sure to call MI_GFX_Open to open the GFX device.
-
pstPalette is an array of MI_GFX_PaletteEntry_t with a capacity of 256. Each MI_GFX_PaletteEntry_t represents a color, and the corresponding subscript in the array represents the index of the color.
-
-
Example
- Please refer to the sample code
2.9. MI_GFX_CreateDev¶
-
Function
Initialize GFX device.
-
Syntax
MI_S32 MI_GFX_CreateDev(MI_GFX_DEV GfxDevId, MI_GFX_DevAttr_t *pstDevAttr);
-
Parameters
Parameter Name Description Input/Output GfxDevId GFX device id Input pstDevAttr Initialization device parameter Input -
Return Value
-
Zero: Successful
-
Non-zero: Failed, see error code for details
-
-
Requirement
-
Header: mi_gfx.h, mi_gfx_datatype.h
-
Library: libmi_gfx.a / libmi_gfx.so
-
-
Note
- MI_GFX_CreateDev is exactly the same as MI_GFX_Open.
2.10. MI_GFX_DestroyDev¶
-
Function
De-initialize GFX device.
-
Syntax
MI_S32 MI_GFX_DestroyDev(MI_GFX_DEV GfxDevId);
-
Parameters
Parameter Name Description Input/Output GfxDevId GFX device id Input -
Return Value
-
Zero: Successful
-
Non-zero: Failed, see error code for details
-
-
Requirement
-
Header: mi_gfx.h, mi_gfx_datatype.h
-
Library: libmi_gfx.a / libmi_gfx.so
-
-
Note
-
This interface should be called after the device has been initialized; otherwise, a failed message will be returned.
-
If this interface is not called after the app exited, the GFX device will be auto de-initialized.
-
MI_GFX_DestroyDev is exactly the same as MI_GFX_Close.
-
2.11. MI_GFX_GetARGB1555To8888AlphaValue¶
-
Function
Get the alpha conversion value.
When the source bitmap and the target bitmap do bitblit operations, they are converted into an intermediate bitmap with a fixed pixel format according to the pixel format of the target bitmap (if the target bitmap is in RGB color space, it is converted to ARGB8888; if the target bitmap is in YUV color space, it is converted to AYUV8888), and then the operation result of the intermediate bitmap is output to the target bitmap. When the source bitmap and the target bitmap pixel format is ARGB1555/RGBA5551/ABGR1555/BGRA5551 and the intermediate bitmap pixel format is ARGB8888, if the alpha bit of ARGB1555/RGBA5551/ABGR1555/BGRA5551 is 0, the alpha of ARGB8888 after conversion is 0; if the alpha bit of ARGB1555/RGBA5551/ABGR1555/BGRA5551 is 1, the alpha of ARGB8888 after conversion is the alpha conversion value.
-
Syntax
MI_S32 MI_GFX_GetARGB1555To8888AlphaValue(MI_GFX_DEV GfxDevId, MI_U8 *pu8AlphaValue);
-
Parameter
Parameter Name Description Input/Output GfxDevId GFX device id Input pu8AlphaValue Pointer to alpha value Output -
Return Value
-
Zero: Successful
-
Non-zero: Failed, see error code for details
-
-
Requirement
-
Header: mi_gfx.h, mi_gfx_datatype.h
-
Library: libmi_gfx.a / libmi_gfx.so
-
-
Note
Not supported currently
2.12. MI_GFX_SetARGB1555To8888AlphaValue¶
-
Function
Set the alpha conversion value.
When the source bitmap and the target bitmap do bitblit operations, they are converted into an intermediate bitmap with a fixed pixel format according to the pixel format of the target bitmap (if the target bitmap is in RGB color space, it is converted to ARGB8888; if the target bitmap is in YUV color space, it is converted to AYUV8888), and then the operation result of the intermediate bitmap is output to the target bitmap. When the source bitmap and the target bitmap pixel format is ARGB1555/RGBA5551/ABGR1555/BGRA5551 and the intermediate bitmap pixel format is ARGB8888, if the alpha bit of ARGB1555/RGBA5551/ABGR1555/BGRA5551 is 0, the alpha of ARGB8888 after conversion is 0; if the alpha bit of ARGB1555/RGBA5551/ABGR1555/BGRA5551 is 1, the alpha of ARGB8888 after conversion is the alpha conversion value.
-
Syntax
MI_S32 MI_GFX_SetARGB1555To8888AlphaValue(MI_GFX_DEV GfxDevId, MI_U8 u8AlphaValue);
-
Parameter
Parameter Name Description Input/Output GfxDevId GFX device id Input u8AlphaValue alpha value Input -
Return Value
-
Zero: Successful
-
Non-zero: Failed, see error code for details
-
-
Requirement
-
Header: mi_gfx.h, mi_gfx_datatype.h
-
Library: libmi_gfx.a / libmi_gfx.so
-
-
Note
Not supported currently
2.13. MI_GFX_GetInitialScalingCoeff¶
-
Function
Gets the scaling coefficient. When the bitblit operation requires scaling, the image geometric center offset of bilinear interpolation = scaling coefficient /1000.
-
Syntax
MI_S32 MI_GFX_GetInitialScalingCoeff(MI_GFX_DEV GfxDevId, MI_U16 *pu16ScalingCoefficient);
-
Parameter
Parameter Name Description Input/Output GfxDevId GFX device id Input pu16ScalingCoefficient Pointer to scaling coefficient Output -
Return Value
-
Zero: Successful
-
Non-zero: Failed, see error code for details
-
-
Requirement
-
Header: mi_gfx.h, mi_gfx_datatype.h
-
Library: libmi_gfx.a / libmi_gfx.so
-
-
Note
Not supported currently
2.14. MI_GFX_SetInitialScalingCoeff¶
-
Function
Set the scaling coefficient. When the bitblit operation requires scaling, the image geometric center offset of bilinear interpolation = scaling coefficient /1000. The default value is 500.
-
Syntax
MI_S32 MI_GFX_SetInitialScalingCoeff(MI_GFX_DEV GfxDevId, MI_U16 u16ScalingCoefficient);
-
Parameter
Parameter Name Description Input/Output GfxDevId GFX device id Input u16ScalingCoefficient Scaling coefficient Input -
Return Value
-
Zero: Successful
-
Non-zero: Failed, see error code for details
-
-
Requirement
-
Header: mi_gfx.h, mi_gfx_datatype.h
-
Library: libmi_gfx.a / libmi_gfx.so
-
-
Note
Not supported currently
2.15. MI_GFX_DrawLine¶
-
Function
Add line drawing operations to the task.
-
Syntax
MI_S32 MI_GFX_DrawLine(MI_GFX_Surface_t *pstDst, MI_GFX_Line_t *pstLine, MI_U16 *pu16Fence);
-
Parameter
Parameter Name Description Input/Output pstDst Target bitmap Input pstLine Line attributes Input pu16Fence Return pointer to Fence Output -
Return Value
-
Zero: Successful
-
Non-zero: Failed, see error code for details
-
-
Requirement
-
Header: mi_gfx.h, mi_gfx_datatype.h
-
Library: libmi_gfx.a / libmi_gfx.so
-
-
Note
-
Before calling this interface, make sure to call MI_GFX_Open to open the GFX device.
-
The line drawing area cannot exceed the size of the target bitmap.
-
The end point of the straight line will not be drawn.
-
If the pixel format of the target bitmap is RGB or ARGB, u32ColorFrom/u32ColorFrom from high to low is A8: R8: G8: B8. If the pixel format of the target bitmap is YUYV422, A8 is invalid, and R corresponds to Y, G corresponds to U, B corresponds to V.
-
-
Example
- Please refer to the sample code
3. GFX DATA TYPE¶
The GFX related data types are defined in the table below:
| Function | Description |
|---|---|
| MI_GFX_ColorFmt_e | Define pixel color format |
| MI_GFX_Surface_t | Define bitmap attribute structure |
| MI_GFX_Rect_t | Define the attribute structure of the operating area |
| MI_GFX_ColorKeyOp_e | Define Colorkey operation mode |
| MI_GFX_ColorKeyValue_t | Define the Colorkey color attribute structure |
| MI_GFX_ColorKeyInfo_t | Define the Colorkey attribute structure |
| MI_GFX_Rotate_e | Define the image rotation angle |
| MI_GFX_Mirror_e | Define image mirror mode |
| MI_GFX_DfbBldOp_e | Define Alpha Blending mode |
| MI_Gfx_DfbBlendFlags_e | Define Alpha Blending flag |
| MI_GFX_BitBltMode_e | Define Bitblt interpolation mode |
| MI_GFX_Opt_t | Define optional attribute structure for Bitblit operation |
| MI_GFX_PaletteEntry_t | Define palette color structure |
| MI_GFX_Palette_t | Define palette structure |
| MI_GFX_DevAttr_t | Define GFX device initialization parameters |
| MI_GFX_Point_t | Define point attribute structure |
| MI_GFX_Line_t | Define line attribute structure |
| MI_GFX_DEV | GFX device id |
3.1. MI_GFX_ColorFmt_e¶
-
Description
Define pixel color format.
-
Definition
typedef enum { E_MI_GFX_FMT_I1 = 0, /* ColorFormat */ E_MI_GFX_FMT_I2, E_MI_GFX_FMT_I4, E_MI_GFX_FMT_I8, E_MI_GFX_FMT_FABAFGBG2266, E_MI_GFX_FMT_1ABFGBG12355, E_MI_GFX_FMT_RGB565, E_MI_GFX_FMT_ARGB1555, E_MI_GFX_FMT_ARGB4444, E_MI_GFX_FMT_ARGB1555_DST, E_MI_GFX_FMT_ARGB8888, E_MI_GFX_FMT_RGBA5551, E_MI_GFX_FMT_RGBA4444, E_MI_GFX_FMT_ABGR8888, E_MI_GFX_FMT_BGRA5551, E_MI_GFX_FMT_ABGR1555, E_MI_GFX_FMT_ABGR4444, E_MI_GFX_FMT_BGRA4444, E_MI_GFX_FMT_BGR565, E_MI_GFX_FMT_RGBA8888, E_MI_GFX_FMT_BGRA8888, E_MI_GFX_FMT_YUV422_YUYV, E_MI_GFX_FMT_YUV422_YVYU, E_MI_GFX_FMT_YUV422_UYVY, E_MI_GFX_FMT_YUV422_VYUY, E_MI_GFX_FMT_MAX } MI_GFX_ColorFmt_e; -
Note
The color formats supported corresponding to the surface. Except for the case where both the source surface and the destination surface are I8, the bitblit function cannot use I8 as the color format for the destination surface. Currently, color formats such as I1/I2/I4/FABAFGBG2266/1ABFGBG12355 are not supported.
-
Related Data Type and Interface
3.2. MI_GFX_Surface_t¶
-
Description
Define bitmap attribute structure.
-
Definition
typedef struct MI_GFX_Surface_s { MI_PHY phyAddr; MI_GFX_ColorFmt_e eColorFmt; MI_U32 u32Width; MI_U32 u32Height; MI_U32 u32Stride; } MI_GFX_Surface_t; -
Member
Member Description u32PhyAddr The bitmap corresponds to the physical address of the memory. eColorFmt Bitmap pixel color format. u32Height The height of the bitmap. u32Width The width of the bitmap. u32Stride The stride of the bitmap. -
Note
-
The physical address of the bitmap corresponding to memory and the stride must adhere to 4-byte alignment.
-
The horizontal starting position and width of the bitmap in YUYV422 format must be even numbers.
-
-
Related Data Type and Interface
3.3. MI_GFX_Rect_t¶
-
Description
Define the attribute structure of the operating area.
-
Definition
typedef struct MI_GFX_Rect_s { MI_S32 s32Xpos; MI_S32 s32Ypos; MI_U32 u32Width; MI_U32 u32Height; } MI_GFX_Rect_t; -
Member
Member Description s32Xpos The starting abscissa of the operation region, in pixels. Valid range: [0, bitmap width) s32Ypos The starting ordinate of the operation region, in pixels. Valid range: [0, bitmap height) u32Width Width of the operation region, in pixels. u32Height Height of the operation region, in pixels. -
Note
The operating range must be within the range of the bitmap.
-
Related Data Type and Interface
3.4. MI_GFX_ColorKeyOp_e¶
-
Description
Define Colorkey operation mode.
-
Definition
typedef enum { E_MI_GFX_RGB_OP_EQUAL = 0, E_MI_GFX_RGB_OP_NOT_EQUAL, E_MI_GFX_ALPHA_OP_EQUAL, E_MI_GFX_ALPHA_OP_NOT_EQUAL, E_MI_GFX_ARGB_OP_EQUAL, E_MI_GFX_ARGB_OP_NOT_EQUAL, E_MI_GFX_CKEY_OP_BUTT, } MI_GFX_ColorKey_e; -
Member
Member Description E_MI_GFX_RGB_OP_EQUAL RGB equal colorkey operation E_MI_GFX_RGB_OP_NOT_EQUAL RGB unequal colorkey operation E_MI_GFX_ ALPHA_OP_EQUAL ALPHA equal colorkey operation E_MI_GFX_ ALPHA_OP_NOT_EQUAL ALPHA unequal colorkey operation E_MI_GFX_ ARGB_OP_EQUAL ARGB equal colorkey operation, See the note E_MI_GFX_ARGB_OP_NOT_EQUAL ARGB unequal colorkey operation, See the note E_MI_GFX_CKEY_OP_BUTT Invalid colorkey operation -
Note
-
When performing color key operation against bitmap, you can set the foreground and background, and the key value can be equal or not.
-
The selection criteria for E_MI_GFX_ARGB_OP_EQUAL are as follows:
Ikayaki:
srcSurface:(Apixel == Acolorkey) || (RGBpixel == RGBcolorkey)
dstSurface:(ARGBpixel == ARGBcolorkey)
Other series:
(ARGBpixel == ARGBcolorkey)
-
The selection criteria for E_MI_GFX_ARGB_OP_NOT_EQUAL are as follows:
Ikayaki:
srcSurface:(ARGBpixel != ARGBcolorkey)
dstSurface:(Apixel != Acolorkey) || (RGBpixel != RGBcolorkey)
Other series:
(ARGBpixel != ARGBcolorkey)
-
-
Related Data Type and Interface
3.5. MI_GFX_ColorKeyValue_t¶
-
Description
Define the Colorkey color attribute structure.
-
Definition
typedef struct MI_GFX_ColorKey_s { MI_U32 u32ColorStart; MI_U32 u32ColorEnd; } MI_GFX_ColorKeyValue_t; -
Member
Member Description u32ColorStart ColorKey color range start value u32ColorEnd ColorKey color range end value -
Note
When only one single color value is to go through colorkey operation, set u32ColorStart = u32ColorEnd = colorVal.
-
Related Data Type and Interface
3.6. MI_GFX_ColorKeyInfo_t¶
-
Description
Define the Colorkey attribute structure.
-
Definition
typedef struct MI_GFX_ColorKeyInfo_s { MI_BOOL bEnColorKey; MI_GFX_ColorKeyOp_e eCKeyOp; MI_GFX_ColorFmt_e eCKeyFmt; MI_GFX_ColorKeyValue_t stCKeyVal; } MI_GFX_ColorKeyInfo_t; -
Member
Member Description bEnColorKey ColorKey operation enable eCKeyOp ColorKey operation mode stCKeyVal ColorKey color range eCKeyFmt ColorKey color format -
Related Data Type and Interface
3.7. MI_GFX_Rotate_e¶
-
Description
Define the image rotation angle.
-
Definition
typedef enum { E_MI_GFX_ROTATE_0 = 0, E_MI_GFX_ROTATE_90, E_MI_GFX_ROTATE_180, E_MI_GFX_ROTATE_270 } MI_GFX_Rotate_e; -
Related Data Type and Interface
3.8. MI_GFX_Mirror_e¶
-
Description
Define image mirror mode.
-
Definition
typedef enum { E_MI_GFX_MIRROR_NONE = 0, E_MI_GFX_MIRROR_HORIZONTAL, E_MI_GFX_MIRROR_VERTICAL, E_MI_GFX_MIRROR_BOTH, E_MI_GFX_MIRROR_MAX } MI_GFX_Mirror_e; -
Member
Member Description E_MI_GFX_MIRROR_NONE Output image mirror operation disabled E_MI_GFX_MIRROR_HORIZONTAL Output image horizontal mirror E_MI_GFX_MIRROR_VERTICAL Output image vertical mirror E_MI_GFX_MIRROR_BOTH Output image horizontal + vertical mirror E_MI_GFX_MIRROR_MAX Invalid mirror type -
Related Data Type and Interface
3.9. MI_GFX_DfbBldOp_e¶
-
Description
Define Alpha Blending mode.
-
Definition
typedef enum { E_MI_GFX_DFB_BLD_ZERO = 0, E_MI_GFX_DFB_BLD_ONE, E_MI_GFX_DFB_BLD_SRCCOLOR, E_MI_GFX_DFB_BLD_INVSRCCOLOR, E_MI_GFX_DFB_BLD_SRCALPHA, E_MI_GFX_DFB_BLD_INVSRCALPHA, E_MI_GFX_DFB_BLD_DESTALPHA, E_MI_GFX_DFB_BLD_INVDESTALPHA, E_MI_GFX_DFB_BLD_DESTCOLOR, E_MI_GFX_DFB_BLD_INVDESTCOLOR, E_MI_GFX_DFB_BLD_SRCALPHASAT, E_MI_GFX_DFB_BLD_NONE, E_MI_GFX_DFB_BLD_MAX, } MI_GFX_DfbBldOp_e; -
Member
Member Description E_MI_GFX_DFB_BLD_OP_ZERO argb *= 0.0 Same as directfb DSBF_ZERO. E_MI_GFX_DFB_BLD_OP_ONE argb *= 1.0 Same as directfb DSBF_ONE. E_MI_GFX_DFB_BLD_OP_SRCCOLOR argb *= Sargb Same as directfb DSBF_SRCCOLOR. E_MI_GFX_DFB_BLD_OP_INVSRCCOLOR argb *= 1.0 - Sargb Same as directfb DSBF_INVSRCCOLOR. E_MI_GFX_DFB_BLD_OP_SRCALPHA argb *= Saaaa Same as directfb DSBF_SRCALPHA. E_MI_GFX_DFB_BLD_OP_INVSRCALPHA argb *= 1.0 – Saaaa Same as directfb DSBF_INVSRCALPHA. E_MI_GFX_DFB_BLD_OP_DESTCOLOR argb *= Dargb Same as directfb DSBF_DESTCOLOR. E_MI_GFX_DFB_BLD_OP_INVDESTCOLOR argb *= 1.0 – Dargb Same as directfb DSBF_INVDESTCOLOR. E_MI_GFX_DFB_BLD_OP_DESTALPHA argb *= Daaaa Same as directfb DSBF_DESTALPHA. E_MI_GFX_DFB_BLD_OP_INVDESTALPHA argb *= 1.0 – Daaaa Same as directfb DSBF_INVDESTALPHA. E_MI_GFX_DFB_BLD_OP_SRCALPHASAT rgb *= min(Sa, 1-Da) Same as directfb DSBF_SRCALPHASAT. E_MI_GFX_DFB_BLD_NONE Invalid alpha blending mode E_MI_GFX_BLD_MAX argb *= 0.0 Same as directfb DSBF_ZERO. -
Note
When the foreground bitmap and background bitmap are superimposed, you can set the superimposition mode of Src channel and Dst channel respectively. Now supports 11 overlay modes. Use MI_GFX_DfbBldOp_e to set the mode.
-
Related Data Type and Interface
3.10. MI_Gfx_DfbBlendFlags_e¶
-
Description
Define Alpha Blending flag.
-
Definition
typedef enum { E_MI_GFX_DFB_BLEND_NOFX = 0x00000000, E_MI_GFX_DFB_BLEND_COLORALPHA = 0x00000001, E_MI_GFX_DFB_BLEND_ALPHACHANNEL = 0x00000002, E_MI_GFX_DFB_BLEND_COLORIZE = 0x00000004, E_MI_GFX_DFB_BLEND_SRC_PREMULTIPLY = 0x00000008, E_MI_GFX_DFB_BLEND_SRC_PREMULTCOLOR = 0x00000010, E_MI_GFX_DFB_BLEND_DST_PREMULTIPLY = 0x00000020, E_MI_GFX_DFB_BLEND_XOR = 0x00000040, E_MI_GFX_DFB_BLEND_DEMULTIPLY = 0x00000080, E_MI_GFX_DFB_BLEND_SRC_COLORKEY = 0x00000100, E_MI_GFX_DFB_BLEND_DST_COLORKEY = 0x00000200, E_MI_GFX_DFB_BLEND_MAX = 0x3FF } MI_Gfx_DfbBlendFlags_e; -
Member
Member Description E_MI_GFX_DFB_BLEND_NOFX No BLD operation E_MI_GFX_DFB_BLEND_COLORALPHA src alpha will operate src.a = const color.a according to const color value; Same as directfb DSBLIT_BLEND_COLORALPHA. E_MI_GFX_DFB_BLEND_ALPHACHANNEL src alpha will operate src.a = src.a * const color.a according to const color value; Same as directfb DSBLIT_BLEND_ALPHACHANNEL. E_MI_GFX_DFB_BLEND_COLORIZE Use const color as the global color, adjust the source color; Same as directfb DSBLIT_COLORIZE. E_MI_GFX_DFB_BLEND_SRC_PREMULTIPLY Use the source alpha to pre-multiply the source color src.r = src.r * src.a; Same as directfb DSBLIT_SRC_PREMULTIPLY. E_MI_GFX_DFB_BLEND_SRC_PREMULTCOLOR Use const alpha to premultiply the source color src.r = src.r * const.a; Same as directfb DSBLIT_SRC_PREMULTCOLOR. E_MI_GFX_DFB_BLEND_DST_PREMULTIPLY Use destination alpha to premultiply destination color dst.r = dst.r * dst.a; Same as directfb DSBLIT_DST_PREMULTIPLY. E_MI_GFX_DFB_BLEND_XOR Adjust and premultiply alpha src.a ^= dst.a; Same as directfb DSBLIT_XOR E_MI_GFX_DFB_BLEND_DEMULTIPLY For conversion from premultiplied to non-premultiplied, it is best not to use such an operation x.r = ((int)x.r << 8) / ((int)x.a + 1); Same as directfb DSBLIT_DEMULTIPLY. E_MI_GFX_DFB_BLEND_SRC_COLORKEY If the color of src is equal to const color, it will be keyed off E_MI_GFX_DFB_BLEND_DST_COLORKEY If the color of dst is equal to const color, it will be keyed off E_MI_GFX_DFB_BLEND_MAX All the above actions will be enabled -
Related Data Type and Interface
3.11. MI_GFX_BitBltMode_e¶
-
Description
Define Bitblt interpolation mode.
-
Definition
typedef enum { E_MI_GFX_BITBLT_MODE_BILINEAR, E_MI_GFX_BITBLT_MODE_NEAREST, } MI_GFX_BitBltMode_e; -
Member
Member Description E_MI_GFX_BITBLT_MODE_BILINEAR Bilinear interpolation mode E_MI_GFX_BITBLT_MODE_NEAREST Nearest interpolation mode -
Related Data Type and Interface
3.12. MI_GFX_Opt_t¶
-
Description
Define optional attribute structure for Bitblit operation.
-
Definition
typedef struct MI_GFX_Opt_s { MI_GFX_Rect_t stClipRect; MI_GFX_ColorKeyInfo_t stSrcColorKeyInfo; MI_GFX_ColorKeyInfo_t stDstColorKeyInfo; MI_GFX_DfbBldOp_e eSrcDfbBldOp; MI_GFX_DfbBldOp_e eDstDfbBldOp; MI_GFX_Mirror_e eMirror; MI_GFX_Rotate_e eRotate; MI_Gfx_DfbBlendFlags_e eDFBBlendFlag; MI_GFX_BitBltMode_e eMode; MI_U32 u32GlobalSrcConstColor; MI_U32 u32GlobalDstConstColor; } MI_GFX_Opt_t; -
Member
Member Description eDFBBlendFlag Dfb blending operation flags stSrcColorKeyInfo Source surface colorkey operation stDstColorKeyInfo Destination surface colorkey operation stClipRect Clip region definition eMirror Image mirror type eSrcDfbBldOp Source surface BLEND operation type eDstDfbBldOp Destination surface BLEND operation type eRotate Image rotation angle: 0, 90, 180, 270° eDFBBlendFlag Blending related operations, such as XOR, AlphaBlending, Colorize, etc. eMode Bitblt interpolation mode u32GlobalSrcConstColor const color for dfb blending operation u32GlobalDstConstColor const color for dfb blending operation -
Note
Currently only u32GlobalSrcConstColor is valid.
-
Related Data Type and Interface
3.13. MI_GFX_PaletteEntry_t¶
-
Description
RGB color definition for an Index Color
-
Definition
typedef union { /// ARGB8888 byte order struct { MI_U8 u8A; MI_U8 u8R; MI_U8 u8G; MI_U8 u8B; } RGB; // u8Data[0] = u8A // u8Data[1] = u8R // u8Data[2] = u8G // u8Data[3] = u8B MI_U8 u8Data[4]; } MI_GFX_PaletteEntry_t; -
Member
Member Description RGB Color component structure for an Index Color u8Data Byte order RGB data for an Index Color -
Note
Please pay attention to the remark in the definition, which will help you understand the color value’s memory layout.
-
Related Data Type and Interface
3.14. MI_GFX_Palette_t¶
-
Description
Define palette structure.
-
Definition
typedef struct MI_GFX_Palette_s { MI_GFX_PaletteEntry_t aunPalette[256]; MI_U16 u16PalStart; MI_U16 u16PalEnd; }MI_GFX_Palette_t; -
Member
Member Description aunPalette Array of RGB colors u16PalStart Starting index u16PalEnd Ending index -
Related Data Type and Interface
3.15. MI_GFX_DevAttr_t¶
-
Description
GFX device initialization parameter.
-
Definition
typedef struct MI_GFX_DevAttr_s { MI_U32 u32DevId; MI_U8 *u8Data; } MI_GFX_DevAttr_t; -
Member
Member Description u32DevId Device ID u8Data Data pointer buffer -
Related Data Type and Interface
3.16. MI_GFX_Point_t¶
-
Description
Define point attribute structure.
-
Definition
typedef struct MI_GFX_Point_s { MI_S16 s16x; MI_S16 s16y; } MI_GFX_Point_t; -
Member
Member Description s16x X coordinate S16y Y coordinate -
Related Data Type and Interface
3.17. MI_GFX_Line_t¶
-
Description
Define line attribute structure.
-
Definition
typedef struct MI_GFX_Line_s { MI_GFX_Point_t stPointFrom; MI_GFX_Point_t srPointTo; MI_U16 u16Width; MI_BOOL bColorGradient; MI_U32 u32ColorFrom; MI_U32 u32ColorTo; } MI_GFX_Line_t; -
Member
Member Description stPointFrom Starting point of the straight line srPointTo The end of the straight line u16Width Straight line width bColorGradient Whether the color gradient u32ColorFrom Gradient starting color u32ColorTo Gradient end color -
Related Data Type and Interface
3.18. MI_GFX_Dev¶
-
Description
GFX device id.
-
Definition
typedef MI_S32 MI_GFX_DEV;
-
Note
Except for Muffin supports 2 devices, all the others only support 1.
-
Related Data Type and Interface
All API interfaces.
4. GFX ERROR CODE¶
The GFX API error codes are as listed in the table below:
| Error Code | Macro Definition | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 0xA00D2003 | MI_ERR_GFX_INVALID_PARAM | Invalid parameter |
| 0xA00D2002 | MI_ERR_GFX_DEV_BUSY | GFX device busy |
| 0xA00D2220 | MI_ERR_GFX_NOT_INIT | Device not initialized |
| 0xA00D2221 | MI_ERR_GFX_DRV_NOT_SUPPORT | Unsupported operation |
| 0xA00D2222 | MI_ERR_GFX_DRV_FAIL_FORMAT | Unsupported format |
| 0xA00D2223 | MI_ERR_GFX_NON_ALIGN_ADDRESS | Address not aligned |
| 0xA00D2224 | MI_ERR_GFX_NON_ALIGN_PITCH | Pitch not aligned |
| 0xA00D2225 | MI_ERR_GFX_DRV_FAIL_OVERLAP | Overlap region found in Option |
| 0xA00D2226 | MI_ERR_GFX_DRV_FAIL_STRETCH | Stretch failed |
| 0xA00D2228 | MI_ERR_GFX_DRV_FAIL_LOCKED | Device locked by other use |
| 0xA00D2229 | MI_ERR_GFX_DRV_FAIL_BLTADDR | Bitblit start address error |
5. PROCFS INTRODUCTION¶
5.1. cat¶
-
Debug info
# cat /proc/mi_modules/mi_gfx/mi_gfx0

-
Debug info analysis
Record GFX current usage status and device attribute which can be dynamically got to debug and test.
-
Parameter Description
Parameter Description device info module init countDevice opened times. Since GFX will be called by multiple modules, and it is not certain which module will call GFX initialization first, the device can be opened multiple times. The opened times will be recorded to determine whether the device is required to be closed. Device id GFX device ID ARGB1555 alpha threshold Convert ARGB8888 to ARGB1555. If the alpha threshold in GFX is greater than N, then alpha is 1, otherwise, alpha is 0. ARGB1555 To ARGB8888 alpha value Convert ARGB1555 to ARGB8888, GFX converts the pixel alpha whose alpha bit of ARGB1555 is 1 to ARGB8888 Alpha Value Scaling coefficient Image geometric center offset