8. Frequently Asked Questions
1. Common Environment Issues¶
Can Docker be set up on Ubuntu or Windows? What is the minimum memory requirement?
Yes, it is recommended to use Docker, with a minimum memory requirement of at least 32GB. If the memory is just barely sufficient, using too many processes during calibration may lead to unexpected errors and interruptions. Currently, developers are operating in an Ubuntu 18.04 environment. Docker on Windows may work as well, but we are uncertain whether issues will arise in the Docker environment set up on Windows.
2. Common Model Conversion Issues¶
Why do I get the error ValueError: Message onnx.ModelProto exceeds maximum protobuf size of 2GB: 2714769235 during model conversion?
Before converting the original ONNX model, it is necessary to optimize the original model structure using the onnxsim or onnxslim tools. During model conversion, you also need to add the --skip_simplify parameter in the ConvertTool.py command line.
Can the IPU_SDK conversion tool be used to directly convert an INT8 model?
Currently, direct input of quantized fixed-point network models into the IPU Toolchain is not supported; models must be converted from floating-point first. You can use the quantization import tool to import existing quantization information into the model.
Why does the floating-point number still output during PC simulation when dequantizations is set to FALSE in input_config.ini?
When the dequantizations in input_config.ini is set to FALSE, the simulator.py completes the process of multiplying the int16 output results by scale. Setting it to TRUE will add the Fix2float operator during the conversion of the Fixed model, and the model will then directly output floating-point data. You can also create an instance of the fixed simulation model using calibrator_custom.fixed_simulator and view the data type of the network output through the get_output_details method.
Why does it get stuck on "Start to analyze model..." when transitioning from a floating-point model to a fixed-point model?
If you encounter this situation, please check the CPU usage of the process. If it is close to 100%, it indicates that the model is currently being converted. If it is close to 0%, please terminate the process and re-quantize using an image to see if there are any error messages.
Why can't I see all layers' comparison results in the output log when using the DumpDebug tool to compare fixed-point models with floating-point models that have precision loss?
This is due to the disableDomainFuseOps in DebugConfig.txt not being enabled, which causes some ops to be fused. Please copy DebugConfig.txt to the execution directory, enable disableDomainFuseOps, and then re-convert the model before generating the sigma_outtensor_dump.bin file with the simulator.
Note
- When generating the actual offline model for deployment, it is necessary to disable disableDomainFuseOps, as it will affect model performance.
Why do I get write file fail... when comparing using the DumpDebug tool?
This is due to the path specified in DebugConfig.txt under path= not existing. Please check the configured path and ensure it is a valid directory. The default path is the user's home directory.
3. Common Issues on the Development Board¶
Why is the output data from the network model on the board different from that on the PC?
Please refer to the Board Precision Issues for analysis.
Are all the floating-point outputs on the board completed by the IPU?
The IPU can complete the conversion from int16 multiplied by scale to float32 data by adding the Fix2float operator. Simply set dequantizations to TRUE in input_config.ini during network conversion, and the Fix2float operator will be added to the corresponding model output after converting to the Fixed model.
How can I check the memory occupied by the model during runtime?
cat /proc/mi_modules/mi_sys_mma/mma_heap_name0 refers to the following explanation
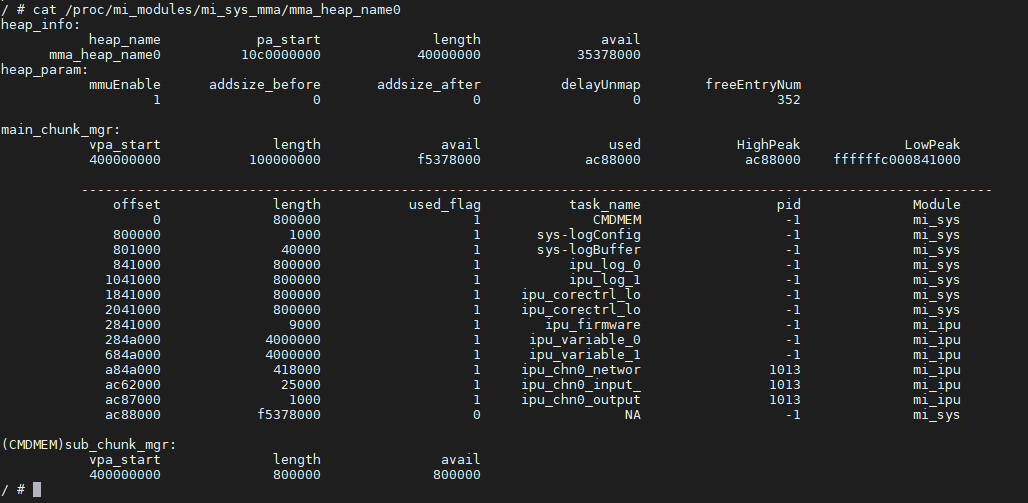
ipu_variable: Memory temporarily used by the IPU core during inference
ipu_log: Memory used for storing logs
ipu_chn0_networ: Memory used by channel 0 to load the network model
ipu_chn0_input_: Memory occupied by channel 0 input tensor (multiple means there are multiple input tensors that can be used simultaneously)
ipu_chn0_output: Memory occupied by channel 0 output tensor (multiple means there are multiple output tensors that can be used simultaneously)
4. Other Common Issues¶
How should the network be designed for efficient execution on the hardware?
It should be noted that the model converted by SGS_IPU_Toolchain has a default data layout of NHWC. For convolution: The larger the C dimension of the convolution input shape, and the smaller the HW dimensions, the higher the efficiency of the convolution. The hardware directly supports Depthwise convolution with a kernel size of 3x3, while kernels of other sizes will be converted to non-Depthwise convolution calculations. For other layers: It is best if the C dimension of other layers is a multiple of 16, as it can accelerate computations, especially for operators such as Gather, Unpack, Pack, Concat, Reshape, Slice, Tile, Transpose, Pad, Split, where acceleration is quite noticeable.
What is the layout of the input image data for the network?
It should be noted that the model converted by SGS_IPU_Toolchain has a default data layout of NHWC. Thus, if it is a model that inputs images in RGB channel order, the image data layout is ...RGBRGB.... If it is a model that inputs images in BGR channel order, the layout is ...BGRBGR....
How to check the IPU frequency?
cat /sys/dla/freq
or
cat /proc/mi_modules/mi_ipu/debug_hal/freq
Note
- The command to check the frequency may differ depending on the chip.
How to check the IPU DRAM information?
cat /sys/devices/system/miu/miu0/dram_info