Conformer
1 Overview¶
1.1 Background Introduction¶
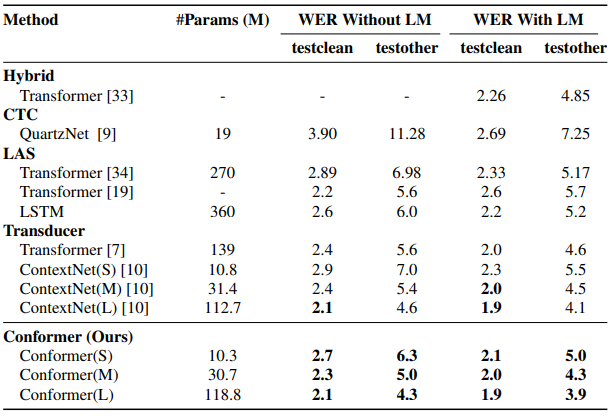
The Conformer model is a hybrid model that combines the self-attention mechanism of Transformer and CNN convolution modules, primarily used in the field of speech recognition. It can convert input audio into the corresponding text sequence, with specific accuracy details as follows:
Since the Conformer official implementation does not provide model weights, the models used in this project come from the Wenet framework. The list of open-source Conformer models provided by Wenet is as follows:
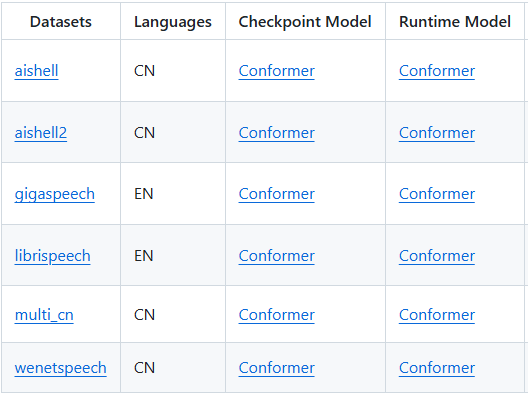
For more details, please refer to the official Wenet documentation:
https://github.com/wenet-e2e/wenet/blob/v3.0.1/docs/pretrained_models.md
The Checkpoint Model we use is based on WenetSpeech training, and can be downloaded at:
https://wenet.org.cn/downloads?models=wenet&version=wenetspeech_u2pp_conformer_exp.tar.gz
1.2 Usage Instructions¶
The Linux SDK-alkaid includes pre-converted offline models and board examples by default. The relevant file paths are as follows:
-
Board example program path:
Linux_SDK/sdk/verify/opendla/source/asr/conformer -
Board offline model path:
Linux_SDK/project/board/${chip}/dla_file/ipu_open_models/asr/conformer_400x80.img -
Board test audio path:
Linux_SDK/sdk/verify/opendla/source/resource/BAC009S0764W0121.wav -
Board test dictionary path:
Linux_SDK/sdk/verify/opendla/source/resource/units_asr_punc_lm.txt
If users do not need to convert models, they can directly jump to section 3.
2 Model Conversion¶
2.1 ONNX Model Conversion¶
-
Python environment setup:
$conda create -n wenet python==3.9 $conda activate wenet $git clone https://github.com/wenet-e2e/wenet.git $cd wenet $pip install -e . -i https://pypi.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/simpleNote: We developed based on wenet-v3.0.1 version. The provided python environment setup is for reference only; please refer to the official source code running tutorial for the specific setup process:
https://github.com/wenet-e2e/wenet/tree/v3.0.1 -
Model Testing:
-
Write the model testing script
predict.py: import wenet model = wenet.load_model('chinese') # or model = wenet.load_model(model_dir='xxx') result = model.transcribe('audio.wav') print(result['text']) -
Run the model testing script to ensure the Wenet environment is configured correctly:
$python predict.py
Note: The testing demo example here comes from the official source code running tutorial.
audio.wavneeds to be prepared by the user; audio files intest/resourcescan be referenced and placed in the same directory as predict.py. -
-
Model Export:
-
Install dependent libraries: $pip install onnx -i https://pypi.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/simple $pip install onnx-simplifier -i https://pypi.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/simple
-
Run the Wenet provided model conversion script to ensure the Wenet environment is configured correctly:
$python wenet/bin/export_onnx_gpu.py \\ --config opendla/train.yaml \\ --checkpoint opendla/final.pt \\ --cmvn_file opendla/global_cmvn \\ --output_onnx_dir opendla/ \\ --num_decoding_left_chunks -1 \\ --reverse_weight 0.3Here,
opendlarefers to the model folder downloaded from the official website, which can be named freely. After successful model conversion, the output log information will print:INFO:wenet/bin/export_onnx_gpu.py:export to onnx encoder succeed!INFO:wenet/bin/export_onnx_gpu.py:export to onnx decoder succeed! -
Optimize the graph structure:
$python -m onnxsim opendla/encoder.onnx opendla/conformer_sim.onnx
At this point, the ONNX model has been converted, but it cannot yet be deployed to our platform, as certain operators need to be modified.
-
-
Model Modification:
-
Modify the original code to change dynamic length input to fixed length input:
-
At line 152 in
wenet/transformer/encoder.py, add the following statement:xs_lens = torch.tensor([xs[:,:,0].bool().sum()]) - Modify lines 69-79 in `wenet/bin/export_onnx_gpu.py` as follows:-
Original Code ctc_log_probs = self.ctc.log_softmax(encoder_out) encoder_out_lens = encoder_out_lens.int() beam_log_probs, beam_log_probs_idx = torch.topk(ctc_log_probs, self.beam_size, dim=2) return ( encoder_out, encoder_out_lens, ctc_log_probs, beam_log_probs, beam_log_probs_idx, )
-
Modified Code ctc_log_probs = self.ctc.ctc_lo(encoder_out) return (ctc_log_probs)
-
-
Modify lines 746-827 in
wenet/bin/export_onnx_gpu.pyas follows:-
Original Code
def export_offline_encoder(model, configs, args, logger, encoder_onnx_path): bz = 32 seq_len = 100 beam_size = args.beam_size feature_size = configs["input_dim"] speech = torch.randn(bz, seq_len, feature_size, dtype=torch.float32) speech_lens = torch.randint(low=10, high=seq_len, size=(bz, ), dtype=torch.int32) encoder = Encoder(model.encoder, model.ctc, beam_size) encoder.eval() torch.onnx.export( encoder, (speech, speech_lens), encoder_onnx_path, export_params=True, opset_version=13, do_constant_folding=True, input_names=["speech", "speech_lengths"], output_names=[ "encoder_out", "encoder_out_lens", "probs" "beam_log_probs", "beam_log_probs_idx", ], dynamic_axes={ "speech": { 0: "B", 1: "T" }, "speech_lengths": { 0: "B" }, "encoder_out": { 0: "B", 1: "T_OUT" }, "encoder_out_lens": { 0: "B" }, "ctc_log_probs": { 0: "B", 1: "T_OUT" }, "beam_log_probs": { 0: "B", 1: "T_OUT" }, "beam_log_probs_idx": { 0: "B", 1: "T_OUT" }, }, verbose=False, ) with torch.no_grad(): o0,o1,o2,o3,o4 = F.log_softmax(encoder(speech, speech_lens), dim=2) providers = ["CUDAExecutionProvider"] ort_session = onnxruntime.InferenceSession(encoder_onnx_path, providers=providers) ort_inputs = { "speech": to_numpy(speech), "speech_lengths": to_numpy(speech_lens), } ort_outs = ort_session.run(None, ort_inputs) # check encoder output test(to_numpy([o0,o1,o2,o3,o4]), ort_outs) logger.info("export offline onnx encoder succeed!") onnx_config = { "beam_size": args.beam_size, "reverse_weight": args.reverse_weight, "ctc_weight": args.ctc_weight, "fp16": args.fp16, } return onnx_config -
Modified Code
def export_offline_encoder(model, configs, args, logger, encoder_onnx_path): bz = 1 seq_len = 400 beam_size = args.beam_size feature_size = configs["input_dim"] speech = torch.randn(bz, seq_len, feature_size, dtype=torch.float32) speech_lens = torch.randint(low=10, high=seq_len, size=(bz, ), dtype=torch.int32) encoder = Encoder(model.encoder, model.ctc, beam_size) encoder.eval() torch.onnx.export( encoder, (speech, speech_lens), encoder_onnx_path, export_params=True, opset_version=13, do_constant_folding=True, input_names=["speech", "speech_lengths"], output_names=["probs"], verbose=False, ) with torch.no_grad(): o0 = F.log_softmax(encoder(speech, speech_lens), dim=2) providers = ["CPUExecutionProvider"] ort_session = onnxruntime.InferenceSession(encoder_onnx_path, providers=providers) ort_inputs = { "speech": to_numpy(speech), # "speech_lengths": to_numpy(speech_lens), } ort_outs = F.log_softmax(torch.tensor(ort_session.run(None, ort_inputs)[0]), dim=2) # check encoder output test(o0, ort_outs) logger.info("export offline onnx encoder succeed!") onnx_config = { "beam_size": args.beam_size, "reverse_weight": args.reverse_weight, "ctc_weight": args.ctc_weight, "fp16": args.fp16, } return onnx_config
-
-
After completing the modifications, execute the model export step again to generate the deployable conformer.onnx model.
-
2.2 Offline Model Conversion¶
2.2.1 Pre & Post-Processing Instructions¶
-
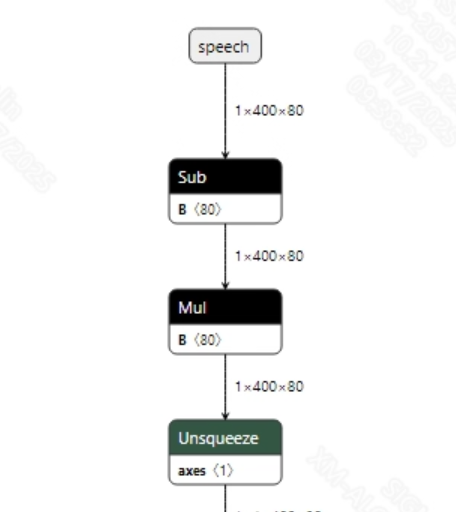
Pre-processing
Before feeding audio into the model, the speech wav needs to be converted to fbank. The input information for the successfully converted conformer_sim.onnx model is shown in the figure below. The required length of the input fbank is (1, 400, 80), where 400 is the time sequence length and 80 is the number of channels.
-
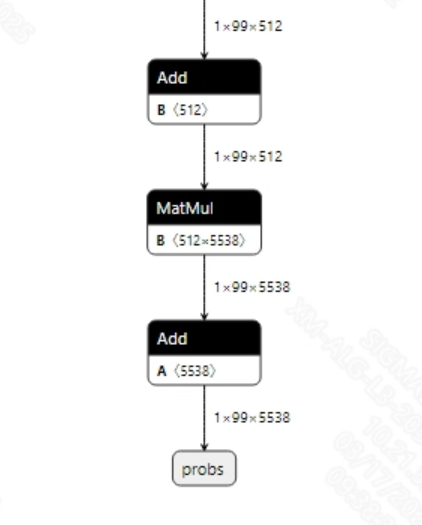
Post-processing
The output information of the successfully converted conformer_sim.onnx model is shown in the figure below, with output dimensions of (1, 99, 5538), where 99 is the length of the output text and 5538 is the number of classes. After obtaining the output features, they need to undergo log_softmax processing, followed by decoding the output features using greedy search to convert them into a text sequence.
2.2.2 Offline Model Conversion Process¶
Note: 1) OpenDLAModel corresponds to the smodel files extracted from the compressed package image-dev_model_convert.tar. 2) The conversion command needs to be run in a Docker environment; please load the SGS Docker environment according to the Docker Development Environment Tutorial.
-
Copy the ONNX model to the conversion code directory:
$cp opendla/conformer_sim.onnx OpenDLAModel/asr/conformer/onnx -
Conversion command:
$cd IPU_SDK_Release/docker $bash run_docker.sh # Enter the OpenDLAModel directory in the Docker environment $cd /work/SGS_XXX/OpenDLAModel $bash convert.sh -a asr/conformer -c config/asr_conformer.cfg -p SGS_IPU_Toolchain(absolute path) -s false -
Final generated model locations:
output/${chip}_${time}/conformer_sim.img output/${chip}_${time}/conformer_sim_fixed.sim output/${chip}_${time}/conformer_sim_float.img
2.2.3 Key Script Parameter Analysis¶
-
input_config.ini
[INPUT_CONFIG] inputs=speech; # ONNX input node name; separate multiple names with commas if necessary; input_formats=RAWDATA_F32_NHWC; # Board input format; can be chosen based on ONNX input format, e.g., float: RAWDATA_F32_NHWC, int32: RAWDATA_S16_NHWC; quantizations=TRUE; # Enable input quantization; do not modify; [OUTPUT_CONFIG] outputs=probs; # ONNX output node name; separate multiple names with commas if necessary; dequantizations=TRUE; # Whether to enable dequantization; fill in according to actual needs; recommended to be TRUE. Set to False for int16 output; set to True for float32 output. [OPTIMIZE_CONFIG] optimize_layernorm_precision=TRUE; -
asr_conformer.cfg
[COMFORMER] CHIP_LIST=pcupid # Platform name; must match the board platform, otherwise the model cannot run Model_LIST=conformer_sim # Input ONNX model name INPUT_SIZE_LIST=0 # Model input resolution INPUT_INI_LIST=input_config.ini # Configuration file CLASS_NUM_LIST=0 # Just fill in 0 SAVE_NAME_LIST=conformer_sim.img # Output model name; can be modified QUANT_DATA_PATH=image_list.txt # Quantization data path
2.3 Model Simulation¶
-
Obtain float/fixed/offline model output:
$bash convert.sh -a asr/conformer -c configs/asr_conformer.cfg -p SGS_IPU_Toolchain(absolute path) -s trueAfter executing the above command, it will default to saving the
floatmodel's output tensor to the txt file inasr/conformer/log/output. Additionally, theasr/conformer/convert.shscript also provides simulation examples forfixedandoffline; users can uncomment the code blocks to obtain the outputs forfixedandofflinemodels respectively. -
Model Accuracy Comparison
Under the condition that the input remains the same as above, enter the environment set up in 2.1. In the
wenet/wenet/bin/export_onnx_gpu.pyscript'sexport_offline_encoderfunction, add the print statement:print(encoder(speech, speech_lens))This will allow you to obtain the output tensor corresponding to the PyTorch model node, allowing you to compare it with the float, fixed, and offline models. Additionally, it should be noted that the output format of the original model is
NCHW, while the formats of float/fixed/offline model outputs areNHWC.
3 Board Deployment¶
3.1 Program Compilation¶
Before compiling the example program for the board, you need to select the deconfig according to the board model (nand/nor/emmc, DDR model, etc.) for the SDK full-package compilation. For details, please refer to the Alkaid SDK SIGDOC "Development Environment Setup" document.
-
Compile the board conformer example:
$cd sdk/verify/opendla $make clean && make source/asr/conformer -j8 -
Final executable file address:
sdk/verify/opendla/out/${AARCH}/app/prog_asr_conformer
3.2 Running Files¶
When running the program, the following files need to be copied to the board:
-
prog_asr_conformer
-
BAC009S0764W0121.wav
-
units_asr_punc_lm.txt
-
conformer_400x80.img
3.3 Running Instructions¶
-
Usage:
./prog_asr_conformer -i wav -m model -d txt(Execution command for the file) -
Required Input:
-
wav: Audio path
-
model: Path to the offline model to be tested
-
txt: Dictionary
-
-
Typical Output:
./prog_asr_conformer -i resource/BAC009S0764W0121.wav -m models/conformer_400x80.img -d resource/units_asr_punc_lm.txt input path: resource/BAC009S0764W0121.wav model path: models/conformer_400x80.img dict path: resource/units_client [907] connected, module:ipu asr_punc_lm.txt num_frames: 418, sizeof(input_buf): 128000 model invoke time: 330.710000 ms load dict... vocabulary size: 5538 decode result... ... (Further processing log output) ------shutdown IPU0------ client [907] disconnected, module:ipu