5. Model Construction Tools
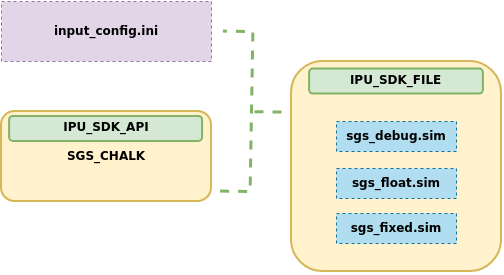
1 Construction Tool sgs_chalk¶
1.1 Basic Introduction to sgs_chalk¶
sgs_chalk is a tool designed for the rapid construction of models, employing usage methods similar to those of the open-source deep learning frameworks PyTorch and TensorFlow. It encapsulates supported operators as APIs, which users can call to create scripts that generate the original debug.sim. By setting appropriate parameters, users can also generate float.sim and fixed.sim in one step. The specific usage methods will be introduced below.
1.2 How to Use sgs_chalk¶
(1) Before use, you need to add the following statement at the beginning of your script:
from calibrator_custom import sgs_chalk
The interface for constructing tensors is sgs_chalk.Tensor. Below is an introduction to the parameters that need to be passed in:
data: The actual data for the tensor, which needs to be in np.array format.
shape: The shape of the tensor to be passed in.
dtype: The data type of the tensor's data. If not provided, the default is 'float32'. Supported data types include uint8, int16, float32, int32, int64, and complex64.
name: The name of the tensor. If not provided, it will default to prefix_ followed by a number, and there is an internal checking mechanism to rename any tensors that have duplicate names
.
prefix: Sets the prefix for the default tensor naming.
In sgs_chalk, constructing tensors is primarily divided into two types. Variable tensors will be returned when constructing operators, so users generally do not need to create them manually.
To create an input tensor for a model, use the sgs_chalk.Input interface:
in0 = sgs_chalk.Input((1,28,28,1),name='input')
An example of creating a constant tensor:
weight1 = np.load("mnist_gen_weights/conv2d_4_kernel.npy")
weight1_tensor = sgs_chalk.Tensor(data=weight1,name='conv2d_4/kernel')
(3) Constructing Operators
The interface for constructing operators varies by operator type, and the parameters required to create each operator may differ, returning an output tensor. For specific details, refer to Section 1.4.3. Below are a few simple examples:
Creating an add operation:
in0 = sgs_chalk.Input((28,512),name='input0')
in1 = sgs_chalk.Input((28,512),name='input1')
out0 = sgs_chalk.Add(in0,in1,name='output')
Creating a convolution operation:
in0 = sgs_chalk.Input((1,28,28,4),name='input0')
in1 = sgs_chalk.Input((8,3,3,4),name='input1')
out0 = sgs_chalk.Conv2d(in0,in1,name='output')
(4) Constructing a Model
The interface for constructing a model is sgs_chalk.Model. Below is an introduction to the parameters to be passed in:
input_tensors: The names of the input tensors provided as a list.
output_tensors: The names of the output tensors provided as a list.
model = sgs_chalk.Model([in0],[out0])
(5) Exporting the Model
The model should be exported after it has been constructed, calling the interface as follows:
model.save(model_path, input_config=None, convert_fixed=False, inputs=None)
This API has several usages:
- To only save the debug model:
model.save('test.sim')
This will generate the debug_test.sim model.
- To save both the debug and float models, the
input_config.inimust be configured:
model.save('test.sim', input_config='./input_config.ini')
This will generate both Debug_test.sim and test.sim.
- To save the fixed model, set
convert_fixed=Trueand add theinputsparameter. This will automatically generate the preprocessing file for the model and run the internal statistical quantization process based on theinputs, such as user-provided images, to generate thefixed.simmodel:
model.save('test.sim', input_config='./input_config.ini', convert_fixed=True, inputs='0.jpg')
This will read the inputs parameter and automatically generate the preprocessing script for the model based on the configuration in input_config.ini, performing quantization to generate the fixed.sim model.
The inputs parameter has several usages:
inputs=/path/to/img_dirorinputs=/path/to/img.jpg
This mode can be used if the input_config.ini has training_input_formats for model inputs set to RGB / BGR / GRAY.
inputs=/path/to/npy_dirorinputs=/path/to/data.npy
This mode can be used if all model inputs in input_config.ini are set to RAWDATA_S16_NHWC, RAWDATA_F32_NHWC, or RAWDATA_COMPLEX64. Note that the input data must be in numpy .npy format.
inputs=/path/to/img.txt
This mode can be used when there are multiple inputs defined in input_config.ini.
inputs='RAWDATA'
This mode can be used if all model inputs in input_config.ini are set to RAWDATA_S16_NHWC, RAWDATA_F32_NHWC, or RAWDATA_COMPLEX64. The 'RAWDATA' mode requires prior configuration of the model input's min/max values, and saving the model will generate min/max input files and preprocessing based on the model input configuration, converting to generate the fixed model. This mode is only used to test whether the constructed model can generate the fixed model following the quantization process tracked internally.
1.3 Using sgs_chalk to Construct Post-Processing Models¶
Below, we will take Quick_Start_Demo/onnx_yolov8s/onnx_yolov8s_postprocess.py as an example to illustrate how to use sgs_chalk to construct a post-processing model.
1.3.1 YOLOv8 Post-Processing Optimization Ideas¶
The output information of the onnx_yolov8s.onnx model is shown in the figure below. Typically, the model converted from YOLOv8 produces output dimensions of (1, 84, 8400), where 8400 is the number of candidate boxes and 84 includes 4 bounding box coordinates and 80 category probabilities. After obtaining the candidate boxes from the model output, all candidate boxes need classification and NMS (Non-Maximum Suppression) to output the correct coordinates.
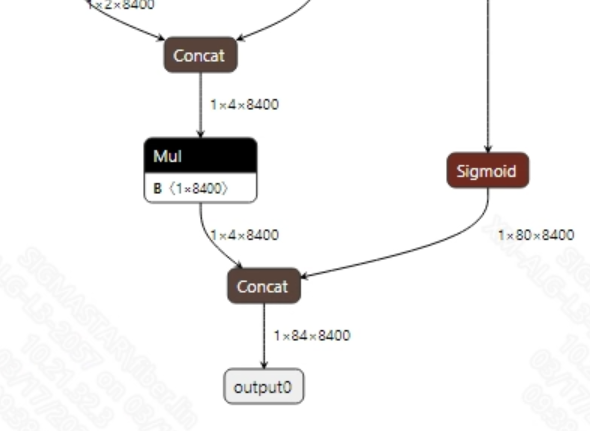
The official YOLOv8 converted offline model has a relatively high CPU utilization rate. The root cause is that YOLOv8 defaults to outputting 8400 candidate detection boxes (Bounding Boxes). In the case of 80 category detection scenarios in the COCO dataset, each candidate box requires 80 computations of category confidence, resulting in a total computational workload of 672,000 calculations per frame (8400×80), leading to a consistently high CPU load.
By using TopK to filter categories and Score_Filter to filter boxes that meet confidence requirements, the number of boxes processed by NMS will be significantly reduced, thus lowering CPU load. The model constructed by sgs_chalk is shown in the figure below:
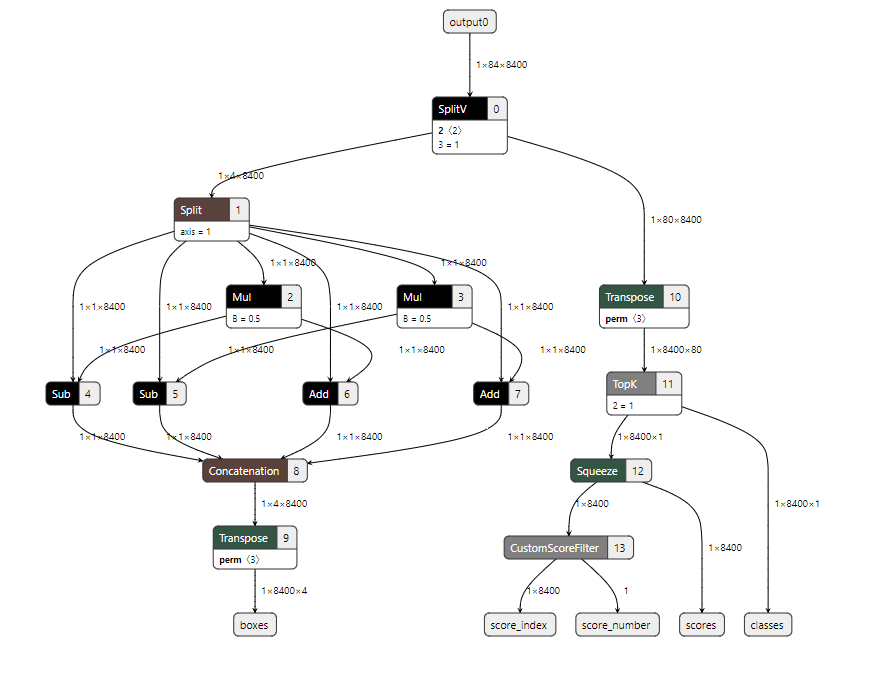
1.3.2 Constructing the YOLOv8s Post-Processing Model¶
The complete code for constructing the YOLOv8s post-processing model using sgs_chalk is as follows:
from calibrator_custom import sgs_chalk
IN_WIDTH = 640
IN_HEIGHT = 640
LAYER_STRIDES = [8, 16, 32]
LAYER_GRIDS = [int((IN_WIDTH / stride) * (IN_HEIGHT / stride)) for stride in LAYER_STRIDES]
ALL_LAYER_GRIDS = 0
for r_grid in LAYER_GRIDS:
ALL_LAYER_GRIDS += r_grid
CONF_THRESHOLD = 0.27
def buildGraph(model_config):
inputs = sgs_chalk.Input(shape=model_config['shape'], name=model_config['input'][0])
[box, score] = sgs_chalk.Split_V(
inputs,
[4, model_config['num_classes']],
axis=1,
name=['box', 'confidence']
)
[cx, cy, w, h] = sgs_chalk.Split(box, 4, axis=1, name=['cx', 'cy', 'w', 'h'])
w_ = sgs_chalk.Mul(w, 0.5)
h_ = sgs_chalk.Mul(h, 0.5)
x1 = sgs_chalk.Sub(cx, w_)
y1 = sgs_chalk.Sub(cy, h_)
x2 = sgs_chalk.Add(cx, w_)
y2 = sgs_chalk.Add(cy, h_)
concat = sgs_chalk.Concatenation([x1, y1, x2, y2], axis=1)
bboxes = sgs_chalk.Transpose(concat, (0, 2, 1), name='boxes')
score = sgs_chalk.Transpose(score, (0, 2, 1))
[max_score, max_index] = sgs_chalk.TopK(score, k=1, name=['max_score', 'classes'])
reshape_score = sgs_chalk.Squeeze(max_score, axis=-1, name='scores')
out_score_index, out_score_num = sgs_chalk.Score_Filter(
reshape_score,
threshold=CONF_THRESHOLD,
input_element_count=ALL_LAYER_GRIDS,
name=['score_index', 'score_number']
)
outfilename = model_config['name'] + '_postprocess.sim'
model = sgs_chalk.Model(
[inputs],
[bboxes, max_index, reshape_score, out_score_index, out_score_num]
)
buf = model.save_buf()
with open(outfilename, 'wb') as f:
f.write(buf)
print('\nWell Done! ' + outfilename + ' generated!\n')
return outfilename
def get_postprocess():
model_config = {
'name': 'onnx_yolov8s',
'input' : ['output0'],
'shape': [1, 84, 8400],
'num_classes': 80,
}
outfilename = buildGraph(model_config)
return outfilename
def model_postprocess():
return get_postprocess()
Usage
- You can quickly construct the desired model structure using the sgs_chalk API. For other APIs, see sgs_chalk Module API.
- After constructing the model, you need to declare
model_postprocess()to call it, which can return the model's buffer or the path of the saved model. - The post-processing model should only save in Debug mode. During the conversion, it will be merged into a single model in the floating-point model stage.
1.3.3 YOLOv8s Post-Processing Model Conversion¶
Initialize SGS_IPU_Toolchain:
cd SGS_IPU_Toolchain
source cfg_env.sh
Navigate to the onnx_yolov8s directory:
cd Quick_Start_Demo/onnx_yolov8s
Run the following command for conversion:
python3 SGS_IPU_Toolchain/Scripts/ConvertTool/SGS_converter.py onnx \
-i coco2017_calibration_set32 \
--model_file onnx_yolov8s.onnx \
--input_shape 1,3,640,640 \
--input_config input_config.ini \
-n onnx_yolov8s_preprocess.py \
--output_file onnx_yolov8s_CHIP.img \
--export_models \
--postprocess onnx_yolov8s_postprocess.py \
--soc_version CHIP
Usage
- The only difference from the conversion command without post-processing is the addition of the
--postprocessparameter.
Adding the --postprocess parameter will generate an input_config.ini starting with autogen_, where the [OUTPUT_CONFIG] parameter outputs is modified to reflect the post-processing model's outputs, but all dequantizations are set to TRUE.
- If you need to customize other output formats, you can independently configure a new
input_config.iniand specify it using the--postprocess_input_configparameter.
1.3.4 YOLOv8s Post-Processing Model Inference¶
Quick_Start_Demo/onnx_yolov8s/yolov8_simulator.py provides inference methods for YOLOv8s both with and without post-processing.
Example of a command to run:
python3 yolov8_simulator.py \
--image 000000562557.jpg \
--model /path/to/float.sim / fixed.sim / offline.img \
-n onnx_yolov8s_preprocess.py \
--draw_result output \
--soc_version CHIP
Using Score_Filter, the boxes that meet confidence requirements are filtered, and the remaining ones are passed for IoU calculation in NMS.
For specific details, refer to the processing flow of the postprocess_lite function in Quick_Start_Demo/onnx_yolov8s/yolov8_simulator.py:
def postprocess_lite(model_outputs, **kwargs):
num_detect = int(model_outputs[4][0])
predictions = []
for i in range(num_detect):
index = int(model_outputs[3][0, i])
prediction = np.concatenate(
[
model_outputs[0][:, index, :],
model_outputs[2][:, index: index + 1],
model_outputs[1][:, index, :]
],
axis=-1
) # box(x1, y1, x2, y2) + score + cls
predictions.append(prediction)
if num_detect > 0:
predictions = np.concatenate(predictions, axis=0)
boxes = torch.from_numpy(predictions[:, :4])
score = torch.from_numpy(predictions[:, 4: 5]).squeeze(1)
kept = torchvision.ops.nms(boxes, score, kwargs.get('iou_thres', 0.7))
predictions = predictions[kept.numpy().tolist()]
else:
predictions = np.array([])
return predictions
1.4 sgs_chalk模块API¶
- Abs:
Computes the absolute value of a tensor.
Given a tensor of integer or floating-point values, this operation returns a tensor of the same type, where each element contains the absolute value of the corresponding element in the input.
Args:
x: A `Tensor`
Returns:
A `Tensor` of same shape and type as `x`.
case0
from calibrator_custom import sgs_chalk
import numpy as np
in0 = sgs_chalk.Input((28,512),name='input0')
out0 = sgs_chalk.Abs(in0,name='output')
model = sgs_chalk.Model([in0],[out0])
model.save('test.sim',input_config='./input_config.ini',convert_fixed=True)
- Add:
Returns x + y element-wise.
Args:
x: A `Tensor`. Must be Variable Tensor.
y: A `Tensor` or `numpy.ndarray`. Must have the same type as `x`, can be Variable or Const Tensor.
Support inner most dimension broadcasting.
name: A name for the output tensor (optional).
Returns:
A Variable `Tensor`. Has the same shape as `x`.
Examples:
case0
from calibrator_custom import sgs_chalk
import numpy as np
in0 = sgs_chalk.Input((28,512),name='input0')
in1 = sgs_chalk.Input((28,512),name='input1')
out0 = sgs_chalk.Add(in0,in1,name='output')
model = sgs_chalk.Model([in0,in1],out0)
model.save('test.sim')
case1
from calibrator_custom import sgs_chalk
import numpy as np
in0 = sgs_chalk.Input((28,512),name='input0')
out0 = sgs_chalk.Add(in0,5.0,name='output')
model = sgs_chalk.Model([in0],out0)
model.save('test.sim')
- Alpha_Blending:
output = [alpha * input0 + (1 - alpha) * input1] ==> output = [alpha * (input0 - input1) + input1]
Args:
x1: A `Tensor`
x2: A `Tensor`
alpha: A `Tensor`
name: A name for the model output tensor (optional).
Returns:
A `Tensor`
Examples:
case0
from calibrator_custom import sgs_chalk
import numpy as np
input1 = sgs_chalk.Input((1,1,36,2048), name='input0')
input2 = sgs_chalk.Input((1,1,36,2048), name='input1')
alpha = sgs_chalk.Input((1,1,36,2048), name='alpha')
out = sgs_chalk.Alpha_Blending(input1,input2,alpha, name='output')
model = sgs_chalk.Model([input1,input2,alpha], out)
model.save('test.sim', input_config='./input_config.ini', convert_fixed=True)
- ArgMin:
Returns the indices of the minimum values along an axis.
Args:
x: A `Tensor`. Must be Variable Tensor.
axis: int
keep_dim: bool
name: A name for the output tensor (optional).
Returns:
A Variable `Tensor`. It has the same shape as `x.shape`
with the dimension along `axis` removed.
Examples:
case0
from calibrator_custom import sgs_chalk
import numpy as np
in0 = sgs_chalk.Input((1, 80, 512),name='input0')
out0 = sgs_chalk.ArgMin(in0, 1, name='output')
model.save('test.sim')
- Argmax:
Returns the indices of the maximum values along an axis.
Args:
x: A `Tensor`. Must be Variable Tensor.
axis: int
keep_dim: bool
name: A name for the output tensor (optional).
Returns:
A Variable `Tensor`. It has the same shape as `x.shape`
with the dimension along `axis` removed.
Examples:
case0
from calibrator_custom import sgs_chalk
import numpy as np
in0 = sgs_chalk.Input((1, 80, 512),name='input0')
out0 = sgs_chalk.Argmax(in0, 1, name='output')
model.save('test.sim')
- Atan:
Args:
input: x `Tensor`. Must be Variable Tensor.
name: A name for the model output tensor (optional).
Returns:
A Variable `Tensor`. Has the same shape as input.
Examples:
case0
from calibrator_custom import sgs_chalk
import numpy as np
input = sgs_chalk.Input((1,224,224,3),name='input')
out = sgs_chalk.Atan(input,name='output')
model = sgs_chalk.Model([input,], out)
model.save('test.sim', input_config='./input_config.ini', convert_fixed=True)
- Atan2:
Element-wise arctangent of input0 and input1 with consideration of the quadrant.
Returns a new tensor with the signed angles in radians between (-pi, pi)
Args:
input:0 A `Tensor`. Must be Variable Tensor.
input1: A `Tensor`. Must be Variable Tensor.
name: A name for the model Output tensor (optional).
Returns:
A Variable `Tensor`. Has the same shape as input.
Examples:
case0
from calibrator_custom import sgs_chalk
input0 = sgs_chalk.Input((1, 22535), name='input0')
input1 = sgs_chalk.Input((1, 22535), name='input1')
out = sgs_chalk.Atan2(input0, input1, name='output')
model = sgs_chalk.Model([input0, input1], out)
model.save('atan2.sim', input_config='./input_config.ini', convert_fixed=True)
- AveragePool2d:
Performs the average pooling on the input.
Each entry in output is the mean of the corresponding size ksize
window in value.
Args:
x: A 4-D `Tensor` of shape `[batch, height, width, channels]`
ksize: A list of `ints` that has length `2`. The size of
the window for each dimension of the input tensor.
strides: An int or list of `ints` that has length `2`. The
stride of the sliding window for each dimension of the input tensor.
padding: a tuple (paddingTop, paddingBottom, paddingLeft, paddingRight).
padding_type: str, only support [SAME, VALID, CAFFE, ONNXINSIDE, ONNXOUTSIDE], default is CAFFE.
SAME or VALID padding_type will not use padding value.
name: Optional name for the operation.
Returns:
The average pooled output tensor.
Examples:
case0
from calibrator_custom import sgs_chalk
import numpy as np
in0 = sgs_chalk.Input((1,28,28,4),name='input0')
out0 = sgs_chalk.AveragePool2d(in0,[2,2],name='output')
model = sgs_chalk.Model([in0],out0)
model.save('test.sim')
case1
from calibrator_custom import sgs_chalk
import numpy as np
in0 = sgs_chalk.Input((1,112,112,3),name='input0')
out0 = sgs_chalk.AveragePool2d(in0,[2,2],name='output')
model = sgs_chalk.Model([in0],out0)
model.save('test.sim',input_config='./input_config.ini',convert_fixed=True)
- AveragePool3d:
Performs the average pooling on the input.
Each entry in output is the mean of the corresponding size ksize
window in value.
Args:
x: A 5D `Tensor` of shape `[batch, height, width, channels]`
ksize: A list of `ints` that has length `3`. The size of
the window for each dimension of the input tensor.
strides: An int or list of `ints` that has length `3`. The
stride of the sliding window for each dimension of the input tensor.
padding: a tuple (paddingI,paddingT,paddingL,paddingO,paddingB,paddingR).
name: Optional name for the operation.
Returns:
The average pooled output tensor.
Examples:
case0
from calibrator_custom import sgs_chalk
import numpy as np
in0 = sgs_chalk.Input((1,3,28,28,4),name='input0')
out0 = sgs_chalk.AveragePool3d(in0, (2,2,2), name='output')
model = sgs_chalk.Model(in0, out0)
model.save('test.sim')
- BatchMatMul:
Multiplies matrix a by matrix b, producing a * b.
The inputs must be tensors of rank >= 2 where the inner 2 dimensions specify valid matrix multiplication arguments, and any further outer dimensions match.
Args:
x: input variable tensor and rank > 1.
y: input tensor with same type and rank as x,can be variable or const tensor.
Examples:
case0
from calibrator_custom import sgs_chalk
import numpy as np
in0 = sgs_chalk.Input((1,28,28,4),name='input0')
in1 = sgs_chalk.Input((1,28,28,4),name='input1')
out0 = sgs_chalk.BatchMatMul(in0,in1,name='output')
model = sgs_chalk.Model([in0,in1],out0)
model.save('test.sim')
case1
from calibrator_custom import sgs_chalk
import numpy as np
input1 = np.ones((1,28,28,4), dtype=np.float32)
in0 = sgs_chalk.Input((1,28,512,4),name='input0')
out0 = sgs_chalk.BatchMatMul(in0,input1,name='output')
model = sgs_chalk.Model([in0],out0)
model.save('test.sim')
- BatchToSpaceND:
BatchToSpace for 4-D tensors of type T.
This operation reshapes the "batch" dimension 0 into M + 1 dimensions of
shape block_shape + [batch], interleaves these blocks back into the grid
defined by the spatial dimensions [1, ..., M], to obtain a result with the
same rank as the input. The spatial dimensions of this intermediate result
are then optionally cropped according to crops to produce the output. This
is the reverse of SpaceToBatch (see tf.space_to_batch).
Args:
x: A `Tensor`
block_size: Must be `Tensor` or `ndarray` or `list`
crops: A 2-D `Tensor` with shape `[2,2]`. Must be one of the
following types: `int32`, `int64`. All values must be >= 0.
`crops[i] = [crop_start, crop_end]` specifies the amount to crop from
input dimension `i + 1`, which corresponds to spatial dimension `i`.
Returns:
A `Tensor` of same type as `x`.
Examples:
case0
from calibrator_custom import sgs_chalk
import numpy as np
in0 = sgs_chalk.Input((4,28,28,512),name='input0')
out0 = sgs_chalk.BatchToSpaceND(in0,2,[[2,2],[2,2]],name='output')
model = sgs_chalk.Model([in0],[out0])
model.save('test.sim',input_config='./input_config.ini',convert_fixed=True)
- BoxDecoder:
postprocess BoxDecoder
Args:
unpacked_box: a list of tensors which are unpacked
Return:
a list of tensors decoded
Examples:
case0
from calibrator_custom import sgs_chalk
import numpy as np
box_num = 9
side_x = 19
side_y = 19
ppw = anchor.ones(3249)
px = anchor.index_div_linear(1,1,0,box_num ,side_x,side_y)
pph = anchor.ones(3249)
py = anchor.index_div_linear(1,1,0,side_x*box_num,side_y,1)
pw = anchor.ones(3249)
ph = anchor.ones(3249)
sx = anchor.ns(3249,1.0/19)
sy = anchor.ns(3249,1.0/19)
biases= [[9.5,9.5],[9.5,9.5],[9.5,9.5],[9.5,9.5],[9.5,9.5],[9.5,9.5],[9.5,9.5],[9.5,9.5],[9.5,9.5]]
sw = [x[0]/(2*19) for x in biases ]*(19*19)
sh = [x[1]/(2*19) for x in biases ]*(19*19)
config = {"shape" : [1,3249],
"tx_func" : (tflite.BuiltinOperator.BuiltinOperator().LOGISTIC,None),#None or 'x_scale'
"ty_func" : (tflite.BuiltinOperator.BuiltinOperator().LOGISTIC,None),#None or 'y_scale'
"tw_func" : (tflite.BuiltinOperator.BuiltinOperator().RESHAPE,None),#None or 'w_scale'
"th_func" : (tflite.BuiltinOperator.BuiltinOperator().RESHAPE,None),#None or 'h_scale'
"x_scale" : 0.1,
"y_scale" : 0.1,
"w_scale" : 1,
"h_scale" : 1,
"anchor_selector" : "constant",
"pw" : pw,
"ph" : ph,
"pw_func" : (None,None),
"ph_func" : (None,None),
"ppw" : ppw,
"px" : px,
"pph" : pph,
"py" : py,
"sx" : sx,
"sy" : sy,
"sw" : sw,
"sh" : sh
}
in0 = sgs_chalk.Input(model_config["input_shape"][0], name = model_config["input"][0])
unpack_out_tensors1 = []
for i in range(7):
unpack_out_tensors1.append("SGS_unpack1_"+str(i))
output_list = sgs_chalk.PostProcess_Unpack(in0,name=unpack_out_tensors1)
bosdecoder_output_list = sgs_chalk.BoxDecoder(config,output_list)
model = sgs_chalk.Model([in0],bosdecoder_output_list)
model.save('test.sim',input_config='./input_config.ini',convert_fixed=True)
- BoxDecoder2:
postprocess BoxDecoder2
Args:
unpacked_box: a list of tensors which are unpacked
Return:
:return:a list of tensors decoded
Examples:
case0
from calibrator_custom import sgs_chalk
import numpy as np
box_num = 9
side_x = 19
side_y = 19
ppw = anchor.ones(3249)
px = anchor.index_div_linear(1,1,0,box_num ,side_x,side_y)
pph = anchor.ones(3249)
py = anchor.index_div_linear(1,1,0,side_x*box_num,side_y,1)
pw = anchor.ones(3249)
ph = anchor.ones(3249)
sx = anchor.ns(3249,1.0/19)
sy = anchor.ns(3249,1.0/19)
biases= [[9.5,9.5],[9.5,9.5],[9.5,9.5],[9.5,9.5],[9.5,9.5],[9.5,9.5],[9.5,9.5],[9.5,9.5],[9.5,9.5]]
sw = [x[0]/(2*19) for x in biases ]*(19*19)
sh = [x[1]/(2*19) for x in biases ]*(19*19)
config = {"shape" : [1,3249],
"tx_func" : (tflite.BuiltinOperator.BuiltinOperator().LOGISTIC,None),#None or 'x_scale'
"ty_func" : (tflite.BuiltinOperator.BuiltinOperator().LOGISTIC,None),#None or 'y_scale'
"tw_func" : (tflite.BuiltinOperator.BuiltinOperator().RESHAPE,None),#None or 'w_scale'
"th_func" : (tflite.BuiltinOperator.BuiltinOperator().RESHAPE,None),#None or 'h_scale'
"x_scale" : 0.1,
"y_scale" : 0.1,
"w_scale" : 1,
"h_scale" : 1,
"anchor_selector" : "constant",
"pw" : pw,
"ph" : ph,
"pw_func" : (None,None),
"ph_func" : (None,None),
"ppw" : ppw,
"px" : px,
"pph" : pph,
"py" : py,
"sx" : sx,
"sy" : sy,
"sw" : sw,
"sh" : sh
}
in0 = sgs_chalk.Input(model_config["input_shape"][0], name = model_config["input"][0])
unpack_out_tensors1 = []
for i in range(7):
unpack_out_tensors1.append("SGS_unpack1_"+str(i))
output_list = sgs_chalk.PostProcess_Unpack(in0,name=unpack_out_tensors1)
bosdecoder_output_list = sgs_chalk.BoxDecoder(config,output_list)
model = sgs_chalk.Model([in0],bosdecoder_output_list)
#model.save('test.sim')
model.save('test.sim',input_config='./input_config.ini',convert_fixed=True)
- Cast:
Casts a tensor to a new type.
Args:
x: A `Tensor`. Must be Variable Tensor.
dtype: The destination type.
name: A name for the output tensor (optional).
Returns:
A Variable `Tensor` with same shape as `x` and same type as `dtype`.
Examples:
case0
from calibrator_custom import sgs_chalk
in0 = sgs_chalk.Input((28,512,1), dtype='float32', name='input')
out = sgs_chalk.Cast(in0, 'int32', name='output')
model = sgs_chalk.Model(in0, out)
model.save('test.sim')
- Ceil:
Ceil the values of a tensor to the nearest integer, element-wise.
Args:
x: A `Tensor`
Returns:
A `Tensor` of same shape and type as `x`.
Examples:
case0
from calibrator_custom import sgs_chalk
import numpy as np
in0 = sgs_chalk.Input((28,512),name='input0')
out0 = sgs_chalk.Ceil(in0,name='output')
model = sgs_chalk.Model([in0],[out0])
model.save('test.sim',input_config='./input_config.ini',convert_fixed=True)
- Clip:
Clips tensor values to a specified min and max.
Given a tensor x, this operation returns a tensor of the same type and
shape as x with its values clipped to min_value and max_value.
Any values less than min_value are set to min_value. Any values
greater than max_value are set to max_value.
Args:
x: A `Tensor`. Must be Variable Tensor.
min_value: A value.
max_value: A value.
name: A name for the output tensor (optional).
Returns:
A Variable `Tensor`. has the same shape as x
Examples:
case0
from calibrator_custom import sgs_chalk
import numpy as np
input = sgs_chalk.Input((1,36,2048), name='input')
output = sgs_chalk.Clip(input,0,1, name='output')
model = sgs_chalk.Model([input,], output)
model.save('test.sim', input_config='./input_config.ini', convert_fixed=True)
- Concatenation:
Concatenates the list of tensors values along dimension axis. If
values[i].shape = [D0, D1, ... Daxis(i), ...Dn], the concatenated
result has shape [D0, D1, ... Raxis, ...Dn] where Raxis = sum(Daxis(i))
That is, the data from the input tensors is joined along the axis
dimension.
The number of dimensions of the input tensors must match, and all dimensions
except axis must be equal.
Args:
values: A list of `Tensor` objects or a single `Tensor`.
axis: 0-D `int32` `Tensor`. Dimension along which to concatenate. Must be
in the range `[-rank(values), rank(values))`. As in Python, indexing for
axis is 0-based. Positive axis in the rage of `[0, rank(values))` refers
to `axis`-th dimension. And negative axis refers to `axis +
rank(values)`-th dimension.
name: A name for the output tensor (optional).
Returns:
A Variable `Tensor`.
Examples:
case0
from calibrator_custom import sgs_chalk
import numpy as np
in0 = sgs_chalk.Input((28,512,1),name='input0')
in1 = sgs_chalk.Input((28,512,2),name='input1')
in2 = sgs_chalk.Input((28,512,3),name='input2')
x = [in0, in1, in2]
out0 = sgs_chalk.Concatenation(x,axis=2,name='output')
model = sgs_chalk.Model(x,out0)
model.save('test.sim')
case1
from calibrator_custom import sgs_chalk
import numpy as np
in0 = sgs_chalk.Input((28,1,512),name='input0')
in1 = sgs_chalk.Input((28,2,512),name='input1')
in2 = sgs_chalk.Input((28,3,512),name='input2')
x = [in0, in1, in2]
out0 = sgs_chalk.Concatenation(x,axis=1,name='output')
model = sgs_chalk.Model(x,out0)
model.save('test.sim')
- CondGreat:
x0[i] > x1 ? x3:x2[i]
Args:
x0: `Tensor`. Must be Variable Tensor.
x1: A value.
x2: `Tensor`. Must be Variable Tensor, has same shape as x0.
x3: A value
name: A name for the model output tensor (optional).
Returns:
A Variable `Tensor`. Has the same shape as input x0.
Examples:
case0
from calibrator_custom import sgs_chalk
import numpy as np
from numpy import random as nr
input0 = sgs_chalk.Input((1,224,224,3),name='input0')
input1 = sgs_chalk.Input((1,224,224,3),name='input1')
out = sgs_chalk.CondGreat(input0,2.0,input1,1.0,name='output')
model = sgs_chalk.Model([input0,input1], out)
model.save('test.sim', input_config='./input_config.ini', convert_fixed=True,inputs='RAWDATA')
- CondLess:
x0[i] < x1 ? x3:x2[i]
Args:
x0: `Tensor`. Must be Variable Tensor.
x1: A value.
x2: `Tensor`. Must be Variable Tensor, has same shape as x0.
x3: A value
name: A name for the model output tensor (optional).
Returns:
A Variable `Tensor`. Has the same shape as input x0.
Examples:
case0
from calibrator_custom import sgs_chalk
import numpy as np
from numpy import random as nr
input0 = sgs_chalk.Input((1,224,224,3),name='input0')
input1 = sgs_chalk.Input((1,224,224,3),name='input1')
out = sgs_chalk.CondLess(input0,2.0,input1,1.0,name='output')
model = sgs_chalk.Model([input0,input1], out)
model.save('test.sim', input_config='./input_config.ini', convert_fixed=True,inputs='RAWDATA')
- Conv2d:
Conv2d
Args:
x : input tensor of shape(1, iH, iW,in_channels)
weight: filters of shape(out_channels, kH, kW, in_channels)
bias: optional bias tensor of shape(out_channels).Default:None
stride: the stride of the convolving kernel. Can be a single number or a tuple(sH,sW).Default: 1
padding: a tuple (paddingTop, paddingBottom, paddingLeft, paddingRight) or a str `SAME`/ `VALID`.
dilation: the spacing between kernel elements. Can be a single number or a tuple(dH,dW).Default: 1
Activation: only support NONE/RELU/RELU_N1_TO_1/RELU6
Examples:
case0
from calibrator_custom import sgs_chalk
import numpy as np
in0 = sgs_chalk.Input((1,28,28,4),name='input0')
in1 = sgs_chalk.Input((8,3,3,4),name='input1')
out0 = sgs_chalk.Conv2d(in0,in1,name='output')
model = sgs_chalk.Model([in0,in1],out0)
model.save('test.sim')
case1
from calibrator_custom import sgs_chalk
import numpy as np
input1 = np.zeros((8,3,3,4), dtype=np.float32)
in0 = sgs_chalk.Input((1,28,28,4),name='input0')
out0 = sgs_chalk.Conv2d(in0,input1, Activation = 'RELU',name='output')
model = sgs_chalk.Model([in0],out0)
model.save('test.sim')
- Conv3d:
Args:
x : input tensor of shape(n, iD, iH, iW,in_channels)
weight: filters of shape(kD, kH, kW, in_channels, out_channels)
bias: optional bias tensor of shape(out_channels).Default:None
stride: the stride of the convolving kernel. Can be a single number or a tuple(sD,sH,sW).Default: 1
padding: a tuple (paddingI,paddingT,paddingL,paddingO,paddingB,paddingR).
dilation: the spacing between kernel elements. Can be a single number or a tuple(dD,dH,dW).Default: 1
Activation: only support NONE/RELU/RELU_N1_TO_1/RELU6
Returns:
The conv3d output tensor(n, oD, oH, oW, out_channels)
Examples:
case0
from calibrator_custom import sgs_chalk
import numpy as np
input1 = np.zeros((3,3,3,64,64), dtype=np.float32)
in0 = sgs_chalk.Input((1,16,56,56,64),name='input0')
out0 = sgs_chalk.Add(in0,0.4)
out1 = sgs_chalk.Conv3d(out0,input1,name='output')
model = sgs_chalk.Model([in0],out0)
model.save('test.sim')
- Conv3dImageConcat:
Args:
x : input tensor of shape(n, iD, iH, iW,in_channels)
weight: filters of shape(kD, kH, kW, in_channels, out_channels)
bias: optional bias tensor of shape(out_channels).Default:None
stride: the stride of the convolving kernel. Can be a single number or a tuple(sD,sH,sW).Default: 1
padding: a tuple (paddingI,paddingT,paddingL,paddingO,paddingB,paddingR).
dilation: the spacing between kernel elements. Can be a single number or a tuple(dD,dH,dW).Default: 1
Activation: only support NONE/RELU/RELU_N1_TO_1/RELU6
Returns:
The conv3d output tensor(n, oD, oH, oW, out_channels)
Examples:
case0
from calibrator_custom import sgs_chalk
import numpy as np
input1 = np.zeros((3,3,3,64,64), dtype=np.float32)
in0 = sgs_chalk.Input((1,16,56,56,64),name='input0')
out0 = sgs_chalk.Add(in0,0.4)
out1 = sgs_chalk.Conv3d(out0,input1,name='output')
model = sgs_chalk.Model([in0],out0)
model.save('test.sim')
- Cos:
Returns Cos(x) element-wise.
Args:
x: A `Tensor`. Must be Variable Tensor.
Returns:
```text
A Variable `Tensor`. Has the same shape as `x`.
Examples:
case0
from calibrator_custom import sgs_chalk
import numpy as np
in0 = sgs_chalk.Input((28,512),name='input0')
out0 = sgs_chalk.Sin(in0,name='output')
model = sgs_chalk.Model([in0],out0)
model.save('test.sim')
- Cumsum:
Cumsum
Args:
input: A `Tensor` or 'Array'. Must be Variable Tensor if it's a Tensor.
asix: A 'Tensor' or 'Array'. Must be Const Tensor if it's a Tensor.
exclusive: Let first sum as 0.
reverse: Reverse the output.
name: A name for the model output tensor (optional).
Returns:
A Variable `Tensor`. Has the same shape as input.
Examples:
case0
from calibrator_custom import sgs_chalk
import numpy as np
input = sgs_chalk.Input((14,3,41,2,1,2,3,5), name='input')
square_out = sgs_chalk.Square(input, name='softplus_out')
model = sgs_chalk.Model([input,], square_out)
model.save('test.sim', input_config='./input_config.ini', convert_fixed=True)
- CustomNotEqual:
FLT_EPSILON = (1.192092896e-07F) if (fabs(x0 - value) < FLT_EPSILON) Output = x0 else Output = x1
Args:
x0: `Tensor`. Must be Variable Tensor.
x1: `Tensor`. Must be Variable Tensor, has same shape as x0.
name: A name for the model output tensor (optional).
Returns:
A Variable `Tensor`. Has the same shape as input x0.
Examples:
case0
from calibrator_custom import sgs_chalk
import numpy as np
from numpy import random as nr
input0 = sgs_chalk.Input((1,224,224,3),name='input0')
input1 = sgs_chalk.Input((1,224,224,3),name='input1')
out = sgs_chalk.CustomNotEqual(input0,input1,1.0,name='output')
model = sgs_chalk.Model([input0,input1], out)
model.save('test.sim', input_config='./input_config.ini', convert_fixed=True,inputs='RAWDATA')
- CustomPow:
Args:
input: x `Tensor`. Must be Variable Tensor.
input: y `Tensor`. Must be Constant Scaler.
name: A name for the model output tensor (optional).
Returns:
A Variable `Tensor`. Has the same shape as input.
Examples:
case0
from calibrator_custom import sgs_chalk
import numpy as np
input = sgs_chalk.Input((14,3,41,2,1,2,3,5), name='input')
input1 = sgs_chalk.Tensor(0.3333333333333333, name='input1')
customPow_out = sgs_chalk.CustomPow(input,input1, name='customPow_out')
model = sgs_chalk.Model([input,], customPow_out)
model.save('test.sim', input_config='./input_config.ini', convert_fixed=True)
- CustomizedMaxpool2d:
Performs the max pooling on the input.
Each entry in output is the mean of the corresponding size ksize
window in value and index.
Args:
x: A 4-D `Tensor` of shape `[batch, height, width, channels]`
ksize: A list of `ints` that has length `1`, `2` or `4`. The size of
the window for each dimension of the input tensor.
strides: An int or list of `ints` that has length `1`, `2` or `4`. The
stride of the sliding window for each dimension of the input tensor.
padding: a tuple (paddingTop, paddingBottom, paddingLeft, paddingRight).
name: Optional name for the operation.
Returns:
The max pooled output tensor
index tensor
Examples:
case0
from calibrator_custom import sgs_chalk
import numpy as np
in0 = sgs_chalk.Input((1,28,28,4),name='input0')
output_list = sgs_chalk.CustomizedMaxpool2d(in0,[2,2],name=['output','index'])
model = sgs_chalk.Model([in0],output_list)
model.save('test.sim')
- DepthWiseConv2d:
DepthWiseConv2D
Args:
x : input tensor of shape(1, iH, iW,in_channels)
weight: filters of shape(1, kH, kW, out_channels) in_channels = out_channels
bias: optional bias tensor of shape(out_channels).Default:None
stride: the stride of the convolving kernel. Can be a single number or a tuple(sH,sW).Default: 1
padding: a tuple (paddingTop, paddingBottom, paddingLeft, paddingRight) or a str `SAME`/ `VALID`.
dilation: the spacing between kernel elements. Can be a single number or a tuple(dH,dW).Default: 1
Activation: only support NONE/RELU/RELU_N1_TO_1/RELU6
Examples:
case0
from calibrator_custom import sgs_chalk
import numpy as np
in0 = sgs_chalk.Input((1,28,28,4),name='input0')
in1 = sgs_chalk.Input((1,3,3,4),name='input1')
out0 = sgs_chalk.DepthWiseConv2D(in0,in1,name='output')
model = sgs_chalk.Model([in0,in1],out0)
model.save('test.sim')
case1
from calibrator_custom import sgs_chalk
import numpy as np
input1 = np.zeros((1,3,3,4), dtype=np.float32)
in0 = sgs_chalk.Input((1,28,28,4),name='input0')
out0 = sgs_chalk.DepthWiseConv2D(in0,input1,bias = None, Activation = 'RELU',name='output')
model = sgs_chalk.Model([in0],out0)
model.save('test.sim')
- Dilation:
Dilation a tensor.
Args:
tensor: A `Tensor`.
name: A name for the output tensor (optional).
Returns:
A `Tensor`. Has the same type as `tensor`.
Examples:
case0
from calibrator_custom import sgs_chalk
import numpy as np
in0 = sgs_chalk.Input((28,512),name='input0')
out0 = sgs_chalk.Dilation(in0,[2,1,0,0],[2,0],name='output')
model = sgs_chalk.Model([in0],out0)
model.save('test.sim')
- Div:
Returns x / y element-wise.
Args:
x: A `Tensor`. Must be Variable Tensor.
y: A `Tensor` or `numpy.ndarray`. Must have the same type as `x`, can be Variable or Const Tensor.
Support inner most dimension broadcasting.
name: A name for the output tensor (optional).
Returns:
A Variable `Tensor`. Has the same shape as `x`.
Examples:
case0
from calibrator_custom import sgs_chalk
import numpy as np
in0 = sgs_chalk.Input((28,512),name='input0')
in1 = sgs_chalk.Input((28,512),name='input1')
out0 = sgs_chalk.Div(in0,in1,name='output')
model = sgs_chalk.Model([in0,in1],out0)
model.save('test.sim')
case1
from calibrator_custom import sgs_chalk
import numpy as np
in0 = sgs_chalk.Input((28,512),name='input0')
out0 = sgs_chalk.Div(in0,5.0,name='output')
model = sgs_chalk.Model([in0],out0)
model.save('test.sim')
case2
from calibrator_custom import sgs_chalk
import numpy as np
input1 = np.ones((28,512), dtype=np.float32)
in0 = sgs_chalk.Input((28,512),name='input0')
out0 = sgs_chalk.Div(in0,input1,name='output')
model = sgs_chalk.Model([in0],out0)
model.save('test.sim',input_config='./input_config.ini',convert_fixed=True)
- Elu:
Args:
x: A `Tensor`. Must be Variable Tensor.
name: A name for the model Input tensor (optional).
Returns:
A Variable `Tensor`. Has the same shape as settings.
Examples:
case0
from calibrator_custom import sgs_chalk
import numpy as np
in0 = sgs_chalk.Input((28,512),name='input0')
out0 = sgs_chalk.Elu(in0,name='output')
model = sgs_chalk.Model([in0],out0)
model.save('test.sim',input_config='./input_config.ini',convert_fixed=True)
- Equal:
Returns the truth value of (x == y) element-wise.
Args:
x: A `Tensor`. Must be Variable Tensor.
y: A `Tensor` or `numpy.ndarray`. Must have the same type as `x`, can be Variable or Const Tensor.
Support inner most dimension broadcasting.
name: A name for the output tensor (optional).
Returns:
A Variable `Tensor`. Has the same shape as `x`.Tensor` of type `bool
Examples:
case0
from calibrator_custom import sgs_chalk
import numpy as np
in0 = sgs_chalk.Input((28,512),name='input0')
in1 = sgs_chalk.Input((28,512),name='input1')
out0 = sgs_chalk.Equal(in0,in1,name='output')
model = sgs_chalk.Model([in0,in1],out0)
model.save('test.sim')
case1
from calibrator_custom import sgs_chalk
import numpy as np
in0 = sgs_chalk.Input((28,512),name='input0')
out0 = sgs_chalk.Equal(in0,5.0,name='output')
model = sgs_chalk.Model([in0],out0)
model.save('test.sim')
case2
from calibrator_custom import sgs_chalk
import numpy as np
input1 = np.zeros((28,512), dtype=np.float32)
in0 = sgs_chalk.Input((28,512),name='input0')
out0 = sgs_chalk.Equal(in0,input1,name='output')
model = sgs_chalk.Model([in0],out0)
model.save('test.sim')
- Erf:
Computes the Gauss error function of x element-wise.
Args:
x: A `Tensor`. Must be Variable Tensor.
name: A name for the output tensor (optional).
Returns:
A Variable `Tensor`. has the same shape as x
Examples:
case0
from calibrator_custom import sgs_chalk
import numpy as np
input = sgs_chalk.Input((1,36,2048), name='input')
output = sgs_chalk.Erf(input,name='output')
model = sgs_chalk.Model([input,], output)
model.save('test.sim', input_config='./input_config.ini', convert_fixed=True)
- Exp:
Computes exponential of x element-wise. (y = e^x).
Args:
x: A `Tensor`. Must be Variable Tensor.
name: A name for the output tensor (optional).
Returns:
A Variable `Tensor`. Has the same shape as `x`.
Examples:
case0
from calibrator_custom import sgs_chalk
import numpy as np
in0 = sgs_chalk.Input((28,512),name='input0')
out0 = sgs_chalk.Exp(in0,name='output')
model = sgs_chalk.Model([in0],out0)
model.save('test.sim')
- Expand_dims:
Expand the shape of a tensor.
Insert a new axis that will appear at the axis position in the expanded tensor shape.
Args:
x: A `Tensor`..
axis: An int or a `Tensor`.
name: A name for the output tensor (optional).
Returns:
A `Tensor`. Output tensor. The number of dimensions is one greater than that of the input tensor.
Examples:
case0
from calibrator_custom import sgs_chalk
import numpy as np
in0 = sgs_chalk.Input((28,512,4), name='input0')
out0 = sgs_chalk.Expand_dims(in0, axis=0, name='output')
model = sgs_chalk.Model(in0, out0)
model.save('test.sim')
</details>
- Fill:
Creates a tensor filled with a scalar value.
Fill creates a tensor of shape `dims` and fills it with `value`.
Args:
```text
dims: A `Tensor`. Must be one of the following types: `int32`, `int64`. 1-D. Represents the shape of the output tensor.
value: A `Tensor`. 0-D (scalar). Value to fill the returned tensor.
name: A name for the output tensor (optional).
returns: A `Tensor`. Has the same type as `value`.
case0
from calibrator_custom import sgs_chalk
in0 = sgs_chalk.Input((28,4,4),name='input0')
out = sgs_chalk.Shape(in0)
out0 = sgs_chalk.Fill(out, 1.0)
model = sgs_chalk.Model(in0, out0)
model.save('test.sim')
x: A `Tensor`
A `Tensor` of same shape and type as `x`.
case0
from calibrator_custom import sgs_chalk
import numpy as np
in0 = sgs_chalk.Input((28,512),name='input0')
out0 = sgs_chalk.Floor(in0,name='output')
model = sgs_chalk.Model([in0],[out0])
model.save('test.sim',input_config='./input_config.ini',convert_fixed=True)
x : input tensor of shape 2 dims
weight: filters of shape 2 dims
bias: optional bias tensor of shape(out_channels). Default:None
Activation: only support NONE/RELU/RELU_N1_TO_1/RELU6
case0
from calibrator_custom import sgs_chalk
import numpy as np
input1 = np.zeros((1000,112), dtype=np.float32)
in0 = sgs_chalk.Input((3,112),name='input0')
out0 = sgs_chalk.Fullyconnected(in0,input1,name='output')
model = sgs_chalk.Model([in0],out0)
model.save('test.sim')
case1
from calibrator_custom import sgs_chalk
import numpy as np
input1 = np.zeros((1000,112), dtype=np.float32)
in0 = sgs_chalk.Input((3,112),name='input0')
out0 = sgs_chalk.Fullyconnected(in0,input1,bias = None, Activation = 'RELU',name='output')
model = sgs_chalk.Model([in0],out0)
model.save('test.sim')
x: A `Tensor`,shape is (L,1,N,input_size) N=batch size L=sequence length
h0:tensor of shape(1,1,1,hidden_size),containing the initial hidden state for each element in the input sequence.
hidden_size : The number of features in the hidden state h
W: A `Tensor`, shape is [1,3*hidden_size,input_size]
R: A `Tensor`, shape is [1,3*hidden_size,hidden_size]
B: A `Tensor`, shape is [1,6*hidden_size]
A `Tensor` list,usually concatenate op should be add after GRU
case0
from calibrator_custom import sgs_chalk
import numpy as np
W_1 = np.ones((1,6,2))
R_1 = np.ones((1,6,2))
B_1 = np.ones((1,12))
in0 = sgs_chalk.Input((2,1,1,2),name='input0')
input1 = np.zeros((1,1,1,2), dtype=np.float32)
out = sgs_chalk.GRU(in0,input1,hidden_size=2,W=W_1,R=R_1,B=B_1,name='gru_output')
model = sgs_chalk.Model([in0],out)
model.save('test.sim')
case1
W_1 = np.ones((1,6,2))
R_1 = np.ones((1,6,2))
B_1 = np.ones((1,12))
in0 = sgs_chalk.Input((2,1,1,2),name='input0')
input1 = np.zeros((1,1,1,2), dtype=np.float32)
out= sgs_chalk.GRU(in0,input1,hidden_size=2,W=W_1,R=R_1,B=B_1,name='gru_output')
out1= sgs_chalk.GRU(out,input1,hidden_size=2,W=W_1,R=R_1,B=B_1,name='gru_output2')
model = sgs_chalk.Model([in0],output_tensor_list_1[0])
model.save('test.sim',input_config='./input_config.ini', convert_fixed=True, inputs='RAWDATA')
case2
from calibrator_custom import sgs_chalk
import numpy as np
W_1 = np.ones((1,6,2))
R_1 = np.ones((1,6,2))
B_1 = np.ones((1,12))
in0 = sgs_chalk.Input((2,1,1,2),name='input0')
input1 = np.zeros((1,1,1,2), dtype=np.float32)
out = sgs_chalk.GRU(in0,input1,hidden_size=2,W=W_1,R=R_1,B=B_1,name='gru_output')
hn = sgs_chalk.Slice(out,[1,0,0,0],[1,1,1,2],name='gru_hn')
model = sgs_chalk.Model([in0],[out,hn])
model.save('test.sim',input_config='./input_config.ini', convert_fixed=True, inputs='RAWDATA')
x: A variable `Tensor`. The tensor from which to gather values.
indices: A `Tensor`. Must be in range `[0, params.shape[axis])`.
axis: A `Tensor`. The axis in `params` to gather `indices` from. Defaults to the first
dimension.
name: A name for the output tensor (optional).
A `Tensor`. Has the same type as `value`.
case0
from calibrator_custom import sgs_chalk
import numpy as np
in0 = sgs_chalk.Input((28,512,4),name='input0')
out0 = sgs_chalk.Gather(in0,[0,2],name='output')
model = sgs_chalk.Model([in0],out0)
model.save('test.sim')
case1
from calibrator_custom import sgs_chalk
import numpy as np
in0 = sgs_chalk.Input((28,512,4),name='input0')
out0 = sgs_chalk.Gather(in0,[[0,1],[0,1]],axis=1,name='output')
model = sgs_chalk.Model([in0],out0)
model.save('test.sim')
x: A variable `Tensor`. The tensor from which to GatherElements values.
indices: A `Tensor`. Must be in range `[0, params.shape[axis])`.
axis: A `Tensor`. The axis in `params` to GatherElements `indices` from. Defaults to the first
dimension.
name: A name for the output tensor (optional).
A `Tensor`. Has the same type as `value`.
case1
from calibrator_custom import sgs_chalk
import numpy as np
in0 = sgs_chalk.Input((28,512,4),name='input0')
out0 = sgs_chalk.GatherElements(in0,[[0,1],[0,1]],axis=1,name='output')
model = sgs_chalk.Model([in0],out0)
model.save('test.sim')
- GatherND:
Args:
input: A `Tensor`. Must be Variable Tensor whose rank r >= 1.
indices: A const Tensor or numpy.array whose rank q >= 1.
batch_dims: The number of batch dimensions. The gather of indexing starts from dimension of data[batch_dims:]
name: A name for the model output tensor (optional).
Returns:
A Variable `Tensor`. Tensor of rank q + r - indices_shape[-1] - 1.
Examples:
case0
from calibrator_custom import sgs_chalk
import numpy as np
input = sgs_chalk.Input((1,64,80,200), name='input')
indices = sgs_chalk.Input((1,64,80,1,1), name='indices')
gatherND_out = sgs_chalk.GatherND(input, indices, 3, name='gatherND_out')
model = sgs_chalk.Model([input,update], gatherND_out)
model.save('test.sim', input_config='./input_config.ini', convert_fixed=True)
- Gelu:
out = input*0.5*(1.0+erff(input/sqrtf(2.0)))
Args:
x1: A `Tensor`
name: A name for the model output tensor (optional).
Returns:
A `Tensor`
case0
from calibrator_custom import sgs_chalk
import numpy as np
input1 = sgs_chalk.Input((1,224,224,3), name='input0')
out = sgs_chalk.Gelu(input1,name='output')
model = sgs_chalk.Model([input1], out)
model.save('test.sim', input_config='./input_config.ini', convert_fixed=True)
- Greater:
greater(x, y, name=None) Returns the truth value of (x > y) element-wise.
Args:
x: A `Tensor`.
y: A `Tensor`. Must have the same type as `x`.
name: A name for the output tensor (optional).
Returns:
A `Tensor` of type `bool`.
Examples:
case0
from calibrator_custom import sgs_chalk
import numpy as np
in0 = sgs_chalk.Input((28,512),name='input0')
in1 = sgs_chalk.Input((28,512),name='input1')
out0 = sgs_chalk.Greater(in0,in1,name='output')
model = sgs_chalk.Model([in0,in1],out0)
model.save('test.sim')
case1
from calibrator_custom import sgs_chalk
import numpy as np
in0 = sgs_chalk.Input((28,512),name='input0')
out0 = sgs_chalk.Greater(in0,5.0,name='output')
model = sgs_chalk.Model([in0],out0)
model.save('test.sim')
case2
from calibrator_custom import sgs_chalk
import numpy as np
input1 = np.zeros((28,512), dtype=np.float32)
in0 = sgs_chalk.Input((28,512),name='input0')
out0 = sgs_chalk.Greater(in0,input1,name='output')
model = sgs_chalk.Model([in0],out0)
model.save('test.sim')
- GreaterEqual:
Returns the truth value of (x >= y) element-wise.
Args:
x: A `Tensor`. Must be Variable Tensor.
y: A `Tensor` or `numpy.ndarray`. Must have the same type as `x`, can be Variable or Const Tensor.
Support inner most dimension broadcasting.
name: A name for the output tensor (optional).
Returns:
A Variable `Tensor`. Has the same shape as `x`.Tensor` of type `bool
Examples:
case0
from calibrator_custom import sgs_chalk
import numpy as np
in0 = sgs_chalk.Input((28,512),name='input0')
in1 = sgs_chalk.Input((28,512),name='input1')
out0 = sgs_chalk.GreaterEqual(in0,in1,name='output')
model = sgs_chalk.Model([in0,in1],out0)
model.save('test.sim')
case1
from calibrator_custom import sgs_chalk
import numpy as np
in0 = sgs_chalk.Input((28,512),name='input0')
out0 = sgs_chalk.GreaterEqual(in0,5.0,name='output')
model = sgs_chalk.Model([in0],out0)
model.save('test.sim')
case2
from calibrator_custom import sgs_chalk
import numpy as np
input1 = np.zeros((28,512), dtype=np.float32)
in0 = sgs_chalk.Input((28,512),name='input0')
out0 = sgs_chalk.GreaterEqual(in0,input1,name='output')
model = sgs_chalk.Model([in0],out0)
model.save('test.sim')
- GroupConv2d:
GroupConv
Args:
x : input tensor of shape(1, iH, iW, in_channels)
weight: filters of shape(out_channels, kH, kW, in_channels)
bias: optional bias tensor of shape(out_channels).Default:None
stride: the stride of the convolving kernel. Can be a single number or a tuple(sH,sW).Default: 1
padding: a tuple (paddingTop, paddingBottom, paddingLeft, paddingRight) or a str `SAME`/ `VALID`.
dilation: the spacing between kernel elements. Can be a single number or a tuple(dH,dW).Default: 1
group: controls the connections between inputs and outputs. in_channels and out_channels must both be divisible by groups. Default: 1
Activation: only support NONE/RELU/RELU_N1_TO_1/RELU6
Examples:
case0
from calibrator_custom import sgs_chalk
import numpy as np
input1 = np.zeros((8,3,3,2), dtype=np.float32)
in0 = sgs_chalk.Input((1,28,28,4),name='input0')
out0 = sgs_chalk.GroupConv(in0,input1,group=2,name='output')
model = sgs_chalk.Model([in0],out0)
model.save('test.sim')
- HardSwish:
Args:
input: x `Tensor`. Must be Variable Tensor.
name: A name for the model output tensor (optional).
Returns:
A Variable `Tensor`. Has the same shape as input.
Examples:
case0
from calibrator_custom import sgs_chalk
import numpy as np
input = sgs_chalk.Input((1,224,224,3),name='input')
out = sgs_chalk.HardSwish(input,name='output')
model = sgs_chalk.Model([input,], out)
model.save('test.sim', input_config='./input_config.ini', convert_fixed=True)
- Input:
As an entry point into a graph.
Args:
shape: `Tuple`.
name: A name for the model Input tensor (optional).
Returns:
A Variable `Tensor`. Has the same shape as settings.
Examples:
case0
from calibrator_custom import sgs_chalk
import numpy as np
in0 = sgs_chalk.Input((28,512),name='input0')
case1
from calibrator_custom import sgs_chalk
import numpy as np
in0 = sgs_chalk.Input((28,512),datatype='complex64', name='input0')
- Instancenorm:
Instancenorm
Args:
x: A `Tensor`
axis: Dimension along which to normalize. A scalar or a vector of
integers.
epsilon: A lower bound value for the norm.
weight: One dim,The value is x.shape[-1]
bias: One dim,The value is x.shape[-1]
Returns:
A `Tensor`,has the same shape as x
Examples:
case0
from calibrator_custom import sgs_chalk
import numpy as np
from numpy import random as nr
import pdb
#in0 = sgs_chalk.Input((4,256,96),name='input0')
weight = nr.uniform(-1, 1, (96)).astype('float32')
bias = nr.uniform(-1, 1, (96)).astype('float32')
in0 = sgs_chalk.Input((4,256,96),name='input0')
# weight = np.ones((96), dtype=np.float32)
# bias = np.ones((96), dtype=np.float32)
out0 = sgs_chalk.Instancenorm(in0,axis=[1],weight=weight,bias=bias,name='output')
model = sgs_chalk.Model([in0],[out0])
#model.save('test.sim',input_config='./input_config.ini',convert_fixed=True)
model.save('test.sim',input_config='./input_config.ini', convert_fixed=True, inputs='RAWDATA')
- L2Norm:
Normalizes along dimension axis using an L2 norm.
For a 1-D tensor with axis = 0, computes
output = x / sqrt(max(sum(x**2), epsilon))
For x with more dimensions, independently normalizes each 1-D slice along
dimension axis.
Args:
x: A `Tensor`
axis: Dimension along which to normalize. A scalar or a vector of
integers.
Returns:
A `Tensor`
Examples:
case0
from calibrator_custom import sgs_chalk
import numpy as np
in0 = sgs_chalk.Input((1,224,224,3),name='input0')
out0 = sgs_chalk.L2Norm(in0,[1,2],name='output')
model = sgs_chalk.Model([in0],[out0])
model.save('test.sim',input_config='./input_config.ini',convert_fixed=True,inputs='RAWDATA')
- LSTM:
Applies a multi-layer long short-term memory (LSTM) RNN to an input sequence.
Args:
x: A `Tensor`,shape is (L,1,N,input_size) N=batch size L=sequence length
h0:tensor of shape(1,1,1,hidden_size),containing the initial hidden state for each element in the input sequence.
c0:tensor of shape(1,1,1,hidden_size),containing the initial cell state for each element in the input sequence.
hidden_size : The number of features in the hidden state h
cn_output: whether output cn ,default false.
W: A `Tensor`, shape is [1,4*hidden_size,input_size]
R: A `Tensor`, shape is [1,4*hidden_size,hidden_size]
B: A `Tensor`, shape is [1,8*hidden_size]
Returns:
A `Tensor` list,usually concatenate op should be add after LSTM
Examples:
case0
from calibrator_custom import sgs_chalk
import numpy as np
W_1 = np.ones((1,128,48))
R_1 = np.ones((1,128,32))
B_1 = np.ones((1,256))
W_2 = np.ones((1,64,32))
R_2 = np.ones((1,64,16))
B_2 = np.ones((1,128))
in0 = sgs_chalk.Input((2,1,1,48),name='input0')
input1 = np.zeros((1,1,1,32), dtype=np.float32)
input2 = np.zeros((1,1,1,32), dtype=np.float32)
input3 = np.zeros((1,1,1,16), dtype=np.float32)
input4 = np.zeros((1,1,1,16), dtype=np.float32)
output_tensor_list = sgs_chalk.LSTM(in0,input1,input2,hidden_size=32,W=W_1,R=R_1,B=B_1,name='lstm_output')
output_tensor_list_1 = sgs_chalk.LSTM(output_tensor_list[0],input3,input4,hidden_size=16,W=W_2,R=R_2,B=B_2,name='lstm1_output')
model = sgs_chalk.Model([in0],output_tensor_list_1[0])
model.save('test.sim',input_config='./input_config.ini', convert_fixed=True, inputs='RAWDATA')
case1
from calibrator_custom import sgs_chalk
import numpy as np
W_1 = np.ones((1,128,48))
R_1 = np.ones((1,128,32))
B_1 = np.ones((1,256))
in0 = sgs_chalk.Input((2,1,1,48),name='input0')
input1 = np.zeros((1,1,1,32), dtype=np.float32)
input2 = np.zeros((1,1,1,32), dtype=np.float32)
output_tensor_list= sgs_chalk.LSTM(in0,input1,input2,hidden_size=32,cn_output=True,W=W_1,R=R_1,B=B_1,name='lstm_output')
model = sgs_chalk.Model([in0],output_tensor_list)
model.save('test.sim',input_config='./input_config.ini', convert_fixed=True, inputs='RAWDATA')
- LSTM_caffe:
- Layernorm:
Layernorm
Args:
x: A `Tensor`
axis: Dimension along which to normalize. A scalar or a vector of
integers.
epsilon: A lower bound value for the norm.
weight: One dim,The value is multiplied by the shape of the corresponding dimension on the axis
bias: One dim,The value is multiplied by the shape of the corresponding dimension on the axis
Returns:
A `Tensor`,has the same shape as x
Examples:
case0
from calibrator_custom import sgs_chalk
import numpy as np
from numpy import random as nr
import pdb
#in0 = sgs_chalk.Input((4,256,96),name='input0')
weight = nr.uniform(-1, 1, (96)).astype('float32')
bias = nr.uniform(-1, 1, (96)).astype('float32')
in0 = sgs_chalk.Input((4,256,96),name='input0')
# weight = np.ones((96), dtype=np.float32)
# bias = np.ones((96), dtype=np.float32)
out0 = sgs_chalk.Layernorm(in0,axis=[2],weight=weight,bias=bias,name='output')
model = sgs_chalk.Model([in0],[out0])
model.save('test.sim',input_config='./input_config.ini',convert_fixed=True)
#model.save('test.sim',input_config='./input_config.ini', convert_fixed=True, inputs='RAWDATA')
- LeakyRelu:
Compute the Leaky ReLU activation function.
Args:
tensor: A `Tensor`.
alpha: Slope of the activation function at x < 0.
name: A name for the output tensor (optional).
Returns:
A `Tensor`. Has the same type as `tensor`.
Examples:
case0
from calibrator_custom import sgs_chalk
import numpy as np
in0 = sgs_chalk.Input((28,512),name='input0')
out0 = sgs_chalk.LeakyRelu(in0,name='output')
model = sgs_chalk.Model([in0],out0)
model.save('test.sim')
- Less:
greater(x, y, name=None) Returns the truth value of (x < y) element-wise.
Args:
x: A `Tensor`.
y: A `Tensor`. Must have the same type as `x`.
name: A name for the output tensor (optional).
Returns:
A `Tensor` of type `bool`.
Examples:
case0
from calibrator_custom import sgs_chalk
import numpy as np
in0 = sgs_chalk.Input((28,512),name='input0')
in1 = sgs_chalk.Input((28,512),name='input1')
out0 = sgs_chalk.Less(in0,in1,name='output')
model = sgs_chalk.Model([in0,in1],out0)
model.save('test.sim')
case1
from calibrator_custom import sgs_chalk
import numpy as np
in0 = sgs_chalk.Input((28,512),name='input0')
out0 = sgs_chalk.Less(in0,5.0,name='output')
model = sgs_chalk.Model([in0],out0)
model.save('test.sim')
case2
from calibrator_custom import sgs_chalk
import numpy as np
input1 = np.zeros((28,512), dtype=np.float32)
in0 = sgs_chalk.Input((28,512),name='input0')
out0 = sgs_chalk.Less(in0,input1,name='output')
model = sgs_chalk.Model([in0],out0)
model.save('test.sim')
- LessEqual:
greater(x, y, name=None) Returns the truth value of (x < y) element-wise.
Args:
x: A `Tensor`.
y: A `Tensor`. Must have the same type as `x`.
name: A name for the output tensor (optional).
Returns:
A `Tensor` of type `bool`.
Examples:
case0
from calibrator_custom import sgs_chalk
import numpy as np
in0 = sgs_chalk.Input((28,512),name='input0')
in1 = sgs_chalk.Input((28,512),name='input1')
out0 = sgs_chalk.LessEqual(in0,in1,name='output')
model = sgs_chalk.Model([in0,in1],out0)
model.save('test.sim')
- Log:
Args:
tensor: A `Tensor`.
name: A name for the output tensor (optional).
Returns:
A `Tensor`. Has the same type as `tensor`.
Examples:
case0
from calibrator_custom import sgs_chalk
import numpy as np
in0 = sgs_chalk.Input((28,512),name='input0')
out0 = sgs_chalk.Log(in0,name='output')
model = sgs_chalk.Model([in0],out0)
model.save('test.sim')
- Logcompress:
Args:
tensor: A `Tensor`.
name: A name for the output tensor (optional).
Returns:
A `Tensor`. Has the same type as `tensor`.
Examples:
case0
from calibrator_custom import sgs_chalk
import numpy as np
in0 = sgs_chalk.Input((1,64,288,4),name='input0')
out0 = sgs_chalk.Logcompress(in0,
p0=[0.08203375339508057, 0.5001068115234375],
p1=[0.13940855860710144, 0.8515274524688721],
p2=[0.16406750679016113, 0.5820490121841431],
p3=[1.0, 1.0],
decom_flag=0,name='output')
model = sgs_chalk.Model([in0],out0)
model.save('test.sim')
- LogicalAnd:
Returns the truth value of x AND y element-wise.
Args:
x: A `Tensor`. Must be Variable Tensor.
y: A `Tensor` or `numpy.ndarray`. Must have the same type as `x`, can be Variable or Const Tensor.
Support inner most dimension broadcasting.
name: A name for the output tensor (optional).sss
Returns:
A Variable `Tensor`. Has the same shape as `x`.Tensor` of type `bool
Examples:
case0
from calibrator_custom import sgs_chalk
import numpy as np
in0 = sgs_chalk.Input((28,512),name='input0')
in1 = sgs_chalk.Input((28,512),name='input1')
out0 = sgs_chalk.LogicalAnd(in0,in1,name='output')
model = sgs_chalk.Model([in0,in1],out0)
model.save('test.sim')
case1
from calibrator_custom import sgs_chalk
import numpy as np
in0 = sgs_chalk.Input((28,512),name='input0')
out0 = sgs_chalk.LogicalAnd(in0,1.0,name='output')
model = sgs_chalk.Model([in0],out0)
model.save('test.sim')
case2
from calibrator_custom import sgs_chalk
import numpy as np
input1 = np.zeros((28,512), dtype=np.float32)
in0 = sgs_chalk.Input((28,512),name='input0')
out0 = sgs_chalk.LogicalAnd(in0,input1,name='output')
model = sgs_chalk.Model([in0],out0)
model.save('test.sim')
- LogicalNot:
Returns the truth value of NOT x element-wise.
Args:
x: A `Tensor`. Must be Variable Tensor.
name: A name for the output tensor (optional).
Returns:
A Variable `Tensor`. Has the same shape as `x`.Tensor` of type `bool
Examples:
case0
from calibrator_custom import sgs_chalk
import numpy as np
in0 = sgs_chalk.Input((28,512),name='input0')
out0 = sgs_chalk.LogicalNot(in0,name='output')
model = sgs_chalk.Model(in0,out0)
model.save('test.sim')
- LogicalOr:
Returns the truth value of x OR y element-wise.
Args:
x: A `Tensor`. Must be Variable Tensor.
y: A `Tensor` or `numpy.ndarray`. Must have the same type as `x`, can be Variable or Const Tensor.
Support inner most dimension broadcasting.
name: A name for the output tensor (optional).sss
Returns:
A Variable `Tensor`. Has the same shape as `x`.Tensor` of type `bool
Examples:
case0
from calibrator_custom import sgs_chalk
import numpy as np
in0 = sgs_chalk.Input((28,512),name='input0')
in1 = sgs_chalk.Input((28,512),name='input1')
out0 = sgs_chalk.LogicalOr(in0,in1,name='output')
model = sgs_chalk.Model([in0,in1],out0)
model.save('test.sim')
case1
from calibrator_custom import sgs_chalk
import numpy as np
in0 = sgs_chalk.Input((28,512),name='input0')
out0 = sgs_chalk.LogicalOr(in0,1.0,name='output')
model = sgs_chalk.Model([in0],out0)
model.save('test.sim')
case2
from calibrator_custom import sgs_chalk
import numpy as np
input1 = np.zeros((28,512), dtype=np.float32)
in0 = sgs_chalk.Input((28,512),name='input0')
out0 = sgs_chalk.LogicalOr(in0,input1,name='output')
model = sgs_chalk.Model([in0],out0)
model.save('test.sim')
- Logistic:
output = 1 / (1 + exp(-x))
Args:
tensor: A `Tensor`.
name: A name for the output tensor (optional).
Returns:
A `Tensor`. Has the same type as `tensor`.
Examples:
case0
from calibrator_custom import sgs_chalk
import numpy as np
in0 = sgs_chalk.Input((28,512),name='input0')
out0 = sgs_chalk.Logistic(in0,name='output')
model = sgs_chalk.Model([in0],out0)
model.save('test.sim')
- MaxPool2d:
Performs the max pooling on the input.
Each entry in output is the max of the corresponding size ksize
window in value.
Args:
x: A 4-D `Tensor` of shape `[batch, height, width, channels]`
ksize: A list of `ints` that has length `2`. The size of
the window for each dimension of the input tensor.
strides: An int or list of `ints` that has length `2`. The
stride of the sliding window for each dimension of the input tensor.
padding: a tuple (paddingTop, paddingBottom, paddingLeft, paddingRight) or a str `SAME`/ `VALID`.
name: Optional name for the operation.
Returns:
The max pooled output tensor
Examples:
case0
from calibrator_custom import sgs_chalk
import numpy as np
in0 = sgs_chalk.Input((1,112,112,3),name='input0')
out0 = sgs_chalk.MaxPool2d(in0, (2,2), name='output')
model = sgs_chalk.Model([in0],out0)
model.save('test.sim',input_config='./input_config.ini',convert_fixed=True)
- MaxPool3d:
Performs the average pooling on the input.
Each entry in output is the mean of the corresponding size ksize
window in value.
Args:
x: A 5D `Tensor` of shape `[batch, height, width, channels]`
ksize: A list of `ints` that has length `3`. The size of
the window for each dimension of the input tensor.
strides: An int or list of `ints` that has length `3`. The
stride of the sliding window for each dimension of the input tensor.
padding: a tuple (paddingI,paddingT,paddingL,paddingO,paddingB,paddingR).
name: Optional name for the operation.
Returns:
The average pooled output tensor.
Examples:
case0
from calibrator_custom import sgs_chalk
import numpy as np
in0 = sgs_chalk.Input((1,3,28,28,4),name='input0')
out0 = sgs_chalk.MaxPool3d(in0,[2,2,2],name='output')
model = sgs_chalk.Model([in0],out0)
model.save('test.sim')
- Maximum:
Returns the max of x and y (i.e. x > y ? x : y) element-wise.
Args:
x: A `Tensor`. Must be Variable Tensor.
y: A `Tensor` or `numpy.ndarray`. Must have the same type as `x`, can be Variable or Const Tensor.
Support inner most dimension broadcasting.
name: A name for the output tensor (optional).
Returns:
A Variable `Tensor`. Has the same shape as `x`.Tensor` of type `bool
Examples:
case0
from calibrator_custom import sgs_chalk
import numpy as np
in0 = sgs_chalk.Input((28,512),name='input0')
in1 = sgs_chalk.Input((28,512),name='input1')
out0 = sgs_chalk.Maximum(in0,in1,name='output')
model = sgs_chalk.Model([in0,in1],out0)
model.save('test.sim')
case1
from calibrator_custom import sgs_chalk
import numpy as np
in0 = sgs_chalk.Input((28,512),name='input0')
out0 = sgs_chalk.Maximum(in0,1.0,name='output')
model = sgs_chalk.Model([in0],out0)
model.save('test.sim')
case2
from calibrator_custom import sgs_chalk
import numpy as np
input1 = np.zeros((28,512), dtype=np.float32)
in0 = sgs_chalk.Input((28,512),name='input0')
out0 = sgs_chalk.Maximum(in0,input1,name='output')
model = sgs_chalk.Model([in0],out0)
model.save('test.sim')
- Mean:
Computes the mean of elements across dimensions of a tensor.
Reduces input_tensor along the dimensions given in axis.
Args:
tensor: A `Tensor`.
axis: The dimensions to reduce.
keep_dim:whether keep dim or not
name: A name for the output tensor (optional).
Returns:
A `Tensor`. The reduced tensor.
Examples:
case0
from calibrator_custom import sgs_chalk
import numpy as np
in0 = sgs_chalk.Input((1,28,28,512),name='input0')
out0 = sgs_chalk.Mean(in0,[1,2],name='output')
model = sgs_chalk.Model([in0],out0)
model.save('test.sim')
- MeanVarianceNorm:
MeanVarianceNorm
Args:
x: A `Tensor`
axis: Dimension along which to normalize. A scalar or a vector of
integers.
epsilon: A lower bound value for the norm.
normalize_variance: Whether to do normalization
Returns:
A `Tensor`,has the same shape as x
Examples:
case0
from calibrator_custom import sgs_chalk
import numpy as np
from numpy import random as nr
import pdb
in0 = sgs_chalk.Input((1,3,4,4),name='input0')
out0 = sgs_chalk.MeanVarianceNorm(in0,axis=[2], normalize_variance=1,name='output')
model = sgs_chalk.Model([in0],[out0])
model.save('test.sim',input_config='./input_config.ini',convert_fixed=True)
#model.save('test.sim',input_config='./input_config.ini', convert_fixed=True, inputs='RAWDATA')
- Minimum:
Returns the min of x and y (i.e. x < y ? x : y) element-wise.
Args:
x: A `Tensor`. Must be Variable Tensor.
y: A `Tensor` or `numpy.ndarray`. Must have the same type as `x`, can be Variable or Const Tensor.
Support inner most dimension broadcasting.
name: A name for the output tensor (optional).
Returns:
A Variable `Tensor`. Has the same shape as `x`.Tensor` of type `bool
Examples:
case0
from calibrator_custom import sgs_chalk
import numpy as np
in0 = sgs_chalk.Input((28,512),name='input0')
in1 = sgs_chalk.Input((28,512),name='input1')
out0 = sgs_chalk.Minimum(in0,in1,name='output')
model = sgs_chalk.Model([in0,in1],out0)
model.save('test.sim')
case1
from calibrator_custom import sgs_chalk
import numpy as np
in0 = sgs_chalk.Input((28,512),name='input0')
out0 = sgs_chalk.Minimum(in0,1.0,name='output')
model = sgs_chalk.Model([in0],out0)
model.save('test.sim')
case2
from calibrator_custom import sgs_chalk
import numpy as np
input1 = np.zeros((28,512), dtype=np.float32)
in0 = sgs_chalk.Input((28,512),name='input0')
out0 = sgs_chalk.Minimum(in0,input1,name='output')
model = sgs_chalk.Model([in0],out0)
model.save('test.sim')
- MirrorPad:
MirrorPads a tensor.
This operation pads a tensor according to the paddings you specify.
paddings is an integer tensor with shape [n, 2], where n is the rank of
tensor. For each dimension D of input, paddings[D, 0] indicates how
many values to add before the contents of tensor in that dimension, and
paddings[D, 1] indicates how many values to add after the contents of
tensor in that dimension.
The padded size of each dimension D of the output is:
paddings[D, 0] + tensor.dim_size(D) + paddings[D, 1]
Args:
tensor: A `Tensor`.
paddings: A `Tensor` of type `int32`.
name: A name for the output tensor (optional).
Returns:
A `Tensor`. Has the same type as `tensor`.
Examples:
case0
from calibrator_custom import sgs_chalk
import numpy as np
in0 = sgs_chalk.Input((28,512),name='input0')
out0 = sgs_chalk.Pad(in0,[[0,0],[10,10]],name='output')
model = sgs_chalk.Model([in0],out0)
model.save('test.sim')
- Mod:
Returns x * y element-wise.
Args:
x: A `Tensor`. Must be Variable Tensor.
y: A `Tensor` or `numpy.ndarray`. Must have the same type as `x`, can be Variable or Const Tensor.
Support inner most dimension broadcasting.
name: A name for the output tensor (optional).
Returns:
A Variable `Tensor`. Has the same shape as `x`.
Examples:
case0
from calibrator_custom import sgs_chalk
import numpy as np
in0 = sgs_chalk.Input((28,512),name='input0')
in1 = sgs_chalk.Input((28,512),name='input1')
out0 = sgs_chalk.Mul(in0,in1,name='output')
model = sgs_chalk.Model([in0,in1],out0)
model.save('test.sim')
</details>
<details>
<summary>case1</summary>
```python
from calibrator_custom import sgs_chalk
import numpy as np
in0 = sgs_chalk.Input((28,512),name='input0')
out0 = sgs_chalk.Mod(in0,5.0,name='output')
model = sgs_chalk.Model([in0],out0)
model.save('test.sim')
- Mul:
Returns x * y element-wise.
Args:
x: A `Tensor`. Must be Variable Tensor.
y: A `Tensor` or `numpy.ndarray`. Must have the same type as `x`, can be Variable or Const Tensor.
Support inner most dimension broadcasting.
name: A name for the output tensor (optional).
Returns:
A Variable `Tensor`. Has the same shape as `x`.
Examples:
case0
from calibrator_custom import sgs_chalk
import numpy as np
in0 = sgs_chalk.Input((28,512),name='input0')
in1 = sgs_chalk.Input((28,512),name='input1')
out0 = sgs_chalk.Mul(in0,in1,name='output')
model = sgs_chalk.Model([in0,in1],out0)
model.save('test.sim')
</details>
<details>
<summary>case1</summary>
```python
from calibrator_custom import sgs_chalk
import numpy as np
in0 = sgs_chalk.Input((28,512),name='input0')
out0 = sgs_chalk.Mul(in0,5.0,name='output')
model = sgs_chalk.Model([in0],out0)
model.save('test.sim')
- MultiplyAdd:
output = input*multiply + add
Args:
x1: A `Tensor`
multiply_value: A `Value`
add_value: A `Value`
name: A name for the model output tensor (optional).
Returns:
A `Tensor`
case0
from calibrator_custom import sgs_chalk
import numpy as np
input1 = sgs_chalk.Input((1,1,36,2048), name='input0')
out = sgs_chalk.MultiplyAdd(input1,1.0,1.0,name='output')
model = sgs_chalk.Model([input1], out)
model.save('test.sim', input_config='./input_config.ini', convert_fixed=True)
- Negative:
Computes the negative value of a tensor.
Given a tensor of integer or floating-point values, this operation returns a tensor of the same type, where each element contains the absolute value of the corresponding element in the input.
Args:
x: A `Tensor`
Returns:
A `Tensor` of same shape and type as `x`.
Examples:
case0
from calibrator_custom import sgs_chalk
import numpy as np
in0 = sgs_chalk.Input((28,512),name='input0')
out0 = sgs_chalk.Negative(in0,name='output')
model = sgs_chalk.Model([in0],[out0])
model.save('test.sim',input_config='./input_config.ini',convert_fixed=True)
- NotEqual:
Returns the truth value of (x != y) element-wise.
Args:
x: A `Tensor`. Must be Variable Tensor.
y: A `Tensor` or `numpy.ndarray`. Must have the same type as `x`, can be Variable or Const Tensor.
Support inner most dimension broadcasting.
name: A name for the output tensor (optional).
Returns:
A Variable `Tensor`. Has the same shape as `x`.Tensor` of type `bool
Examples:
case0
from calibrator_custom import sgs_chalk
import numpy as np
in0 = sgs_chalk.Input((28,512),name='input0')
in1 = sgs_chalk.Input((28,512),name='input1')
out0 = sgs_chalk.NotEqual(in0,in1,name='output')
model = sgs_chalk.Model([in0,in1],out0)
model.save('test.sim')
case1
from calibrator_custom import sgs_chalk
import numpy as np
in0 = sgs_chalk.Input((28,512),name='input0')
out0 = sgs_chalk.NotEqual(in0,5.0,name='output')
model = sgs_chalk.Model([in0],out0)
model.save('test.sim')
case2
from calibrator_custom import sgs_chalk
import numpy as np
input1 = np.zeros((28,512), dtype=np.float32)
in0 = sgs_chalk.Input((28,512),name='input0')
out0 = sgs_chalk.NotEqual(in0,input1,name='output')
model = sgs_chalk.Model([in0],out0)
model.save('test.sim')
- Pack:
Stacks a list of rank-R tensors into one rank-(R+1) tensor.
Packs the list of tensors in values into a tensor with rank one higher than
each tensor in values, by packing them along the axis dimension.
Given a list of length N of tensors of shape (A, B, C);
if axis == 0 then the output tensor will have the shape (N, A, B, C).
if axis == 1 then the output tensor will have the shape (A, N, B, C).
Etc.
Args:
x: A list of `Tensor` objects with the same shape and type. Must be Variable Tensor.
axis: An `int`. The axis to stack along. Defaults to the first dimension.
Negative values wrap around, so the valid range is `[-(R+1), R+1)`.
name: A name for the output tensor (optional).
Returns:
A Variable `Tensor`.
Examples:
case0
from calibrator_custom import sgs_chalk
import numpy as np
in0 = sgs_chalk.Input((28,512,1),name='input0')
in1 = sgs_chalk.Input((28,512,1),name='input1')
in2 = sgs_chalk.Input((28,512,1),name='input2')
x = [in0, in1, in2]
out0 = sgs_chalk.Pack(x,axis=2,name='output')
model = sgs_chalk.Model(x,out0)
model.save('test.sim')
- Pad:
Pads a tensor.
This operation pads a tensor according to the paddings you specify.
paddings is an integer tensor with shape [n, 2], where n is the rank of
tensor. For each dimension D of input, paddings[D, 0] indicates how
many values to add before the contents of tensor in that dimension, and
paddings[D, 1] indicates how many values to add after the contents of
tensor in that dimension.
The padded size of each dimension D of the output is:
paddings[D, 0] + tensor.dim_size(D) + paddings[D, 1]
Args:
tensor: A `Tensor`.
paddings: A `Tensor` of type `int32`.
name: A name for the output tensor (optional).
Returns:
A `Tensor`. Has the same type as `tensor`.
Examples:
case0
from calibrator_custom import sgs_chalk
import numpy as np
in0 = sgs_chalk.Input((28,512),name='input0')
out0 = sgs_chalk.Pad(in0,[[0,0],[10,10]],name='output')
model = sgs_chalk.Model([in0],out0)
model.save('test.sim')
case1
from calibrator_custom import sgs_chalk
import numpy as np
in0 = sgs_chalk.Input((28,512,512,4),name='input0')
out0 = sgs_chalk.Pad(in0,[[1,1],[2,2],[3,3],[4,4]],name='output')
model = sgs_chalk.Model([in0],out0)
model.save('test.sim')
- PhaseModify:
if x0 > x1[0] Output = x0 + x1[1] else if x0 < x1[2] Output = x0 + x1[3]; else Output = x0
Args:
x0: `Tensor`. Must be Variable Tensor.
x1: A list. must include 4 elements.
name: A name for the model output tensor (optional).
Returns:
A Variable `Tensor`. Has the same shape as input x0.
Examples:
case0
from calibrator_custom import sgs_chalk
import numpy as np
input0 = sgs_chalk.Input((1,224,224,3),name='input0')
out = sgs_chalk.PhaseModify(input0,[1.0,2.0,3.0,4.0],name='output')
model = sgs_chalk.Model([input0], out)
model.save('test.sim', input_config='./input_config.ini', convert_fixed=True)
- PostProcess_Max:
postprocess max
Args:
num_classes: number of classes
is_skip_background: please note background must be the first one
Examples:
case0
from calibrator_custom import sgs_chalk
import numpy as np
mbox_conf_softmax = sgs_chalk.Tensor(shape=model_config["input_shape"][1],name = model_config["input"][1])
cus_options = [(b"scores_lengh",21,"int"),
(b"skip",1,"int")]
postprocess_max_output_list = sgs_chalk.PostProcess_Max(mbox_conf_softmax,num_classes=21,skip=1)
model = sgs_chalk.Model([mbox_conf_softmax],postprocess_max_output_list)
model.save('test.sim',input_config='./input_config.ini',convert_fixed=True)
- PostProcess_Unpack:
postprocess unpack
Args:
num_classes: number of classes
Examples:
case0
from calibrator_custom import sgs_chalk
import numpy as np
in0 = sgs_chalk.Input((1,3249,6), name = 'x')
unpack_out_tensors1 = []
for i in range(4):
unpack_out_tensors1.append("SGS_unpack1_"+str(i))
output_list = sgs_chalk.PostProcess_Unpack(in0,scores_lengh=80,name=unpack_out_tensors1)
model = sgs_chalk.Model([in0],output_list)
#model.save('test.sim')
model.save('test.sim',input_config='./input_config.ini',convert_fixed=True)
- Prelu:
Parametric Rectified Linear Unit.
It follows:
f(x) = alpha * x for x < 0,
f(x) = x for x >= 0,
where alpha is a learned array with the same shape as x.
Args:
tensor: A `Tensor`.
slope: Slope of the activation function at x < 0.
name: A name for the output tensor (optional).
Returns:
A `Tensor`. Has the same type as `tensor`.
Examples:
case0
from calibrator_custom import sgs_chalk
import numpy as np
in0 = sgs_chalk.Input((28,512),name='input0')
out0 = sgs_chalk.Prelu(in0,5,name='output')
model = sgs_chalk.Model([in0],out0)
model.save('test.sim')
case1
from calibrator_custom import sgs_chalk
import numpy as np
input1 = np.zeros((512,), dtype=np.float32)
in0 = sgs_chalk.Input((3,28,512),name='input0')
out0 = sgs_chalk.Prelu(in0,5,name='output')
model = sgs_chalk.Model([in0],out0)
model.save('test.sim')
- RNN:
Applies a multi-layer gated recurrent unit RNN to an input sequence.
Args:
x: A `Tensor`,shape is (L,1,N,input_size) N=batch size L=sequence length
h0:tensor of shape(1,1,1,hidden_size),containing the initial hidden state for each element in the input sequence.
hidden_size : The number of features in the hidden state h
W: A `Tensor`, shape is [1,hidden_size,input_size]
R: A `Tensor`, shape is [1,hidden_size,hidden_size]
B: A `Tensor`, shape is [1,2*hidden_size]
Returns:
A `Tensor` list,usually concatenate op should be add after RNN
Examples:
case0
from calibrator_custom import sgs_chalk
import numpy as np
W_1 = np.ones((1,2,2))
R_1 = np.ones((1,2,2))
B_1 = np.ones((1,4))
in0 = sgs_chalk.Input((2,1,1,2),name='input0')
input1 = np.zeros((1,1,1,2), dtype=np.float32)
out_1 = sgs_chalk.RNN(in0,input1,hidden_size=2,W=W_1,R=R_1,B=B_1,name=['rnn_output'])
model = sgs_chalk.Model([in0],[out_1])
model.save('test.sim')
case1
W_1 = np.ones((1,2,2))
R_1 = np.ones((1,2,2))
B_1 = np.ones((1,4))
in0 = sgs_chalk.Input((2,1,1,2),name='input0')
input1 = np.zeros((1,1,1,2), dtype=np.float32)
out0 = sgs_chalk.RNN(in0,input1,hidden_size=2,W=W_1,R=R_1,B=B_1,name=['rnn_output0'])
out1 = sgs_chalk.RNN(out0,input1,hidden_size=2,W=W_1,R=R_1,B=B_1,name=['rnn_output1'])
model = sgs_chalk.Model([in0], [out1])
model.save('test.sim',input_config='./input_config.ini', convert_fixed=True, inputs='RAWDATA')
case2
from calibrator_custom import sgs_chalk
import numpy as np
W_1 = np.ones((1,2,2))
R_1 = np.ones((1,2,2))
B_1 = np.ones((1,4))
in0 = sgs_chalk.Input((2,1,1,2),name='input0')
input1 = np.zeros((1,1,1,2), dtype=np.float32)
out1= sgs_chalk.RNN(in0,input1,hidden_size=2,hn_output=True,W=W_1,R=R_1,B=B_1,name=['rnn_output0'])
hn = sgs_chalk.Slice(out,[1,0,0,0],[1,1,1,2],name='rnn_hn')
model = sgs_chalk.Model([in0],[out1,hn])
model.save('test.sim',input_config='./input_config.ini', convert_fixed=True, inputs='RAWDATA')
- RSqrt:
Computes square root of x element-wise. I.e., (y = rsqrt{x} ).
Args:
x: A `Tensor`
Returns:
A `Tensor` of same shape and type as `x`.
Examples:
case0
from calibrator_custom import sgs_chalk
import numpy as np
in0 = sgs_chalk.Input((28,512),name='input0')
out0 = sgs_chalk.RSqrt(in0,name='output')
model = sgs_chalk.Model([in0],[out0])
model.save('test.sim',input_config='./input_config.ini',convert_fixed=True)
- Range:
Creates a sequence of numbers that begins at start and extends by
increments of delta up to but not including limit.
Args:
start: A 0-D `Tensor` (scalar). Acts as first entry in the range.
limit: A 0-D `Tensor` (scalar). Upper limit of sequence, exclusive.
delta: A 0-D `Tensor` (scalar). Number that increments `start`.
name: A name for the output tensor (optional).
Returns:
A `Tensor`. Has the same type as `tensor`.
Examples:
case0
from calibrator_custom import sgs_chalk
import numpy as np
in0 = sgs_chalk.Input((), name='input')
out0 = sgs_chalk.Range(0.0, in0, 1.0, name='output')
model = sgs_chalk.Model(in0, out0)
model.save('test.sim')
- Reciprocal:
Computes the Reciprocal value of a tensor.
Given a tensor of integer or floating-point values, this operation returns a tensor of the same type, where each element contains the absolute value of the corresponding element in the input.
Args:
x: A `Tensor`
Returns:
A `Tensor` of same shape and type as `x`.
Examples:
case0
from calibrator_custom import sgs_chalk
import numpy as np
in0 = sgs_chalk.Input((28,512),name='input0')
out0 = sgs_chalk.Reciprocal(in0,name='output')
model = sgs_chalk.Model([in0],[out0])
model.save('test.sim',input_config='./input_config.ini',convert_fixed=True)
- ReduceMax:
Computes the maxmum of elements across dimensions of a tensor.
Reduces input_tensor along the dimensions given in axis.
Unless keepdims is true, the rank of the tensor is reduced by 1 for each
entry in axis. If keepdims is true, the reduced dimensions
are retained with length 1.
Args:
input:A `Tensor` or 'Array'. Must be Variable Tensor if it's a Tensor.
asix: A `Tensor` or 'Array'. Must be Const Tensor if it's a Tensor.
keepdims: A one dimension array or list.
name: A name for the model output tensor (optional).
Returns:
A Variable `Tensor`. Has the same shape as input.
Examples:
case0
from calibrator_custom import sgs_chalk
import numpy as np
in0 = sgs_chalk.Input((1,28,512,33),name='input0')
axis = np.array([-2,1],dtype=np.int32)
out0 = sgs_chalk.ReduceMax(in0, axis, keepdims=1, name='output')
model = sgs_chalk.Model([in0],out0)
model.save('reducemax.sim',input_config='./input_config.ini', convert_fixed=True, inputs='RAWDATA')
- ReduceMin:
Computes the minimum of elements across dimensions of a tensor.
Reduces input_tensor along the dimensions given in axis.
Unless keepdims is true, the rank of the tensor is reduced by 1 for each
entry in axis. If keepdims is true, the reduced dimensions
are retained with length 1.
Args:
input: A `Tensor` or 'Array'. Must be Variable Tensor if it's a Tensor.
asix: A `Tensor` or 'Array'. Must be Const Tensor if it's a Tensor.
keepdims: A one dimension array or list.
name: A name for the model output tensor (optional).
Returns:
A Variable `Tensor`. Has the same shape as input.
Examples:
case0
from calibrator_custom import sgs_chalk
import numpy as np
in0 = sgs_chalk.Input((1,28,512,33),name='input0')
axis = np.array([-2,1],dtype=np.int32)
out0 = sgs_chalk.ReduceMin(in0, axis, keepdims=1, name='output')
model = sgs_chalk.Model([in0],out0)
model.save('reducemin.sim',input_config='./input_config.ini', convert_fixed=True, inputs='RAWDATA')
- Relu:
Computes rectified linear: max(x, 0).
Args:
tensor: A `Tensor`.
name: A name for the output tensor (optional).
Returns:
A `Tensor`. Has the same type as `tensor`.
Examples:
case0
from calibrator_custom import sgs_chalk
import numpy as np
in0 = sgs_chalk.Input((28,512),name='input0')
out0 = sgs_chalk.Relu(in0,name='output')
model = sgs_chalk.Model([in0],out0)
model.save('test.sim')
- Relu1:
Clips tensor values to a specified min and max.
Given a tensor x, this operation returns a tensor of the same type and
shape as x with its values clipped to min_value and max_value.
Any values less than min_value are set to min_value. Any values
greater than max_value are set to max_value.
Args:
x: A `Tensor`. Must be Variable Tensor.
Returns:
A Variable `Tensor`. has the same shape as x
Examples:
case0
from calibrator_custom import sgs_chalk
import numpy as np
input = sgs_chalk.Input((1,36,2048), name='input')
output = sgs_chalk.Relu1(input,name='output')
model = sgs_chalk.Model([input], output)
model.save('test.sim', input_config='./input_config.ini', convert_fixed=True)
- Relu6:
Computes Rectified Linear 6: `min(max(features, 0), 6)
Args:
tensor: A `Tensor`.
name: A name for the output tensor (optional).
Returns:
A `Tensor`. Has the same type as `tensor`.
Examples:
case0
from calibrator_custom import sgs_chalk
import numpy as np
in0 = sgs_chalk.Input((28,512),name='input0')
out0 = sgs_chalk.Relu6(in0,name='output')
model = sgs_chalk.Model([in0],out0)
model.save('test.sim')
- Relu_N1_TO_1:
Args:
tensor: A `Tensor`.
name: A name for the output tensor (optional).
Returns:
A `Tensor`. Has the same type as `tensor`.
Examples:
case0
from calibrator_custom import sgs_chalk
import numpy as np
in0 = sgs_chalk.Input((28,512),name='input0')
out0 = sgs_chalk.Relu_N1_TO_1(in0,name='output')
model = sgs_chalk.Model([in0],out0)
model.save('test.sim')
- Reshape:
As an entry point into a graph. reshape(a, newshape, order='C') Gives a new shape to an array without changing its data.
Examples:
case0
from calibrator_custom import sgs_chalk
import numpy as np
in0 = sgs_chalk.Input((28,512),name='input0')
out0 = sgs_chalk.Reshape(in0,(28,256,2),name='output')
model = sgs_chalk.Model([in0],out0)
model.save('test.sim')
case1
from calibrator_custom import sgs_chalk
import numpy as np
in0 = sgs_chalk.Input((28,512),name='input0')
out0 = sgs_chalk.Reshape(in0,(28,256,-1),name='output')
model = sgs_chalk.Model([in0],out0)
model.save('test.sim')
- ResizeBilinear:
ResizeBilinear
Args:
x: A `Tensor`
size : output H W size
Returns:
A `Tensor`
Examples:
case0
from calibrator_custom import sgs_chalk
import numpy as np
in0 = sgs_chalk.Input((1,224,224,3),name='input0')
out0 = sgs_chalk.ResizeBilinear(in0,[1120,1120],name='output')
model = sgs_chalk.Model([in0],[out0])
model.save('test.sim',input_config='./input_config.ini',convert_fixed=True)
- ResizeNearestNeighbor:
ResizeNearestNeighbor
Args:
x: A `Tensor`
size : output H w size
Returns:
A `Tensor`
Examples:
case0
from calibrator_custom import sgs_chalk
import numpy as np
in0 = sgs_chalk.Input((1,224,224,3),name='input0')
out0 = sgs_chalk.ResizeNearestNeighbor(in0,[1120,1120],name='output')
model = sgs_chalk.Model([in0],[out0])
model.save('test.sim',input_config='./input_config.ini',convert_fixed=True,inputs='RAWDATA')
- RoiPooling:
RoiPooling
Args:
x: A `Tensor`. Must be Variable Tensor.
RoiInfo: must be two dim, and the second dim is 5.
kernel_size : output kernel size.
spatial_scale ; A value
name: A name for the output tensor (optional).
Returns:
A Variable `Tensor`. shape is [RoiInfo.shape[0],kernel_size[0],kernel_size[1],x.shape[3]]
Examples:
case0
from calibrator_custom import sgs_chalk
import numpy as np
input = sgs_chalk.Input((1,25,32,256), name='input')
RoiInfo = sgs_chalk.Input((304,5), name='input0')
output = sgs_chalk.RoiPooling(input,RoiInfo,[6,6], 0.0625,name='output')
model = sgs_chalk.Model([input,RoiInfo], output)
#model.save('test.sim', input_config='./input_config.ini', convert_fixed=True)
model.save('test.sim', input_config='./input_config.ini', convert_fixed=True,inputs='RAWDATA')
- RootSumSquares2:
Output = sqrt(x0 * x0 + x1 * x1)
Args:
x0: `Tensor`. Must be Variable Tensor.only support int
x1: `Tensor`. Must be Variable Tensor,has same shape as x0.
name: A name for the model output tensor (optional).
Returns:
A Variable `Tensor`. Has the same shape as input x0.
Examples:
case0
from calibrator_custom import sgs_chalk
import numpy as np
input0 = sgs_chalk.Input((1,224,224,3),name='input0')
input1 = sgs_chalk.Input((1,224,224,3),name='input1')
out = sgs_chalk.RootSumSquares2(input0,input1,name='output')
model = sgs_chalk.Model([input0,input1], out)
model.save('test.sim', input_config='./input_config.ini', convert_fixed=True)
- Round:
Rounds the values of a tensor to the nearest integer, element-wise.
Args:
x: A `Tensor`
Returns:
A `Tensor` of same shape and type as `x`.
Examples:
case0
from calibrator_custom import sgs_chalk
import numpy as np
in0 = sgs_chalk.Input((28,512),name='input0')
out0 = sgs_chalk.Round(in0,name='output')
model = sgs_chalk.Model([in0],[out0])
model.save('test.sim',input_config='./input_config.ini',convert_fixed=True)
- ScatterElements:
ScatterElements
Args:
x: A `Tensor`
indices: Tensor of rank q >= 1.
updates: Tensor of rank q + r - indices_shape[-1] - 1.
reduction: none (default), add, mul, max, min.
axis:int,Which axis to scatter on.
Returns:
A `Tensor`,has the same shape as x
Examples:
case0
from calibrator_custom import sgs_chalk
import numpy as np
from numpy import random as nr
import pdb
in0 = sgs_chalk.Input((1,1,500,11),name='input0')
data0 = np.random.randint(0, high=10, size=(1,1,500,1,4))
data0_tensor = sgs_chalk.Tensor(data=data0)
data1 = np.random.randint(0, high=10, size=(1,1,500,1))
data1_tensor = sgs_chalk.Tensor(data=data1)
out0 = sgs_chalk.ScatterElements(in0,data0_tensor,data1_tensor,name='output')
model = sgs_chalk.Model([in0],out0)
model.save('test.sim')
#model.save('test.sim',input_config='./input_config.ini', convert_fixed=True, inputs='RAWDATA')
- ScatterND:
Args:
input: A `Tensor`. Must be Variable Tensor whose rank r >= 1.
indices: A const Tensor or numpy.array whose rank q >= 1.
update: A Tensor whose rank is q+r-indices.shape[-1]-1
name: A name for the model output tensor (optional).
Returns:
A Variable `Tensor`. Has the same shape as input.
Examples:
case0
from calibrator_custom import sgs_chalk
import numpy as np
input = sgs_chalk.Input((14,3,41,2,1,2,3,5), name='input')
indices = np.array([[5, 0, 1], [10, 2, 33]])
update = sgs_chalk.Input((2,2,1,2,3,5), name='update')
scatterND_out = sgs_chalk.ScatterND(input, indices, update, 0, name='scatterND_out')
model = sgs_chalk.Model([input,update], scatterND_out)
model.save('test.sim', input_config='./input_config.ini', convert_fixed=True)
- Score_Filter:
Score_Filter
Args:
tensor: A `Tensor`.
name: A name for the output tensor (optional).
Returns:
A `Tensor`. Score index
A `Tensor`. valid box number
Examples:
case0
from calibrator_custom import sgs_chalk
import numpy as np
in0 = sgs_chalk.Input((1,7875),name='input0')
out0,out1 = sgs_chalk.Score_Filter(in0,threshold=0.5,input_element_count=7875,name='output')
model = sgs_chalk.Model([in0],[out0,out1])
model.save('test.sim',input_config='./input_config.ini', convert_fixed=True)
- Select:
where(condition, x=None, y=None, name=None)
Return the elements, either from x or y, depending on the condition. (deprecated)
If both x and y are None, then this operation returns the coordinates of
true elements of condition. The coordinates are returned in a 2-D tensor
where the first dimension (rows) represents the number of true elements, and
the second dimension (columns) represents the coordinates of the true
elements. Keep in mind, the shape of the output tensor can vary depending on
how many true values there are in input. Indices are output in row-major
order.
If both non-None, x and y must have the same shape.
The condition tensor must be a scalar if x and y are scalar.
If x and y are vectors of higher rank, then condition must be either a
vector with size matching the first dimension of x, or must have the same
shape as x.
The condition tensor acts as a mask that chooses, based on the value at each
element, whether the corresponding element / row in the output should be taken
from x (if true) or y (if false).
If condition is a vector and x and y are higher rank matrices, then it
chooses which row (outer dimension) to copy from x and y. If condition
has the same shape as x and y, then it chooses which element to copy from
x and y.
Args:
condition: A `Tensor` of type `float32`
x: A Tensor which may have the same shape as `condition`. If `condition` is
rank 1, `x` may have higher rank, but its first dimension must match the
size of `condition`.
y: A `tensor` with the same shape and type as `x`.
name: A name of the operation (optional)
Returns:
A `Tensor` with the same type and shape as `x`, `y` if they are non-None.
Otherwise, a `Tensor` with shape `(num_true, rank(condition))`.
Examples:
case0
from calibrator_custom import sgs_chalk
import numpy as np
in0 = sgs_chalk.Input((28,512),name='input0')
in1 = sgs_chalk.Input((28,512),name='input1')
in2 = sgs_chalk.Input((28,512),name='input2')
out0 = sgs_chalk.Select(in0,in1,in2,name='output')
model = sgs_chalk.Model([in0,in1,in2],out0)
model.save('test.sim')
case1
from calibrator_custom import sgs_chalk
import numpy as np
in0 = sgs_chalk.Input((28,512),name='input0')
in1 = sgs_chalk.Input((28,512),name='input1')
out0 = sgs_chalk.Select(in0,5.0,in1,name='output')
model = sgs_chalk.Model([in0,in1],out0)
model.save('test.sim')
case2
from calibrator_custom import sgs_chalk
import numpy as np
input1 = np.zeros((28,512), dtype=np.float32)
in0 = sgs_chalk.Input((28,512),name='input0')
in1 = sgs_chalk.Input((28,512),name='input1')
out0 = sgs_chalk.Select(input1,in0,in1,name='output')
model = sgs_chalk.Model([in0,in1],out0)
model.save('test.sim')
- Shape:
Computes the shape of a tensor.
Given a tensor of integer or floating-point values, this operation returns a tensor of the same type, where each element contains the absolute value of the corresponding element in the input.
Args:
x: A `Tensor`
dtype: Output data type. Only support int32 or int64
Returns:
A `Tensor` of same shape and type as `x`.
Examples:
case0
from calibrator_custom import sgs_chalk
import numpy as np
in0 = sgs_chalk.Input((28,512),name='input0')
out0 = sgs_chalk.Shape(in0,name='output')
model = sgs_chalk.Model([in0],[out0])
model.save('test.sim',input_config='./input_config.ini',convert_fixed=True)
- Sign:
Args:
tensor: A `Tensor`.
name: A name for the output tensor (optional).
Returns:
A `Tensor`. Has the same type as `tensor`.
Examples:
case0
from calibrator_custom import sgs_chalk
import numpy as np
in0 = sgs_chalk.Input((28,512),name='input0')
out0 = sgs_chalk.Sign(in0,name='output')
model = sgs_chalk.Model([in0],out0)
model.save('test.sim')
- Silu:
Args:
input: A `Tensor`. Must be Variable Tensor.
name: A name for the model output tensor (optional).
Returns:
A Variable `Tensor`. Has the same shape as input.
Examples:
case0
from calibrator_custom import sgs_chalk
import numpy as np
input = sgs_chalk.Input((14,3,41,2,1,2,3,5), name='input')
silu_out = sgs_chalk.Silu(input, name='silu_out')
model = sgs_chalk.Model([input,], silu_out)
model.save('test.sim', input_config='./input_config.ini', convert_fixed=True)
- Sin:
Returns sin(x) element-wise.
Args:
x: A `Tensor`. Must be Variable Tensor.
Returns:
```text
A Variable `Tensor`. Has the same shape as `x`.
Examples:
case0
from calibrator_custom import sgs_chalk
import numpy as np
in0 = sgs_chalk.Input((28,512),name='input0')
out0 = sgs_chalk.Sin(in0,name='output')
model = sgs_chalk.Model([in0],out0)
model.save('test.sim')
- Slice:
Extracts a slice from a tensor.
This operation extracts a slice of size size from a tensor input starting
at the location specified by begin. The slice size is represented as a
tensor shape, where size[i] is the number of elements of the 'i'th dimension
of input that you want to slice. The starting location (begin) for the
slice is represented as an offset in each dimension of input. In other
words, begin[i] is the offset into the 'i'th dimension of input that you
want to slice from.
Args:
x: A `Tensor`. Must be Variable Tensor.
begin: const Tensor
size: const Tensor
name: A name for the output tensor (optional).
Returns:
A Variable `Tensor`. Has the same shape as `size`.
Examples:
case0
from calibrator_custom import sgs_chalk
import numpy as np
in0 = sgs_chalk.Input((28,512),name='input0')
out0 = sgs_chalk.Slice(in0,[0,0],[28,512],name='output')
model = sgs_chalk.Model([in0],out0)
model.save('test.sim')
case1
from calibrator_custom import sgs_chalk
import numpy as np
in0 = sgs_chalk.Input((28,512),name='input0')
out0 = sgs_chalk.Slice(in0,[0,0],[14,510],name='output')
model = sgs_chalk.Model([in0],out0)
model.save('test.sim')
- Softmax:
Computes softmax activations.
Args:
tensor: A `Tensor`.
name: A name for the output tensor (optional).
Returns:
A `Tensor`. Has the same type as `tensor`.
Examples:
case0
from calibrator_custom import sgs_chalk
import numpy as np
in0 = sgs_chalk.Input((28,512),name='input0')
out0 = sgs_chalk.Softmax(in0,name='output')
model = sgs_chalk.Model([in0],out0)
model.save('test.sim')
- Softplus:
Args:
input: A `Tensor`. Must be Variable Tensor.
name: A name for the model output tensor (optional).
Returns:
A Variable `Tensor`. Has the same shape as input.
Examples:
case0
from calibrator_custom import sgs_chalk
import numpy as np
input = sgs_chalk.Input((14,3,41,2,1,2,3,5), name='input')
softplus_out = sgs_chalk.Softplus(input, name='softplus_out')
model = sgs_chalk.Model([input,], softplus_out)
model.save('test.sim', input_config='./input_config.ini', convert_fixed=True)
- SpaceToBatchND:
SpaceToBatch for 4-D tensors of type T.
This operation divides "spatial" dimensions [1, ..., M] of the input into a
grid of blocks of shape block_size, and interleaves these blocks with the
"batch" dimension (0) such that in the output, the spatial dimensions
[1, ..., M] correspond to the position within the grid, and the batch
dimension combines both the position within a spatial block and the original
batch position. Prior to division into blocks, the spatial dimensions of the
input are optionally zero padded according to paddings.
Args:
x: A `Tensor`
block_size: Must be `Tensor` or `ndarray` or `list`
paddings: A 2-D `Tensor` with shape `[2,2]`. Must be one of the
following types: `int32`, `int64`. All values must be >= 0.
`paddings[i] = [pad_start, pad_end]` specifies the amount to crop from
input dimension `i + 1`, which corresponds to spatial dimension `i`.
Returns:
A `Tensor` of same type as `x`.
Examples:
case0
from calibrator_custom import sgs_chalk
import numpy as np
in0 = sgs_chalk.Input((1,28,28,512),name='input0')
in1 = sgs_chalk.Add(in0,1.0)
out0 = sgs_chalk.SpaceToBatchND(in1,2,[[2,2],[2,2]],name='output')
model = sgs_chalk.Model([in0],[out0])
model.save('test.sim',input_config='./input_config.ini',convert_fixed=True)
- Split:
Splits a tensor into sub tensors.
NumSplits is an integer, then value is split along dimension
axis into NumSplits smaller tensors. This requires that NumSplits evenly
divides value.shape[axis].
Args:
input: A `Tensor`. 1-D or higher.
NumSplits: an integer indicating the number of splits along split_dim
axis: An integer or scalar `int32` `Tensor`. The dimension along which to
split. Must be in the range `[-rank(value), rank(value))`. Defaults to 0.
name: A name for the output tensor (optional).
Returns:
returns `num_or_size_splits` `Tensor` objects;
Examples:
case0
from calibrator_custom import sgs_chalk
import numpy as np
in0 = sgs_chalk.Input((28,4,4),name='input0')
output_list = sgs_chalk.Split(in0,NumSplits=2, axis=2,name=['output0','output1'])
model = sgs_chalk.Model([in0],output_list)
model.save('test.sim',input_config='./input_config.ini',convert_fixed=True)
- Split_V:
Splits a tensor into sub tensors.
Sizesplits is a 1-D Tensor (or list), and value is split into len(size_splits)
elements. The shape of the i-th element has the same size as the value except along dimension axis where
the size is size_splits[i].
Args:
input: A `Tensor`. 1-D or higher.
SizeSplits: Python list containing the sizes of each output tensor along split_dim.
the sum of sizes along the split dimension must match that of x
axis: An integer or scalar `int32` `Tensor`. The dimension along which to
split. Must be in the range `[-rank(value), rank(value))`. Defaults to 0.
name: A name for the output tensor (optional).
Returns:
returns `size_splits` `Tensor` objects;
Examples:
case0
from calibrator_custom import sgs_chalk
import numpy as np
in0 = sgs_chalk.Input((28,4,4),name='input0')
output_list = sgs_chalk.Split_V(in0,SizeSplits=[1,2,1], axis=2,name=['output0','output1','output2'])
model = sgs_chalk.Model([in0],output_list)
model.save('test.sim',input_config='./input_config.ini',convert_fixed=True)
case1
from calibrator_custom import sgs_chalk
import numpy as np
in0 = sgs_chalk.Input((28,4,3),name='input0')
output_list = sgs_chalk.Split_V(in0,SizeSplits=[2,2], axis=1,name=['output0','output1'])
model = sgs_chalk.Model([in0],output_list)
model.save('test.sim',input_config='./input_config.ini',convert_fixed=True)
- Sqrt:
Computes square root of x element-wise. I.e., (y = sqrt{x} = x^{½}).
Args:
x: A `Tensor`
Returns:
A `Tensor` of same shape and type as `x`.
Examples:
case0
from calibrator_custom import sgs_chalk
import numpy as np
in0 = sgs_chalk.Input((28,512),name='input0')
out0 = sgs_chalk.Sqrt(in0,name='output')
model = sgs_chalk.Model([in0],[out0])
model.save('test.sim',input_config='./input_config.ini',convert_fixed=True)
- Square:
Args:
input: A `Tensor`. Must be Variable Tensor.
name: A name for the model output tensor (optional).
Returns:
A Variable `Tensor`. Has the same shape as input.
Examples:
case0
from calibrator_custom import sgs_chalk
import numpy as np
input = sgs_chalk.Input((14,3,41,2,1,2,3,5), name='input')
square_out = sgs_chalk.Square(input, name='softplus_out')
model = sgs_chalk.Model([input,], square_out)
model.save('test.sim', input_config='./input_config.ini', convert_fixed=True)
- Squeeze:
Remove single-dimensional entries from the shape of a tensor. Selects a subset of the single-dimensional entries in the shape. If an axis is selected with shape entry greater than one, an error is raised.
Args:
x: A `Tensor`..
axis: int or list or tuple of ints
name: A name for the output tensor (optional).
Returns:
A `Tensor`. The input tensor, but with all or a subset of the
dimensions of length 1 removed.
Examples:
case0
from calibrator_custom import sgs_chalk
import numpy as np
in0 = sgs_chalk.Input((1,28,512,4), name='input0')
out0 = sgs_chalk.Squeeze(in0, axis=0, name='output')
model = sgs_chalk.Model(in0, out0)
model.save('test.sim')
</details>
- StridedSlice:
Extracts a strided slice of a tensor (generalized python array indexing).
Roughly speaking, this op extracts a slice of size `(end-begin)/stride`
from the given `input_` tensor. Starting at the location specified by `begin`
the slice continues by adding `stride` to the index until all dimensions are
not less than `end`.
Note that a stride can be negative, which causes a reverse slice.
Given a Python slice `input[spec0, spec1, ..., specn]`,
this function will be called as follows.
`begin`, `end`, and `strides` will be vectors of length n.
n in general is not equal to the rank of the `input_` tensor.
Args:
```text
x: A `Tensor`. Must be Variable Tensor.
begin: const Tensor
size: const Tensor
begin_mask: An `int32` mask.
end_mask: An `int32` mask.
ellipsis_mask: An `int32` mask.
new_axis_mask: An `int32` mask.
shrink_axis_mask: An `int32` mask.
name: A name for the output tensor (optional).
A Variable `Tensor`. Has the same shape as `x`. (end-begin)/stride
case0
from calibrator_custom import sgs_chalk
import numpy as np
in0 = sgs_chalk.Input((28,512,4),name='input0')
out0 = sgs_chalk.StridedSlice(in0,[1,0,0],[28,512,4],[1,2,1],name='output')
model = sgs_chalk.Model([in0],out0)
model.save('test.sim')
x: A `Tensor`. Must be Variable Tensor.
y: A `Tensor` or `numpy.ndarray`. Must have the same type as `x`, can be Variable or Const Tensor.
Support inner most dimension broadcasting.
name: A name for the output tensor (optional).
A Variable `Tensor`. Has the same shape as `x`.
case0
from calibrator_custom import sgs_chalk
import numpy as np
in0 = sgs_chalk.Input((28,512),name='input0')
in1 = sgs_chalk.Input((28,512),name='input1')
out0 = sgs_chalk.Sub(in0,in1,name='output')
model = sgs_chalk.Model([in0,in1],out0)
model.save('test.sim')
case1
from calibrator_custom import sgs_chalk
import numpy as np
in0 = sgs_chalk.Input((28,512),name='input0')
out0 = sgs_chalk.Sub(in0,5.0,name='output')
model = sgs_chalk.Model([in0],out0)
model.save('test.sim')
tensor: A `Tensor`.
axis: The dimensions to reduce.
keep_dim:whether keep dim or not
name: A name for the output tensor (optional).
A `Tensor`. The reduced tensor.
case0
from calibrator_custom import sgs_chalk
import numpy as np
in0 = sgs_chalk.Input((1,28,28,512),name='input0')
out0 = sgs_chalk.Sum(in0,[0,1,2,3],name='output')
model = sgs_chalk.Model([in0],out0)
model.save('test.sim')
case1
from calibrator_custom import sgs_chalk
import numpy as np
in0 = sgs_chalk.Input((1,28,28,512),name='input0')
out0 = sgs_chalk.Sum(in0,[1,2],name='output')
model = sgs_chalk.Model([in0],out0)
model.save('test.sim')
max_detection: max number pf output dectection bboxes
num_classes:number of classes
is_need_index : outputs include index or not
case0
from calibrator_custom import sgs_chalk
import numpy as np
bosdecoder_output_list = sgs_chalk.BoxDecoder(config,output_list)
confidence_tensor = sgs_chalk.Logistic(output_list[4],name="confidence_tensor")
SGS_score0 = sgs_chalk.Logistic(output_list[5],name="score0_tensor")
SGS_score1 = sgs_chalk.Mul(confidence_tensor,SGS_score0,name="SGS_score1")
out1 = sgs_chalk.TFLite_Detection_NMS(bosdecoder_output_list[0],bosdecoder_output_list[1],bosdecoder_output_list[2],
bosdecoder_output_list[3],confidence_tensor,SGS_score1,output_list[6],mode='YOLO',
max_detections=100,nms_score_threshold=0.4,
nms_iou_threshold=0.45,num_classes=80,is_need_index=False)
case1
from calibrator_custom import sgs_chalk
import numpy as np
bosdecoder_output_list = sgs_chalk.BoxDecoder(config,output_list)
mbox_conf_softmax = sgs_chalk.Input(model_config["input_shape"][1], name = model_config["input"][1])
postprocess_max_output_list = sgs_chalk.PostProcess_Max(mbox_conf_softmax,scores_lengh=21,skip=1)
out1 = sgs_chalk.TFLite_Detection_NMS(bosdecoder_output_list[0],bosdecoder_output_list[1],bosdecoder_output_list[2],
bosdecoder_output_list[3],postprocess_max_output_list[0],postprocess_max_output_list[1],
mode='SSD',max_detections=10,nms_score_threshold=0.01,
nms_iou_threshold=0.45,num_classes=20,is_need_index=False)
tensor: A `Tensor`.
name: A name for the output tensor (optional).
A `Tensor`. Has the same type as `tensor`.
case0
from calibrator_custom import sgs_chalk
import numpy as np
in0 = sgs_chalk.Input((28,512),name='input0')
out0 = sgs_chalk.Tanh(in0,name='output')
model = sgs_chalk.Model([in0],out0)
model.save('test.sim')
input: A `Tensor`. 1-D or higher.
multiples: A `Tensor`. Length must be the same as the number of dimensions in `input`
name: A name for the output tensor (optional).
A `Tensor`. Has the same type as `input`.
case0
from calibrator_custom import sgs_chalk
import numpy as np
in0 = sgs_chalk.Input((28,512,4),name='input0')
out0 = sgs_chalk.Tile(in0,(1,1,2),name='output')
model = sgs_chalk.Model([in0],out0)
model.save('test.sim')
input: 1-D or higher `Tensor` with last dimension at least `k`.
k: 0-D `int32`. Number of top elements to look for along the last dimension (along each row for matrices).
use_value: 0 or 1. Whether the value output tensor has consumers.
use_index: 0 or 1. Whether the index output tensor has consumers.
name: A name for the model output tensor (optional).
values: The `k` largest elements along each last dimensional slice.
indices: The indices of `values` within the last dimension of `input`.
case0
from calibrator_custom import sgs_chalk
import numpy as np
input = sgs_chalk.Input((1,36,2048), name='input')
output_list = sgs_chalk.TopK(input,k=[1], name=['value','index'])
model = sgs_chalk.Model([input,], output_list)
model.save('test.sim', input_config='./input_config.ini', convert_fixed=True)
input: A `Tensor`. 1-D or higher.
perm: A permutation of the dimensions of `a`.
name: A name for the output tensor (optional).
A transposed `Tensor`.
case0
from calibrator_custom import sgs_chalk
import numpy as np
in0 = sgs_chalk.Input((28,512,4),name='input0')
out0 = sgs_chalk.Transpose(in0,(0,2,1),name='output')
model = sgs_chalk.Model([in0],out0)
model.save('test.sim')
case1
from calibrator_custom import sgs_chalk
import numpy as np
in0 = sgs_chalk.Input((28,512,4),name='input0')
in1 = sgs_chalk.Input((28,512,4),name='input1')
out0 = sgs_chalk.Add(in0,in1)
out1 = sgs_chalk.Transpose(out0,(0,2,1),name='output')
model = sgs_chalk.Model([in0,in1],out1)
model.save('test.sim',input_config='./input_config.ini',convert_fixed=True)
x : input tensor of shape(1, iH, iW,in_channels)
weight: filters of shape(out_channels, kH, kW, in_channels)
bias: optional bias tensor of shape(out_channels).Default:None
stride: the stride of the convolving kernel. Can be a single number or a tuple(sH,sW).Default: 1
padding: a tuple (paddingTop, paddingBottom, paddingLeft, paddingRight)
Activation: only support NONE/RELU/RELU_N1_TO_1/RELU6
case0
from calibrator_custom import sgs_chalk
import numpy as np
in0 = sgs_chalk.Input((1,28,28,4),name='input0')
in1 = sgs_chalk.Input((8,3,3,4),name='input1')
out0 = sgs_chalk.TransposeConv2d(in0,in1,name='output')
model = sgs_chalk.Model([in0,in1],out0)
model.save('test.sim')
x: A `Tensor`. Must be Variable Tensor.
axis: An `int`. The axis to unstack along. Defaults to the first dimension.
Negative values wrap around, so the valid range is `[-R, R)
num: An `int`. The length of the dimension `axis`. Automatically inferred if
`None` (the default).
name: A name for the output tensor (optional).
The list of `Tensor` objects unstacked from `value`.
case0
from calibrator_custom import sgs_chalk
import numpy as np
in0 = sgs_chalk.Input((28,4,3),name='input0')
output_list = sgs_chalk.Unpack(in0,axis=2,name=['output0','output1','output2'])
model = sgs_chalk.Model([in0],output_list)
model.save('test.sim',input_config='./input_config.ini',convert_fixed=True)
case1
from calibrator_custom import sgs_chalk
import numpy as np
in0 = sgs_chalk.Input((28,4,3),name='input0')
output_list = sgs_chalk.Unpack(in0,axis=1,name=['output0','output1','output2','output3'])
model = sgs_chalk.Model([in0],output_list)
model.save('test.sim',input_config='./input_config.ini',convert_fixed=True)
x0: `Tensor`. Must be Variable Tensor.only support int
x1: `Tensor`. Must be Variable Tensor,has same shape as x0.only support int
x2: A list. must include 5 elements.
name: A name for the model output tensor (optional).
A Variable `Tensor`. Has the same shape as input x0.
case0
from calibrator_custom import sgs_chalk
import numpy as np
input0 = sgs_chalk.Input((1,224,224,3),name='input0')
input1 = sgs_chalk.Input((1,224,224,3),name='input1')
out = sgs_chalk.WiggleErr(input0,input1,[1.0,2.0,3.0,4.0,5.0],name='output')
model = sgs_chalk.Model([input0,input1], out)
model.save('test.sim', input_config='./input_config.ini', convert_fixed=True)