MI AO API
REVISION HISTORY¶
| Revision No. | Description |
Date |
|---|---|---|
| 3.50 | 12/04/2020 | |
| 3.51 | 07/19/2021 | |
| 08/25/2021 | ||
| 3.52 | 09/08/2021 | |
| 12/29/2021 | ||
| 3.53 | 02/17/2022 | |
| 3.54 | 03/29/2022 | |
| 05/19/2022 | ||
| 3.55 | 02/28/2023 | |
| 06/10/2023 | ||
| 07/03/2023 | ||
| 11/21/2023 | ||
| 02/05/2024 | ||
| 04/22/2025 |
1. Overview¶
1.1. Module Description¶
Audio Output (AO) is responsible for implementing the output path of digital audio signals to physical devices. This module manages hardware resources such as audio codecs, DMA controllers, and clock sources, and provides interfaces such as parameter configuration, enabling audio output devices, PCM data push, and volume setting for the operating system and applications.
Keyword Description
-
Device (audio output device)
AO Device refers to the RDMA of the audio codec. Device is the abstraction of DMA in the audio codec by audio3.0. There is a one-to-one correspondence between RDMA in the audio codec and AO Device. For example, AO Device0 corresponds to RDMA1 in the audio codec, AO Device1 corresponds to RDMA2 in the audio codec, and so on. The data streams of audio3.0 are all connected in series with DMA as the center.
Audio3.0 also includes another type of device, that is, AI devices that directly send data streams to AO devices without going through DMA, such as (Amic→Lineout). This type of device is called passthrough device, or passthrough, and currently only supports MI_AUDIO_PASSTHROUGH_DEV_1.
-
Interface (audio output peripheral)
AO's Interface refers to the abstraction of the audio output peripheral interface of the audio codec, such as Speaker/I2S Codec/HDMI and other interfaces.
-
Attach
AO attach refers to mounting the interface to RDMA. For AO Device, attach is to connect the output signal of RDMA to a specific interface so that the peripheral can output audio signals. AO Device supports dynamic attach.
When the same AO Interface is attached to two AO Devices, the output of the AO Interface is the mixed result of the two AO Device outputs (supported by the Mochi series).
When the usage scenario includes Passthrough, you need to attach AI first and then attach AO, otherwise it will not work properly.
The following figure shows the result of attaching I2S TX and DAC0/1 to RDMA1. After gain adjustment by DPGA, the signal output from RDMA1 is divided into three branches and reaches DAC0, DAC1 and I2S TX respectively. The Attach of Ao Device is to set the flow direction of these branches.
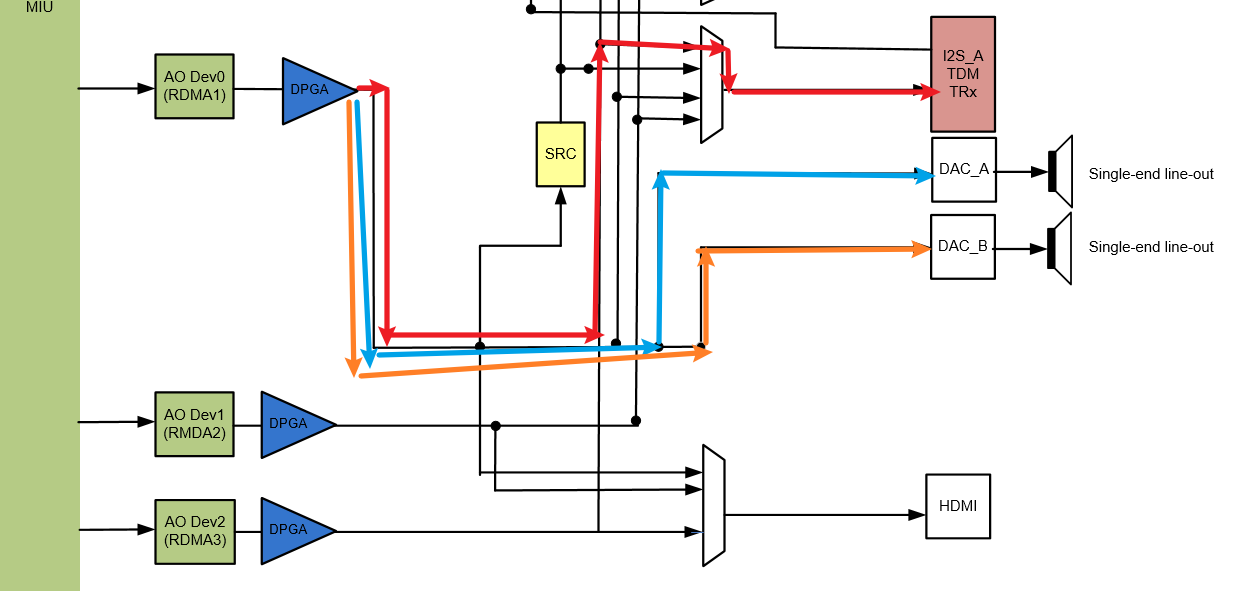
-
Detach
AO's detach means disconnecting the connection between Interface and RDMA.
-
Echo
AO's Echo refers to the reference data of AEC. As can be seen from the audio codec block diagram, the input of SRC is the signal output by RDMA and amplified by DPGA, and the output of SRC is the signal after resampling the input, which can be sent to WDMA through Multi Channel as the echo reference data of the AEC algorithm.
For AI Device, Echo means the output signal of SRC in the audio codec block diagram. For AO Device, Echo means connecting the output of AO Device to the input of SRC. The following figure shows the data flow of AI Device and AO Device using Echo at the same time in a simple block diagram, so that the application can obtain the aligned AEC far end and near end data.
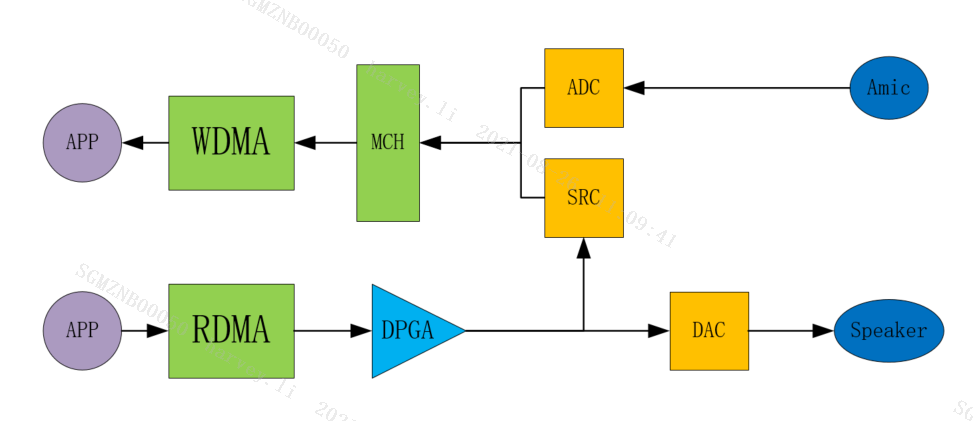
-
Sound Mode
AO's Sound Mode refers to the number of audio channels, such as mono or stereo.
-
Channel Mode (Channel Output Mode)
Support static and dynamic Channel Mode settings. Muffin series chips do not support dynamic Channel Mode settings.
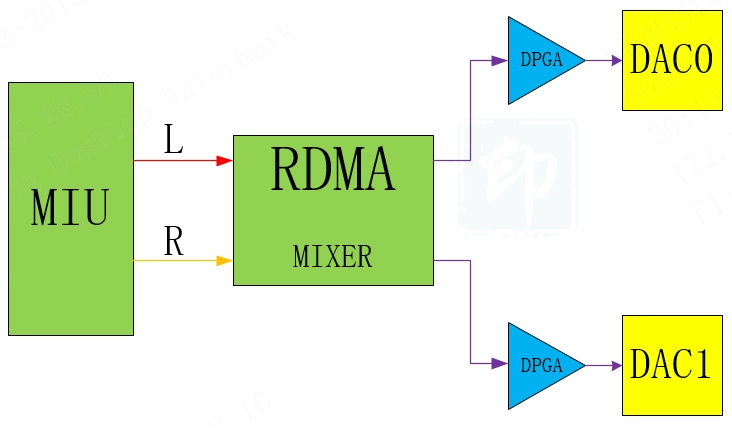
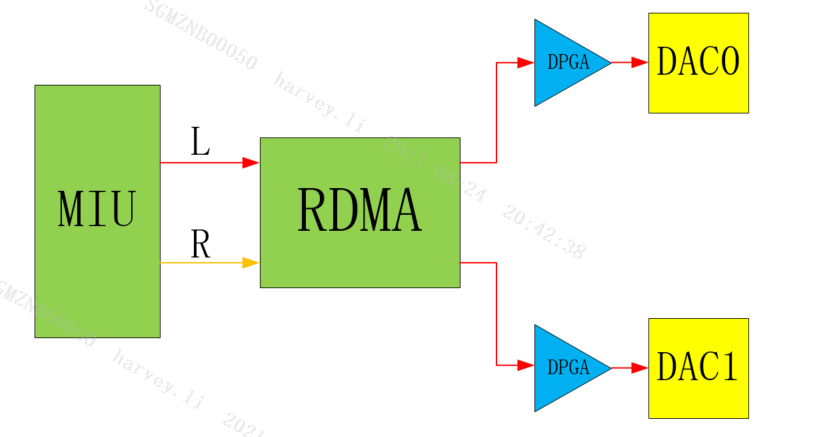
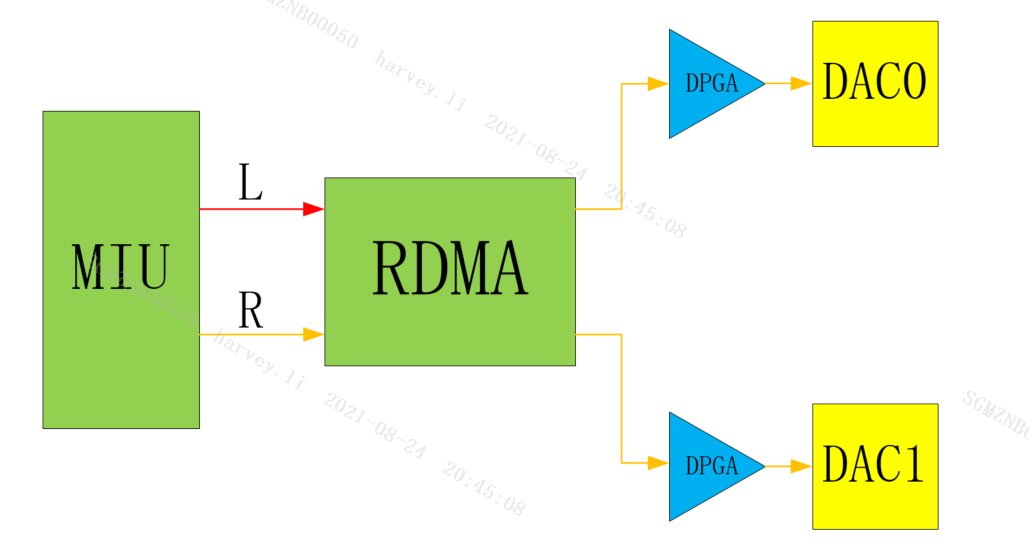
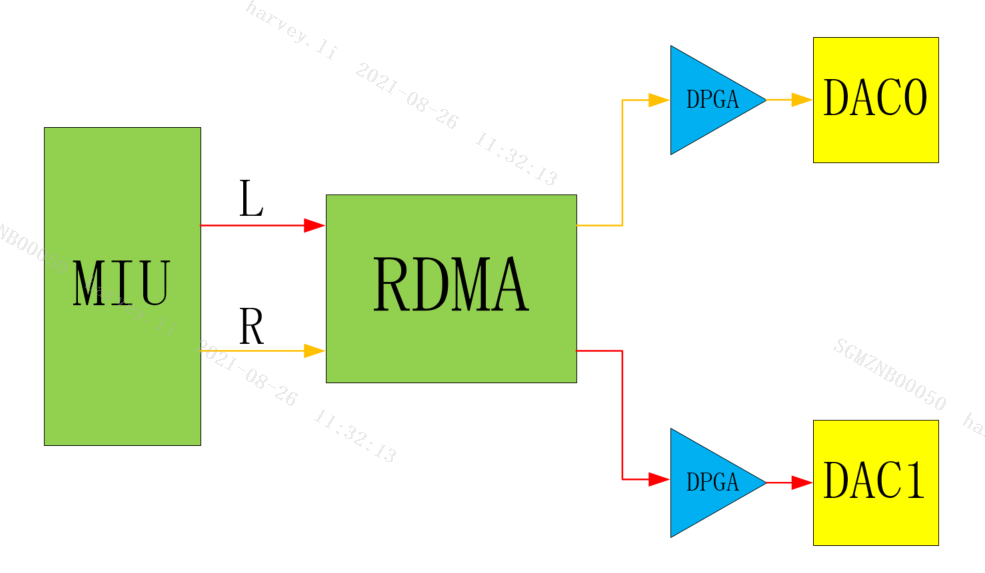
AO 's Channel Mode refers to the output mode of the RDMA channel. For AO Device, Channel Mode determines the correspondence between the audio data channel and the left and right channels of the Interface output. The following diagram illustrates the role of Channel Mode.
-
E_MI_AO_CHANNEL_MODE_STEREO
Normal stereo mode.
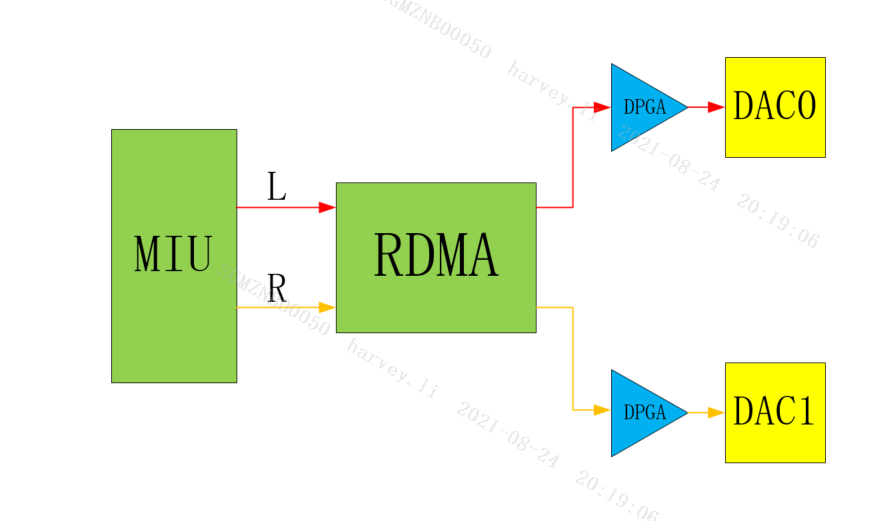
-
E_MI_AO_CHANNEL_MODE_DOUBLE_MONO
Double Mono: The left and right channels are output as the same mono data.
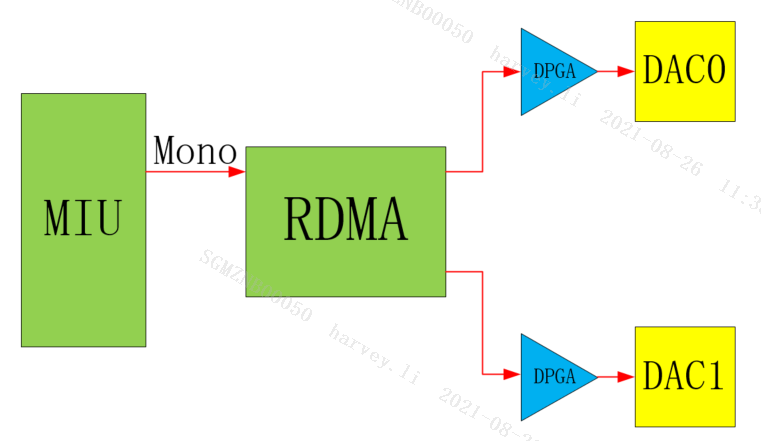
Double Mono stereo, the left and right channel outputs are the data after the left and right channels are mixed, and the left and right channel outputs are the same.
-
E_MI_AO_CHANNEL_MODE_DOUBLE_LEFT
Double Left stereo, the left and right channels are output as left channel data.
-
E_MI_AO_CHANNEL_MODE_DOUBLE_RIGHT
Double Right stereo, the left and right channels are output as right channel data.
-
E_MI_AO_CHANNEL_MODE_EXCHANGE
Exchange stereo, the left and right channel output is the left and right channel exchange data.
-
E_MI_AO_CHANNEL_MODE_ONLY_LEFT
Only Left is mono, and only the left channel is output as mono data.
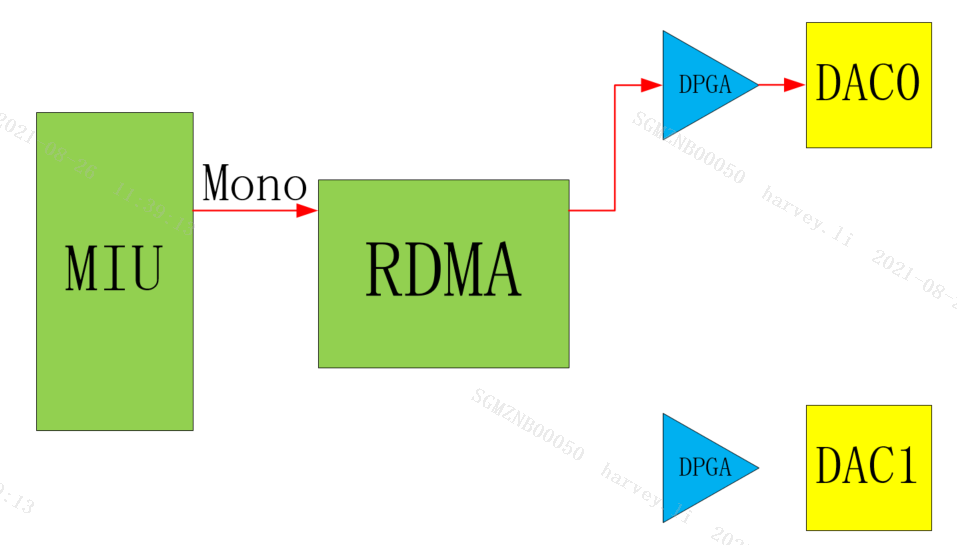
Only Left stereo, only the left channel is output as stereo data.
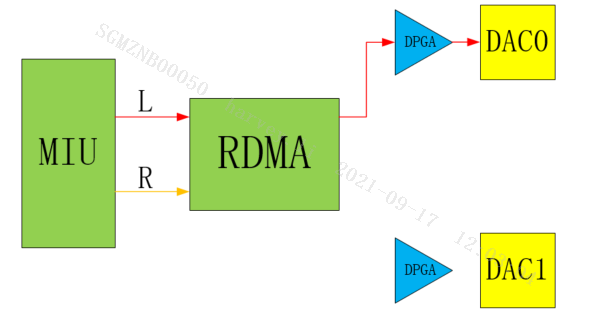
-
E_MI_AO_CHANNEL_MODE_ONLY_RIGHT
Only Right is mono, and only the right channel is output as mono data.
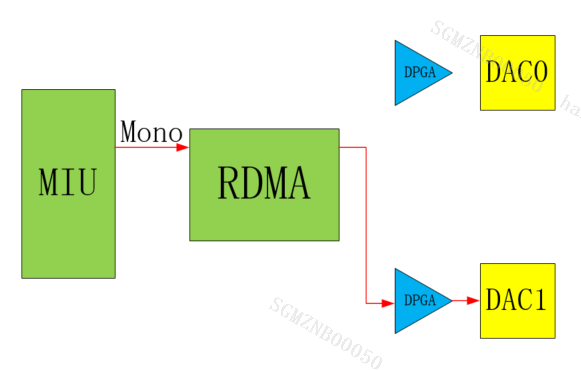
Only Right stereo, only the right channel is output as stereo data.
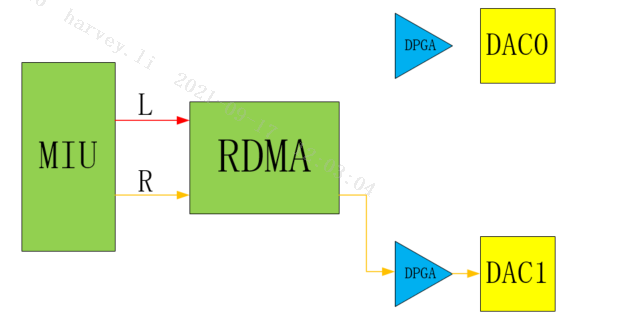
-
-
Gain
AO's Gain is divided into two categories in the audio3.0 architecture. One is the DPGA Gain associated with the Device, that is, the DPGA in the audio codec block diagram, and the other is the Gain unique to the Interface, that is, the IF Gain in the audio codec block diagram (also implemented by DPGA, unique to the Interface). See the block diagram for specific support.
-
Format
Format, that is, what data format is used to represent an audio sample. Currently, only the S16_LE format (PCM Linear 16bit (Little Endian)) is supported.
-
Sample Rate
Sample Rate, that is, the playback sampling rate.
-
Period Size
For AO Device, Period Size indicates the default start condition of AO Device (playback will start only when the number of samples in the cache is greater than Period Size).
-
I2S parameters
-
I2S Mode
I2S Mode determines the working mode of I2S, whether it is standard I2S mode or Tdm I2S mode (2Channel or multi-channel), Master or Slave (Master provides synchronous clock, Slave receives synchronous clock). Generally speaking, there is no restriction on the working mode, as long as it can match the external Codec clock.
-
I2S BitWidth
I2S data transmission and reception currently supports 16/32 bits (Souffle series only supports 16 bits), but the hardware can only process 16 bits, which means that when the bit width is 32 bits, the lower 16 bits are invalid data.(Pcupid supports 16/24/32-bit)
-
I2S Format
The I2S Format is the I2S alignment method. Currently, only I2S Philips and Left-justified alignment are supported. The following figures are waveform diagrams of these two formats.
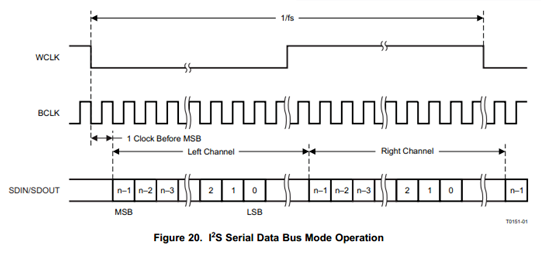
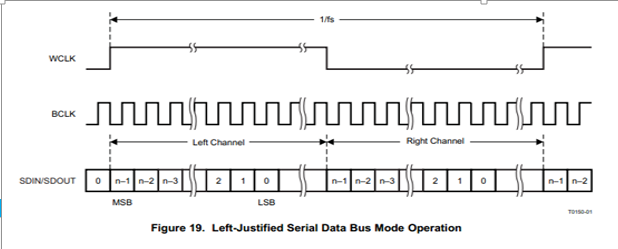
In the I2S Philips alignment format, the first data bit of the sample data appears after the first BCLK (serial clock) of the WCLK (i.e., left and right channel switching clock) transition. In the left alignment format, the first data bit of the sample data appears within the first BCLK (serial clock) of the WCLK (i.e., left and right channel switching clock) transition, and the polarity of WCLK is opposite to that of the I2S Philips alignment format.
-
I2S Sample Rate
The sampling frequency of I2S transmission and reception.
-
Mclk
Mclk, called the master clock, also called the system clock, is generally 256 or 384 times the sampling frequency. It is used to enable better synchronization between systems and is not necessary. Currently, 12.288M, 16.384M, 18.432M, 24.576M, 24M, 48M, etc. are supported (see the data type for specific MCLKs supported).
-
bSyncClock/4-Wire/6-Wire Mode
SigmaStar's I2S has two wiring modes. One is the 4-Wire mode, including four wires: RX_WCK, RX_BCK, RX_SDI, and TX_SDO. In this mode, TX does not have an independent clock, and all clocks are provided by RX. Therefore, in this mode, TX needs to rely on RX to use , and TX cannot be used alone, and the parameters of I2S TX must be consistent with I2S RX. The other is the 6-Wire mode, including six wires: RX_WCK, RX_BCK, RX_SDI, TX_WCK, TX_BCK, and TX_SDO. In this mode, RX and TX are independent and unrelated.
The choice of 4-Wire/6-Wire Mode needs to be determined according to the specific scenario.
If bSyncClock in the MI API I2S parameter is TRUE, 4-Wire Mode is used, and if FALSE, 6-Wire Mode is used. In addition, the RX and TX of the same I2S group cannot be set to 4-Wire Mode on one side and 6-Wire Mode on the other side.
-
Slot
Slot indicates the number of channels transmitted by I2S. Currently, 2slots are supported in I2S mode, and 4/8/16slots are supported in Tdm mode (Mochi series and Souffle series support 16slots). However, the valid data of I2S TX is 2slots. When the number of slots for I2S TX is set to be greater than 2, except for slot0 and slot1, the others are invalid data.
-
-
PCM
The standard I2S (2Chn) protocol is the most commonly used PCM protocol. PCM can transmit multi-channel data, such as 4channel, 8channel, 16channel, etc., which is the TDM protocol (different from the specific format of the standard I2S (2chn) protocol). It is generally used to transmit mono data and is often called PCM (except for the commonly used standard I2S and TDM, others are collectively called PCM). In addition to the standard I2S (2chn) settings, Sigmastar Audio also puts other Timing related settings including 1Chn PCM into the TDM parameters.
-
Passthrough
Passthrough refers to the channel that directly transmits data streams from AI devices to AO devices without DMA. Take ADC_AB→DAC_AB as an example, as shown in the red path in the Figure below:
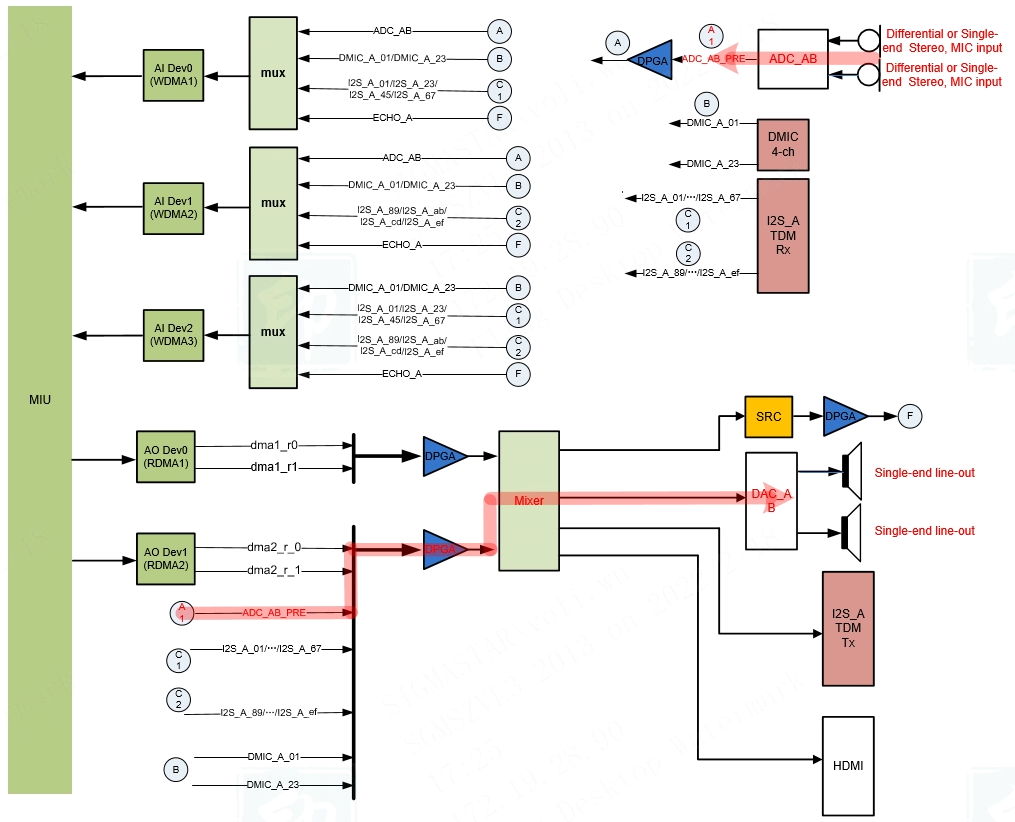
Muffin series chips only support passthrough from the input device ADC_AB to the output device DAC_AB.
Mochi series chips support any combination of passthrough from input devices ADC_AB/DMIC_A_01/ DMIC_A_23/I2S_A_01/…/ I2S_A_EF to output devices DAC_AB/I2S_TX/ HDMI. The current limitations of passthrough in Mochi series chips are: only support sampling rate 48K; Passthrough Device does not support Channel Mode setting; in passthrough + DMA mixing scenario, the output device only supports DAC_AB.
1.2. Basic structure¶
For the audio subsystem of the Pcupid chip, please refer to the introduction in 1.2.6. Pcupid Series.
1.2.1. Audio Codec Device Description¶
-
DMA
DMA stands for Direct Memory Access. DMA transfer copies data from one address space to another, providing high-speed data transfer between peripherals and memory or between memory and memory. When the CPU initiates the transfer action, the transfer action itself is implemented and completed by the DMA controller. The DMA transfer method does not require the CPU to directly control the transfer, nor does it have the process of retaining and restoring the scene like the interrupt processing method. It opens a channel for direct data transmission for RAM and IO devices through hardware, greatly improving the efficiency of the CPU.
-
WDMA
WDMA stands for Direct Memory Access Writer.
-
RDMA
RDMA stands for Direct Memory Access Reader.
-
MUX
MUX is a multiplexer data selector. In the process of multi-channel data transmission, it can select any of the multiple channels according to the needs. The Mux in front of WDMA selects multiple data sources for WDMA, and can support the selection of ½/4 data sources (the data sources can be the same or different, and the Souffle series chips support the selection of up to 8 data sources 16Chn). Each data source has two channels, that is, 2/4/8/16 channels of data are selected to be written to DRAM by WDMA (except for the Souffle series chips that support 16 channels, other series support up to 8 channels), playing the role of a multiple-way switch. The Mux close to the output peripheral interface (such as I2S TX/HDMI/DAC, etc.) realizes the function of selecting one from multiple or selecting many from one.
-
DPGA
DPGA stands for Digital Programmable Gain Amplifier, which is a very versatile amplifier whose amplification factor can be controlled by program as needed.
-
DMIC
DMIC stands for Digital Microphone Interface. The audio codec only provides a DMIC interface, not a complete DMIC. The DMIC interface provides the clock signal required for DMIC operation and receives the PDM signal from DMIC.
-
ADC
ADC stands for Analog Digital Conversion, which is an electronic component that converts analog signals into digital signals.
-
I2S
I2S stands for Inter-IC Sound integrated circuit built-in audio bus, which is a bus standard developed by Philips for audio data transmission between digital audio devices. Sigmastar's I2S bus only supports the standard I2S data format and the left-aligned I2S data format. It also supports TDM, which is Time-Division Multiplexing technology, to interweave different signals in different time periods and transmit them along the same channel, and can support 4/8/16 channel data transmission at the same time.
-
DAC
DAC stands for Digital Analog Conversion, which is an electronic component that converts digital signals into analog signals.
-
SRC
SRC stands for Sample Rate Convert, which converts the sampling rate of voice digital signals.
-
HDMI
HDMI (High Definition Multimedia Interface), AO output interface, is a fully digital video and sound transmission interface that can send uncompressed audio and video signals.
-
Mixer
Mixer , hardware mixing, uses a linear superposition averaging algorithm (if the volume of a certain audio channel is particularly low, the volume of the entire mixing result will be lowered). After mixing, the output sampling rate can be set.
1.2.2. Muffin Series¶
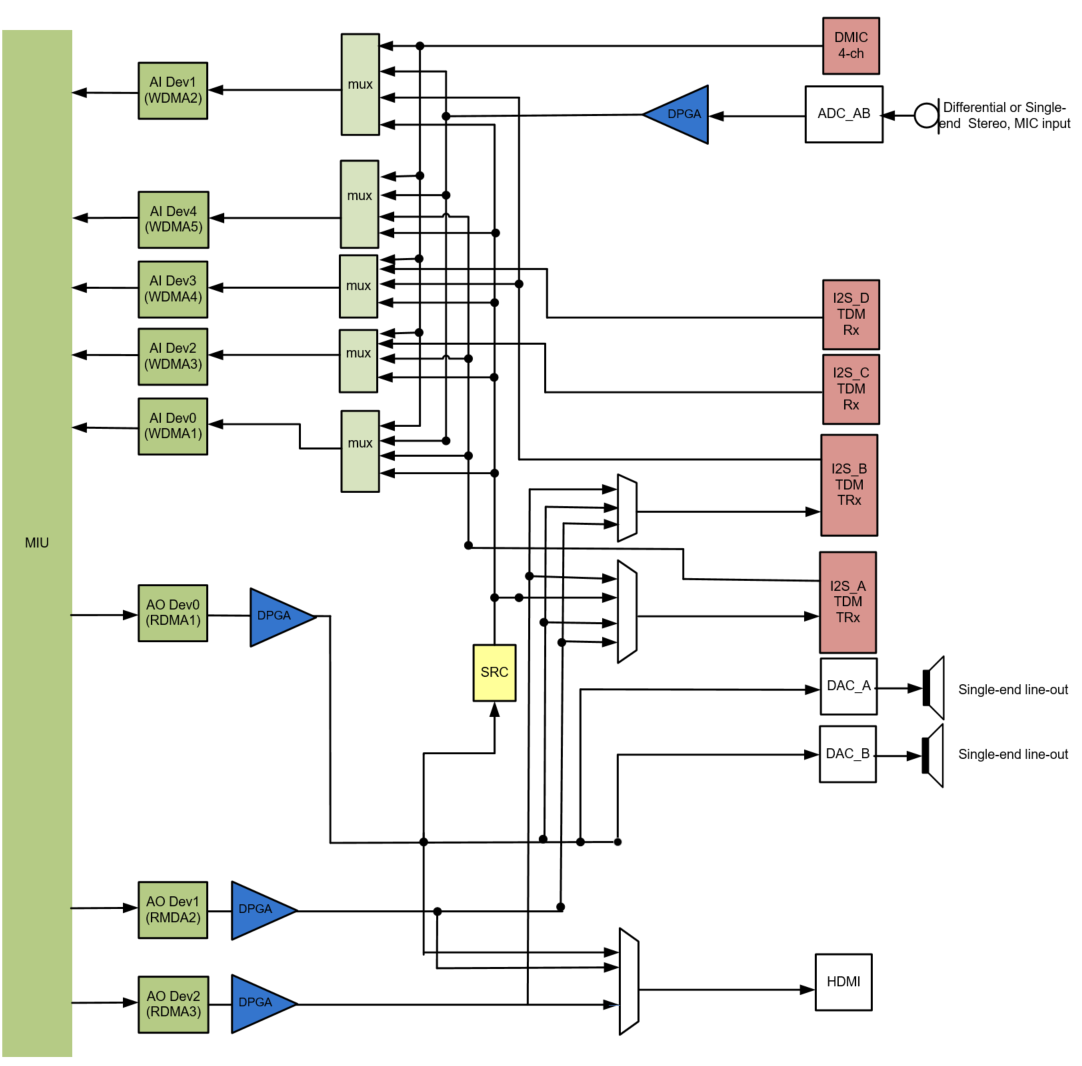
The audio codec of the Muffin series chips has the following resources:
-
WDMA * 5
-
RDMA * 3
-
DMIC interface (supports 4Chn DMIC signal) * 1
-
ADC (supports 2Chn Amic/Linein) * 2
-
I2S-TDM RX * 4
-
I2S-TDM TX * 2
-
DAC (supports 2Chn Lineout) * 2
-
SRC * 1
-
HDMI TX * 1
1.2.3. Mochi Series¶
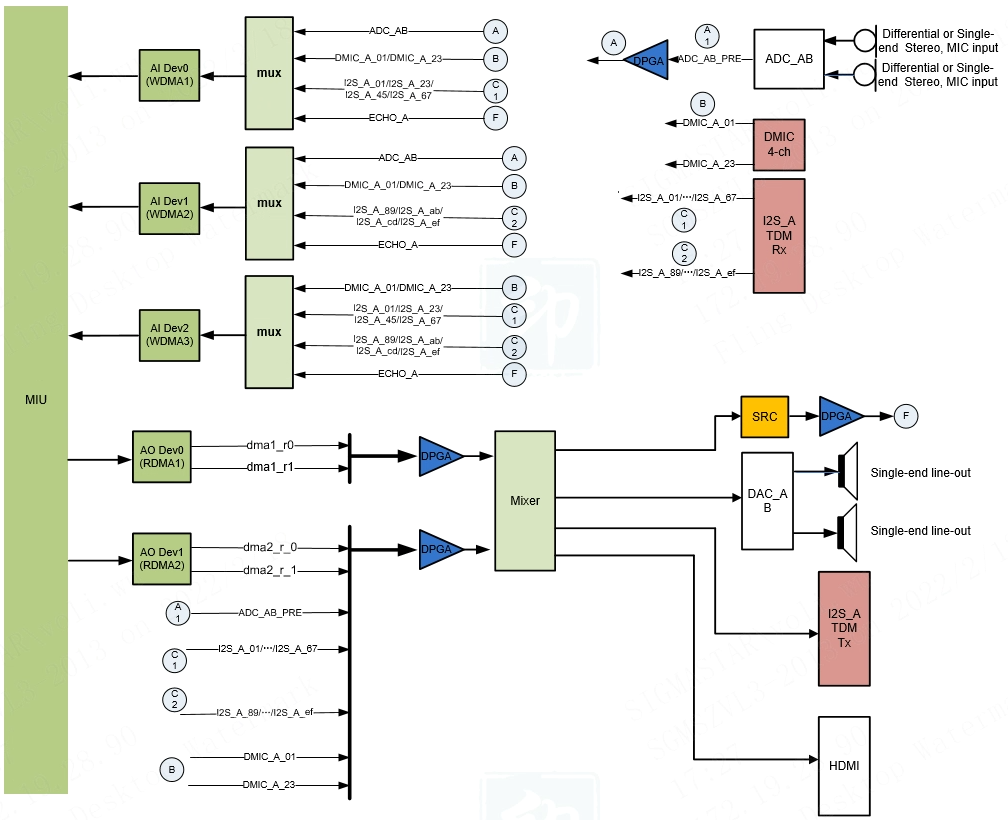
The audio codec of the Mochi series chips has the following resources:
-
WDMA * 3
-
RDMA * 2
-
DMIC interface (supports 4Chn DMIC signal) * 1
-
ADC (supports 2Chn Amic/Linein) * 2
-
I2S-TDM RX (16 slots) * 1
-
I2S-TDM TX (16 slots, but only 2 channels of valid data) * 1
-
DAC (supports 2Chn Lineout) * 2
-
SRC * 1
-
HDMI TX * 1
1.2.4. Maruko series¶
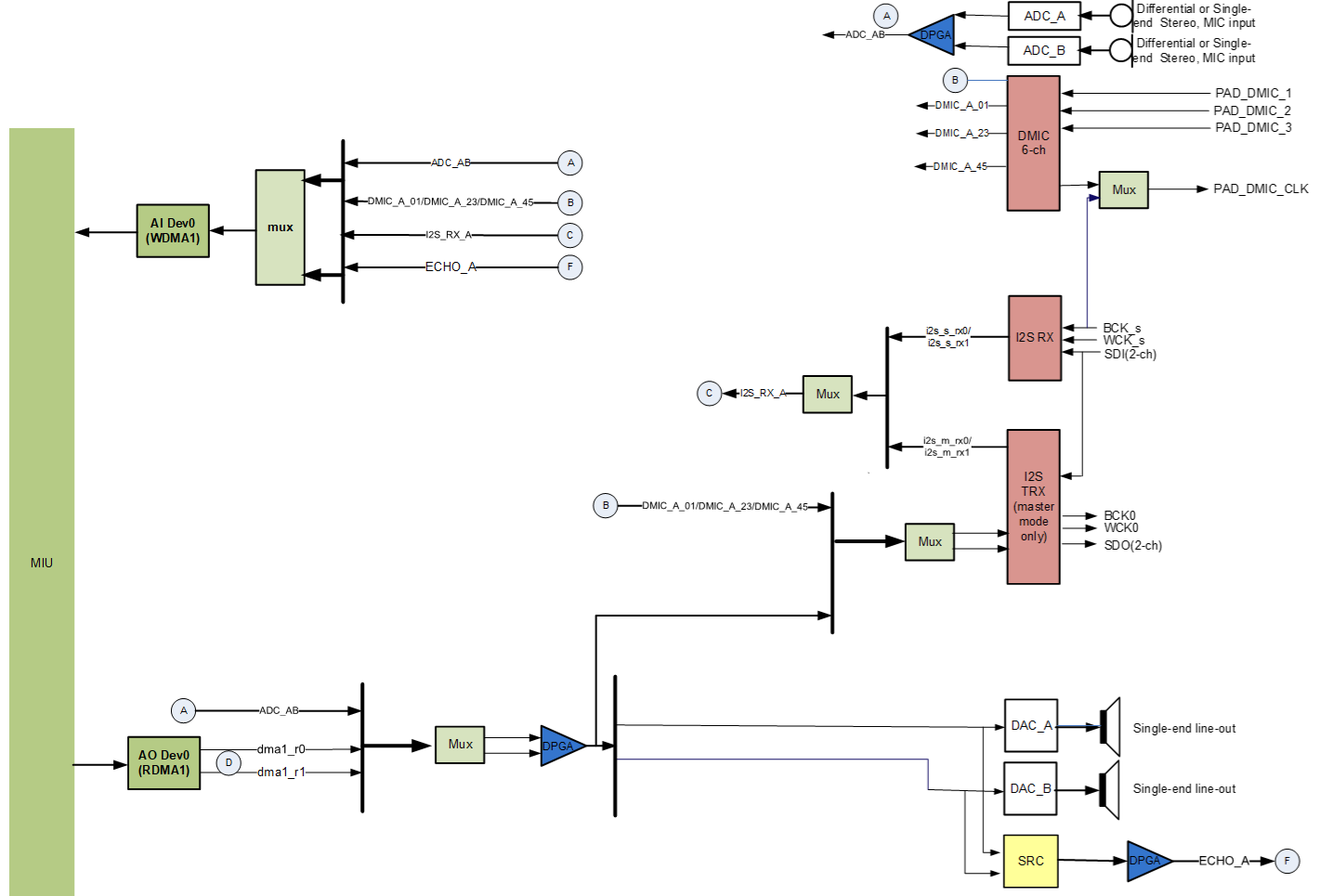
The audio codec of the Maruko series chip has the following resources:
-
WDMA * 1
-
RDMA * 1
-
DMIC interface (supports 6Chn DMIC signal) * 1
-
ADC (supports 2Chn Amic/Linein) * 2
-
I2S RX(2 slots) * 2
-
I2S TX(2 slots) * 1
-
DAC (supports 2Chn Lineout) * 2
-
SRC*1
1.2.5. Souffle Series¶
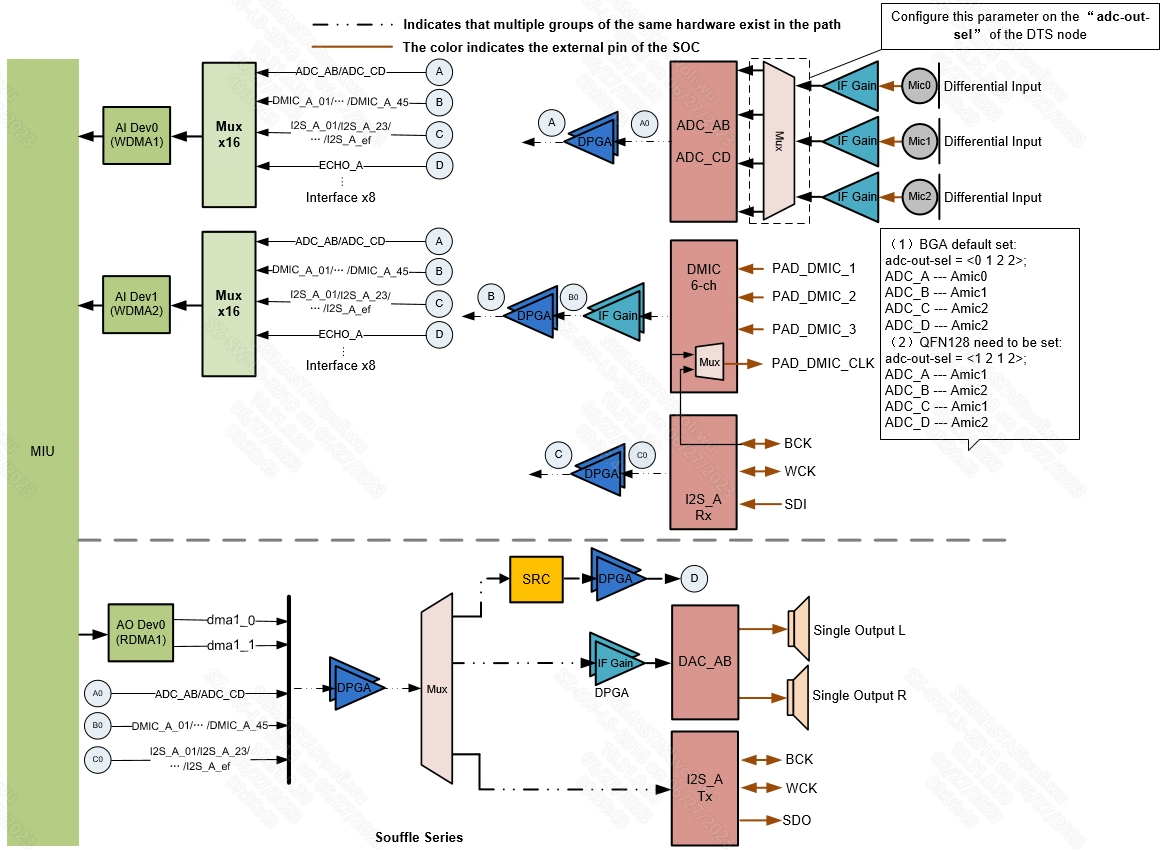
The audio codec of the Souffle series chips has the following resources:
-
WDMA * 2
-
RDMA * 1
-
DMIC interface (supports 6Chn DMIC signal, DMIC CLK can be shared with I2S_RX BCK) * 1
-
ADC (supports 3Chn Amic/Linein Differential Input) * 3
-
I2S RX(16 slot) * 1
-
I2S TX(16 slots) * 1
-
DAC (supports 2Chn Lineout Single Output) * 2
-
SRC (2 physical channels) * 1
1.2.6. Pcupid Series ¶
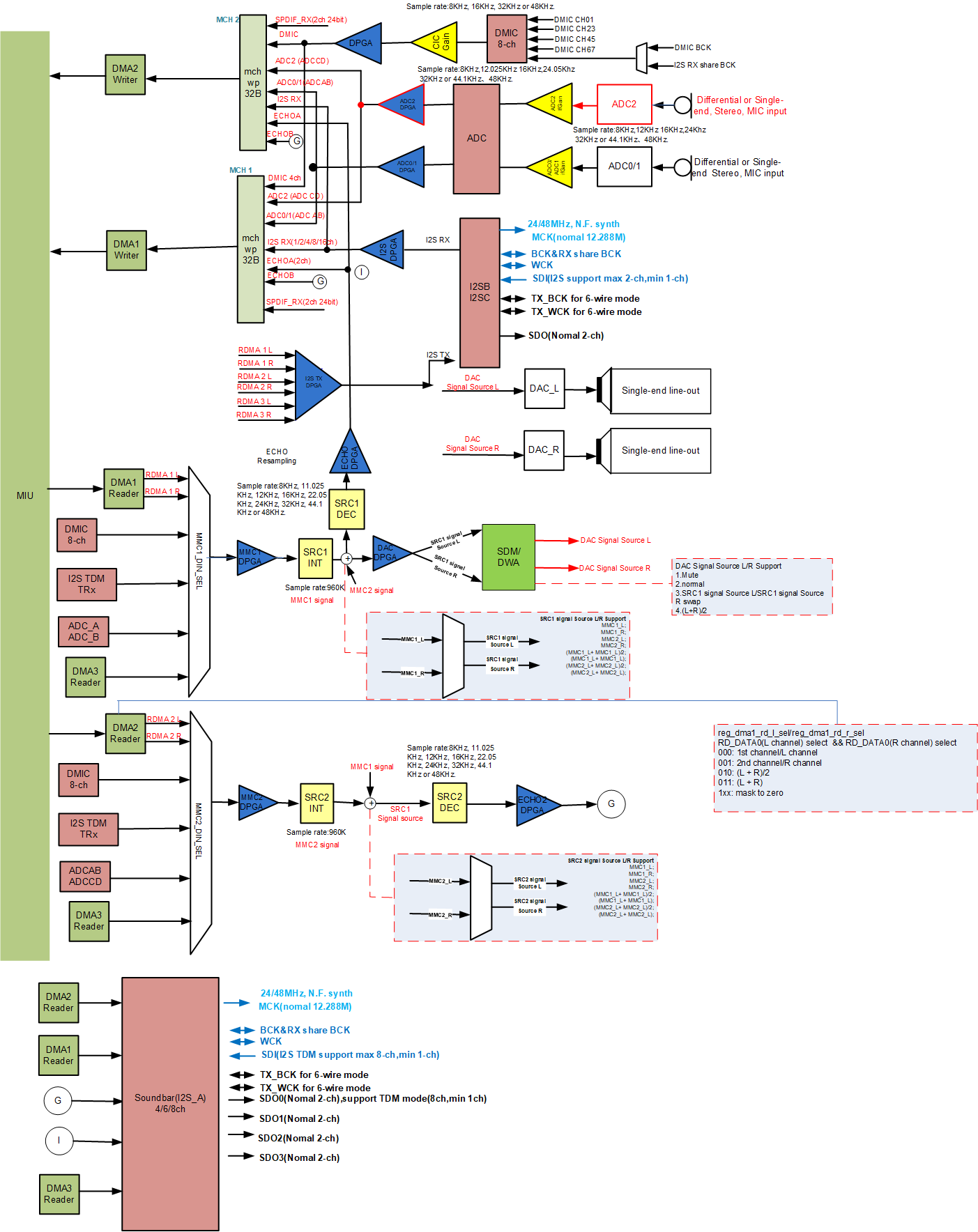
The audio codec of the Pcupid series chips has the following resources:
-
WDMA * 2
-
RDMA * 3
-
DMIC interface (supports 8Chn DMIC signal) * 1
-
ADC (supports 2Chn Amic/Linein) * 2
-
I2S-TDM RX * 3
-
I2S-TDM TX * 3
-
DAC (supports 2Chn Lineout) * 2
-
SRC * 2
1.3. Function Introduction¶
Audio Out mainly supports the following functions:
-
Convert digital audio stream into analog signal output through DAC
-
Support I2S/TDM/SPDIF/HDMI-TX digital audio protocol output
-
Support 8-channel synchronous output through 4 independent SDOs
-
Provide -64dB~+64dB range gain control
-
Support master/slave mode switching and external clock synchronization
-
Support 16/24/32bit bit width
1.3.1 DMA¶
-
Data bit width : Support 16/24/32bit data access
-
Multi-channel support :
- RDMA supports 2/6/8 channels parallel output
1.3.2 DAC¶
-
DAC Features :
- Output mode: 2-way single-ended output
1.3.3 I2S¶
-
I2S Master Interface :
-
Send channel: 2-channel output (including multiple independent SDO)
-
Bit width support: 16/24/32bit
-
Sampling rate range:
-
TX: 8/11.025/12/16/22.05/24/32/44.1/48/96/192KHz
-
Working mode: TX supports master and slave modes, TDM mode
-
1.3.4. DPGA¶
-
Gain Range : -63.875dB ~ +64dB
-
Adjustment accuracy : 0.125dB/Step
-
Fading step : 1/ 2/ 4/ 8/ 16/ 32/ 64/ 128
1.4. Application scenarios¶
MI_AO can be applied to the following scenarios:
-
Pure Linux scenario
In the Linux environment, it supports development based on the API interface provided by MI_AI, and is also compatible with the standard ALSA interface for audio development. For ALSA development, please refer to Audio Development Guide.
-
Pure RTOS scenario
In the RTOS environment, applications can be developed based on the API interface provided by MI_AO.
-
Dualos scenario
In the dualOS environment, applications running on the Linux side or the RTOS side are all developed based on the MI_AO API.
1.5. Chip Differences¶
For the audio subsystem of the Pcupid chip, please refer to the introduction in 1.5.5. Pcupid Series.
1.5.1. Muffin Series¶
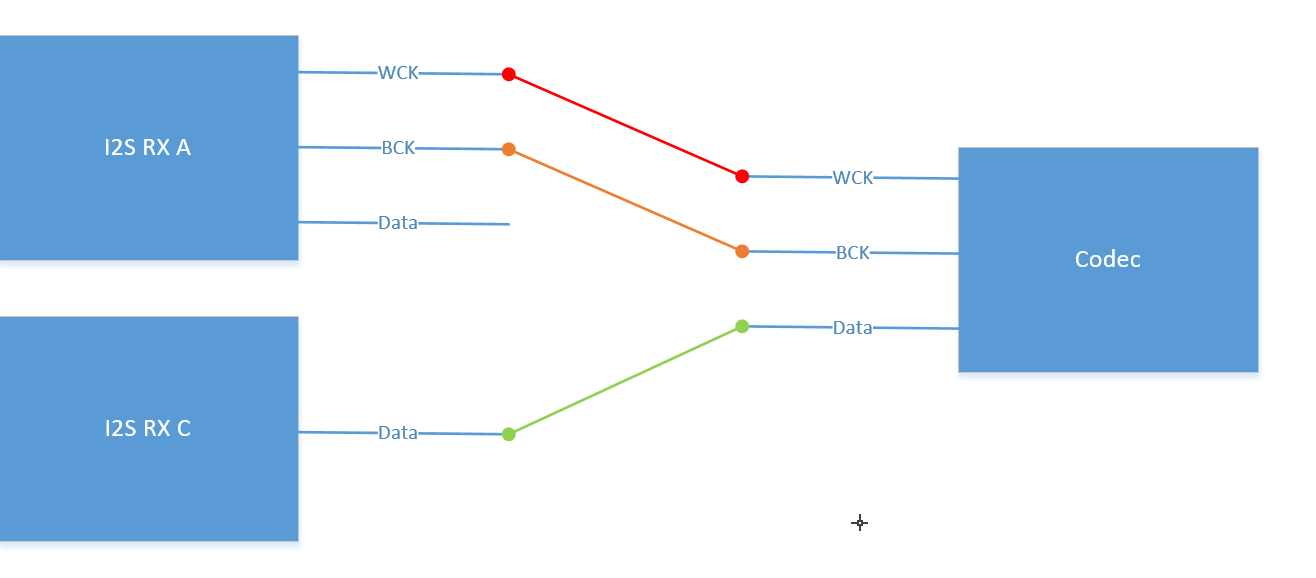
Muffin series chips have I2S RX * 4, but I2S RX C and I2S RX D have two modes, one is called share mode, and the other is called slave mode. In share mode, I2S RX C and I2S RX A share I2S Clock (Wck and Bck), and I2S RX D and I2S RX B share I2S Clock (Wck and Bck). When I2S RX A and I2S RX C need to be used at the same time, the I2S parameters of the two must be completely consistent. The Codec connected to I2S RX C needs to connect the I2S Clock pin (Wck and Bck) to the I2S Clock (Wck and Bck) of I2S RX A, and the Data pin to the Data of I2S RX C. The hardware connection is shown in the figure below. The relationship between I2S RX D and I2S RX B is the same as that between I2S RX C and I2S RX A. In slave mode, I2S RX C and I2S RX D have independent clocks, but can only be used as slaves. These two modes can be set through i2s-rx-mode under the dts sound node, 0 is slave mode, 1 is share mode.
1.5.2. Mochi Series¶
The audio codec of the Mochi series chips has the following resources: WDMA * 3, RDMA * 2, DMIC interface (supports 4Chn DMIC signal) * 1, ADC (supports 2Chn Amic/Linein) * 2, I2S-TDM RX (16 slots) * 1, DAC (supports 2Chn Lineout) * 2, SRC * 1, HDMI TX * 1.
Mochi series chips support up to 16 slots in I2S, and the sampling rate supports 96K/192K. Note: In the I2S usage scenario, the maximum I2S BCK cannot exceed 30MHz (such as: BCK=16bit * 16slots * 192K=49.152M or BCK=32bit * 16slots * 192K=98.304M, BCK> 30MHz is not supported).
Support mixing of two AO devices, represented by Mixer in the Audio Codec block diagram. After mixing, the output sampling rate can be set to 8K/16K/32K/48K.
Note: ADC_AB_PRE in the Audio Codec block diagram of the Mochi series chips represents the audio signal before passing through DPGA.
1.5.3. Maruko series¶
Although the Maruko series chips have two sets of I2S RX, the two sets of I2S RX cannot be used at the same time. The following are the usage scenarios of the two sets of I2S RX:
-
I2S RX:
-
The external codec transmits non-I2S signals, so Wck and Bck need to be adjusted, such as receiving PCM signals.
-
Need to share clock with Dmic to achieve Dmic and I2S RX synchronization.
-
The external codec works in master mode.
-
I2S TRX:
-
Need to use I2S TX.
The two I2S RX groups are selected through i2s-pcm under the dts sound node, 1 is I2S RX, 0 is I2S TRX. In addition, whether I2S RX shares the Dmic clock is configured through dmic-bck-share in dts, 1 is shared clock, 0 is independent clock.
1.5.4. Souffle Series¶
The Souffle series chip I2S supports a maximum of 16 slots, a sampling rate of 96K/192K, and 1Chn PCM, but does not support 32-bit bit width transmission and reception. Compared with the old SOC, it supports the output of more frequency MCLK.
MUX currently supports a maximum of 16 channels and supports attaching 16 channels of audio data to the same DMA at the same time.
I2S RX 'BCK' supports sharing clock with Dmic 'CLK'. Whether I2S RX shares clock with Dmic is configured through dmic-bck-share. 1 means sharing clock, 0 means independent clock.
I2S supports short FF mode (configured through the nodes i2s-rx-short-ff-mode/i2s-tx-short-ff-mode in dts), supports WS_DLY=1~3, where WS_DLY=0 means NO short FF mode. The following Figures are the timings corresponding to normal mode and short-FF-mode respectively.
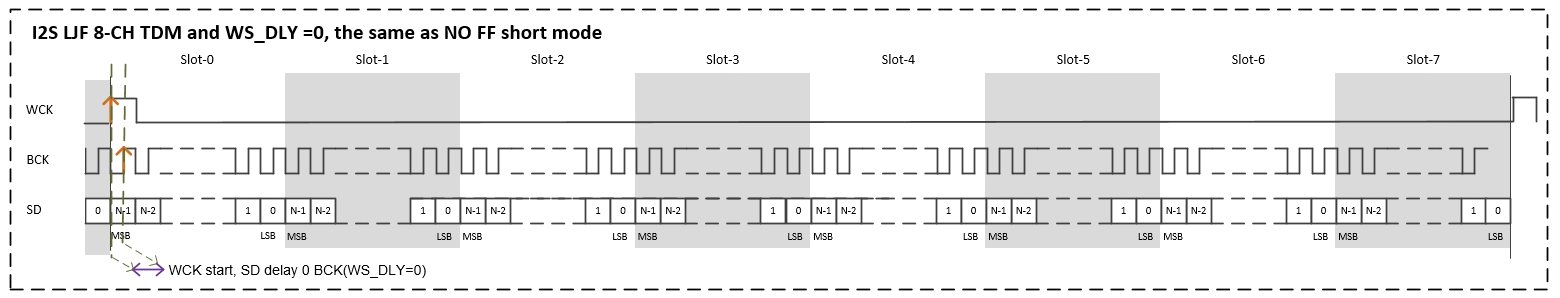
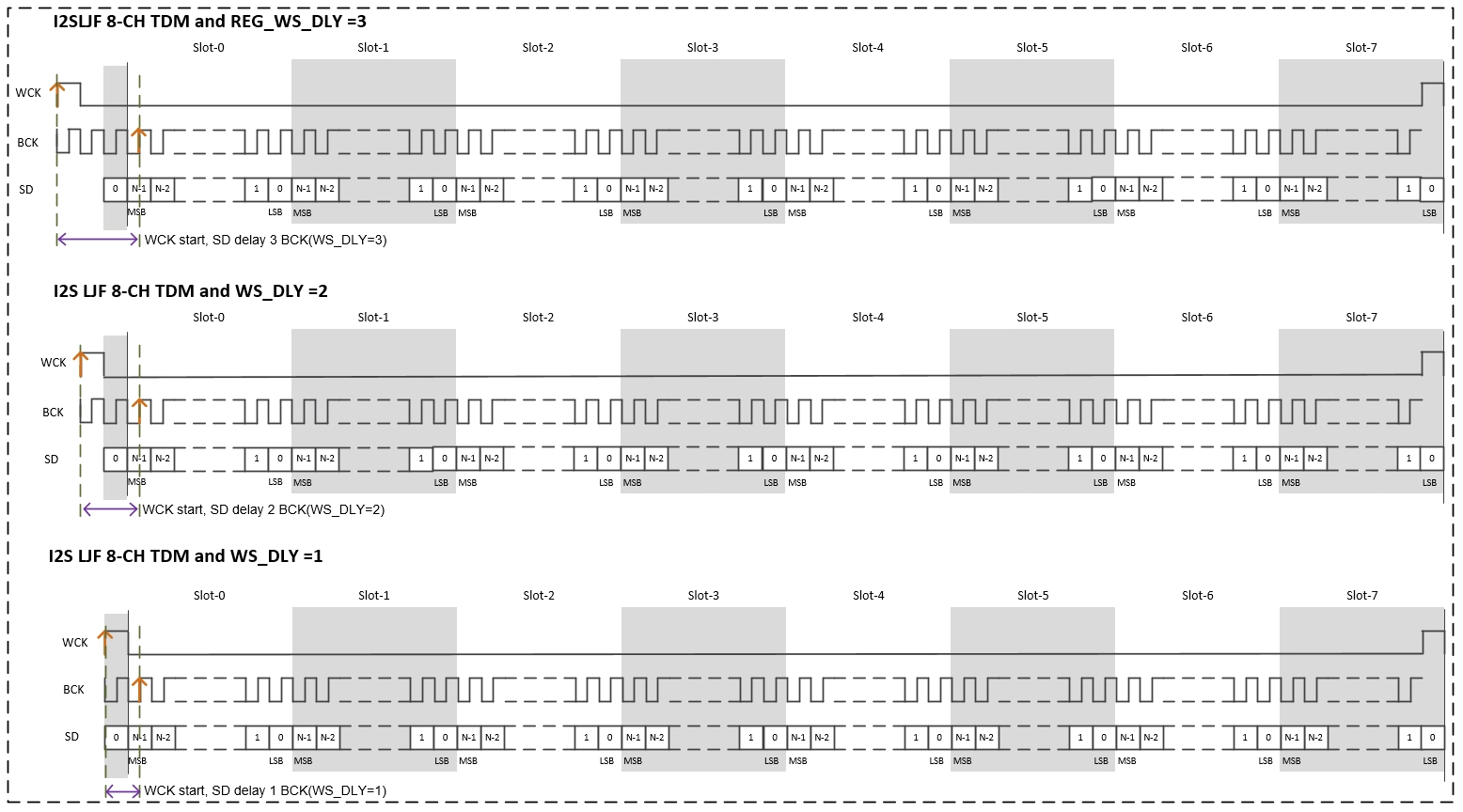
Note: In the I2S usage scenario, the maximum I2S BCK cannot exceed 30MHz (for example: BCK=16bit * 16slots * 192K=49.152M, the usage of BCK> 30MHz is not supported).
1.5.5. Pcupid Series ¶
The Pcupid series chip I2S supports a maximum of 8 slots, a sampling rate of 96K/192K, 1Chn PCM, and 16/24/32bit bit width for transmission and reception.
WDMA0 currently supports a maximum of 16 channels and supports attaching 16 channels of audio data to the same DMA at the same time. WDMA1 currently supports a maximum of 8 channels and supports attaching 8 channels of audio data to the same DMA at the same time.
I2S RX0 'BCK' supports sharing clock with Dmic 'CLK'. Whether I2S RX0 shares clock with Dmic is configured through dmic-bck-share. 1 is shared clock, 0 is independent clock.
I2S supports short FF mode (configured through the nodes i2s-rx-short-ff-mode/i2s-tx-short-ff-mode in dts), and supports WS_DLY=1~3, where WS_DLY=0 means NO short FF mode.
1.5.6. Summary of differences¶
The following table shows the hardware differences between different chip series:
| Function | Pcupid | Tiramisu | Mochi | Muffin | Maruko | Opera | Souffle |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| WDMA | 2 | 2 | 2 | 5 | 1 | 2 | 2 |
| ADC | 3 | 3 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 3 | 3 |
| I2S_RX | 2 8ch 16/24/32bit 8k~192k |
1 8ch 16bit |
1 8ch 16bit |
3 8ch 16bit |
1 8ch 16bit |
2 16ch 16bit 8/16/32/44.1/48k |
1 16ch 16bit |
| SPDIF_RX | 1 24bit 32k~192k |
N | N | N | N | N | N |
| HDMI_RX | N | N | N | N | N | 1 2ch 16bit 32/44.1/48k |
N |
| DMIC | 8ch | 4ch | 4ch | 4ch | 6ch | 8ch | 6ch |
| RDMA | 3 | 2 | 2 | 3 | 1 | 2 | 2 |
| DAC | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 |
| I2S_TX | 3 2ch 16/24/32bit |
1 | 1 2ch 16bit |
3 2ch 16bit |
1 2ch 16bit |
2 2ch 16bit |
1 2ch 16bit |
| SPDIF_TX | N | N | N | N | N | 1 | N |
| HDMI_TX | N | N | N | N | N | N | N |
| ECHO | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y |
1.6. Development Process¶
1.6.1. Compilation Configuration¶
-
Enter the alkaid project root directory, make menuconfig
-
Press Enter to enter the Sdk Config sub-option
-
Press Enter to enter the Interface Compile Config sub-option
-
Use the spacebar to select the aio and ao submodules and recompile the project
After compilation is complete, mi_ao.ko will be generated under sdk/interface/src/ao, and mi_aio.ko will be generated under sdk/interface/src/aio. At the same time, release mi_ao.h, mi_ao_datatype.h and mi_aio_datatype.h to the project/release directory. In a pure Linux environment, it will be packaged into images by default.
1.6.2. Device Tree¶
1.6.2.1 Linux DTS
The Linux device tree is used to describe the hardware platform and its peripheral properties. The file is located in linux/arch/{arm}/boot/dts/{chipName}.dtsi , and the audio related file is sound :
sound: sound {
compatible = "sstar,audio";
interrupts=<GIC_SPI INT_IRQ_BACH IRQ_TYPE_LEVEL_HIGH>;
amp-pad = <PAD_UNKNOWN 1 PAD_UNKNOWN 1 PAD_UNKNOWN 1 PAD_UNKNOWN 1>;
clocks = <&CLK_au_sys_384>, <&CLK_aupll_384m>, <&CLK_au_sys_dyn_384>;
// I2S TX0 TDM
i2s-tx0-tdm-mode = <1>; // 1:master 2:slave
i2s-tx0-tdm-fmt = <1>; // 1:i2s justify 2:left justify
i2s-tx0-tdm-wiremode = <2>; // 1:4wire 2:6 wire
i2s-tx0-channel = <2>;
i2s-tx0-soundbar-mode = <1>; //0:OFF 1:ON
i2s-tx0-tdm-ws-pgm = <0>; // 0: OFF 1: ON
i2s-tx0-tdm-ws-width = <0>; // value: 0~31 (width = value + 1)
i2s-tx0-tdm-ws-inv = <0>; // 0: normal 1: inverse WCK
i2s-tx0-tdm-bck-inv = <0>; // 0: normal 1: inverse BCK
i2s-tx0-tdm-ch-swap = <0 0 0 0>; // 0: OFF 1: ON
i2s-tx0-tdm-active-slot = <0xFFFF>; // value: 0x00 ~ 0xFF (bit0->slot0, bit1->slot1, ... )
i2s-tx0-short-ff-mode = <0>;
i2s-tx0-tx-mode = <1>; // Control the internal i2s clock invert or not
debug-level = <0>;
status = "okay";
};
The properties of the device tree configuration are as follows:
| Properties | Description | Notes |
| -------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- |
| interrupts | Specify hardware interrupt number | Modification prohibited |
| clocks | Specify clock source | Modification prohibited |
| amp_gpio | Specify AMP enable pin | When enabling Padmux, the settings in Padmux are used first |
| i2s-tdm-mode | Master-slave mode | 1: Master mode
2: Slave mode |
| i2s-tdm-fmt | I2S format | 1: Standard format
2: Left-aligned format |
| i2s-tdm-wiremode | Configure I2S wiring mode | 1: 4-wire mode
2: 6-wire mode |
| i2s-channel | Configure the number of I2S channels | Value range: 1, 2, 4, 8 |
| i2s-tdm-ws-pgm | TDM programmable mode | 0: OFF, width attribute is not effective, WCK duty cycle is fixed to 50%
1: ON, WCK width is (width+1)*bclk |
| i2s-tdm-ws-width | Configure the width of tdm WCK | 0~31 (width = value + 1) |
| i2s-tdm-ws-inv | I2S wck inversion | 0: Do not invert
1: Invert |
| i2s-tdm-bck-inv | I2S bck inversion | 0: Do not invert
1: Invert |
| i2s-tdm-ch-swap | Configure rx i2s channel swap | <0 0 0 0>
<0 1 0 0>
<1 0 0 0>
<1 1 0 0> |
| i2s-short-ff-mode | short FF mode | 0: Disable
1: Enable |
| i2s-tx-soundbar-mode | Configure Soundbar mode | 1: On
2: Off, when on, I2S data will output audio data from SDO0/½/3 at the same time |
| i2s-tx-tx-mode | I2S internal clock inversion | 0: Disable
1: Enable |
| i2s-tx-tdm-active-slot | Configure I2S tx active channel | 0x0000 ~ 0xFFFF (bit0->slot0, bit1->slot1, ...) |
| debug-level | Control dump level | 0x00000001: debug fot test
0x00000002: Dump dma LOG information
0x00000004: Dump analog part information
0x00000008: Dump I2S information
0x00000010: Dump DMIC information
0x00000020: Dump interrupt information
0x00000040: Dump delay
0x00000080: Dump attach path information
0x00000100: Dump power information
0x00000200: Dump Clock information
0x00000400: Dump pcm data
0x00000800 : Dump SPDIF information|
1.6.2.2 RTOS SYS
{chipName}_xxx.sys file is used to describe the properties of peripheral hardware. The property values contained in the peripheral node can be used to configure the peripheral, similar to the Linux device tree. The file is located in sc/driver/sysdriver/sysdesc/hal/{chipName}/pub , and the audio related file is sound :
<sound>
[compatible_str] "sstar,audio";
[interrupts_u8] INT_IRQ_BACH;
[camclk_u16] CAMCLK_upll_480m, CAMCLK_bachpll_384m, CAMCLK_aupll_384m;
[amp_gpio_u16] PAD_PM_GPIO0, 1, PAD_UNKNOWN, 1, PAD_PM_GPIO0, 1;
[debug_level_u32] 0x0000;
[i2s_tx0_tdm_active_slot_u32] 0xffff;
[i2s_tx1_tdm_active_slot_u32] 0xffff;
[i2s_tx2_tdm_active_slot_u32] 0xffff;
The properties supported by the RTOS audio driver are as follows:
| Properties | Description | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| interrupts_u8 | Specify hardware interrupt number | Modification prohibited |
| camclk_u16 | Specify clock source | Modification prohibited |
| amp_gpio_u16 | Specify AMP enable pin | When Padmux is enabled, the settings in Padmux are used first |
| debug_level_u32 | debug log level | can be modified as needed |
| i2s_tx0_tdm_active_slot_u32 | Configure I2S tx active channel | Can be modified as needed |
| i2s_tx1_tdm_active_slot_u32 | Configure I2S tx active channel | Can be modified as needed |
| i2s_tx2_tdm_active_slot_u32 | Configure I2S tx active channel | Can be modified as needed |
- debug level
| Property name | Description | Value range |
|---|---|---|
| debug-level | Control print level | 0x00000001: debug fot test 0x00000002: Dump dma LOG information 0x00000004: Dump analog part information 0x00000008: Dump I2S information 0x00000010: Dump DMIC information 0x00000020: Dump interrupt information 0x00000040: Dump delay 0x00000080: Dump attach path information 0x00000100: Dump power information 0x00000200: Dump Clock information 0x00000400: Dump pcm data 0x00000800: Dump SPDIF information |
-
I2S tx valid channel
Property name Description Value range i2s-tx0-tdm-active-slot Configure I2S tx active channel 0x0000 ~ 0xFFFF (bit0->slot0, bit1->slot1, ...) i2s-tx1-tdm-active-slot Configure I2S tx active channel 0x0000 ~ 0xFFFF (bit0->slot0, bit1->slot1, ...) i2s-tx2-tdm-active-slot Configure I2S tx active channel 0x0000 ~ 0xFFFF (bit0->slot0, bit1->slot1, ...)
1.6.3. Interface call¶
MI_AO_Open: Open AO deviceMI_AO_SetI2SConfig: configure i2s propertiesMI_AO_AttachIf: Attach peripherals to DMA devicesMI_AO_SetIfVolume: Set the volume of the peripheralMI_AO_SetVolume: Set volumeMI_AO_Write: Write audio frame dataMI_AO_Start: Start DMA and start playing dataMI_AO_Pause,MI_AO_Resume: Pause, resume playback.MI_AO_Stop: Pause DMAMI_AO_DetachIf: Detach the peripheralMI_AO_Close: Close the Audio AO device
1.7. Example Introduction¶
This section introduces the use of the Audio Out interface based on 1.6.3. Interface Call. The following sample code implements the complete process of initializing, configuring, playing audio files, and releasing resources of the audio output subsystem.
#include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> #include <unistd.h> #include <string.h> #include <sys/types.h> #include <sys/stat.h> #include <sys/time.h> #include <pthread.h> #include <signal.h> #include <errno.h> #include <fcntl.h> #include "mi_common_datatype.h" #include "mi_sys.h" #include "mi_ao.h" #include "st_common_audio.h" #include "st_common.h" MI_U32 ST_PlayAoData(char *pPlayFileName, MI_AUDIO_DEV AoDevId) { WaveFileHeader_t stWavHeader; MI_U32 playfd; MI_S32 s32ReadSize = 0; char * pTmpBuf = NULL; MI_U32 writeBufferSize = 4096; MI_U32 s32Ret; MI_BOOL bAoExit = FALSE; // open play file playfd = open((char *)pPlayFileName, O_RDONLY, 0666); if (playfd < 0) { printf("Failed to open input file error[%s] \n", strerror(errno)); return -1; } // read header memset(&stWavHeader, 0, sizeof(WaveFileHeader_t)); s32Ret = read(playfd, &stWavHeader, sizeof(WaveFileHeader_t)); if (s32Ret < 0) { close(playfd); printf("Failed to read wav header.\n"); return -1; } pTmpBuf = malloc(writeBufferSize); if (NULL == pTmpBuf) { close(playfd); printf("Failed to alloc data buffer of file.\n"); return -1; } memset(pTmpBuf, 0, sizeof(writeBufferSize)); // play audio form input file while (FALSE == bAoExit) { s32ReadSize = read(playfd, pTmpBuf, writeBufferSize); if (s32ReadSize != writeBufferSize) { lseek(playfd, sizeof(WaveFileHeader_t), SEEK_SET); s32ReadSize = read(playfd, pTmpBuf, writeBufferSize); bAoExit = TRUE; } s32Ret = MI_AO_Write(AoDevId, pTmpBuf, s32ReadSize, 0, -1); if (s32Ret != MI_SUCCESS) { printf("Failed to call MI_AO_Write of Ao DevICE %d , error is 0x%x.\n", AoDevId, s32Ret); } } free(pTmpBuf); close(playfd); return MI_SUCCESS; } int main(int argc, char **argv) { // init sys MI_SYS_Init(0); // init ao MI_AO_Attr_t stAoSetAttr; MI_AO_Attr_t *pstAoDevAttr = &stAoSetAttr; MI_AUDIO_DEV stAoDevId = 0; MI_AO_If_e aenAoIfs[] = {E_MI_AO_IF_DAC_AB}; memset(&stAoSetAttr, 0x0, sizeof(MI_AO_Attr_t)); pstAoDevAttr->enFormat = E_MI_AUDIO_FORMAT_PCM_S16_LE; pstAoDevAttr->enSoundMode = E_MI_AUDIO_SOUND_MODE_MONO; pstAoDevAttr->enSampleRate = E_MI_AUDIO_SAMPLE_RATE_8000; pstAoDevAttr->u32PeriodSize = 1024; pstAoDevAttr->enChannelMode = E_MI_AO_CHANNEL_MODE_DOUBLE_MONO; MI_AO_Open(stAoDevId, pstAoDevAttr) MI_AO_AttachIf(stAoDevId, aenAoIfs[0], 0); MI_AO_SetIfVolume(aenAoIfs[0], 0, 0); MI_AO_SetVolume(stAoDevId, 0, 0, 0); char *input_file = "resource/input/audio/ao_8K_16bit_MONO_30s.wav"; printf("input_file = %s\n", input_file); // play audio form input file ST_PlayAoData(input_file, stAoDevId); // deinit ao MI_AO_Close(stAoDevId); // deinit sys MI_SYS_Exit(0); }
The main process of the example code:
-
System Initialization :
- Call
MI_SYS_Init(0);to initialize the system.
- Call
-
Audio output device configuration :
- Create and configure the MI_AO_Attr_t structure stAoSetAttr , set the audio format to PCM 16-bit little endian, mono, sample rate to 8000 Hz, period size to 1024, and channel mode to dual mono.
- Use the
MI_AO_Openfunction to open the audio output device with device ID 0.
-
Set audio output interface and volume :
- Bind the audio output interface
E_MI_AO_IF_DAC_ABthrough theMI_AO_AttachIffunction. - Use
MI_AO_SetIfVolumeto set the peripheral volume to 0. - Use
MI_AO_SetVolumeto set the volume to 0.
- Bind the audio output interface
-
Play audio file :
- Specify the input file path
resource/input/audio/ao_8K_16bit_MONO_30s.wav. - Call
MI_AO_Writeto write audio data.
- Specify the input file path
-
Close and release resources :
- Use
MI_AO_Closeto close the audio output device and release resources. - Call
MI_SYS_Exit(0);to exit system initialization.
- Use
2. API REFERENCE¶
Audio output (AO) is mainly used to enable audio output devices, send audio frames to output channels and other functions.
| API name | Features |
|---|---|
| MI_AO_Open | Open audio output device |
| MI_AO_OpenWithCfgFile | Open the audio output device and initialize it according to the config file |
| MI_AO_Close | Close AO devices |
| MI_AO_AttachIf | Mount peripherals to AO device |
| MI_AO_DetachIf | Disconnect peripherals from audio output device |
| MI_AO_Write | Write audio data |
| MI_AO_Start | Start the AO device and start playing |
| MI_AO_Stop | Stop the AO device and stop playing |
| MI_AO_Pause | Pause AO device |
| MI_AO_Resume | Resume AO device |
| MI_AO_SetVolume | Set AO device volume |
| MI_AO_GetVolume | Get AO device volume |
| MI_AO_SetMute | Set AO device mute parameter |
| MI_AO_GetMute | Get AO device mute parameter |
| MI_AO_SetIfVolume | Set AO peripheral volume |
| MI_AO_GetIfVolume | Get AO peripheral volume |
| MI_AO_SetIfMute | Set AO peripheral mute parameter |
| MI_AO_GetIfMute | Get AO peripheral mute parameter |
| MI_AO_SetI2SConfig | Set I2S TX config info |
| MI_AO_GetI2SConfig | Get I2S TX config info |
| MI_AO_AdjustSpeed | Adjust the playback speed of AO device |
| MI_AO_GetTimestamp | Get the current playback timestamp and cached data volume of the AO device |
| MI_AO_GetLatency | Get the delay of AO device |
| MI_AO_InitDev | Initialize AO device |
| MI_AO_DeinitDev | De-Initialize AO device |
| MI_AO_GetAttr | Get AO device attributes |
| MI_AO_SetChannelMode | Dynamically set the channel output mode (Muffin series chips not support) |
2.1. MI_AO_Open¶
-
Features
Open audio output device.
-
Syntax
MI_S32 MI_AO_Open (MI_AUDIO_DEV AoDevId, const MI_AO_Attr_t *pstAttr);
-
Parameters
parameter name description Input/Output AoDevId AO device number Input pstAttr AO device attribute pointer Input -
Return Value
-
Zero: Successful
-
Non-zero: Failed, see error code for details
-
Requirement
-
Header files: mi_ao.h
-
Library file: libmi_ao.a/libmi_ao.so
-
Note
Audio output device attributes include data format, sound mode, sampling rate, Playback threshold, and channel output mode.
-
Audio data format(MI_AUDIO_Format_e)
The data format of the sampled samples. Only S16_LE is supported.(Pcupid supports S16_LE/S24_LE/S32_LE)
-
Audio sound mode(MI_AUDIO_SoundMode_e)
Channels of the data to be played, such as mono/stereo.
-
Audio sampling rate(MI_AUDIO_SampleRate_e)
Number of samples in one second, the higher the sampling rate, the smaller the distortion, but the amount of data processed also increases. The 8k sampling rate is used for voice, and the 32k or higher sampling rate is used for audio.
-
Playback threshold (u32PeriodSize)
Only when the data cache meets this sample will it start playing. After this parameter is set, it is recommended to write audio data in this size. When the period size is 0, APP needs to actively call [MI_AO_Start](#27-mi_ao_start) to start playing.
-
Channel output mode (MI_AO_ChannelMode_e)
It determines the output mode of the audio data in the audio device.
-
The behavior of Maruko series chip I2S TX is not affected by the MI_AO_ChannelMode_e parameter.
-
After calling MI_AO_Open and MI_AO_AttachIf, or calling MI_AO_OpenWitCfgFile, the Enable state of AO Device can be obtained by MI_SYS_QureyDevChnPortState.
-
Example
A simple example is as follow:
1. MI_AO_Attr_t stAoSetAttr; 2. memset(&stAoSetAttr, 0x0, sizeof(MI_AO_Attr_t)); 3. stAoSetAttr.enFormat = E_MI_AUDIO_FORMAT_PCM_S16_LE; 4. stAoSetAttr.enSoundMode = E_MI_AUDIO_SOUND_MODE_MONO; 5. stAoSetAttr.enSampleRate = E_MI_AUDIO_SAMPLE_RATE_8000; 6. stAoSetAttr.u32PeriodSize = 1024; 7. stAoSetAttr.enChannelMode = E_MI_AO_CHANNEL_MODE_DOUBLE_MONO; 8. ExecFunc(MI_AO_Open(AoDevId, &stAoSetAttr), MI_SUCCESS);
The detailed example is as follow:
1. MI_AUDIO_DEV AoDevId = 0; 2. MI_AO_Attr_t stAoSetAttr, stAoGetAttr; 3. MI_S16 s16LeftVolume, s16RightVolume; 4. MI_AO_GainFading_e eGainFading; 5. 6. memset(&stAoSetAttr, 0x0, sizeof(MI_AO_Attr_t)); 7. 8. // Set the Format of AO Device to S16_LE 9. stAoSetAttr.enFormat = E_MI_AUDIO_FORMAT_PCM_S16_LE; 10. 11. // Set the Sound Mode of AO Device to Mono 12. stAoSetAttr.enSoundMode = E_MI_AUDIO_SOUND_MODE_MONO; 13. 14. // Set the sample rate of AO Device to 8KHz 15. stAoSetAttr.enSampleRate = E_MI_AUDIO_SAMPLE_RATE_8000; 16. 17. // Set the starting condition of AO Device to 1024 sampling samples 18. stAoSetAttr.u32PeriodSize = 1024; 19. 20. // Set the Channel Mode of AO Device to Double Mono 21. stAoSetAttr.enChannelMode = E_MI_AO_CHANNEL_MODE_DOUBLE_MONO; 22. 23. // Open AO Device 24. ExecFunc(MI_AO_Open(AoDevId, &stAoSetAttr), MI_SUCCESS); 25. 26. // Get AO Device attributes 27. ExecFunc(MI_AO_GetAttr(AoDevId, &stAoGetAttr), MI_SUCCESS); 28. 29. // Attach DAC_AB to AO Device 30. ExecFunc(MI_AO_AttachIf(AoDevId, E_MI_AO_IF_DAC_AB, 0), MI_SUCCESS); 31. 32. // Dynamically set the audio channel mode to Only-Left 33. ExecFunc(MI_AO_SetChannelMode(AoDevId, E_MI_AO_CHANNEL_MODE_ONLY_LEFT), MI_SUCCESS); 34. 35. // Set Dpga Gain 36. s16LeftVolume = 0; 37. s16RightVolume = 0; 38. eGainFading = E_MI_AO_GAIN_FADING_OFF; 39. ExecFunc(MI_AO_SetVolume(AoDevId, s16LeftVolume, s16RightVolume, eGainFading), MI_SUCCESS); 40. 41. // Write data to AO Device 42. MI_AO_Write(AoDevId, u8TempBuf, s32ReadSize, 0, -1); 43. 44. // Detach DAC_AB 45. ExecFunc(MI_AO_DetachIf(AoDevId, E_MI_AO_IF_DAC_AB), MI_SUCCESS); 46. 47. // Close AO Device 48. ExecFunc(MI_AO_Close(MI_AO_DEV_1), MI_SUCCESS);
2.2. MI_AO_OpenWithCfgFile¶
-
Features
Open the audio output device and initialize it according to the config file.
-
Syntax
MI_S32 MI_AO_OpenWithCfgFiile(MI_AUDIO_DEV AoDevId, const char *pCfgPath);
-
Parameters
parameter name description Input/Output AoDevId AO device number Input pCfgPath Path of config file Input -
Return Value
-
Zero: Successful
-
Non-zero: Failed, see error code for details
-
Requirement
-
Header files: mi_ao.h
-
Library file: libmi_ao.a/libmi_ao.so
-
Note
-
This interface is equivalent to the combination of MI_AO_Open and MI_AO_AttachIf.
-
If the audio output device is enabled, it returns success.
-
On Muffin/Mochi series SOC, the configuration file is in INI format. On Maruko/Souffle/Pcupid series SOC, the configuration file is in JSON format.
-
In the dual os environment, the configuration file must provide an absolute path.
-
After calling MI_AO_Open and MI_AO_AttachIf, or calling MI_AO_OpenWitCfgFile, the Enable state of AO Device can be obtained by MI_SYS_QureyDevChnPortState.
-
The INI config file template is as follow:
1. ; Device attr section 2. [DEV] 3. ; enFormat determines the data format of the sample, only supports S16_LE now. 4. ; 0[S16_lE] 5. enFormat = 0 6. ; enSoundMode determines the sound mode of AO Device. 7. ; 1[Mono] 2[Stereo] 8. enSoundMode = 2 9. ; enSampleRate determines the sample rate of AO Device. 10. ; 8000[8KHz] 16000[16KHz] 32000[32KHz] 48000[48KHz] 11. enSampleRate = 8000 12. ; u32PeriodSize(samples) determines the time to start RDMA. 13. u32PeriodSize = 1024 14. ; enChannelMode determines the channel mode of AO Device. 15. ; 0[Stereo] 1[Double Mono] 2[Double Left] 3[Double Right] 4[Exchange] 5[Only Left] 6[Only Right] 16. enChannelMode = 0 17. ; attach interface 18. ; 1[DAC_AB] 2[DAC_CD] 4[I2S_A] 8[I2S_B] 16[ECHO_A] 32[HDMI_A] 19. ; if you want to attach DAC_AB and DAC_CD, so enAoIfs = DAC_AB | DAC_CD = 1 | 2 = 3. 20. enAoIfs = 5 21. 22. ; I2S TX attr section 23. ; It is not necessarywhen you're not using I2S TX 24. [I2S_A] 25. ; enMode determines the working mode of I2S Tx 26. ; 0[I2S Master] 1[I2S Slave] 2[Tdm Master] 3[Tdm Slave] 27. enMode = 0 28. ; enBitWidth determines the bit with of I2S Tx 29. ; 0[16 bit] 1[32bit] 30. enBitWidth = 0 31. ; enFormat determines the waveform alignment of I2S Tx 32. ; 0[I2S Philips] 1[I2S Left-justify] 33. enFormat = 0 34. ; enSampleRate determines the sample rate of I2S Tx 35. ; 8000[8KHz] 16000[16KHz] 32000[32KHz] 48000[48KHz] 36. enSampleRate = 8000 37. ; enMclk determines the frequency of Mclk 38. ; 0[disable Mclk] 1[12.288M] 2[16.384M] 3[18.432M] 4[24.576M] 5[24M] 6[48M] 39. enMclk = 0 40. ; bSyncClock: 1[4-wire mode] 0[6-wire mode] 41. bSyncClock = 0 42. ; u32TdmSlots determines the slot number of I2S Tx 43. u32TdmSlots = 2 [AO template.ini](mymedia/ao/AO template.ini) -
The JSON config file template is as follow:
1. { 2. "DEV":{ 3. "enFormat":0, 4. "enSoundMode":2, 5. "enSampleRate":8000, 6. "u32PeriodSize":1024, 7. "enChannelMode":0, 8. "enAoIfs":[1,4] 9. }, 10. "I2S_A":{ 11. "enMode":0, 12. "enBitWidth":0, 13. "enFormat":0, 14. "enSampleRate":8000, 15. "enMclk":0, 16. "bSyncClock":0, 17. "u32TdmSlots":2 18. } 19. } The “DEV” node contains parameters required by [MI_AO_Open](#21-mi_ao_open) and [MI_AO_AttachIf](#24-mi_ao_attachif). “enFormat”, “enSoundMode”, “enSampleRate”, “u32PeriodSize”, and “enChannelMode” are the configuration information required by [MI_AO_Open](#21-mi_ao_open), please refer to the description of [MI_AO_Attr_t](#36-mi_ao_attr_t). “enAoIfs” is the configuration information required by [MI_AO_AttachIf](#24-mi_ao_attachif), please refer to [MI_AO_If_e](#37-mi_ao_if_e) for details. The “I2S_A” node contains configuration information required by [MI_AO_SetI2SConfig](#219-mi_ao_seti2sconfig), please refer to [MI_AUDIO_I2sConfig_t](#313-mi_audio_i2sconfig_t) for details. [AO template.json](mymedia/ao/AO template.json) In the above configuration information, enFormat = 0 means AO Device adopts S16_LE format, enSoundMode = 1 means Sound Mode adopts Mono, enSampleRate = 8000 means AO Device uses 8KHz sampling frequency, u32PeriodSize = 1024 means that the starting condition is 1024 sampling points, enChannelMode = 1 means Double Mono, enAoIfs=1 means attach DAC0/1 to RDMA. If you need to use I2S TX, you also need to set the parameters of I2S TX. The above configuration works on I2S_A, enMode = 0 means using I2S Master mode, enBitWidth = 0 means I2S receiving bit width is 16bit, enFormat = 0 means aligning according to I2S Philips mode, enSampleRate = 8000 means that the sampling frequency of I2S RX is 8KHz, enMclk = 0 means that Mclk is not used, bSyncClock = 1 means 4-wire mode, and u32TdmSlots means receiving 2-channel data. -
Example
1. char *path = "/tmp/Dev0Cfg.json"; // char *path = "/tmp/Dev0Cfg.ini"; 2. ExecFunc(MI_AO_OpenWithCfgFile(AoDevId, path), MI_SUCCESS);
2.3. MI_AO_Close¶
-
Features
Close AO devices.
-
Syntax
MI_S32 MI_AO_Close (MI_AUDIO_DEV AoDevId);
-
Parameters
parameter name description Input/Output AoDevId AO device number Input -
Return Value
-
Zero: Successful
-
Non-zero: Failed, see error code for details
-
Requirement
-
Header files: mi_ao.h
-
Library file: libmi_ao.a/libmi_ao.so
-
Note
-
If the AO device is already closed, it will return Success directly.
-
After calling MI_AO_Close, or without initializing the AO Device, the Disabled state of AO Device can be obtained by MI_SYS_QureyDevChnPortState.
-
Example
A simple example is as follow:
1. ExecFunc(MI_AO_Close(MI_AO_DEV_1), MI_SUCCESS);
For detailed examples, please refer to MI_AO_Open.
2.4. MI_AO_AttachIf¶
-
Features
Mount peripherals to AO device.
-
Syntax
MI_S32 MI_AO_AttachIf (MI_AUDIO_DEV AoDevId, MI_AO_If_e enAoIfs, MI_U32 u32AudioDelay);
-
Parameters
parameter name description Input/Output AoDevId AO device number Input enAoIfs AO Interface, the peripheral information that needs to be mounted to the AO device, you can use "|" to indicate that multiple peripherals are mounted Input u32AudioDelay Delay parameters(reserved) Input -
Return Value
-
Zero: Successful
-
Non-zero: Failed, see error code for details
-
Requirement
-
Header files: mi_ao.h
-
Library file: libmi_ao.a/libmi_ao.so
-
Note
-
This interface can only be called after MI_AI_Open succeeds.
-
If you need to mount the I2S TX to the AO device, please call MI_AI_SetI2SConfig first to initialize the I2S TX.
-
If you want to obtain echo reference data, attach E_MI_AO_IF_ECHO_A to AO module and attach E_MI_AI_IF_ECHO_A to AI module.
-
After calling MI_AO_Open and MI_AO_AttachIf, or calling MI_AO_OpenWitCfgFile, the Enable state of AO Device can be obtained by MI_SYS_QureyDevChnPortState.
-
Example
1. ExecFunc(MI_AO_AttachIf(AoDevId, E_MI_AO_IF_DAC_AB, 0), MI_SUCCESS);
2.5. MI_AO_DetachIf¶
-
Features
Disconnect peripherals from audio output device.
-
Syntax
MI_S32 MI_AO_DetachIf (MI_AUDIO_DEV AoDevId, MI_AO_If_e enAoIfs);
-
Parameters
parameter name description Input/Output AoDevId AO device number Input enAoIfs AO Interface, the peripheral information that needs to be unmounted to the AO device, you can use "|" to indicate that multiple peripherals are mounted Input -
Return Value
-
Zero: Successful
-
Non-zero: Failed, see error code for details
-
Requirement
-
Header files: mi_ao.h
-
Library file: libmi_ao.a/libmi_ao.so
-
Note
-
It can only be called after MI_AO_AttachIf succeeds.
-
The I2S TX and ECHO of Maruko series chips do not support Detach.
-
Example
A simple example is as follow:
1. ExecFunc(MI_AO_DetachIf(AoDevId, E_MI_AO_IF_DAC_AB), MI_SUCCESS);
For detailed examples, please refer to MI_AO_Open.
2.6. MI_AO_Write¶
-
Features
Write audio data.
-
Syntax
MI_S32 MI_AO_Write (MI_AUDIO_DEV AoDevId, const void *pvBuffer, MI_U32 u32Bytes, MI_U64 u64Pts, MI_S32 s32TimeoutMs);
-
Parameters
parameter name description Input/Output AoDevId AO device number Input pvBuffer Audio data pointer Input u32Bytes Audio data length Input u64Pts Audio data timestamp (reserved) Input s32TimeoutMs Timeout for writing audio data. -1: blocking mode, waiting for no data; 0 means non-blocking mode, when there is no data, it will return an error; >0: blocking s32TimeoutMs milliseconds, and it will report an error and return when it times out. Input -
Return Value
-
Zero: Successful
-
Non-zero: Failed, see error code for details
-
Requirement
-
Header files: mi_ao.h
-
Library file: libmi_ao.a/libmi_ao.so
-
Note
-
This interface can only be called after MI_AI_Open and MI_AI_AttachIf succeed.
-
s32TimeoutMs must be greater than or equal to -1, when it is equal to -1, use blocking mode to write data, when it is equal to 0, use non-blocking mode to write data, when it is greater than 0, after blocking s32MilliSec for milliseconds, it will return a timeout and report an error.
-
Example
A simple example is as follow:
1. MI_U8 u8TempBuf[1024] = {0}; 2. MI_S32 s32ReadSize; 3. s32ReadSize = read(s32Fd, pu8TempBuf, sizeof(u8TempBuf)); 4. if (s32ReadSize > 0) 5. { 6. MI_AO_Write(AoDevId, u8TempBuf, s32ReadSize, 0, -1); 7. }For detailed examples, please refer to MI_AO_Open.
2.7. MI_AO_Start¶
-
Features
Start the AO device and start playing.
-
Syntax
MI_S32 MI_AO_Start (MI_AUDIO_DEV AoDevId);
-
Parameters
parameter name description Input/Output AoDevId AO device number Input -
Return Value
-
Zero: Successful
-
Non-zero: Failed, see error code for details
-
Requirement
-
Header files: mi_ao.h
-
Library file: libmi_ao.a/libmi_ao.so
-
Note
-
It can only be called after MI_AO_Open succeeds.
-
When this interface is called, even if the playback threshold < u32PeriodSize, it can be played immediately.
-
Example
1. ExecFunc(MI_AO_Start(AoDevId),MI_SUCCESS);
2.8. MI_AO_Stop¶
-
Features
Stop the AO device and stop playing.
-
Syntax
MI_S32 MI_AO_Stop (MI_AUDIO_DEV AoDevId);
-
Parameters
parameter name description Input/Output AoDevId AO device number Input -
Return Value
-
Zero: Successful
-
Non-zero: Failed, see error code for details
-
Requirement
-
Header files: mi_ao.h
-
Library file: libmi_ao.a/libmi_ao.so
-
Note
-
It can only be called after MI_AO_Open succeeds.
-
When the interface is called, the playback stops immediately, and the original cached data will also be lost.
-
Example
1. ExecFunc(MI_AO_Stop(AoDevId),MI_SUCCESS);
2.9. MI_AO_Pause¶
-
Features
Pause AO device.
-
Syntax
MI_S32 MI_AO_Pause (MI_AUDIO_DEV AoDevId);
-
Parameters
parameter name description Input/Output AoDevId AO device number Input -
Return Value
-
Zero: Successful
-
Non-zero: Failed, see error code for details
-
Requirement
-
Header files: mi_ao.h
-
Library file: libmi_ao.a/libmi_ao.so
-
Note
-
It can only be called after MI_AO_Open succeeds.
-
When the interface is called, the playback will be paused immediately
-
Example
1. ExecFunc(MI_AO_Pause(AoDevId),MI_SUCCESS);
2.10. MI_AO_Resume¶
-
Features
Resume AO device.
-
Syntax
MI_S32 MI_AO_Resume (MI_AUDIO_DEV AoDevId);
-
Parameters
parameter name description Input/Output AoDevId AO device number Input -
Return Value
-
Zero: Successful
-
Non-zero: Failed, see error code for details
-
Requirement
-
Header files: mi_ao.h
-
Library file: libmi_ao.a/libmi_ao.so
-
Note
-
It can only be called after MI_AO_Pause succeeds.
-
When the interface is called, the playback will be resume immediately
-
Example
1. ExecFunc(MI_AO_Resume(AoDevId),MI_SUCCESS);
2.11. MI_AO_SetVolume¶
-
Features
Set AO device volume.
-
Syntax
MI_AO_SetVolume (MI_AUDIO_DEV AoDevId, MI_S16 s16LeftVolume, MI_S16 s16RightVolume, MI_AO_GainFading_e enFading);
-
Parameters
parameter name description Input/Output AoDevId AO device number Input s16LeftVolume Left channel volume (-60 ~ 30dB, 1dB/step) Input s16RightVolume Right channel volume (-60 ~ 30dB, 1dB/step) Input eFading The changing speed of audio gain Input -
Return Value
-
Zero: Successful
-
Non-zero: Failed, see error code for details
-
Requirement
-
Header files: mi_ao.h
-
Library file: libmi_ao.a/libmi_ao.so
-
Note
-
It can only be called after MI_AO_Open succeeds.
-
The meanings of 'Gain' and 'Volume' are the same.
-
In version 3.55 and later, the data type of all volume Gain values was changed from S8 to S16, as in the old function prototype: MI_AO_SetVolume(MI_AUDIO_DEV AoDevId, MI_S8 s8LeftVolume, MI_S8 s8RightVolume, MI_AO_GainFading_e enFading); Same as above for other API related to volume Gain.
-
The Gain value of Souffle/Pcupid series chips is different from that of other series chips. The Gain value is not the corresponding Db value, but a mapping relationship with the range [-508, 512] corresponding to [-63.5Db, 64Db], where 0 corresponds to 0Db and 0.125dB/step.
-
Except for the Souffle/Pcupid series chips, as16Gains is set in the range of [-60Db, 30Db], 1dB/step.
-
Muffin series chips support the 'MI_AO_SetIfVolume' setting, and its Gain value setting range is the same as that of 'MI_AO_SetVolume'.
-
Example
1. MI_S16 s16LeftVolume, s16RightVolume; 2. MI_AO_GainFading_e eGainFading; 3. s16LeftVolume = 0; 4. s16RightVolume = 0; 5. eGainFading = E_MI_AO_GAIN_FADING_OFF; 6. ExecFunc(MI_AO_SetVolume(AoDevId, s16LeftVolume, s16RightVolume, eGainFading), MI_SUCCESS);
2.12. MI_AO_GetVolume¶
-
Features
Get AO device volume.
-
Syntax
MI_S32 MI_AO_GetVolume (MI_AUDIO_DEV AoDevId, MI_S16 *ps16LeftVolume, MI_S16 *ps16RightVolume);
-
Parameters
parameter name description Input/Output AoDevId AO device number Input ps16LeftVolume Left channel volume pointer Output ps16RightVolume Right channel volume pointer Output -
Return Value
-
Zero: Successful
-
Non-zero: Failed, see error code for details
-
Requirement
-
Header files: mi_ao.h
-
Library file: libmi_ao.a/libmi_ao.so
-
Note
-
It can only be called after MI_AO_SetVolume succeeds.
-
Example
1. MI_S16 s16LeftVolume, s16RightVolume; 2. ExecFunc(MI_AO_GetVolume(AoDevId, &s16LeftVolume, &s16RightVolume), MI_SUCCESS);
2.13. MI_AO_SetMute¶
-
Features
Set AO device mute parameter.
-
Syntax
MI_S32 MI_AO_SetMute (MI_AUDIO_DEV AoDevId, MI_BOOL bLeftMute, MI_BOOL bRightMute, MI_AO_GainFading_e enFading);
-
Parameters
parameter name description Input/Output AoDevId AO device number Input bLeftMute Left channel mute parameter Input bRightMute Right channel mute parameter Input eFading The changing speed of audio gain (reserved) Input -
Return Value
-
Zero: Successful
-
Non-zero: Failed, see error code for details
-
Requirement
-
Header files: mi_ao.h
-
Library file: libmi_ao.a/libmi_ao.so
-
Note
-
It can only be called after MI_AO_Open succeeds.
-
When using MI_AO_SetVolume to adjust the volume, it will automatically exit the mute state.
-
Example
1. MI_BOOL bLeftMute = TRUE; 2. MI_BOOL bRightMute = TRUE; 3. MI_AO_GainFading_e eGainFading = E_MI_AO_GAIN_FADING_OFF; 4. ExecFunc(MI_AO_SetMute(AoDevId, bLeftMute, bRightMute, eGainFading), MI_SUCCESS);
2.14. MI_AO_GetMute¶
-
Features
Get AO device mute parameter.
-
Syntax
MI_S32 MI_AO_GetMute (MI_AUDIO_DEV AoDevId, MI_BOOL *pbLeftMute, MI_BOOL *pbRightMute);
-
Parameters
parameter name description Input/Output AoDevId AO device number Input pbLeftMute Left channel mute parameter pointer Output pbRightMute Right channel mute parameter pointer Output -
Return Value
-
Zero: Successful
-
Non-zero: Failed, see error code for details
-
Requirement
-
Header files: mi_ao.h
-
Library file: libmi_ao.a/libmi_ao.so
-
Note
-
It can only be called after MI_AO_Open succeeds.
-
Example
1. MI_BOOL bLeftMute; 2. MI_BOOL bRightMute; 3. ExecFunc(MI_AO_GetMute(AoDevId, bLeftMute, bRightMute), MI_SUCCESS);
2.15. MI_AO_SetIfVolume¶
-
Features
Set AO peripheral volume.
-
Syntax
MI_S32 MI_AO_SetIfVolume (MI_AO_If_e enAoIf, MI_S16 s16LeftVolume, MI_S16 s16RightVolume);
-
Parameters
parameter name description Input/Output enAoIf AO peripheral Input s16LeftVolume Left channel volume Input s16RightVolume Right channel volume Input -
Return Value
-
Zero: Successful
-
Non-zero: Failed, see error code for details
-
Requirement
-
Header files: mi_ao.h
-
Library file: libmi_ao.a/libmi_ao.so
-
Note
-
No interface supports it.
-
Currently, only the interface of the Souffle/Pcupid series chips supports this function, and the hardware is also implemented by DPGA, see 'IF Gain' in the Codec block diagram.
-
The Gain(Volume) setting range is the same as that of MI_AO_SetVolume.
-
Example
1. MI_S16 s16LeftVolume = 0; 2. MI_S16 s16RightVolume = 0; 3. ExecFunc(MI_AO_SetIfVolume(E_MI_AO_IF_DAC_AB, s16LeftVolume, s16RightVolume), MI_SUCCESS);
2.16. MI_AO_GetIfVolume¶
-
Features
Get AO peripheral volume.
-
Syntax
MI_S32 MI_AO_GetIfVolume (MI_AO_If_e enAoIf, MI_S16 *ps16LeftVolume, MI_S16 *ps16RightVolume);
-
Parameters
Parameter Name Description Input/Output enAoIf AO peripheral Input ps16LeftVolume Left channel volume pointer Output ps16RightVolume Left channel volume pointer Output -
Return Value
-
Zero: Successful
-
Non-zero: Failed, see error code for details
-
Requirement
-
Header: mi_ao.h
-
Library: libmi_ao.a/libmi_ao.so
-
Example
1. MI_S16 s16LeftVolume = 0; 2. MI_S16 s16RightVolume = 0; 3. ExecFunc(MI_AO_GetIfVolume(E_MI_AO_IF_DAC_AB, &s16LeftVolume, &s16RightVolume), MI_SUCCESS);
2.17. MI_AO_SetIfMute¶
-
Features
Set AO peripheral mute parameter.
-
Syntax
MI_S32 MI_AO_SetIfMute (MI_AO_If_e enAoIf, MI_BOOL bLeftMute, MI_BOOL bRightMute);
-
Parameters
Parameter Name Description Input/Output enAoIf AO peripheral Input bLeftMute Left channel mute parameter Input bRightMute Right channel mute parameter Input -
Return Value
-
Zero: Successful
-
Non-zero: Failed, see error code for details
-
Requirement
-
Header: mi_ao.h
-
Library: libmi_ao.a/libmi_ao.so
-
Note
-
For details about whether to support this interface, see the specific Codec block diagram.
-
Example
1. MI_BOOL bLeftMute = 0; 2. MI_BOOL bRightMute = 0; 3. ExecFunc(MI_AO_SetIfMute(E_MI_AO_IF_DAC_AB, bLeftMute, bRightMute), MI_SUCCESS);
2.18. MI_AO_GetIfMute¶
-
Features
Get AO peripheral mute parameter.
-
Syntax
MI_S32 MI_AO_GetIfMute (MI_AO_If_e enAoIf, MI_BOOL *pbLeftMute, MI_BOOL *pbRightMute);
-
Parameters
Parameter Name Description Input/Output enAoIf AO peripheral Input pbLeftMute Left channel mute parameter pointer Output pbRightMute Right channel mute parameter pointer Output -
Return Value
-
Zero: Successful
-
Non-zero: Failed, see error code for details
-
Requirement
-
Header files: mi_ao.h
-
Library file: libmi_ao.a/libmi_ao.so
-
Example
1. MI_BOOL bLeftMute = 0; 2. MI_BOOL bRightMute = 0; 3. ExecFunc(MI_AO_GetIfMute(E_MI_AO_IF_DAC_AB, &s16LeftVolume, &s16RightVolume), MI_SUCCESS);
2.19. MI_AO_SetI2SConfig¶
-
Features
Set I2S TX config info.
-
Syntax
MI_S32 MI_AO_SetI2SConfig (MI_AO_If_e enAoI2SIf, const MI_AUDIO_I2sConfig_t *pstConfig);
-
Parameters
Parameter Name Description Input/Output enAiI2Sif Audio I2S TX output peripheral Input pstConfig Audio I2S TX config info Input -
Return Value
-
Zero: Successful
-
Non-zero: Failed, see error code for details
-
Requirement
-
Header files: mi_ao.h
-
Library file: libmi_ao.so/libmi_ao.a
-
Note
-
The enSampleRate in MI_AUDIO_I2sConfig_t must be the same as the enSampleRate in MI_AI_Attr_t, otherwise attach will report an error.
-
When the same I2S TX interface is detached by all devices, that is, no device is attached to the I2S TX interface, the I2S TX parameters will be reset. If you need to attach to a device, you must first reset the I2S parameters.
-
Example
1. MI_AUDIO_I2sConfig_t stAoI2sACfg; 2. memset(&stAoI2sACfg, 0x0, sizeof(stAoI2sACfg)); 3. stAoI2sACfg.enMode = E_MI_AUDIO_I2S_MODE_I2S_MASTER; 4. stAoI2sACfg.enFormat = E_MI_AUDIO_I2S_FMT_I2S_MSB; 5. stAoI2sACfg.enSampleRate = E_MI_AUDIO_SAMPLE_RATE_8000; 6. stAoI2sACfg.enMclk = E_MI_AUDIO_I2S_MCLK_0; 7. stAoI2sACfg.bSyncClock = TRUE; 8. stAoI2sACfg.u32TdmSlots = 2; 9. stAoI2sACfg.enBitWidth = E_MI_AUDIO_BIT_WIDTH_16; 10. ExecFunc(MI_AO_SetI2SConfig(E_MI_AO_IF_I2S_A, &stAoI2sACfg), MI_SUCCESS);
2.20. MI_AO_GetI2SConfig¶
-
Features
Get I2S TX config info.
-
Syntax
MI_S32 MI_AO_GetI2SConfig (MI_AO_If_e enAoI2SIf, MI_AUDIO_I2sConfig_t *pstConfig);
-
Parameters
Parameter Name Description Input/Output enAiI2SIf Audio I2S TX output peripheral Input pstConfig Audio I2S TX config info Output -
Return Value
-
Zero: Successful
-
Non-zero: Failed, see error code for details
-
Requirement
-
Header files: mi_ao.h
-
Library file: libmi_ao.so/libmi_ao.a
-
Example
1. MI_AUDIO_I2sConfig_t stAoI2sACfg; 2. memset(&stAoI2sACfg, 0x0, sizeof(stAoI2sACfg)); 3. ExecFunc(MI_AO_GetI2SConfig(E_MI_AO_IF_I2S_A, &stAoI2sACfg), MI_SUCCESS);
2.21. MI_AO_AdjustSpeed¶
-
Features
Adjust the playback speed of AO device.
-
Syntax
MI_S32 MI_AO_AdjustSpeed (MI_AUDIO_DEV AoDevId, MI_S32 s32Speed);
-
Parameters
Parameter Name Description Input/Output AoDevId AO device number Input s32Speed Sampling rate of playback Input -
Return Value
-
Zero: Successful
-
Non-zero: Failed, see error code for details
-
Requirement
-
Header files: mi_ao.h
-
Library file: libmi_ao.so/libmi_ao.a
-
Note
-
Not supported.
-
Example
1. ExecFunc(MI_AO_AdjustSpeed(AoDevId, 8000), MI_SUCCESS);
2.22. MI_AO_GetTimestamp¶
-
Features
Get the current playback timestamp and cached data volume of the AO device.
-
Syntax
MI_S32 MI_AO_GetTimestamp (MI_AUDIO_DEV AoDevId, MI_U32 *pu32Remaining, MI_U64 *pu64TStamp);
-
Parameters
Parameter Name Description Input/Output AoDevId AO device number Input pu32Remaining Current cached data Output pu64TStamp Current playback timestamp (reserved) Output -
Return Value
-
Zero: Successful
-
Non-zero: Failed, see error code for details
-
Requirement
-
Header files: mi_ao.h
-
Library file: libmi_ao.so/libmi_ao.a
-
Note
-
This interface can only be called after MI_AO_Open succeeds.
-
This interface can be used to replace Audio 2.0 'MI_AO_QueryChnStat' API, and the size of the entire cache space can be seen by dumping PROCFS information.
-
Example
1. MI_U32 u32Remaining; 2. MI_U64 u64TStamp; 3. ExecFunc(MI_AO_GetTimestamp(AoDevId, &u32Remaining, &u64TStamp), MI_SUCCESS);
2.23. MI_AO_GetLatency¶
-
Features
Get the delay of AO device.
-
Syntax
MI_S32 MI_AO_GetLatency (MI_AUDIO_DEV AoDevId, MI_U32 *pu32Latency);
-
Parameters
Parameter Name Description Input/Output AoDevId AO device number Input pu32Latency Delay time (ms) Output -
Return Value
-
Zero: Successful
-
Non-zero: Failed, see error code for details
-
Requirement
-
Header files: mi_ao.h
-
Library file: libmi_ao.so/libmi_ao.a
-
Note
-
This interface can only be called after MI_AO_Open succeeds.
-
The specific function of this interface has not been implemented yet.
-
Example
1. MI_U32 u32Latency; 2. ExecFunc(MI_AO_GetLatency(AoDevId, &u32Latency), MI_SUCCESS);
2.24. MI_AO_InitDev¶
-
Features
Initialize AO device.
-
Syntax
MI_S32 MI_AO_InitDev (MI_AO_InitParam_t *pstInitParam);
-
Parameters
Parameter Name Description Input/Output pstInitParam Device initialization parameter Input -
Return Value
-
Zero: Successful
-
Non-zero: Failed, see error code for details
-
Requirement
-
Header files: mi_ao.h
-
Library file: libmi_ao.so/libmi_ao.a
-
Note
-
It must be used in pairs with MI_AO_DeinitDev, and cannot be called repeatedly, otherwise it returns to fail.
-
Only used to reinitialize the AO module after the STR state is enabled.
2.25. MI_AO_DeInitDev¶
-
Features
De- Initialize AO device.
-
Syntax
MI_S32 MI_AO_DeInitDev (void);
-
Return Value
-
Zero: Successful
-
Non-zero: Failed, see error code for details
-
Requirement
-
Header files: mi_ao.h
-
Library file: libmi_ao.so/libmi_ao.a
-
Note
-
This function must be called after the device is initialized, otherwise, it returns to fail.
-
If it is not called before the app exits, the device will be automatically deinitialized internally
-
It must be used in pairs with MI_AO_InitDev, and cannot be called repeatedly, otherwise it returns to fail.
2.26. MI_AO_GetAttr¶
-
Features
Get audio output device attributes.
-
Syntax
MI_S32 MI_AO_GetAttr(MI_AUDIO_DEV AoDevId, MI_AO_Attr_t *pstAttr);
-
Parameters
Parameter Name Description Input/Output AoDevId Audio output device ID Input pstAttr Audio output device attributes Output -
Return Value
-
Zero: Successful
-
Non-zero: Failed, see error code for details
-
Requirement
-
Header: mi_ao.h
-
Library: libmi_ao.so/libmi_ao.a
-
Note
-
This function must be called after opening the device successfully, otherwise it will return failed.
2.27. MI_AO_SetChannelMode¶
-
Features
Dynamically set the channel output mode.
-
Syntax
MI_S32 MI_AO_SetChannelMode(MI_AUDIO_DEV AoDevId, MI_AO_ChannelMode_e enChannelMode);
-
Parameters
Parameter Name Description Input/Output AoDevId Audio output device ID Input enChannelMode Channel output mode Input -
Return Value
-
Zero: Successful
-
Non-zero: Failed, see error code for details
-
Requirement
-
Header: mi_ao.h
-
Library: libmi_ao.so/libmi_ao.a
-
Note
-
This function can only be called after MI_AO_AttachIf succeeds.
-
Only Mochi series chips support this setting.
-
Example
A simple example is as follows:
2. ExecFunc(MI_AO_SetChannelMode(AoDevId, E_MI_AO_CHANNEL_MODE_ONLY_LEFT), MI_SUCCESS);
For detailed examples, please refer to MI_AO_Open.
3. AO DATA TYPE¶
The AO module related data types are defined as follows:
| Data type | Definition |
|---|---|
| MI_AUDIO_DEV | Define the audio Input/Output device number |
| MI_AUDIO_Format_e | Define audio data format |
| MI_AUDIO_SoundMode_e | Define audio sound mode |
| MI_AUDIO_SampleRate_e | Define the audio sample rate |
| MI_AO_ChannelMode_e | Define the channel output mode of the audio device |
| MI_AO_Attr_t | Define AO device attribute structure |
| MI_AO_If_e | Define audio peripheral interface |
| MI_AO_GainFading_e | Define the changing speed of audio device gain |
| MI_AUDIO_I2sMode_e | Define the working mode of audio I2S TXRX/TX |
| MI_AUDIO_I2sBitWidth_e | Define audio I2S TXRX/TX bit width |
| MI_AUDIO_I2sFormat_e | Define the data transmission format of audio I2S RX/TX |
| MI_AUDIO_I2sMclk_e | Define the mclk frequency of audio I2S RX/TX |
| MI_AUDIO_I2sConfig_t | Define I2S RX/TX config info |
| MI_AO_InitParam_t | Audio output device initialization parameter |
3.1. MI_AUDIO_DEV¶
-
Description
Define the audio Input/Output device number.
-
Definition
typedef MI_S32 MI_AUDIO_DEV
3.2. MI_AUDIO_Format_e¶
-
Description
Define audio data format.
-
Definition
typedef enum { E_MI_AUDIO_FORMAT_INVALID = -1, E_MI_AUDIO_FORMAT_PCM_S16_LE = 0, E_MI_AUDIO_FORMAT_PCM_S24_LE, E_MI_AUDIO_FORMAT_PCM_S32_LE, } MI_AUDIO_Format_e; -
Member
Member name description E_MI_AUDIO_FORMAT_INVALID Invalid data format E_MI_AUDIO_FORMAT_PCM_S16_LE PCM Linear 16bit (Little Endian) E_MI_AUDIO_FORMAT_PCM_S24_LE PCM Linear 24bit (Little Endian) E_MI_AUDIO_FORMAT_PCM_S32_LE PCM Linear 32bit (Little Endian) -
Related data types and interfaces
3.3. MI_AUDIO_SoundMode_e¶
-
Description
Define audio sound mode.
-
Definition
typedef enum { E_MI_AUDIO_SOUND_MODE_MONO = 1, E_MI_AUDIO_SOUND_MODE_STEREO = 2, E_MI_AUDIO_SOUND_MODE_4CH = 4, E_MI_AUDIO_SOUND_MODE_6CH = 6, E_MI_AUDIO_SOUND_MODE_8CH = 8, E_MI_AUDIO_SOUND_MODE_10CH = 10, E_MI_AUDIO_SOUND_MODE_12CH = 12, E_MI_AUDIO_SOUND_MODE_14CH = 14, E_MI_AUDIO_SOUND_MODE_16CH = 16, }MI_AUDIO_SoundMode_e -
Member
Member name description E_MI_AUDIO_SOUND_MODE_MONO MONO E_MI_AUDIO_SOUND_MODE_STEREO STEREO E_MI_AUDIO_SOUND_MODE_4CH 4-channels; not supported E_MI_AUDIO_SOUND_MODE_6CH 6-channels; not supported E_MI_AUDIO_SOUND_MODE_8CH 8-channels; not supported E_MI_AUDIO_SOUND_MODE_10CH 10-channels; not supported E_MI_AUDIO_SOUND_MODE_12CH 12-channels; not supported E_MI_AUDIO_SOUND_MODE_14CH 14-channels; not supported E_MI_AUDIO_SOUND_MODE_16CH 16-channels; not supported -
Related data types and interfaces
3.4. MI_AUDIO_SampleRate_e¶
-
Description
Define the audio sample rate.
-
Definition
typedef enum { E_MI_AUDIO_SAMPLE_RATE_8000 = 8000, E_MI_AUDIO_SAMPLE_RATE_11052 = 11025, E_MI_AUDIO_SAMPLE_RATE_12000 = 12000, E_MI_AUDIO_SAMPLE_RATE_16000 = 16000, E_MI_AUDIO_SAMPLE_RATE_22050 = 22050, E_MI_AUDIO_SAMPLE_RATE_24000 = 24000, E_MI_AUDIO_SAMPLE_RATE_32000 = 32000, E_MI_AUDIO_SAMPLE_RATE_44100 = 44100, E_MI_AUDIO_SAMPLE_RATE_48000 = 48000, E_MI_AUDIO_SAMPLE_RATE_96000 = 96000, E_MI_AUDIO_SAMPLE_RATE_192000 = 192000, }MI_AUDIO_SampleRate_e; -
Member
Member name description E_MI_AUDIO_SAMPLE_RATE_8000 8kHz sampling rate E_MI_AUDIO_SAMPLE_RATE_11025 11.025kHz sampling rate E_MI_AUDIO_SAMPLE_RATE_12000 12kHz sampling rate E_MI_AUDIO_SAMPLE_RATE_16000 16kHz sampling rate E_MI_AUDIO_SAMPLE_RATE_22050 22.05kHz sampling rate E_MI_AUDIO_SAMPLE_RATE_24000 24kHz sampling rate E_MI_AUDIO_SAMPLE_RATE_32000 32kHz sampling rate E_MI_AUDIO_SAMPLE_RATE_44100 44.1kHz sample rate E_MI_AUDIO_SAMPLE_RATE_48000 48kHz sampling rate E_MI_AUDIO_SAMPLE_RATE_96000 96kHz sampling rate E_MI_AUDIO_SAMPLE_RATE_192000 192kHz sampling rate -
Note
-
Except I2S TX which supports 8/16/32/48/96/192kHz, and I2S TX can only be attached separately when using 96/192kHz, other AO peripherals only support 8/16/32/48kHz.
-
Muffin's I2S RX only supports 8/16/32/48/96 kHz.
-
Related data types and interfaces
3.5. MI_AO_ChannelMode_e¶
-
Description
Define the channel output mode of the audio device.
-
Definition
typedef enum { E_MI_AO_CHANNEL_MODE_STEREO, E_MI_AO_CHANNEL_MODE_DOUBLE_MONO, E_MI_AO_CHANNEL_MODE_DOUBLE_LEFT, E_MI_AO_CHANNEL_MODE_DOUBLE_RIGHT, E_MI_AO_CHANNEL_MODE_EXCHANGE, E_MI_AO_CHANNEL_MODE_ONLY_LEFT, E_MI_AO_CHANNEL_MODE_ONLY_RIGHT, }MI_AO_ChannelMode_e; -
Member
Member name description E_MI_AO_CHANNEL_MODE_STEREO Stereo mode E_MI_AO_CHANNEL_MODE_DOUBLE_MONO Stereo: the left and right channels output mixed data Mono: the left and right channels output the same mono data E_MI_AO_CHANNEL_MODE_DOUBLE_LEFT Stereo: left and right channels output left channel data E_MI_AO_CHANNEL_MODE_DOUBLE_RIGHT Stereo: left and right channels output right channel data E_MI_AO_CHANNEL_MODE_EXCHANGE Stereo: the data output of the left and right channels are interchanged E_MI_AO_CHANNEL_MODE_ONLY_LEFT Stereo: the left channel output left channel data Mono: the left channel outputs mono data E_MI_AO_CHANNEL_MODE_ONLY_RIGHT Stereo: the right channel output is right channel data Mono: the right channel is output as mono data -
Note
-
Muffin don’t support E_MI_AO_CHANNEL_MODE_DOUBLE_MONO (stereo) / E_MI_AO_CHANNEL_MODE_DOUBLE_LEFT (stereo) / E_MI_AO_CHANNEL_MODE_DOUBLE_RIGHT (stereo).
-
Related data types and interfaces
3.6. MI_AO_Attr_t¶
-
Description
Define AO device attribute structure.
-
Definition
typedef struct MI_AO_Attr_s { MI_AUDIO_Format_e enFormat; MI_AUDIO_SoundMode_e enSoundMode; MI_AUDIO_SampleRate_e enSampleRate; MI_U32 u32PeriodSize; MI_AO_ChannelMode enChannelMode; MI_AUDIO_SampleRate_e enMixerSampleRate; } MI_AO_Attr_t; -
Member
Member name description enFormat Audio data format. Static attributes. enSoundMode Audio sound mode. Static attributes. enSampleRate Audio sampling rate. Static attributes. u32PeriodSize Playback threshold. Static attributes. enChannelMode Channel output mode. Static attributes. enMixerSampleRate (Some support)Output sample rate after mixing.
Static property, it only takes effect in the use scene of the mix, if this parameter is not set, the default is 48K, no need to set it in other scenes. -
Note
-
The member 'enMixerSampleRate' currently supports this setting only on Mochi series chips.
-
Related data types and interfaces
3.7. MI_AO_If_e¶
-
Description
Define audio peripheral interface.
-
Definition
typedef enum { E_MI_AO_IF_NONE = 0x0u, E_MI_AO_IF_DAC_AB = 0x1u, E_MI_AO_IF_DAC_CD = 0x02u, E_MI_AO_IF_I2S_A = 0x4u, E_MI_AO_IF_I2S_B = 0x8u, E_MI_AO_IF_ECHO_A = 0x10u, E_MI_AO_IF_HDMI_A = 0x20u, E_MI_AO_IF_I2S_C = 0x40u, E_MI_AO_IF_I2S_A_SRC = 0x10000u, E_MI_AO_IF_I2S_B_SRC = 0x20000u, E_MI_AO_IF_I2S_C_SRC = 0x40000u, E_MI_AO_IF_MAX, } MI_AO_If_e; -
Member
Member name description E_MI_AO_IF_NONE None E_MI_AO_IF_DAC_AB DAC0/ 1 E_MI_AO_IF_DAC_CD DAC2/ 3 E_MI_AO_IF_I2S_A I2S TX A E_MI_AO_IF_I2S_B I2S TX B E_MI_AO_IF_ECHO_A SRC data(echo) E_MI_AO_IF_HDMI_A HDMI TX E_MI_AO_IF_I2S_C I2S TX C E_MI_AO_IF_I2S_A_SRC I2S TX A Mixer E_MI_AO_IF_I2S_B_SRC I2S TX B Mixer E_MI_AO_IF_I2S_C_SRC I2S TX C Mixer -
Related data types and interfaces
3.8. MI_AO_GainFading_e¶
-
Description
Define the changing speed of audio device gain.
-
Definition
typedef enum{ E_MI_AO_GAIN_FADING_OFF = 0, E_MI_AO_GAIN_FADING_1_SAMPLE, E_MI_AO_GAIN_FADING_2_SAMPLE, E_MI_AO_GAIN_FADING_4_SAMPLE, E_MI_AO_GAIN_FADING_8_SAMPLE, E_MI_AO_GAIN_FADING_16_SAMPLE, E_MI_AO_GAIN_FADING_32_SAMPLE, E_MI_AO_GAIN_FADING_64_SAMPLE, }MI_AO_GainFading_e; -
Member
Member name description E_MI_AO_GAIN_FADING_OFF Disable Fading function, set gain takes effect immediately E_MI_AO_GAIN_FADING_1_SAMPLE Enable Fading function, 1 sample point change 0.5dB E_MI_AO_GAIN_FADING_2_SAMPLE Enable Fading function, 2 sample points change 0.5dB E_MI_AO_GAIN_FADING_4_SAMPLE Enable Fading function, 4 sample points change 0.5dB E_MI_AO_GAIN_FADING_8_SAMPLE Enable Fading function, 8 sample points change 0.5dB E_MI_AO_GAIN_FADING_16_SAMPLE Enable Fading function, 16 sample points change 0.5dB E_MI_AO_GAIN_FADING_32_SAMPLE Enable Fading function, 32 sample points change 0.5dB E_MI_AO_GAIN_FADING_64_SAMPLE Enable Fading function, 64 sample points change 0.5dB -
Related data types and interfaces
3.9. MI_AUDIO_I2sMode_e¶
-
Description
Define the working mode of audio I2S TXRX/TX.
-
Definition
typedef enum { E_MI_AUDIO_I2S_MODE_I2S_MASTER, E_MI_AUDIO_I2S_MODE_I2S_SLAVE, E_MI_AUDIO_I2S_MODE_TDM_MASTER, E_MI_AUDIO_I2S_MODE_TDM_SLAVE, } MI_AUDIO_I2sMode_e; -
Member
Member name description E_MI_AUDIO_I2S_MODE_I2S_MASTER I2S master mode E_MI_AUDIO_I2S_MODE_I2S_SLAVE I2S slave mode E_MI_AUDIO_I2S_MODE_TDM_MASTER TDM master mode E_MI_AUDIO_I2S_MODE_TDM_SLAVE TDM slave mode -
Note
Determine whether to support the master/slave mode according to different chips.
-
Related data types and interfaces
3.10. MI_AUDIO_I2sBitWidth_e¶
-
Description
Define audio I2S TXRX/TX bit width.
-
Definition
typedef enum { E_MI_AUDIO_BIT_WIDTH_16, E_MI_AUDIO_BIT_WIDTH_24, E_MI_AUDIO_BIT_WIDTH_32, } MI_AUDIO_I2sBitWidth_e; -
Member
Member name description E_MI_AUDIO_BIT_WIDTH_16 I2S bit width is 16. E_MI_AUDIO_BIT_WIDTH_24 I2S bit width is 24. E_MI_AUDIO_BIT_WIDTH_32 I2S bit width is 32. -
Note
-
At present, I2S supports 32bit sequential data reception, when I2S is configured as 32bit, that is, the high level is effective and the data arrangement must be guaranteed in 1,3,5,7,...,slots.
-
Related data types and interfaces
3.11. MI_AUDIO_I2sFormat_e¶
-
Description
Define the data transmission format of audio I2S RX/TX.
-
Definition
typedef enum { E_MI_AUDIO_I2S_FMT_I2S_MSB, E_MI_AUDIO_I2S_FMT_LEFT_JUSTIFY_MSB, } MI_AUDIO_I2sFormat_e; -
Member
Member name description E_MI_AUDIO_I2S_FMT_I2S_MSB I2S standard format; Highest priority E_MI_AUDIO_I2S_FMT_LEFT_JUSTIFY_MSB I2S left-justified format; Highest priority -
Related data types and interfaces
3.12. MI_AUDIO_I2sMclk_e¶
-
Description
Define the mclk frequency of audio I2S RX/TX.
-
Definition
typedef enum { E_MI_AUDIO_I2S_MCLK_0, E_MI_AUDIO_I2S_MCLK_12_288M, E_MI_AUDIO_I2S_MCLK_16_384M, E_MI_AUDIO_I2S_MCLK_18_432M, E_MI_AUDIO_I2S_MCLK_24_576M, E_MI_AUDIO_I2S_MCLK_24M, E_MI_AUDIO_I2S_MCLK_48M, E_MI_AUDIO_I2S_MCLK_22_5792M, E_MI_AUDIO_I2S_MCLK_32_768M, E_MI_AUDIO_I2S_MCLK_36_864M, E_MI_AUDIO_I2S_MCLK_49_152M, E_MI_AUDIO_I2S_MCLK_76_8M, } MI_AUDIO_I2sMclk_e; -
Member
Member name description E_MI_AUDIO_I2S_MCLK_0 Disable MCLK E_MI_AUDIO_I2S_MCLK_12_288M Set MCLK to 12.88M E_MI_AUDIO_I2S_MCLK_16_384M Set MCLK to 16.384M E_MI_AUDIO_I2S_MCLK_18_432M Set MCLK to 18.432M E_MI_AUDIO_I2S_MCLK_24_576M Set MCLK to 24.576M E_MI_AUDIO_I2S_MCLK_24M Set MCLK to 24M E_MI_AUDIO_I2S_MCLK_48M Set MCLK to 48M E_MI_AUDIO_I2S_MCLK_22_5792M Set MCLK to 22.5792M E_MI_AUDIO_I2S_MCLK_32_768M Set MCLK to 32.768M E_MI_AUDIO_I2S_MCLK_36_864M Set MCLK to 36.864M E_MI_AUDIO_I2S_MCLK_49_152M Set MCLK to 49.152M E_MI_AUDIO_I2S_MCLK_76_8M Set MCLK to 76.8M -
Note
The header file determines which MCLK are supported on different SOC.
-
Related data types and interfaces
3.13. MI_AUDIO_I2sConfig_t¶
-
Description
Define I2S RX/TX config info.
-
Definition
typedef struct MI_AUDIO_I2sConfig_s { MI_AUDIO_I2sMode_e enMode; MI_AUDIO_I2sBitWidth_e enBitWidth; MI_AUDIO_I2sFormat_e enFormat; MI_AUDIO_SampleRate_e enSampleRate; MI_AUDIO_I2sMclk_e enMclk; MI_BOOL bSyncClock; MI_U32 u32TdmSlots; } MI_AUDIO_I2sConfig_t; -
Member
Member name description enMode I2S working mode enBitWidth I2S bit width enFormat I2S transmission data format. enSampleRate I2S sampling rate enMclk I2S mclk frequency bSyncClock Whether I2S RX and I2S TX share the clock. u32TdmSlots I2S TDM slot number(Only valid in TDM mode) -
Note
Souffle/Pcupid series chips support 1Chn PCM. To use this function, enMode must work in E_MI_AUDIO_I2S_MODE_TDM_MASTER and E_MI_AUDIO_I2S_MODE_TDM_SLAVE mode, and u32TdmSlots must be set to 1.
-
Related data types and interfaces
3.14. MI_AO_InitParam_t¶
-
Description
Audio output device initialization parameter.
-
Definition
typedef struct MI_AO_InitParam_s { MI_AUDIO_DEV AoDevId; MI_U8 *u8Data; } MI_AO_InitParam_t; -
Member
Member Name Description AoDevId AO device number u8Data Parameter pointer (reserved) -
Related data types and interfaces
4. ERROR CODE¶
The AO API error codes are shown in the table below:
| Error Code | Definition | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 0xA0052001 | MI_AO_ERR_INVALID_DEVID | Invalid audio output device number |
| 0xA0052003 | MI_AO_ERR_ILLEGAL_PARAM | Invalid audio output parameter setting |
| 0xA0052006 | MI_AO_ERR_NULL_PTR | Input parameter empty indicator error |
| 0xA0052007 | MI_AO_ERR_NOT_CONFIG | Audio output device properties are not set |
| 0xA0052008 | MI_AO_ERR_NOT_SUPPORT | Operation is not supported |
| 0xA0052009 | MI_AO_ERR_NOT_PERM | Operation not allowed |
| 0xA005200C | MI_AO_ERR_NOMEM | Fail to allocate memory |
| 0xA005200D | MI_AO_ERR_NOBUF | Insufficient audio output buffer |
| 0xA005200E | MI_AO_ERR_BUF_EMPTY | Audio output buffer is empty |
| 0xA005200F | MI_AO_ERR_BUF_FULL | Audio output buffer is full |
| 0xA0052010 | MI_AO_ERR_SYS_NOTREADY | Audio output system is not initialized |
| 0xA0052012 | MI_AO_ERR_BUSY | Audio output system is busy |
| 0xA0052017 | MI_AO_ERR_NOT_ENABLED | Audio output device or channel is not enabled |
| 0xA005201D | MI_AO_ERR_NOVASPACE | Audio device mapping buffer failed |
5. PROCFS AND DEBUG INTRODUCTION¶
5.1. Cat¶
-
Debug info
# cat proc/mi_modules/mi_ao/mi_ao0
-
Debug info analysis
Record the current AO usage status and device attributes, and can dynamically obtain information, which is convenient for debugging and testing.
-
Parameter Description
Parameter Description AO Device Attr DevStatus AO device status
uninit: uninit
opened: open sucessfullyFormat Audio format (Bit width and size end, etc)
Currently only support S16_LE (16bit, small end mode)SoundMode Sound mode: mono / stereo SampleRate Sample rate
8k/11.025k/12k/16k/22.05k/24k/32k/44.1k/48k/...PeriodSize AO starting condition (sample points) ChannelMode AO channel mode(Please refer to 'Keyword')
Stereo
DoubleMono
DoubleLeft
DoubleRight
Exchange
OnlyLeft
OnlyRightMixerSampleRate (Some support)Output sample rate after mixing.
8k/16k/32k/48kDmaBufSize DMA buffer size DmaBusySize DMA buffer busy size DmaFreeSize DMA buffer free size TmpBufSize Temporal buffer size bStart AO start DMA or not bPause AO pause DMA or not FrmCnt Write data frame count bXrun (Some support) Whether the current state is Xrun, the state is Xrun between the time the interruption occurs and Reset XrunIsrCnt (some support) The count of Xrun interrupts occur LastStart2XrunUs (Some support) If Xrun occurs, the time taken to Start Xrun, Us;If XrunIsrCnt == 0,this parameter is invalid LastStart2XrunBytes (Some support) If Xrun occurs, the write size Start to Xrun, bytes; LastAppWriteSize (Some support) The last time the APP called 'MI_AO_Write' to send data SIZE DpgaGain Digital gain: left channel gain, right channel gain DpgaMute DPGA mute: left channel mute, right channel mute MI If MI bind all interface information, that is, all interface information bound to the application layer Mhal Left If MHAL RDMA_L bind all interface information Mhal Right If MHAL RDMA_R bind all interface information If Info Interface volume, mute and other information
Volume (left channel gain, right channel gain)
Mute (left channel mute, right channel mute)
bIsMixing (Some support,Whether the current Interface mixing occurs)AO I2S Status I2sMode I2S Tx work mode (Only valid when interface is I2S Tx)
i2s-master
i2s-slave
tdm-master
tdm-slaveI2sMclk I2S Tx Mclk frequency (Only valid when interface is I2S Tx)
disable: not use Mclk
Other values are the current Mclk frequencyI2sFmt I2S Tx data format (Only valid when interface is I2S Tx)
I2S-MSB: I2S format
LEFT-MSB: I2S left-justified formatbI2sSync Whether I2S RX and TX share clock (Only valid when interface is I2S Tx)
1: 4 wire mode,RX and TX share clock
0: 6 wire mode,RX and TX have independent clocksTdmSlots I2S Tx TDM slot number (Tx is TDM mode when interface is I2S) I2sBitWidth I2S TX bit width (Only valid when interface is I2S Tx and the chip supports TDM mode)
5.2. Echo¶
| Features | Dynamically enable/disable AO device DPGA mute mode |
|---|---|
| Command | echo set_dpga_mute [LeftMute] [RightMute] [Fading] > /proc/mi_modules/mi_ao/mi_ao[ID] |
| Parameter Description | [ON/on/1, OFF/off/0] Enable/Disable mute [Fading] Set the fading speed [ID] Device ID |
| Example | echo set_dpga_mute 1 0 0 > /proc/mi_modules/mi_ao/mi_ao0 |
| Features | Dynamically enable/disable AO device interface mute mode |
|---|---|
| Command | echo set_inf_mute [If] [LeftMute] [RightMute] > /proc/mi_modules/mi_ao/mi_ao[ID] |
| Parameter Description | [If]Interface to be set [ON/on/1, OFF/off/0] Enable/Disable mute [ID] Device ID |
| Example | echo set_inf_mute 1 1 0 > /proc/mi_modules/mi_ao/mi_ao0 |
| Features | Dynamically set AO DPGA volume |
|---|---|
| Command | echo set_dpga_volume [LeftVolume] [RightVolume] [Fading] > /proc/mi_modules/mi_ao/mi_ao[ID] |
| Parameter Description | [LeftVolume] [RightVolume] Left channel volume, right channel volume [Fading]Set the fading speed of volume |
| Example | echo set_dpga_volume -10 -10 0 > /proc/mi_modules/mi_ao/mi_ao0 |
| Features | (Some support)Dynamically set AO Interface volume |
|---|---|
| Command | echo set_inf_volume [If] [LeftVolume] [RightVolume] > /proc/mi_modules/mi_ao/mi_ao[ID] |
| Parameter Description | [If]Interface to be set [LeftVolume] [RightVolume] Left channel volume, right channel volume |
| Example | echo set_inf_volume 1 -10 -10 > /proc/mi_modules/mi_ao/mi_ao0 |
| Features | Dynamically enable/disable the dump data function of AO device |
|---|---|
| Command | echo dump_data [Path] [ON/on/1, OFF/off/0] > /proc/mi_modules/mi_ao/mi_ao[ID] |
| Parameter Description | [Path] Path to dump data [ON/on/1, OFF/off/0] Enable/Disable the dump data function |
| Example | echo dump /mnt 1 > /proc/mi_modules/mi_ao/mi_ao0 |
| Function | Dynamically enable/disable Singen of AO device |
|---|---|
| Command | echo singen [SinGen Index] [Enable] > /proc/mi_modules/mi_ao/mi_ao[ID] |
| Parameter Description | [SinGen Index] Singen ID [Enable] Enable/Disable Singen |
| Example | echo singen 0 1 > /proc/mi_modules/mi_ao/mi_ao0 |
| Function | (Some support)Dynamically set channel mode of AO device |
|---|---|
| Command | echo set_chn_mode [channelMode] > /proc/mi_modules/mi_ao/mi_ao[ID] |
| Parameter Description | [channelMode] channel mode of AO device |
| Example | echo set_chn_mode 0 > /proc/mi_modules/mi_ao/mi_ao0 |
5.3. MI User Mode Debug¶
| Function | Before run the APP, dump the data sent to AO by the MI user mode APP by specifying the environment variable export |
|---|---|
| Description | [MI_AO_DUMP_ENABLE] Enable the dump of data sent to the AO by the MI user mode APP [MI_AO_DUMP_PATH] dump file path |
| Example | export MI_AO_DUMP_ENABLE=1 export MI_AO_DUMP_PATH=/mnt |
6. Insmod Parameter And MODPARAM.json INTRODUCTION¶
6.1. Parameter Name, Support Chip And Usage¶
| parameter name | use insmod parameter chip | use MODPARAM.json parameter chip | default | whether support it | function |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DmaBufferSize | Muffin/Mochi | Maruko/Souffle/Pcupid | calculate the value | Y | Modify AI DMA and TMP Buffer size |
6.2. Insmod Parameter Usage¶
Example:
insmod mi_ao.ko DmaBufferSize=32 # Unit:K, 4K align.
6.3. MODPARAM.json Parameter Usage¶
Example: vim /config/modparam.json:
{
"E_MI_MODULE_ID_AO" :
{
"DmaBufferSize" : 32 // Unit:K, 4K align.
}
}