Introduction to OpenDLA
1 Overall Introduction¶
OpenDLAModel & OpenDLA is a development suite provided for users to enable quick deployment on the SGS platform. Among them, OpenDLAModel is the conversion code for open-source models, while OpenDLA serves as the running example for the converted offline models. To facilitate customer conversion of open-source models, OpenDLAModel includes files such as ONNX models, parameter configuration examples, and data processing scripts, and it has encapsulated the conversion command script convert.sh for the IPU Toolchain.
OpenDLAModel and OpenDLA rely on IPU_SDK and Linux_SDK respectively, and the specific calling flow is as follows:
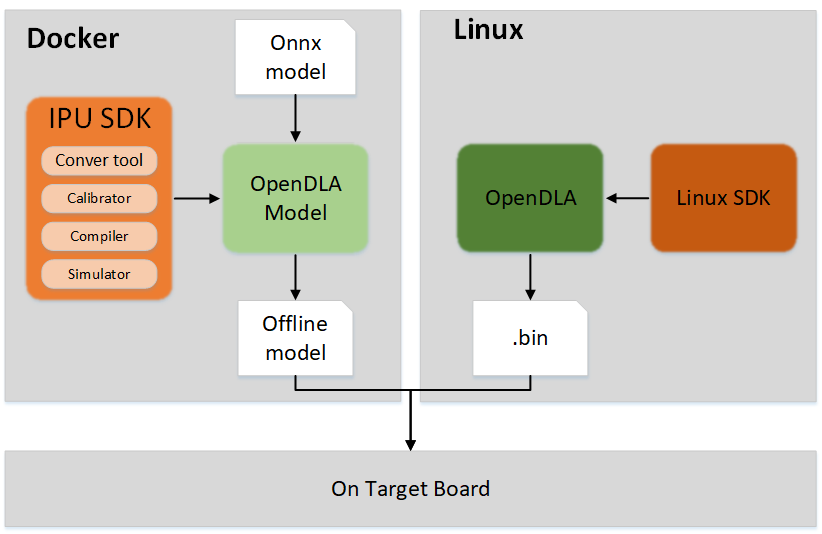
1.1 OpenDLAModel & OpenDLA¶
The specific directory structure of OpenDLAModel is as follows:
├── detection
└── yolov5
└── yolov8
└── quant_data # A small quantization dataset, only for reference
└── onnx # Path to store ONNX models
└── input_config.ini # Input parameter configuration file
└── new_offline_input_config.ini # Post-processing model input configuration file
└── modify_out_nodes.py # Modify ONNX model output nodes
└── yolov8_pre.py # Pre-processing script
└── yolov8_post.py # Post-processing model building script
└── convert.sh # Model conversion command
└── convert_ipu.sh # Command to add post-processing model conversion
└── yolov11_obb
├── pose
└── yolov8
├── segmentation
└── yolov8
├── ocr
└── lpr
└── ppocr
├── llm
└── punc
└── transformerlm
├── vlm
└── clip
└── mobilesam
└── yolo_world
├── asr
└── conformer
├── speaker
└── resnet
├── vad
└── nemo
├── tts
└── vits
├── separation
└── sepformer
├── sed
└── eat
├── config
├── convert.sh
Among them, the parameters for running convert.sh are as follows:
-a: Algorithm path
-c: Path to the algorithm's cfg file
-p: Path to the IPU SDK, absolute path is required
-s: Whether to enable model simulation
-d: Whether to enable post-processing optimization mode for v8/v5 detection models
For specific running instructions, refer to the documentation of the specific algorithms.
The list of specific open-source algorithms in OpenDLA is as follows:
├── Benchmark # Used to test the overhead of offline models
├── Resource # Stores files such as images/audio/text/dictionaries for board operation
├── classification # C/C++ specific example code
├── detection
└── yolov5
└── yolov8
└── yolov11_obb
├── pose
└── yolov8
├── segmentation
└── yolov8
├── ocr
└── lpr
└── ppocr
├── llm
└── punc
└── transformerlm
├── vlm
└── clip
└── mobilesam
└── yolo_world
├── asr
└── conformer
├── speaker
├── vad
└── nemo
├── tts
└── vits
├── separation
└── sepformer
├── sed
└── eat
2 Development Tools¶
The development tools used by users during deployment are provided by FAE. The specific directory structure is as follows:
- ReleaseForCus
└────Linux_SDK_Release └────sdk └────verify/opendla └────project └────release/chip/${chip_name}/sigma_common_libs/${toolchain}/${version}/arm/release/static/*.lib └────kernel └────boot └────IPU_SDK_Release └────docker └────SGS_IPU_Toolchain └────OpenDLAModel
For details about Linux_SDK_Release, please refer to "Development Environment Setup," and for IPU_SDK_Release, please refer to the IPU Doc.
3 Supported Model List¶
The table below shows the supported model list on the SGS platform. The support status of open-source models varies across different platforms, primarily due to the following reasons:
-
Platform operators are not yet supported
-
Platform computing power limitations
| chip | algorithm |
|---|---|
| muffin | classification/yolov5/yolov8/yolov8-pose/yolov8-seg/lpr/ppocr/conformer/sed/punc/vad/transformerlm/vits/clip/yolov8_world/mobilesam |
| ifackel | classification/yolov5/yolov8/yolov8-pose/yolov8-seg/lpr/ppocr/conformer/sed/punc/vad/transformerlm/vits/clip/yolov8_world/mobilesam |
| souffle | classification/yolov5/yolov8/yolov8-pose/yolov8-seg/lpr/ppocr/conformer/sed/punc/vad/transformerlm/vits/clip/yolov8_world/mobilesam |
| maruko | classification/yolov5/yolov8/yolov8-pose/yolov8-seg/lpr/conformer/sed |
| iford | classification/yolov5/yolov8/yolov8-pose/yolov8-seg/lpr/conformer/sed |
| ifado | classification/yolov5/yolov8/yolov8-pose/yolov8-seg/lpr/conformer/sed |
| pcupid | classification/yolov5/yolov8/yolov8-pose/yolov8-seg/lpr/ppocr/conformer/sed/punc/vad/transformerlm/vits/clip/yolov8_world/mobilesam |
| opera | classification/yolov5/yolov8/yolov8-pose/yolov8-seg/lpr/ppocr/conformer/sed/punc/vad/transformerlm/vits/clip/yolov8_world/mobilesam |
| mochi | classification/yolov5/yolov8/yolov8-pose/yolov8-seg/lpr/conformer/sed |