EAT
1 Overview¶
1.1 Background Introduction¶
The open-source sound event detection algorithm is derived from Alibaba's open-source speech algorithm repository, featuring lightweight and high stability. However, since this GitHub repository only provides the code and not the models, users will need to train the models themselves. For detailed information about the model, please visit:
https://github.com/Alibaba-MIIL/AudioClassfication
The released model has been trained on the ESC-50 dataset, and the training command is:
python trainer.py \
--max_lr 3e-4 \
--run_name r1 \
--emb_dim 128 \
--dataset esc50 \
--seq_len 114688 \
--mix_ratio 1 \
--epoch_mix 12 \
--mix_loss bce \
--batch_size 128 \
--n_epochs 3500 \
--ds_factors 4 4 4 4 \
--amp \
--save_path outputs
The ESC-50 dataset can be downloaded from:
https://github.com/karoldvl/ESC-50/archive/master.zip
1.2 Usage Instructions¶
The Linux SDK-alkaid includes pre-converted offline models and board examples by default. The relevant file paths are as follows:
-
Board example program path:
Linux_SDK/sdk/verify/opendla/source/sed -
Board offline model path:
Linux_SDK/project/board/${chip}/dla_file/ipu_open_models/eat.img -
Board test audio path:
Linux_SDK/sdk/verify/opendla/source/resource/1-137-A-32_22.05k.wav
If users do not need to convert models, they can directly jump to section 3.
2 Model Conversion¶
2.1 ONNX Model Conversion¶
-
Python environment setup:
$conda create -n sed python==3.10 $conda activate sed $git clone https://github.com/Alibaba-MIIL/AudioClassfication.git $cd AudioClassfication $conda install pytorch=1.12.1 torchaudio=0.12.1 cudatoolkit=11.3 -c pytorch -c conda-forgeNote: The provided Python environment setup is for reference only; please refer to the official source code running tutorial for the specific setup process: https://github.com/Alibaba-MIIL/AudioClassfication/blob/main/README.md
-
Model Testing:
- Run the model testing script to ensure that the sed environment is configured correctly: $python inference.py --f_res outputs/r1 Here, outputs/r1 is the path where the model is stored.
-
Model Export:
-
Install the required packages:
$pip install onnx -i https://pypi.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/simple $pip install onnx-simplifier -i https://pypi.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/simple $pip install onnxruntime -i https://pypi.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/simple -
Write the model conversion script
export_onnx.py:import torch from torch.utils.data import DataLoader from pathlib import Path import argparse import yaml from utils.helper_funcs import accuracy, count_parameters, mAP, measure_inference_time import numpy as np import torch.nn.functional as F import os import onnx import onnxsim import onnxruntime device = "cpu" def parse_args(): parser = argparse.ArgumentParser() parser.add_argument("--f_res", default=None, type=Path) args = parser.parse_args() return args def run(): args = parse_args() f_res = args.f_res # add_noise = args.add_noise with (args.f_res / Path("args.yml")).open() as f: args = yaml.load(f, Loader=yaml.Loader) try: args = vars(args) except: if 'net' in args.keys(): del args['net'] args_orig = args args = {} for k, v in args_orig.items(): if isinstance(v, dict): for kk, vv in v.items(): args[kk] = vv else: args[k] = v args['f_res'] = f_res # args['add_noise'] = add_noise with open(args['f_res'] / "args.yml", "w") as f: yaml.dump(args, f) print(args) ####################### # Load PyTorch Models # ####################### from modules.soundnet import SoundNetRaw as SoundNet ds_fac = np.prod(np.array(args['ds_factors'])) * 4 net = SoundNet(nf=args['nf'], dim_feedforward=args['dim_feedforward'], clip_length=args['seq_len'] // ds_fac, embed_dim=args['emb_dim'], n_layers=args['n_layers'], nhead=args['n_head'], n_classes=args['n_classes'], factors=args['ds_factors'], ) print('***********************************************') print("#params: {}M".format(count_parameters(net)/1e6)) if torch.cuda.is_available() and device == torch.device("cuda"): t_b1 = measure_inference_time(net, torch.randn(1, 1, args['seq_len']))[0] print('inference time batch=1: {:.2f}[ms]'.format(t_b1)) # t_b32 = measure_inference_time(net, torch.randn(32, 1, args['seq_len']))[0] # print('inference time batch=32: {:.2f}[ms]'.format(t_b32)) print('***********************************************') if (f_res / Path("chkpnt.pt")).is_file(): chkpnt = torch.load(f_res / "chkpnt.pt", map_location=torch.device(device)) model = chkpnt['model_dict'] else: raise ValueError if 'use_dp' in args.keys() and args['use_dp']: from collections import OrderedDict state_dict = OrderedDict() for k, v in model.items(): name = k.replace('module.', '') state_dict[name] = v net.load_state_dict(state_dict, strict=True) else: net.load_state_dict(model, strict=True) net.to(device) if torch.cuda.device_count() > 1: from utils.helper_funcs import parse_gpu_ids args['gpu_ids'] = [i for i in range(torch.cuda.device_count())] net = torch.nn.DataParallel(net, device_ids=args['gpu_ids']) net.to('cuda:0') net.eval() x = torch.randn((1,1,114688)).to(device) torch_out = net(x) print(torch_out) f = 'outputs/r1/eat.onnx' # filename torch.onnx.export(net, x, f, verbose=False, opset_version=13, input_names=['images'], output_names=['output']) model_onnx = onnx.load(f) # load onnx model onnx.checker.check_model(model_onnx) # check onnx model ort_session = onnxruntime.InferenceSession(f,providers=['CPUExecutionProvider']) def to_numpy(tensor): return tensor.detach().cpu().numpy() if tensor.requires_grad else tensor.cpu().numpy() # compute ONNX Runtime output prediction ort_inputs = {ort_session.get_inputs()[0].name: to_numpy(x)} ort_outs = ort_session.run(None, ort_inputs) print(ort_outs) model_onnx, check = onnxsim.simplify(model_onnx) onnx.save(model_onnx, f.replace('eat','eat_sim')) if __name__ == '__main__': run() -
Run the model conversion script
export_onnx.py:python export_onnx.py --f_res output_r1
-
2.2 Offline Model Conversion¶
2.2.1 Pre & Post-Processing Instructions¶
-
Pre-processing
Before feeding audio into the model, typically, the
torchaudio.loadinterface is used to convert the audio data into tensors suitable for model input, followed by zero-padding to set a fixed input length; finally, normalization is applied. The model input information is shown below:
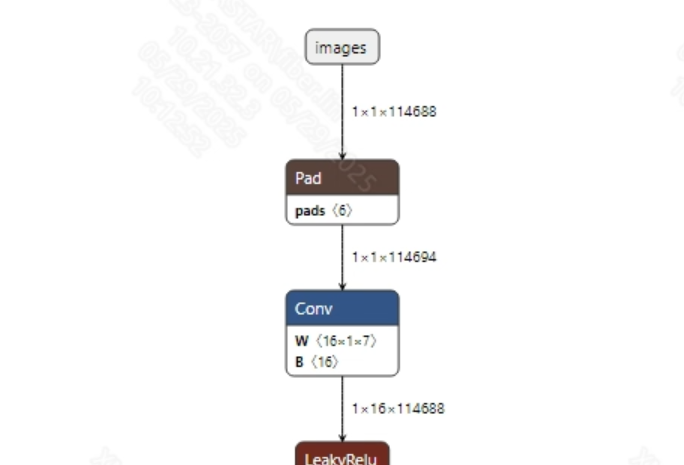
-
Post-processing
The sound classification model does not require post-processing. After obtaining the model output, the final result can be obtained through softmax and argmax processing. The model output information is shown below:
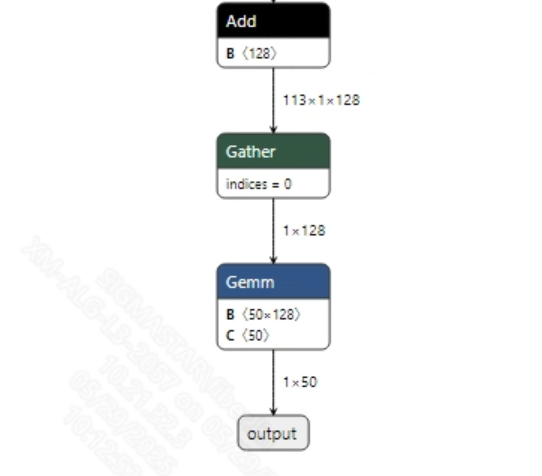
2.2.2 Offline Model Conversion Process¶
Note: 1) OpenDLAModel corresponds to the smodel files extracted from the compressed package image-dev_model_convert.tar. 2) The conversion command needs to be run in a Docker environment; please load the SGS Docker environment according to the Docker Development Environment Tutorial.
-
Copy the ONNX model to the conversion code directory:
$cp outputs/r1/eat_sim.onnx OpenDLAModel/sed/eat/onnx -
Conversion command:
$cd IPU_SDK_Release/docker $bash run_docker.sh # Enter the OpenDLAModel directory in the Docker environment $cd /work/SGS_XXX/OpenDLAModel $bash convert.sh -a sed/eat -c config/sed_eat.cfg -p SGS_IPU_Toolchain(absolute path) -s false -
Final generated model locations:
output/${chip}_${time}/eat.img output/${chip}_${time}/eat_fixed.sim output/${chip}_${time}/eat_float.sim
2.2.3 Key Script Parameter Analysis¶
-
input_config.ini [INPUT_CONFIG] inputs=images; # ONNX input node name; separate multiple names with commas if necessary; training_input_formats=RAWDATA_F32_NHWC; # Input format of the training data for the model input_formats=RAWDATA_F32_NHWC; # Board input format; choose based on ONNX input format; e.g., float: RAWDATA_F32_NHWC, int32: RAWDATA_S16_NHWC; quantizations=TRUE; # Enable input quantization; do not modify; [OUTPUT_CONFIG] outputs=output; # ONNX output node name; separate multiple names with commas if necessary; dequantizations=FALSE; # Whether to enable dequantization; fill according to actual needs; recommended to be TRUE. Set to False for int16 output; set to True for float32 output. [CONV_CONFIG] #input_format="ALL_INT16";
-
sed_eat.cfg [EAT] CHIP_LIST=pcupid # Platform name; must match the board platform, otherwise the model cannot run Model_LIST=eat_sim # Input ONNX model name INPUT_SIZE_LIST=0 # Model input resolution INPUT_INI_LIST=input_config.ini # Configuration file CLASS_NUM_LIST=0 # Just fill in 0 SAVE_NAME_LIST=eat.img # Output model name QUANT_DATA_PATH=quant_data # Quantization data path
2.3 Model Simulation¶
-
Obtain float/fixed/offline model output:
$bash convert.sh -a sed/eat -c config/sed_eat.cfg -p SGS_IPU_Toolchain(absolute path) -s trueAfter executing the above command, the output tensor of the
floatmodel will be saved by default to a txt file in thesed/eat/log/outputpath. Additionally, thesed/eat/convert.shscript also provides simulation examples forfixedandoffline; users can uncomment the code blocks to obtain the outputs forfixedandofflinemodels respectively. -
Model Accuracy Comparison
Under the condition that the input remains the same as above, enter the environment set up in 2.1. Add the print statement at line 157 in the
AudioClassfication/inference.pyfile:print(pred)This will allow you to obtain the output tensor corresponding to the PyTorch model node and compare it with the float, fixed, and offline models. Additionally, it should be noted that the output format of the original model is
NCHW, while the formats of float/fixed/offline model outputs areNHWC.
3 Board Deployment¶
3.1 Program Compilation¶
Before compiling the example program for the board, you need to select the deconfig according to the board model (nand/nor/emmc, DDR model, etc.) for the SDK full-package compilation. For details, please refer to the Alkaid SDK SIGDOC "Development Environment Setup" document.
-
Compile the board eat example:
$cd sdk/verify/opendla $make clean && make source/sed/eat -j8 -
Final executable file address:
sdk/verify/opendla/out/${AARCH}/app/prog_sed_eat
3.2 Running Files¶
When running the program, the following files need to be copied to the board:
- prog_sed_eat
- 1-137-A-32_22.05k.wav
- eat.img
3.3 Running Instructions¶
-
Usage:
./prog_sed_eat -i wav -m model(Execution command for the file) -
Required Input:
- -i: Path to the audio file
- -m: Path to the model file
-
Typical Output:
./prog_sed_eat -i 1-137-A-32_22.05k.wav -m models/eat.img inputs: 1-137-A-32_22.05k.wav model path: models/eat.img threshold: 0.500000 client [836] connected, module:ipu unknown element format 5 found 1 images! the input image: ./1-137-A-32_22.05k.wav model invoke time: 57.121000 ms post process time: 0.181000 ms class id: 32