YOLOv5
1 Overview¶
1.1 Background Introduction¶
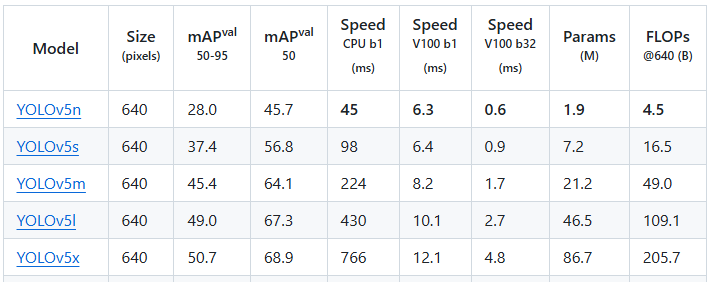
YOLOv5 is an advanced real-time object detection algorithm that improves detection accuracy and robustness while maintaining a fast detection speed. The official YOLOv5 provides various detection model sizes: n, s, m, l, x, and the accuracies of these open-source models are as follows:
For more details, please refer to the official YOLOv5 documentation:
https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5
The download link for the YOLOv5 open-source models is as follows:
1.2 Usage Instructions¶
The Linux SDK-alkaid comes with pre-converted offline models and board-side examples by default. The relevant file paths are as follows:
-
Board-side example program path
Linux_SDK/sdk/verify/opendla/source/detection/yolov5 -
Board-side offline model paths
Linux_SDK/project/board/${chip}/dla_file/ipu_open_models/detection/yolov5s_640x640.img -
Board-side test image path
Linux_SDK/sdk/verify/opendla/source/resource/bus.jpg
If the user does not need to convert the model, they can jump directly to section 3.
2 Model Conversion¶
2.1 ONNX Model Conversion¶
-
Setting up the Python environment $conda create -n yolov5 python==3.10 $conda activate yolov5 $git clone https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5 $cd yolov5 $pip install -r requirements.txt -i https://pypi.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/simple Note: The provided Python environment setup is only a reference example; for the specific setup process, please refer to the official source running tutorial:
https://docs.ultralytics.com/zh/yolov5/quickstart_tutorial/ -
Model Testing
- Run the model testing script to ensure the YOLOv5 environment is configured correctly. $python detect.py --weights ./yolov5s.pt --source './bus.jpg' For specific details, please refer to the official YOLOv5 testing documentation https://docs.ultralytics.com/zh/yolov5/quickstart_tutorial/#inference-with-detectpy
-
Model Export
- Run the model conversion script $python export.py --weights ./yolov5s.pt --include onnx
- Optimize the graph structure $python -m onnxsim ./yolov5s.onnx ./yolov5s.onnx
2.2 Offline Model Conversion¶
2.2.1 Preprocessing & Postprocessing Instructions¶
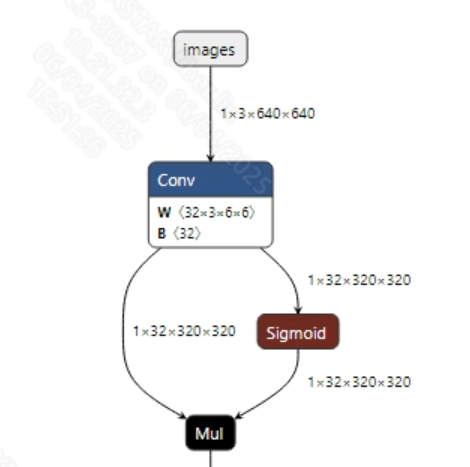
- Preprocessing The input information for the successfully converted yolov5s.onnx model is shown in the figure below, with an input image size of (1, 3, 640, 640), and the pixel values must be normalized to the range [0, 1].
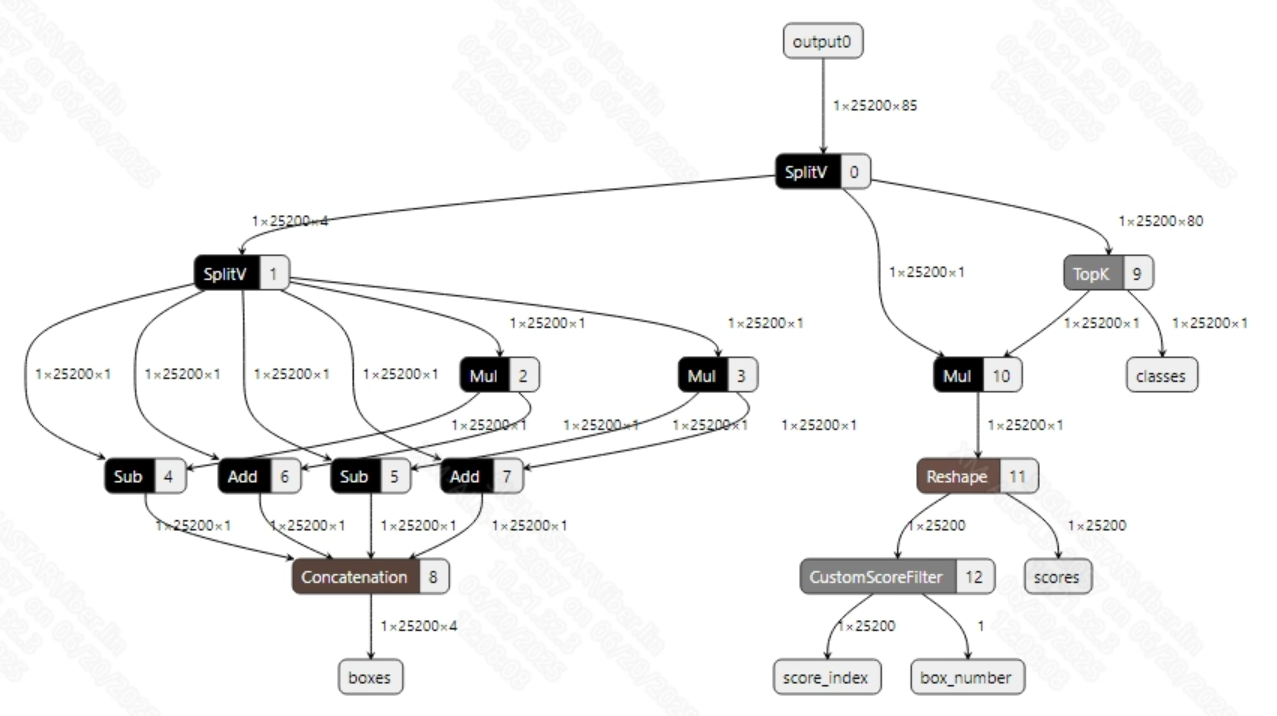
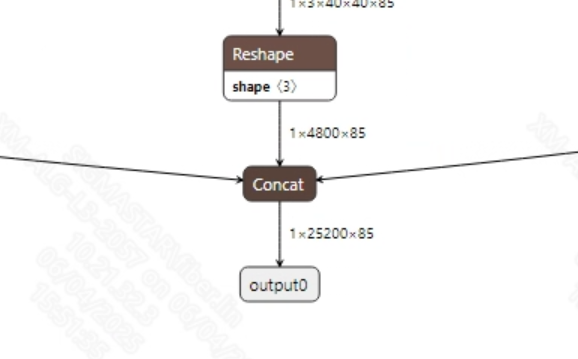
- Postprocessing The output information for the successfully converted yolov5s.onnx model is shown in the figure below. The output dimensions of the YOLOv5s model are typically (1, 25200, 85). Here, 25200 is the number of candidate boxes, and 85 includes 1 confidence score, 4 bounding box coordinates, and 80 class probabilities. After obtaining the candidate boxes from the model output, all candidate box classes need to be judged and NMS (Non-Maximum Suppression) must be performed to output the correct bounding boxes.
2.2.2 Offline Model Conversion Process¶
Note: 1) OpenDLAModel corresponds to the smodel file extracted from the compressed package image-dev_model_convert.tar. 2) The conversion command must be run in a Docker environment; please load the SGS Docker environment according to the Docker development environment tutorial.
- Copy the ONNX model to the conversion code directory $cp opendla/yolov5s.onnx OpenDLAModel/detection/yolov5/onnx
- Conversion command $cd IPU_SDK_Release/docker $bash run_docker.sh # Enter the OpenDLAModel directory in the Docker environment $cd /work/SGS_XXX/OpenDLAModel $bash convert.sh -a detection/yolov5 -c config/detection_yolov5.cfg -p SGS_IPU_Toolchain (absolute path) -s false
- Final generated model locations output/{chip}_/yolov5s_640x640.img output/{chip}_/yolov5s_640x640_fixed.sim output/{chip}_/yolov5s_640x640_float.sim
2.2.3 Key Script Parameter Analysis¶
- input_config.ini
[INPUT_CONFIG]
inputs = images; # ONNX input node names, separated by commas if there are multiple;
training_input_formats = RGB; # Input format during model training, usually RGB;
input_formats = YUV_NV12; # Board-side input format, can choose BGRA or YUV_NV12 based on the situation;
quantizations = TRUE; # Enable input quantization, do not modify;
mean_red = 0; # Mean, related to model preprocessing, configure according to actual conditions;
mean_green = 0; # Mean, related to model preprocessing, configure according to actual conditions;
mean_blue = 0; # Mean, related to model preprocessing, configure according to actual conditions;
std_value = 255; # Variance, related to model preprocessing, configure according to actual conditions;
[OUTPUT_CONFIG]
outputs = output0; # ONNX output node names, separated by commas if there are multiple;
dequantizations = TRUE; # Whether to enable dequantization, fill according to actual needs, recommended to be TRUE. If set to False, output will be int16; if set to True, output will be float32.
- detection.cfg
[YOLOV5]
CHIP_LIST=pcupid # Platform name, must match the board platform; otherwise, the model cannot run
Model_LIST=yolov5s # Input ONNX model name
INPUT_SIZE_LIST=640x640 # Model input resolution
INPUT_INI_LIST=input_config.ini # Configuration file
CLASS_NUM_LIST=0 # Just fill in 0
SAVE_NAME_LIST=yolov5s_640x640.img # Output model name
QUANT_DATA_PATH=quant_data # Path for quantization images
2.3 Model Simulation¶
- Obtain float/fixed/offline model outputs
$bash convert.sh -a detection/yolov5 -c config/detection.cfg -p SGS_IPU_Toolchain (absolute path) -s true
After executing the above command, the output tensor of the
floatmodel will be saved by default in a txt file under the pathdetection/yolov5/log/output. Additionally, thedetection/yolov5/convert.shscript also provides simulation examples forfixedandoffline, allowing users to obtain outputs for thefixedandofflinemodels by uncommenting code blocks during execution. - Model Accuracy Comparison
With the input being the same as the aforementioned models, enter the environment built in section 2.1, and add the following print statement at line 114 in the
yolov5/models/yolo.pyfile: print(z) This will obtain the output tensor of the corresponding node in the PyTorch model, allowing for comparison with the float, fixed, and offline models. It should also be noted that the original model's output format isNCHW, while the output formats of the float/fixed/offline models areNHWC.
3 Board-side Deployment¶
3.1 Program Compilation¶
Before compiling the example program, it is necessary to select the appropriate deconfig based on the board (nand/nor/emmc, ddr model, etc.) for the complete SDK compilation. For details, refer to the alkaid SDK sigdoc document "Development Environment Setup." - Compile the board-side YOLOv5 example. $cd sdk/verify/opendla make clean && make source/detection/yolov5 -j8 - Final generated executable file location sdk/verify/opendla/out//app/prog_detection_yolov5
3.2 Running Files¶
When running the program, you need to copy the following files to the board:
- prog_detection_yolov5
- bus.jpg
- yolov5s_640x640.img
3.3 Running Instructions¶
- Usage:
./prog_detection_yolov5 -i image -m model [-t threshold](command to run the executable) - Required Input:
- image: path to the image folder/single image
- model: path to the offline model to be tested
- Optional Input:
- threshold: detection threshold (0.0~1.0, default is 0.5)
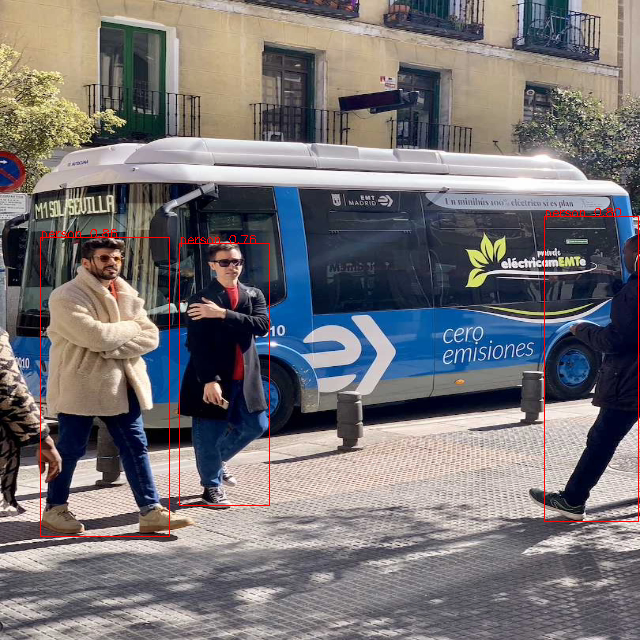
- Typical output: >./prog_detection_yolov5 -m ./yolov5s_640x640.img -i ./resource/bus.jpg demo_args: inImages=./; modelPath=./yolov5s_640x640.img; threshold=0.5 found 1 images! [0] processing ./resource/bus.jpg... model invoke time: 14.361000 ms post process time: 0.436000 ms outImagePath: ./output/2108/bus.png

4 Algorithm Optimization¶
4.1 Postprocessing Optimization¶
-
Existing Issues
The official YOLOv5 converted offline model outputs 25600 candidate detection boxes (Bounding Boxes). The conventional approach is to filter out most candidate boxes on the CPU by setting a threshold, but remaining candidate boxes will still increase CPU loading during computation.
-
Solution Construct a post-processing model using the SGS_IPU_Toolchain (as shown in the figures below), and then concatenate it with the official YOLOv5 model. This allows the computation of all candidate boxes to be performed on the IPU without changing the structure of the official YOLOv5 model. Therefore, while converting the model and running the board-side example:
- The ONNX model remains unchanged; refer to 2.1
- Offline model conversion command
$bash convert.sh -a detection/yolov5 -c config/detection_yolov5.cfg -p SGS_IPU_Toolchain (absolute path) -s false -d ipu
Relevant optimizations can be found in
OpenDLAModel/detection/yolov5/yolov5_post.py - Board-side deployment, refer to 3
-
Note The method of building IPU operators through the SGS_IPU_Toolchain requires the user to be familiar with the IPU Toolchain. For specifics, refer to the documentation for using the IPU Toolchain.