ULOG User Guide
REVISION HISTORY¶
| Revision No. | Description |
Date |
|---|---|---|
| 1.0 | 09/11/2025 |
1. Overview¶
This document describes how to use the ULOG feature on the SigmaStar platform. ULOG, short for Uart Log, can save U-Boot serial port logs to the eMMC. When U-Boot fails, you can dump the log data to assist with debugging.
2. Functional Description¶
The ULOG function can save the U-Boot serial port log to a specified partition of the eMMC. When the module is running, it will first save the UART log to the memory buffer, and write the data in the buffer to the eMMC when one of the following conditions is met:
-
Condition 1: When the data in the buffer exceeds the specified size
-
Condition 2: When U-Boot is in the console idle state for longer than the specified timeout
In addition, you can also call a specific API to actively write the data in the buffer to eMMC immediately.
Please note: Because U-Boot is single-threaded and has no interrupts, if U-Boot hangs while executing a task and is reset by the watchdog after a period of time, the log before the hang cannot be written to the eMMC. You can actively call ulog_flush() after executing the key task to write the log in the buffer to eMMC.
When the log is full in the ULOG partition, new log data will be automatically written from the beginning of the ULOG partition to overwrite the old data.
3. U-Boot Usage Introduction¶
3.1. U-Boot Configuration¶
The configurations you need to select when compiling U-Boot are as follows:
make menuconfig # [*] SigmaStar drivers ---> # [*] SigmaStar Uart Log Driver ---> # [*] Ulog Default Status On # (ulog) Ulog Partition Name # (512) Ulog Flush Size (byte) # (100) Ulog Flush Timeout (ms) # Command line interface ---> # SigmaStar common commands ---> # -*- ulog # General setup ---> # -*- Enable malloc() pool before relocation # (0x4000) Size of malloc() pool before relocation
Configuration description:
| CONFIG | Description |
|---|---|
| CONFIG_SSTAR_ULOG | The main switch of the ULOG module |
| CONFIG_SSTAR_ULOG_DEFAULT_ON | The default state (on/off) of the ULOG function when U-Boot starts |
| CONFIG_SSTAR_ULOG_PARTITION_NAME | The partition name for saving U-Boot logs |
| CONFIG_SSTAR_ULOG_FLUSH_SIZE | The log buffer will be automatically written to eMMC if it exceeds this value |
| CONFIG_SSTAR_ULOG_FLUSH_TIMEOUT | If U-Boot is in the console idle state for longer than this value, it will automatically write to the eMMC |
| CONFIG_CMD_SSTAR_ULOG | Whether to enable the U-Boot command line ulog command |
| CONFIG_SYS_MALLOC_F | Whether to enable early malloc() function |
| CONFIG_SYS_MALLOC_F_LEN | The size of the early malloc() pool. ULOG requires at least 0x1000 bytes |
3.2. U-Boot Command Line Reference¶
| Command | Function |
|---|---|
| ulog enable | Enable the ULOG function, and the subsequent U-Boot log will be written to eMMC |
| ulog disable | Disable the ULOG function, and the subsequent U-Boot log will not be written to eMMC |
3.3. U-Boot API Reference¶
| API | Function |
|---|---|
| ulog_enable | Enable the ULOG function |
| ulog_disable | Disable the ULOG function |
| ulog_flush | Write the log data in the buffer to eMMC immediately |
3.3.1. ulog_enable¶
-
Function
Enable the ULOG function, and the subsequent U-Boot log will be written to eMMC.
-
Syntax
ulog_enable();
-
Parameters
None
-
Return Value
None
-
Dependency
- Header File: drivers/sstar/ulog/drv_ulog.h
-
Note
None
3.3.2. ulog_disable¶
-
Function
Disable the ULOG function, and the subsequent U-Boot log will not be written to eMMC.
-
Syntax
ulog_disable();
-
Parameters
None
-
Return Value
None
-
Dependency
- Header File: drivers/sstar/ulog/drv_ulog.h
-
Note
None
3.3.3. ulog_flush¶
-
Function
Write the log data in the buffer to eMMC immediately.
-
Syntax
ret = ulog_flush();
-
Parameters
None
-
Return Value
-
0: Indicates that all log data in the buffer are successfully written to the eMMC.
-
-1: Indicates that there is no log data in the buffer that needs to be written to the eMMC.
-
-
Dependency
- Header File: drivers/sstar/ulog/drv_ulog.h
-
Note
None
4. Add ULOG Partition¶
The name of the ULOG partition must be the same as the value of CONFIG_SSTAR_ULOG_PARTITION_NAME in U-Boot. The default value of CONFIG_SSTAR_ULOG_PARTITION_NAME is "ulog".
Add a new ulog partition in the partition configuration file
-
Modify IMAGE_LIST
IMAGE_LIST = boot riscvfw kernel rootfs misc miservice pstore vendor_storage ulog customer
-
Add ulog partition
# ulog ulog$(FSTYPE) = ulog ulog$(PATSIZE) = 0x200000 ulog$(PATNAME) = ulog ulog$(MOUNTTG) = /dev/mmcblk0p8
5. Dump Log Data¶
5.1. Dump Method¶
When U-Boot fails, you can dump the U-Boot log data from the ULOG partition to assist with debugging. The following are the steps to dump the data:
Step 1. Determine the location of the ULOG partition in eMMC. You can check this by executing the "mmc part" command in U-Boot:
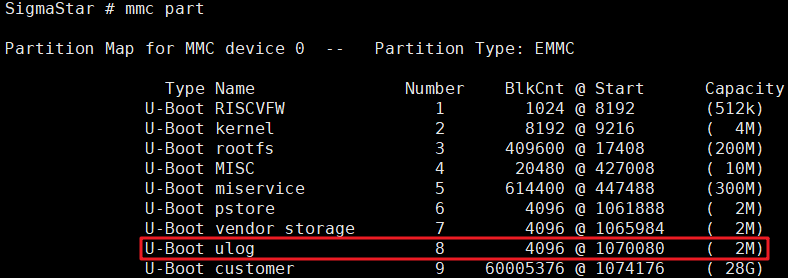
The above figure shows that the starting address of the ULOG partition (i.e. ulog partition) in emmc is 1070080 and the partition size is 2MB.
Step 2. Use Flash Tool to dump the ULOG partition data to the local PC:
Please note: Before dumping, you must first close the SoC serial port (type "debug" and press Enter in U-Boot, type "11111" in Linux), and disconnect the PC terminal connection (Xshell/MobaXterm).
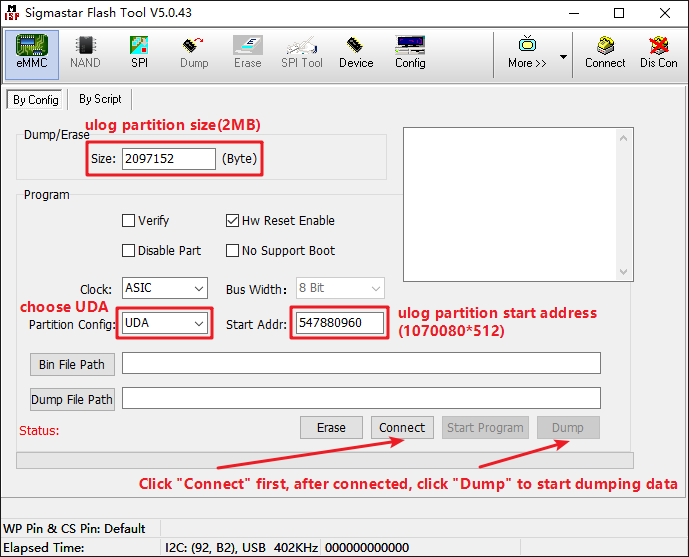
The successful dump interface is shown below:
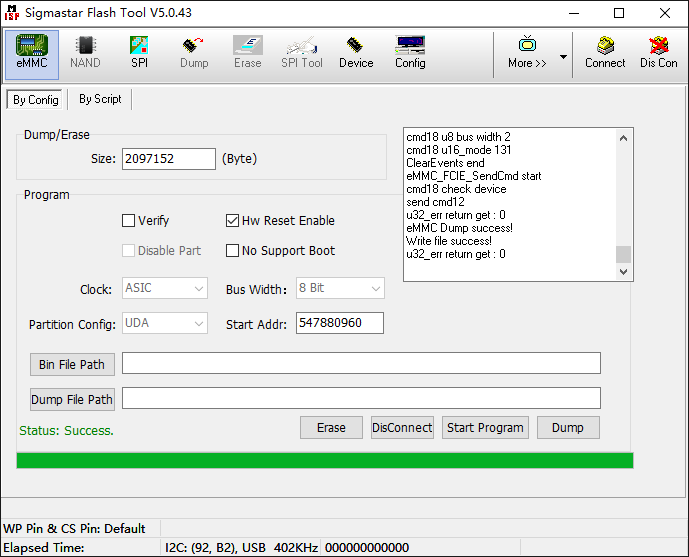
After the dump is successful, the data will be saved in the EMMC_DATA_UDA.bin file in the Flash Tool directory.
Step 3. Use the "strings" command to convert the data into a text file:
strings EMMC_DATA_UDA.bin > log.txt
5.2. Log Content Format¶
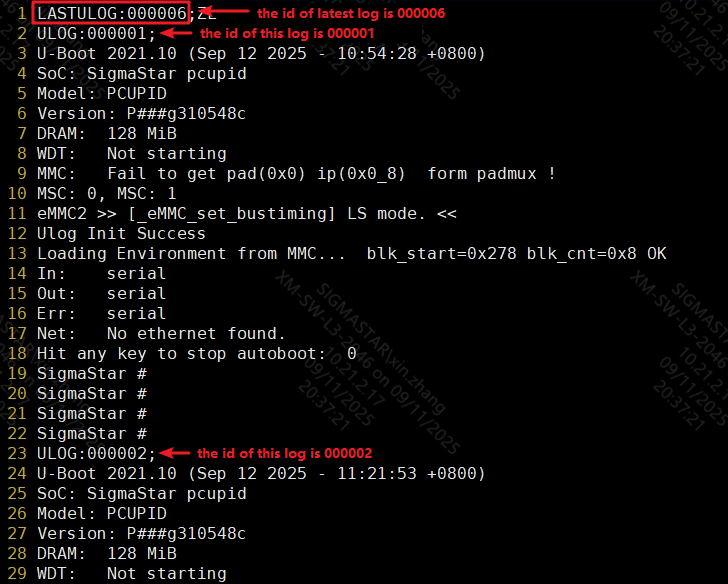
The ULOG feature adds an ID to each U-Boot log file to identify the chronological order of log generation. This ID automatically increments with each U-Boot boot. In text files generated using the "strings" command, the first line "LASTULOG:XXXXXX" contains the latest log ID, making it easy for developers to quickly locate the most recent log.