4. Model Accuracy Debugging
1. Overview of IPU Accuracy Issues¶
When the model accuracy does not meet expectations, IPU provides several common debugging strategies for accuracy issues, which can be categorized into three types:
- Accuracy issues between the original framework model and Float.sim model
- Accuracy issues between Float.sim model and Fixed.sim model
- Accuracy issues on the board
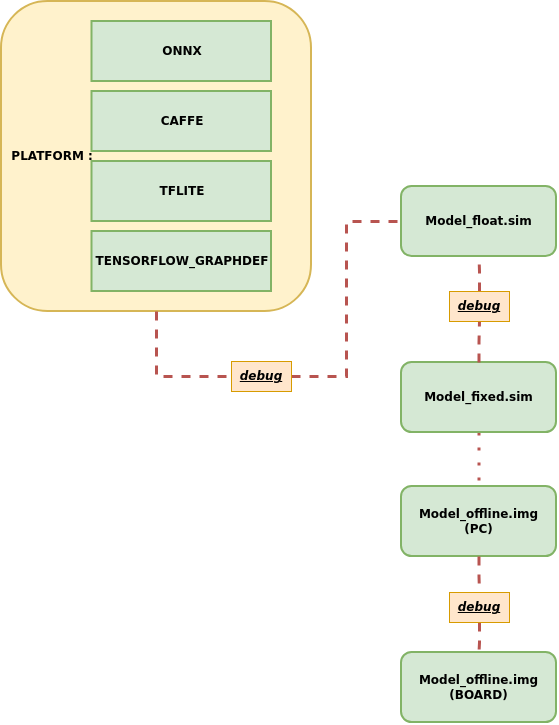
2. Accuracy Issues Between Original Framework Model and Float.sim Model¶
When model accuracy does not meet expectations, the first step is to check whether the inference results of the original framework model are consistent with those of the Float.sim model. Ensuring that the floating point model results are consistent is important before investigating any quantization issues.
2.1 How to Run the Original AI Framework Model¶
-
Use
SGS_IPU_Toolchain/DumpDebug/code/run_caffe.pyto run the Caffe modelUsage example:
python3 run_caffe.py \ -i 000775.jpg \ --model ./caffe_mobilenet_v2.prototxt \ --weight ./caffe_mobilenet_v2.caffemodel \ -n ./caffe_mobilenet_v2.py \ --input_config ./input_config.ini -
Use
SGS_IPU_Toolchain/DumpDebug/code/run_onnx.pyto run the Onnx modelUsage example:
python3 run_onnx.py \ -i 000775.jpg \ --model ./mobilenet_v2.onnx \ -n ./mobilenet_v2.py \ --input_config ./input_config.ini -
Use
SGS_IPU_Toolchain/DumpDebug/code/run_tflite.pyto run the Tflite modelUsage example:
python3 run_tflite.py \ -i 000775.jpg \ --model ./mobilenet_v2.tflite \ -n ./mobilenet_v2.py
Compare the inference results of the original AI framework model with those of Float.sim, and if they are inconsistent, you need to dump data layer by layer to identify the earliest operator causing the model result discrepancy.
Usage
-
First, ensure that the preprocessing results of the original model and Float.sim model are consistent.
-
The output of the original model inference is saved in the output directory, while the Float.sim model inference results are saved in the log/output directory. Remember to rename the generated files after each inference to avoid overwriting.
2.2 How to Dump Inference Data from Original AI Framework Models¶
2.2.1 Dumping Data from Caffe Model¶
-
The tool is located at
SGS_IPU_Toolchain/DumpDebug/code/caffe_dump_data.py. -
The
caffe_dump_data.pyscript needs to be run using python3 (the IPU Toolchain environment includes the caffe Python runtime), and is used to dump the data for each layer of the Caffe original model in string or binary form. -
Usage example:
python3 caffe_dump_data.py \
--model_file caffe_mobilenet_v2.prototxt \
--weight_file caffe_mobilenet_v2.caffemodel \
--image ./img.bmp \
--dump_bin True \
-n ./caffe_mobilenet_v2.py
- Parameter explanations:
① Required parameter explanations:
-
--model_file: Path to the Caffe original model prototxt file. -
--weight_file: Path to the Caffe original model caffemodel file. -
-i,--image: Path to an image file, image folder, or specified image path list file. -
--dump_bin: Whether to dump each layer's results in binary form, optional True / False.
Usage
- True: The dump result will be saved in binary form in the current running directory, automatically creating a folder named
dumpData, wherecaffe_NHWC_outtensor_dump.binwill be stored../dumpData/caffe_NHWC_outtensor_dump.bin(4D tensor layout format is NHWC, consistent with the IPU model) - False: The dump result will be saved as a string in the current running directory, automatically creating a folder named
dumpData, where you will findcaffe_NHWC_outtensor_dump.txtand folders for NHWC and NCHW../dumpData/caffe_NHWC_outtensor_dump.txt(4D tensor layout format is NHWC, consistent with the IPU model)./dumpData/NHWC(each layer's output generates a separate file, 4D tensor layout format is NHWC, consistent with the IPU model)./dumpData/NCHW(each layer's output generates a separate file, 4D tensor layout format is NCHW, consistent with the original model layout) - If you need to analyze data using
dump_debug.pyscript, be sure to use True.
-n,--preprocess: Preprocessing method; please directly specify the path to the preprocessing Python file. Use the preprocessing file used when running the sim model.
② Optional parameter explanations:
--input_config: Path to the input_config.ini file. If the model has input_layouts=NCHW, you can add configurations in input_config.ini to align the data layout with -n, --preprocess within caffe_dump_data.py.
Usage
- If the model is multi-input, the
-n,--preprocessparameter can require multiple preprocessing methods, e.g., -n preprocess1.py,preprocess2.py or --preprocess preprocess1.py,preprocess2.py. - If the model is multi-input, the
-i/--imageparameter should be provided in the form of a specified image path list file.
2.2.2 Dumping Data from ONNX Model¶
-
The tool is located at
SGS_IPU_Toolchain/DumpDebug/code/onnx_dump_data.py. -
The
onnx_dump_data.pyscript needs to be run using python3 (same as the IPU Toolchain environment) and is used to dump the data for each layer of the ONNX original model in string or binary form. -
Usage example:
python3 onnx_dump_data.py \
--model_file onnx_mobilenet_v2.onnx \
--image ./img.bmp \
--dump_bin True \
-n onnx_mobilenet_v2.py
- Parameter explanations:
① Required parameter explanations:
--model_file: Path to the ONNX refined model file (will be generated with ConvertTool.py) or the path to an ONNX model containing shape information for each layer.-i,--image: Path to an image file, image folder, or specified image path list file.--dump_bin: Whether to dump each layer's results in binary form, optional True / False.
Usage
- True: The dump result will be saved in binary form in the current running directory, automatically creating a folder named
dumpData, whereonnx_NHWC_outtensor_dump.binwill be stored../dumpData/onnx_NHWC_outtensor_dump.bin(4D tensor layout format is NHWC, consistent with the IPU model) - False: The dump result will be saved as a string in the current running directory, automatically creating a folder named
dumpData, where you will findonnx_NHWC_outtensor_dump.txtand folders for NHWC and NCHW../dumpData/onnx_NHWC_outtensor_dump.txt(4D tensor layout format is NHWC, consistent with the IPU model)./dumpData/NHWC(each layer's output generates a separate file, 4D tensor layout format is NHWC, consistent with the IPU model)./dumpData/NCHW(each layer's output generates a separate file, 4D tensor layout format is NCHW, consistent with the original model layout) - If you need to analyze data using
dump_debug.pyscript, be sure to use True.
-n,--preprocess: Preprocessing method; please directly specify the path to the preprocessing Python file. Use the preprocessing file used when running the sim model.
② Optional parameter explanations:
--input_config: Path to the input_config.ini file. If the model has input_layouts=NCHW, you can add configurations in input_config.ini to align the data layout with -n, --preprocess within onnx_dump_data.py.
Usage
- If the model is multi-input, the
-n,--preprocessparameter can require multiple preprocessing methods, e.g., -n preprocess1.py,preprocess2.py or --preprocess preprocess1.py,preprocess2.py. - If the model is multi-input, the
-i/--imageparameter should be provided in the form of a specified image path list file.
2.3 How to Dump Inference Data from Float.sim and Fixed.sim Models¶
Before performing a layer-by-layer dump of floating-point and fixed-point models, first copy the file SGS_IPU_Toolchain/cfg/DebugConfig.txt to the execution directory, and enable the following switches. Then use SGS_IPU_Toolchain/Scripts/calibrator/simulator.py to simulate both the floating-point and fixed-point models. This will generate the sigma_outtensor_dump.bin file in the specified directory.
- DebugConfig.txt
dumpTensor # Master switch to dump data for each layer of the network model (must be enabled). (Default is off)
eliminateGarbage # Enable removal of useless data when dumping network model data.
dequantFixed # For fixed-point network models, convert integer data to floating-point data (must be enabled). (Default is off)
#dumpasstring # Dump network model data as strings; if turned off, the type will be binary files. (If needing to use auto_dump_debug.sh script for data analysis, this option must be turned off).
#disableDomainFuseOps # Disable operator fusion during conversion of fixed-point network models (suggest to turn off).
path= # Specify the full output path for generated files (path= must be followed by an absolute path like **/home/user**. If there is no content after path= or if path= is completely omitted, the output will default to the **$HOME** location. Path length should not exceed 122 bytes.)
Usage
- After the dump is completed, the results will be stored in the
sigma_outtensor_dump.binfile. If you need to rename it, do not change the file extension .bin. - A new dump will overwrite the existing
sigma_outtensor_dump.binfile; please be careful to save it if running again. - Explanation of the
disableDomainFuseOpsoption in DebugConfig.txt:- It is effective during the conversion of fixed-point network models and should ideally be turned off.
- By default, this option is turned off, which means that during the conversion of the floating-point network model to the fixed-point network model, operator fusion will be performed. If this option is enabled, the fusion functionality will be disabled.
- When this option is off, the fixed-point network model and offline network model can optimize the operators during conversion, speeding up model execution, but it may affect the layer structure of the network, causing some operator outputs not to be dumped into
sigma_outtensor_dump.bin. - If the data for each layer of the network model is required, you can turn on the
disableDomainFuseOpsoption and rerun the calibrator to convert the fixed-point network model, ensuring the output for each layer's data without fusion optimizations.
- Offline models do not support Dump Debug, as the layer structure of the offline model has already been fused, preventing data from being dumped for each layer of the network model.
2.3.1 Dump Inference Data from Float.sim Model¶
Using the SGS_IPU_Toolchain/Scripts/calibrator/simulator.py tool to simulate the floating-point model will create the sigma_outtensor_dump.bin file in the specified directory, while the simulation inference results are saved in the ./log/output folder of the execution directory.
Usage example:
python3 ~/SGS_IPU_Toolchain/Scripts/calibrator/simulator.py \
-m ./mobilenet_v1_float.sim \
-i ./000775.jpg \
-n ./pre.py \
--soc_version CHIP
2.3.2 Dump Inference Data from Fixed.sim Model¶
Using the SGS_IPU_Toolchain/Scripts/calibrator/simulator.py tool to simulate the fixed-point model will create the sigma_outtensor_dump.bin file in the specified directory, while the simulation inference results are saved in the ./log/output folder of the execution directory.
Usage example:
python3 ~/SGS_IPU_Toolchain/Scripts/calibrator/simulator.py \
-m ./mobilenet_v1_fixed.sim \
-i ./000775.jpg \
-n ./pre.py \
--soc_version CHIP
Usage
- Remember to rename the generated
sigma_outtensor_dump.binfile and thelog/outputfiles if they have the same name after simulation to avoid overwriting. - Please promptly remove the
DebugConfig.txtfile from the execution directory if not performing dump data operations, to avoid affecting model conversion operations.
3 Using auto_dump_debug.sh Script to Analyze Data¶
3.1 Accuracy Issues Between Original Framework Model and Float.sim Model¶
If the inference results from the original framework model are inconsistent with those of the Float.sim model, you can use the SGS_IPU_Toolchain/DumpDebug/auto_dump_debug.sh tool to compare the dumped bin files layer by layer. By comparing the COS, MSE, and RMSE of the same output tensor layer between the sample bin and benchmark bin, you can identify which layer's operator results are incorrect, leading to inaccurate model outputs.
Run the SGS_IPU_Toolchain/DumpDebug/auto_dump_debug.sh script to check the erroneous layer.
Usage example:
./auto_dump_debug.sh \
/home/user/SGS_IPU_Toolchain \
/path/to/float_sim_sigma_outtensor_dump.bin \
/path/to/caffe_NHWC_outtensor_dump.bin
① Compare with Caffe original model:
./auto_dump_debug.sh \
/home/user/SGS_IPU_Toolchain \
/home/user/sigma_outtensor_dump.bin \
/home/user/caffe_NHWC_outtensor_dump.bin
② Compare with ONNX original model:
./auto_dump_debug.sh \
/home/user/SGS_IPU_Toolchain \
/home/user/sigma_outtensor_dump.bin \
/home/user/onnx_NHWC_outtensor_dump.bin
Related parameter explanations:
-
Param1: Path to SGS_IPU_Toolchain; if in the current directory, just pass the directory name. -
Param2: Path to the already dumped sample bin file that needs to be compared (this should be the bin file dumped from the IPU network model, either float or fixed). -
Param3: Path to the already dumped benchmark bin file that should be the original model (Caffe or Onnx) that has been dumped.
3.2 Accuracy Issues Between Float.sim and Fixed.sim Models¶
If there are significant errors between Float.sim and Fixed.sim, you can debug using the following workflow:
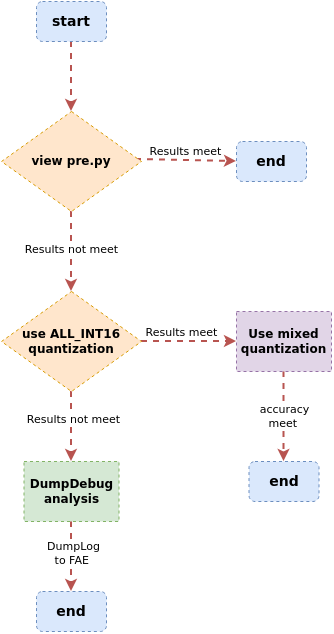
Use the SGS_IPU_Toolchain/DumpDebug/auto_dump_debug.sh tool to compare the inference of the Float.sim model with that of the Fixed.sim model by dumping their bin files. You can determine which layer's operator has a large precision loss by comparing the COS, MSE, and RMSE of the same output tensor layer between the sample bin and benchmark bin.
Usage example:
./auto_dump_debug.sh \
/home/user/SGS_IPU_Toolchain \
/home/user/sample.bin \
/home/user/benchmark.bin
Related parameter explanations:
-
Param1: Path to SGS_IPU_Toolchain; if in the current directory, just pass the directory name. -
Param2: Path to the already dumped sample bin file that needs to be compared (this should be the bin file dumped from the fixed-point network model). -
Param3: Path to the already dumped benchmark bin file that should be the bin file dumped from the floating-point network model.
Usage
- The comparison results from the
auto_dump_debug.shscript will be influenced by thedisableDomainFuseOpsoption inDebugConfig.txt.
① When the disableDomainFuseOps option is not enabled, the analysis results will display as follows (partial output):
0) data MSE: 0.028521 COS: 0.990174 RMSE: 0.191048
1) conv1/bn_xx_xx MSE: 0.000060 COS: 0.999969 RMSE: 0.007786
2) conv2_1/expand/bn_xx_xx MSE: 0.000133 COS: 0.999922 RMSE: 0.010600
3) conv2_1/dwise/bn_xx_xx MSE: 0.001055 COS: 0.999604 RMSE: 0.026628
4) conv2_1/linear/bn_xx MSE: 0.008872 COS: 0.997960 RMSE: 0.077780
5) conv2_2/expand/bn_xx_xx MSE: 0.000849 COS: 0.999145 RMSE: 0.034236
6) conv2_2/dwise/bn_xx_xx MSE: 0.002526 COS: 0.998491 RMSE: 0.054812
7) conv2_2/linear/bn_xx MSE: 0.016800 COS: 0.995695 RMSE: 0.100490
8) conv3_1/expand/bn_xx_xx MSE: 0.000814 COS: 0.997401 RMSE: 0.067148
9) conv3_1/dwise/bn_xx_xx MSE: 0.003532 COS: 0.993593 RMSE: 0.096485
10) block_3_1 MSE: 0.054808 COS: 0.992504 RMSE: 0.127393
11) conv3_2/expand/bn_xx_xx MSE: 0.002223 COS: 0.995493 RMSE: 0.076465
12) conv3_2/dwise/bn_xx_xx MSE: 0.003252 COS: 0.997917 RMSE: 0.058834
13) conv3_2/linear/bn_xx MSE: 0.030526 COS: 0.995008 RMSE: 0.099188
14) conv4_1/expand/bn_xx_xx MSE: 0.000484 COS: 0.998078 RMSE: 0.053329
15) conv4_1/dwise/bn_xx_xx MSE: 0.001138 COS: 0.995249 RMSE: 0.085869
16) block_4_1 MSE: 0.041154 COS: 0.993904 RMSE: 0.108148
17) conv4_2/expand/bn_xx_xx MSE: 0.000628 COS: 0.997298 RMSE: 0.064804
18) conv4_2/dwise/bn_xx_xx MSE: 0.001379 COS: 0.994016 RMSE: 0.094983
19) block_4_2 MSE: 0.047413 COS: 0.992955 RMSE: 0.115523
20) conv4_3/expand/bn_xx_xx MSE: 0.001276 COS: 0.997816 RMSE: 0.054641
21) conv4_3/dwise/bn_xx_xx MSE: 0.004304 COS: 0.996268 RMSE: 0.078860
22) conv4_3/linear/bn_xx MSE: 0.019364 COS: 0.992479 RMSE: 0.122014
23) conv4_4/expand/bn_xx_xx MSE: 0.000678 COS: 0.996980 RMSE: 0.070730
24) conv4_4/dwise/bn_xx_xx MSE: 0.001787 COS: 0.993290 RMSE: 0.109461
25) block_4_4 MSE: 0.031072 COS: 0.992266 RMSE: 0.123066
26) conv4_5/expand/bn_xx_xx MSE: 0.000657 COS: 0.995815 RMSE: 0.085172
27) conv4_5/dwise/bn_xx_xx MSE: 0.001807 COS: 0.993433 RMSE: 0.106439
28) block_4_5 MSE: 0.043631 COS: 0.991963 RMSE: 0.125202
29) conv4_6/expand/bn_xx_xx MSE: 0.000639 COS: 0.995696 RMSE: 0.087078
30) conv4_6/dwise/bn_xx_xx MSE: 0.001854 COS: 0.994223 RMSE: 0.098243
31) block_4_6 MSE: 0.061734 COS: 0.991830 RMSE: 0.125977
32) conv4_7/expand/bn_xx_xx MSE: 0.001029 COS: 0.994616 RMSE: 0.095454
33) conv4_7/dwise/bn_xx_xx MSE: 0.003071 COS: 0.996565 RMSE: 0.072931
34) conv4_7/linear/bn_xx MSE: 0.014118 COS: 0.992815 RMSE: 0.117115
35) conv5_1/expand/bn_xx_xx MSE: 0.000649 COS: 0.997619 RMSE: 0.061338
36) conv5_1/dwise/bn_xx_xx MSE: 0.001037 COS: 0.995496 RMSE: 0.087281
37) block_5_1 MSE: 0.022231 COS: 0.993252 RMSE: 0.114678
38) conv5_2/expand/bn_xx_xx MSE: 0.000522 COS: 0.996605 RMSE: 0.078887
39) conv5_2/dwise/bn_xx_xx MSE: 0.001216 COS: 0.995946 RMSE: 0.079409
40) block_5_2 MSE: 0.031804 COS: 0.993276 RMSE: 0.115544
41) conv5_3/expand/bn_xx_xx MSE: 0.000592 COS: 0.995792 RMSE: 0.085456
42) conv5_3/dwise/bn_xx_xx MSE: 0.001892 COS: 0.997871 RMSE: 0.053695
43) conv5_3/linear/bn_xx MSE: 0.008352 COS: 0.994394 RMSE: 0.104836
44) conv6_1/expand/bn_xx_xx MSE: 0.000359 COS: 0.997728 RMSE: 0.062928
45) conv6_1/dwise/bn_xx_xx MSE: 0.000522 COS: 0.996774 RMSE: 0.072542
46) block_6_1 MSE: 0.012969 COS: 0.995122 RMSE: 0.098212
47) conv6_2/expand/bn_xx_xx MSE: 0.000311 COS: 0.997588 RMSE: 0.068856
48) conv6_2/dwise/bn_xx_xx MSE: 0.000694 COS: 0.996954 RMSE: 0.066177
49) block_6_2 MSE: 0.018713 COS: 0.994592 RMSE: 0.103677
50) conv6_3/expand/bn_xx_xx MSE: 0.000360 COS: 0.995374 RMSE: 0.095421
51) conv6_3/dwise/bn_xx_xx MSE: 0.001144 COS: 0.998021 RMSE: 0.047618
52) conv6_3/linear/bn_xx MSE: 0.005441 COS: 0.991614 RMSE: 0.128396
53) conv6_4/bn_xx_xx MSE: 0.022556 COS: 0.991828 RMSE: 0.135669
54) pool6 MSE: 0.004184 COS: 0.995849 RMSE: 0.094941
55) fc7 MSE: 0.081746 COS: 0.995249 RMSE: 0.104243
56) prob MSE: 0.000000 COS: 1.000000 RMSE: 0.000914
② When the disableDomainFuseOps option is enabled, the analysis results will display as follows (partial output):
0) data MSE: 0.028521 COS: 0.990174 RMSE: 0.191048
1) conv1/bn_xx_xx MSE: 0.000060 COS: 0.999969 RMSE: 0.007786
2) conv2_1/expand/bn_xx_xx MSE: 0.000133 COS: 0.999922 RMSE: 0.010600
3) conv2_1/dwise/bn_xx_xx MSE: 0.001055 COS: 0.999604 RMSE: 0.026628
4) conv2_1/linear/bn_xx MSE: 0.008872 COS: 0.997960 RMSE: 0.077780
5) conv2_2/expand/bn_xx_xx MSE: 0.000849 COS: 0.999145 RMSE: 0.034236
6) conv2_2/dwise/bn_xx_xx MSE: 0.002526 COS: 0.998491 RMSE: 0.054812
7) conv2_2/linear/bn_xx MSE: 0.016800 COS: 0.995695 RMSE: 0.100490
8) conv3_1/expand/bn_xx_xx MSE: 0.000814 COS: 0.997401 RMSE: 0.067148
9) conv3_1/dwise/bn_xx_xx MSE: 0.003532 COS: 0.993593 RMSE: 0.096485
10) conv3_1/linear/bn_xx MSE: 0.026856 COS: 0.987982 RMSE: 0.156977
11) block_3_1 MSE: 0.054808 COS: 0.992504 RMSE: 0.127393
12) conv3_2/expand/bn_xx_xx MSE: 0.002223 COS: 0.995493 RMSE: 0.076465
13) conv3_2/dwise/bn_xx_xx MSE: 0.003252 COS: 0.997917 RMSE: 0.058834
14) conv3_2/linear/bn_xx MSE: 0.030526 COS: 0.995008 RMSE: 0.099188
15) conv4_1/expand/bn_xx_xx MSE: 0.000484 COS: 0.998078 RMSE: 0.053329
16) conv4_1/dwise/bn_xx_xx MSE: 0.001138 COS: 0.995249 RMSE: 0.085869
17) conv4_1/linear/bn_xx MSE: 0.008352 COS: 0.991382 RMSE: 0.126459
18) block_4_1 MSE: 0.041154 COS: 0.993904 RMSE: 0.108148
19) conv4_2/expand/bn_xx_xx MSE: 0.000628 COS: 0.997298 RMSE: 0.064804
20) conv4_2/dwise/bn_xx_xx MSE: 0.001379 COS: 0.994016 RMSE: 0.094983
21) conv4_2/linear/bn_xx MSE: 0.005679 COS: 0.990344 RMSE: 0.133938
22) block_4_2 MSE: 0.047413 COS: 0.992955 RMSE: 0.115523
23) conv4_3/expand/bn_xx_xx MSE: 0.001276 COS: 0.997816 RMSE: 0.054641
24) conv4_3/dwise/bn_xx_xx MSE: 0.004304 COS: 0.996268 RMSE: 0.078860
25) conv4_3/linear/bn_xx MSE: 0.019364 COS: 0.992479 RMSE: 0.122014
26) conv4_4/expand/bn_xx_xx MSE: 0.000678 COS: 0.996980 RMSE: 0.070730
27) conv4_4/dwise/bn_xx_xx MSE: 0.001787 COS: 0.993290 RMSE: 0.109461
28) conv4_4/linear/bn_xx MSE: 0.009286 COS: 0.991433 RMSE: 0.132465
29) block_4_4 MSE: 0.031072 COS: 0.992266 RMSE: 0.123066
30) conv4_5/expand/bn_xx_xx MSE: 0.000657 COS: 0.995815 RMSE: 0.085172
31) conv4_5/dwise/bn_xx_xx MSE: 0.001807 COS: 0.993433 RMSE: 0.106439
32) conv4_5/linear/bn_xx MSE: 0.011957 COS: 0.989749 RMSE: 0.144398
33) block_4_5 MSE: 0.043631 COS: 0.991963 RMSE: 0.125202
34) conv4_6/expand/bn_xx_xx MSE: 0.000639 COS: 0.995696 RMSE: 0.087078
35) conv4_6/dwise/bn_xx_xx MSE: 0.001854 COS: 0.994223 RMSE: 0.098243
36) conv4_6/linear/bn_xx MSE: 0.018842 COS: 0.989861 RMSE: 0.140551
37) block_4_6 MSE: 0.061734 COS: 0.991830 RMSE: 0.125977
38) conv4_7/expand/bn_xx_xx MSE: 0.001029 COS: 0.994616 RMSE: 0.095454
39) conv4_7/dwise/bn_xx_xx MSE: 0.003071 COS: 0.996565 RMSE: 0.072931
40) conv4_7/linear/bn_xx MSE: 0.014118 COS: 0.992815 RMSE: 0.117115
41) conv5_1/expand/bn_xx_xx MSE: 0.000649 COS: 0.997619 RMSE: 0.061338
42) conv5_1/dwise/bn_xx_xx MSE: 0.001037 COS: 0.995496 RMSE: 0.087281
43) conv5_1/linear/bn_xx MSE: 0.008186 COS: 0.992600 RMSE: 0.123085
44) block_5_1 MSE: 0.022231 COS: 0.993252 RMSE: 0.114678
45) conv5_2/expand/bn_xx_xx MSE: 0.000522 COS: 0.996605 RMSE: 0.078887
46) conv5_2/dwise/bn_xx_xx MSE: 0.001216 COS: 0.995946 RMSE: 0.079409
47) conv5_2/linear/bn_xx MSE: 0.010952 COS: 0.992991 RMSE: 0.118647
48) block_5_2 MSE: 0.031804 COS: 0.993276 RMSE: 0.115544
49) conv5_3/expand/bn_xx_xx MSE: 0.000592 COS: 0.995792 RMSE: 0.085456
50) conv5_3/dwise/bn_xx_xx MSE: 0.001892 COS: 0.997871 RMSE: 0.053695
51) conv5_3/linear/bn_xx MSE: 0.008352 COS: 0.994394 RMSE: 0.104836
52) conv6_1/expand/bn_xx_xx MSE: 0.000359 COS: 0.997728 RMSE: 0.062928
53) conv6_1/dwise/bn_xx_xx MSE: 0.000522 COS: 0.996774 RMSE: 0.072542
54) conv6_1/linear/bn_xx MSE: 0.004180 COS: 0.995212 RMSE: 0.099410
55) block_6_1 MSE: 0.012969 COS: 0.995122 RMSE: 0.098212
56) conv6_2/expand/bn_xx_xx MSE: 0.000311 COS: 0.997588 RMSE: 0.068856
57) conv6_2/dwise/bn_xx_xx MSE: 0.000694 COS: 0.996954 RMSE: 0.066177
58) conv6_2/linear/bn_xx MSE: 0.006447 COS: 0.995696 RMSE: 0.095621
59) block_6_2 MSE: 0.018713 COS: 0.994592 RMSE: 0.103677
60) conv6_3/expand/bn_xx_xx MSE: 0.000360 COS: 0.995374 RMSE: 0.095421
61) conv6_3/dwise/bn_xx_xx MSE: 0.001144 COS: 0.998021 RMSE: 0.047618
62) conv6_3/linear/bn_xx MSE: 0.005441 COS: 0.991614 RMSE: 0.128396
63) conv6_4/bn_xx_xx MSE: 0.022556 COS: 0.991828 RMSE: 0.135669
64) pool6 MSE: 0.004184 COS: 0.995849 RMSE: 0.094941
65) fc7 MSE: 0.081746 COS: 0.995249 RMSE: 0.104243
66) prob MSE: 0.000000 COS: 1.000000 RMSE: 0.000914
Undefined_xxx.bin_DumpDebug_out folder in the running path (where xxx.bin is the name of the bin file).Inside this folder, there are numbered folders starting from 0, with the numbering matching the numbers printed before the corresponding tensor names in the metrics.
The detailed data is arranged in rows of 16 values each. If you need a format that displays one value per line, set the environment variable before running ./auto_dump_debug.sh:
export SAVE_ONE_ROW=1
3.2.1 Check Preprocessing¶
1)Image Input to the Model
In the definition of the image_preprocess function within the preprocessing Python file, two parameters are required:
- Image path
- Normalization flag (norm=True)
The normalization flag is used to determine whether image normalization needs to be applied. When running the Float.sim model, the normalized image must be provided, and True should be passed for the norm parameter during the image_preprocess call. Therefore, the normalization action should occur under the condition where norm is True. When running the Fixed.sim and Offline models, the UINT8-sized image corresponding to the model input size is required, and normalization is not necessary. Thus, it is important to check whether the normalization flag has been correctly used and properly processed before inputting the image to the model. Additionally, the mean and std values configured in input_config.ini and the preprocessing Python file must remain consistent.
2)Non-Image Input Models
Please refer to Preprocessing File Writing Instructions to ensure that the preprocessing Python file implements and outputs numpy.ndarray type data that corresponds to the model input size.
3.2.2 View Results Using ALL_INT16 Quantization¶
Add the following content to input_config.ini:
[CONV_CONFIG]
input_format=ALL_INT16;
It is necessary to regenerate Float.sim from the original model for this change to take effect.
3.2.3 Analyze Using DumpDebug Tool¶
Compare the precision of each layer's results between Float.sim and Fixed.sim, outputting MSE, COS, and RMSE information for each tensor as references.
Since the Fixed.sim model will have operator fusion, some tensors may not be able to output dump data. You can enable the disableDomainFuseOps option in DebugConfig.txt, regenerate the Fixed.sim model, dump the data again, and then use dump_debug.py for comparison to obtain more detailed comparison information.
3.2.4 Use Training Quantization Tool to Improve Accuracy¶
SGS_IPU_Toolchain/Scripts/calibrator/torch_calibrator.py
This script provides two levels of quantization; it is recommended to use the Q2 quantization level for better accuracy, though it requires additional GPU setup, or the training time may be extended. After training, the optimal quantization parameters will be automatically selected to generate the Fixed.sim model.
3.2.5 Can You Clearly Identify the Layer Where Precision Loss Occurs?¶
By using the MSE, COS, and RMSE information obtained from the DumpDebug tool, past experience shows that when COS < 0.99 or RMSE > 0.1, the precision of that layer may not meet requirements.
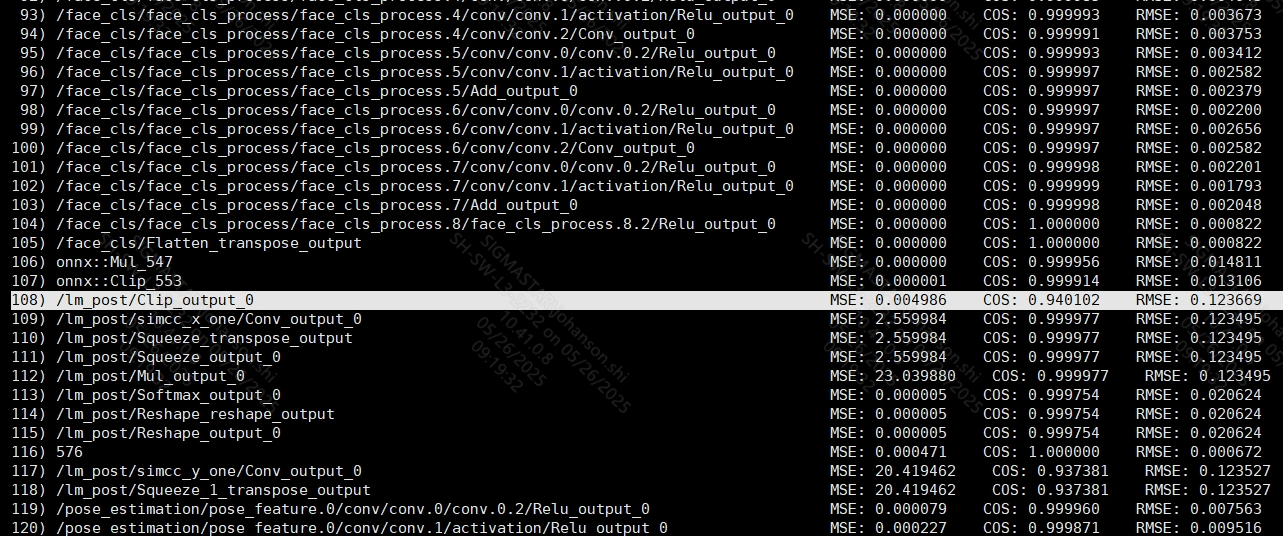
As shown in the image above, if the information obtained from the DumpDebug tool indicates that these three metrics fluctuate, such as COS oscillating between 0.99 and 0.98 and RMSE fluctuating between 0.01 and 0.1, you may proceed to compare again after using the training quantization tool. If it becomes clear that there is a significant change in MSE, COS, and RMSE metrics starting from a certain layer or layers, it indicates that the issues originate from that particular layer. If these three metrics do not show abrupt changes, for example, if COS gradually decreases from 0.99 or RMSE gradually increases from 0.1, you can identify the first layer where the aforementioned two metrics exceed their empirical thresholds as a target for further investigation.
3.2.6 Can It Be Resolved by Manually Modifying Parameters?¶
The main purpose of manually modifying parameters is to adjust poorly-performing tensors to use INT16 quantization to see if the accuracy can be improved. When a suspicious tensor is identified, the first step is to use the Netron tool provided in the SGS_IPU_Toolchain to open both the Float.sim and Fixed.sim models simultaneously and locate the problematic operator.
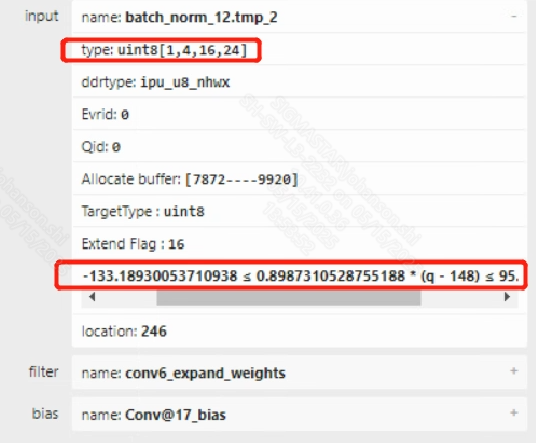
In the Fixed.sim model, you can click on the corresponding operator and check the input and output tensor’s quantization information in the pop-up window on the right. As shown in the image above, if you notice that the min/max range of the tensor exceeds 20 and the tensor is still UINT8 quantized, you can modify input_config.ini to upgrade the convolution layer to INT16 quantization.
Since in input_config.ini, only the input tensor of the convolution can be configured to INT16 quantization, if the operator is not a convolution, you can configure a few preceding and following convolution layers to INT16 and observe if the accuracy improves.
3.2.7 Provide Relevant Analysis Data¶
If you can provide the original model or the Float.sim and Fixed.sim models, it will help reproduce the issue quickly. If the model cannot be provided, dump the data from Float.sim and Fixed.sim, and use the following script to dump the quantization information of the Fixed.sim model:
python3 SGS_IPU_Toolchain/Scripts/examples/save_quant_param.py \
-m mobilenet_v1_fixed.sim
This will generate the mobilenet_v1_fixed.sim.json file in the directory where mobilenet_v1_fixed.sim is located.
Usage
- Provide the accuracy comparison results for each layer.
- If you can locate the operator causing the precision loss, provide the input and output data for the floating-point version of that operator, as well as the input and output data for its fixed-point version.
- If you cannot identify the operator causing the precision loss, give the first step comparison data to the FAE team for assistance in determining the exact data that needs to be provided.
4. Board Accuracy Issues¶
When the results on the board do not match the offline simulation results on the PC, first ensure that the simulation results of the fixed model on the PC match those of the offline model. If they are consistent, you can proceed with the following methods to identify the reasons for the discrepancies between the board model results and the PC simulation offline model results.
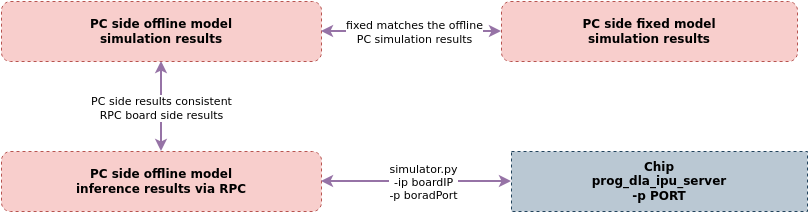
4.1 Use Simulator Method to Validate Consistency Between Fixed Model and Offline Model Results¶
On the PC, use SGS_IPU_Toolchain/Scripts/calibrator/simulator.py to run both the Fixed model and Offline model, and compare their output results for consistency.
Example of running the Fixed model:
python3 SGS_IPU_Toolchain/Scripts/calibrator/simulator.py \
-i 000775.jpg \
-m mobilenet_v1_fixed.sim \
-n mobilenet_v1_preprocess.py \
--soc_version CHIP
Usage
- Any errors during execution will be logged in the
./log/output/directory. Remember to rename the log directory (e.g., log_fixed) to avoid overwriting.
Example of running the Offline model:
python3 SGS_IPU_Toolchain/Scripts/calibrator/simulator.py \
-i 000775.jpg \
-m mobilenet_v1_fixed.sim_sgsimg.img \
-n mobilenet_v1_preprocess.py \
--soc_version CHIP
Usage
- Any errors during execution will be logged in the
./log/output/directory. Remember to rename the log directory (e.g., log_offline) to avoid overwriting.
If the results from the Fixed model are consistent with those from the Offline model, proceed to identify the reasons for the discrepancies in the board model results compared to the PC simulation Offline model results.
4.2 Use Simulator Method to Validate Consistency Between Offline Model Board Results and PC Results¶
On the PC, use the SGS_IPU_Toolchain/Scripts/calibrator/simulator.py tool to invoke the offline model running on the board via RPC protocol. This will write the inference results from the board back to the PC’s output directory, making it easier for customers to compare the board's inference results with the PC's reference results, eliminating inconsistencies due to preprocessing and other factors, and allowing customers to quickly locate the issue.
The Linux SDK-alkaid provides the app located at sdk/verify/release_feature/source/dla/ipu_server.
Run the prog_dla_ipu_server application on the board to enable the RPC service. The SGS_IPU_Toolchain/Scripts/calibrator/simulator.py on the PC will then access the board application via IP address and port number, dispatching the PC model to run the inference on the board and returning the results to the PC.
Example of starting the RPC service on the board:
./prog_dla_ipu_server -p PORT
Run the inference instance on the board through the RPC service from the PC:
python3 SGS_IPU_Toolchain/Scripts/calibrator/simulator.py \
-i 000775.jpg \
-m mobilenet_v1_fixed.sim_sgsimg.img \
-n mobilenet_v1_preprocess.py \
--host <board_ip_address> \
--port PORT \
--soc_version CHIP
Usage
Relevant parameter explanations:
- --host HOST IPU Server host.
- --port PORT IPU Server port.
- --timeout TIMEOUT Set timeout seconds, default is 60s.
- --model_onboard_path MODEL_ONBOARD_PATH Model on board path.
After execution, compare the inference results from the PC simulation with the inference results from the board via the RPC service to see if they match. If the results do not match, you can contact the corresponding FAE for support. If the results do match, you should check the board demo to locate the bug causing the incorrect inference results on the board.
5. Summary of Common Errors in Model Conversion¶
This section systematically organizes typical error scenarios that may occur throughout the model conversion process, covering key links such as the parsing of the original model format, intermediate representation conversion, and adaptation to the target platform. Through structured classification and root cause analysis, it helps developers quickly locate issues and formulate solutions.
5.1 Root Cause Analysis During Floating-Point Model Conversion¶
| Floating-Point Model Conversion | Error Phenomenon | Cause Analysis |
|---|---|---|
| “`input_formats` is BGR only support `training_input_formats` is BGR!” | When executing the ConvertTool command, there is a mismatch between the training_input_formats and input_formats settings in the ini configuration file. | |
| “KeyError: 'output1'” | When executing the ConvertTool command, there is a discrepancy between the inputs/outputs in the ini configuration file and the model to be converted. | |
| “configparser.MissingSectionHeaderError: File contains no section headers.” | There is a syntax error in the ini configuration file when executing the ConvertTool command. | |
| “Loopback in graph is not supported!” | The model file contains a cyclic graph error when executing the ConvertTool command. | |
| “Nodes in a graph must be topologically sorted; however, input 'Transpose_7_o0_rewrite' of node:name: Conv13 OpType: Conv is not output of any previous nodes.” | There is an error in the order of operator execution in the original model file when executing the ConvertTool command. | |
| “Please export the ONNX with opset_version <= 20” | The opset version of the ONNX model is too high when executing the ConvertTool command, exceeding the currently supported version limit. | |
| “ONNX PAD axis should not be given as input” | The axis parameter of the ONNX PAD operator does not support tensor format. | |
| “ONNX MVN input is expected to have four dimensions” | The ONNX MVN operator only supports 4-dimensional input. | |
| “ONNX EXPAND shape input only supports const tensor” | The ONNX EXPAND operator only supports const type shape information. | |
| “RNN only supports sequence_lens empty tensor” | Parameter support limitations of the ONNX RNN operator. | |
| “ONNX RNN does not support clip” | Parameter support limitations of the ONNX RNN operator. | |
| “Do not support activation_beta” | Parameter support limitations of the ONNX RNN operator. | |
| “activation_alpha only supports 0.01” | Parameter support limitations of the ONNX RNN operator. | |
| “ONNX RNN does not support direction reverse” | Parameter support limitations of the ONNX RNN operator. | |
| “ONNX RNN activation only supports [Sigmoid tanh tanh]” | Parameter support limitations of the ONNX RNN operator. | |
“ONNX Pad only supports constant and reflect mode” |
Parameter support limitations of the ONNX PAD operator. | |
| “ONNX MOD only supports fmod 0” | Parameter support limitations of the ONNX MOD operator. | |
| “LSTM does not support sequence_lens variable tensor” | Parameter support limitations of the ONNX LSTM operator. | |
| “ONNX LSTM does not support clip” | Parameter support limitations of the ONNX LSTM operator. | |
| “Do not support activation_beta” | Parameter support limitations of the ONNX LSTM operator. | |
| “activation_alpha only supports 0.01” | Parameter support limitations of the ONNX LSTM operator. | |
| “ONNX LSTM layout only supports 0” | Parameter support limitations of the ONNX LSTM operator. | |
| “ONNX LSTM input_forget only supports 0” | Parameter support limitations of the ONNX LSTM operator. | |
| “ONNX LSTM does not support direction reverse” | Parameter support limitations of the ONNX LSTM operator. | |
| “ONNX LSTM activation only supports [Sigmoid tanh tanh]” | Parameter support limitations of the ONNX LSTM operator. | |
| “ONNX LayerNormalization does not support stash_type is 0” | Parameter support limitations of the ONNX LayerNormalization operator. | |
| “ONNX LayerNormalization does not support axis is 0” | Parameter support limitations of the ONNX LayerNormalization operator. | |
| “GRU does not support sequence_lens variable tensor” | Parameter support limitations of the ONNX GRU operator. | |
| “ONNX GRU layout only supports 0” | Parameter support limitations of the ONNX GRU operator. | |
| “ONNX GRU only supports forward and bidirectional” | Parameter support limitations of the ONNX GRU operator. | |
| “ONNX GRU does not support clip” | Parameter support limitations of the ONNX GRU operator. | |
| “gru activation only supports Sigmoid and tanh” | Parameter support limitations of the ONNX GRU operator. | |
| “ONNX GRU does not support activation_alpha” | Parameter support limitations of the ONNX GRU operator. | |
| “Not supported yet!” | The operator is not supported. | |
| “Exception: ONNX Upsample only supports height and width resize:” | Detected that a model's operator specification exceeds the capabilities of the target chip; refer to error messages for details. | |
| “Exception: ONNX TOPK SGS only supports the top-K sorted elements along a specified axis:/TopK” | Detected that a model's operator specification exceeds the capabilities of the target chip; refer to error messages for details. | |
| “Exception: ONNX TOPK SGS only supports the top-K largest elements along a specified axis:/TopK” | Detected that a model's operator specification exceeds the capabilities of the target chip; refer to error messages for details. | |
| “Exception: ONNX Sum only supports 2 inputs:” | Detected that a model's operator specification exceeds the capabilities of the target chip; refer to error messages for details. | |
| “ValueError: Split_V outputs number exceeds the limit.” | Detected that a model's operator specification exceeds the capabilities of the target chip; refer to error messages for details. | |
| “sub0 has wrong dynamic shape that cannot be figured out! please check if source shape is graph input” | Detected that there are errors in operator attributes in the model file that prevent the output tensor from being calculated. | |
| “Exception: ONNX ScatterND reduction attrs didn't support 1 attribute yet!” | Parameter support limitations of the ONNX ScatterND operator. | |
| “Exception: ONNX ScatterElements include unsupported reduction type:/ScatterElements” | Parameter support limitations of the ONNX ScatterElements operator. | |
| “Exception: ONNX RESIZE only supports 'nearest_mode': round_prefer_floor/floor/round_prefer_ceil:” | Parameter support limitations of the ONNX RESIZE operator. | |
| “Exception: ONNX RESIZE only supports nearest or linear:” | Parameter support limitations of the ONNX RESIZE operator. | |
| “Exception: resize does not support keep_aspect_ratio_policy” | Parameter support limitations of the ONNX RESIZE operator. | |
| “Exception: ONNX RESIZE unsupported 'exclude_outside' non-zero value:” | Parameter support limitations of the ONNX RESIZE operator. | |
| “Exception: ONNX RESIZE only supports 'coordinate_transformation_mode': align_corners/asymmetric/half_pixel/pytorch_half_pixel:” | Parameter support limitations of the ONNX RESIZE operator. | |
| “Exception: resize antialias only supports 0” | Parameter support limitations of the ONNX RESIZE operator. | |
| “Exception: ONNX RESIZE scale tensor only supports height and width resize:” | Parameter support limitations of the ONNX RESIZE operator. | |
| “Exception: ONNX RESHAPE unsupported allowedzero set 1:” | Parameter support limitations of the ONNX RESHAPE operator. | |
| “DYNSHAPESYM sub lacks shape info, please check DYNAMIC_CONFIG in ini!” | Detected that there are errors in operator attributes in the model file that prevent the output tensor from being calculated. | |
| “Exception: do not support noop_with_empty_axes not 0:” | Parameter support limitations of the ONNX ReduceSum/ReduceMin/ReduceMax/ReduceMean/ReduceL2 operators. | |
| “Exception: not support ONNX op type OneHot yet” | Detected that there is an unsupported operator in the model file. | |
| “Exception: ONNX DepthToSpace c must be divisible by blocksize^2” | Parameter support limitations of the ONNX DepthToSpace operator. | |
| "Exception: ONNX CUMSUM reverse only supports 0:" | Parameter support limitations of the ONNX CUMSUM operator. | |
| "Exception: ONNX CUMSUM exclusive only supports 0:" | Parameter support limitations of the ONNX CUMSUM operator. | |
| "Exception: ONNX ConvTranspose3d filter node /convtranspose3d/ConvTranspose does not support kernel size 3 dilation 1 padding 4 4" | Parameter support limitations of the ONNX ConvTranspose operator. | |
| "Exception: ONNX ConvTranspose does not support attribute output_shape:" | Parameter support limitations of the ONNX ConvTranspose operator. | |
| "ValueError: Conv3d strideW strideH cannot be larger than 31!!!" | Parameter specification of ONNX ConvTranspose exceeds the capabilities of the target chip. | |
| "Exception: Not support group conv3d yet:/conv3d/Conv" | Parameter support limitations of the ONNX Conv operator. | |
| "Assertion `s32InputCount <= ((10000))' failed." | Parameter specification of ONNX CONCAT exceeds the capabilities of the target chip. | |
| "Exception: ONNX BatchNormalization does not support training_mode not 0:" | Parameter support limitations of the ONNX BatchNormalization operator. | |
| "BatchNormalization does not support spatial not 1:" | Parameter support limitations of the ONNX BatchNormalization operator. | |
| "BatchNormalization does not support is_test not 0:" | Parameter support limitations of the ONNX BatchNormalization operator. | |
| "Exception: ONNX AveragePool node does not support kernel size 180 180 stride 300 300" | Parameter specification of ONNX AveragePool exceeds the capabilities of the target chip. | |
| "Exception: ONNX AveragePool does not support padding over 255" | Parameter specification of ONNX AveragePool exceeds the capabilities of the target chip. | |
| "Exception: ONNX AveragePool node does not support kernel size 300 300 stride 1 1" | Parameter specification of ONNX AveragePool exceeds the capabilities of the target chip. | |
| "Exception: ONNX AVGPOOL only supports dilation 1:" | Parameter specification of ONNX AveragePool exceeds the capabilities of the target chip. | |
| "Exception: ONNX ARGMAX select_last_index only supports 0:" | Parameter support limitations of the ONNX ArgMax operator. | |
| "Exception: ONNX ARGMIN select_last_index only supports 0:" | Parameter support limitations of the ONNX ArgMin operator. | |
| “ValueError: Not support soc_version: xxx” | xxx is not in the supported chip list. | |
| “Input graph file {} does not exist!” | The model file does not exist. | |
| “google.protobuf.message.DecodeError: Protobuf decoding consumed too few bytes: 1 out of 736” | When executing the ConvertTool command, the original model file does not match the configured model type. | |
| “`input_formats` is RGB only support `training_input_formats` is RGB!” | There is a mismatch between the training_input_formats and input_formats settings in the ini configuration file. | |
| “RuntimeError: The model doesn't have input named \"images1\"” | There is a discrepancy between the inputs/outputs in the ini configuration file and the model to be converted. | |
| “configparser.MissingSectionHeaderError: File contains no section headers.” | There is a syntax error in the ini configuration file. | |
| “sub 0, tensor [output] has dynamic shape that cannot be figured out!” | There is an unknown input preventing shape inference from completing. | |
| “Assert!!! Errors happened in At most one dimension of the new shape can be -1” | The reshape operator has multiple dimensions marked as -1. |
5.2 Root Cause Analysis During Fixed-Point Model Conversion¶
| Fixed-Point Model Conversion | Error Phenomenon | Cause Analysis |
|---|---|---|
| “FileNotFoundError: No images found in” | When executing the calibrator command, the file format in the txt does not match the training set, or the file does not exist, or there is an error in the txt file format. | |
| “void SGS_CheckPoolFilterSize(OperationType, SGS_S32, SGS_S32, SGS_S32, SGS_S32): Assertion `0' failed.” | The kernel parameter of MXAPOOL exceeds the capabilities of the target chip. | |
| “ERROR: no schedule info. weight name:/Constant_output_0” | Detected that Conv parameters exceed hardware specifications. | |
| “ValueError: Not support soc_version: xxx” | The soc_version xxx chip model is not in the supported chip list. | |
| “ValueError: Not recognized model.” | The model file format is incorrect when executing the calibrator command. |
5.3 Root Cause Analysis During Offline Model Conversion¶
| Offline Model Conversion | Error Phenomenon | Cause Analysis |
|---|---|---|
| “FileNotFoundError: No such model:” | The model file does not exist when executing the Compiler command. | |
| “ValueError: Not support soc_version: xxx” | The soc_version xxx is not in the supported chip list when executing the Compiler command. | |
| “ValueError: Not recognized model” | The model format is incorrect when executing the compiler command. |
5.4 Root Cause Analysis During Model Accuracy Debugging¶
| Accuracy Debugging Stage | Error Phenomenon | Cause Analysis |
|---|---|---|
| “Assert!!! Errors happened in Image Header output 0 ExtFlag check failed” | There is an output ExtFlag error in the offline file; please re-convert the model. | |
| “Assert!!! Errors happened in Image Header Input 0 ExtFlag check failed” | There is an input ExtFlag error in the offline file; please re-convert the model. | |
| “Assert!!! Errors happened in Image Header Input 0 Height alignment check failed” | There is a height alignment error in the offline file; please re-convert the model. | |
| “Assert!!! Errors happened in Image Header Input 0 Width alignment check failed” | There is a width alignment error in the offline file; please re-convert the model. | |
| “Assert!!! Errors happened in Image Header output 0 Aligned Buffer Size check failed” | There is an aligned buffer size error in the offline file; please re-convert the model. | |
| “Assert!!! Errors happened in Image Header Input 0 Aligned Buffer Size check failed” | There is an aligned buffer size error in the offline file; please re-convert the model. | |
| “Assert!!! Errors happened in Image Header output 0 Scalar check failed” | There is a scalar error in the offline file; please re-convert the model. | |
| “Assert!!! Errors happened in Image Header Input 0 Scalar check failed” | There is a scalar error in the offline file; please re-convert the model. | |
| “Assert!!! Errors happened in Image Header output 0 ZPoint check failed” | There is a ZPoint error in the offline file; please re-convert the model. | |
| “Assert!!! Errors happened in Image Header Input 0 ZPoint check failed” | There is a ZPoint error in the offline file; please re-convert the model. | |
| “Assert!!! Errors happened in Image Header output 0 Shape check failed” | There is a shape error in the offline file; please re-convert the model. | |
| “Assert!!! Errors happened in Image Header Input 0 Shape check failed” | There is a shape error in the offline file; please re-convert the model. | |
| “Assert!!! Errors happened in Image Header output 0 Element format check failed” | There is an element format error in the offline file; please re-convert the model. | |
| “Assert!!! Errors happened in Image Header Input 0 Element format check failed” | There is an element format error in the offline file; please re-convert the model. | |
| “Assert!!! Errors happened in Image Header output 0 dim check failed” | There is a tensor dimension error in the offline file; please re-convert the model. | |
| “Assert!!! Errors happened in Image Header Input 0 dim check failed” | There is an input dimension error in the offline file; please re-convert the model. | |
| “Assert!!! Errors happened in Image Header Batch mode check failed” | There is a batch mode error in the offline file; please re-convert the model. | |
| “FileNotFoundError:” | The model path is incorrect when executing the simulator command. | |
| “Not recognized model” | The model file format is incorrect when executing the simulator command. | |
| “ValueError: Got different num of preprocess_methods and images!” | There is a discrepancy between the number of preprocessing scripts and model inputs when executing the simulator command. | |
| “ValueError: Cannot set input tensor: Got tensor of type Unknown TensorType but expected type FLOAT32 for input 0, name: images ” | There is an output format error in the preprocessing file. | |
| “ValueError: Cannot set tensor: Dimension mismatch. Got 160 but expected 640 for dimension 1 of input 0, name: images” | There is a parameter error in the preprocessing file. | |
| “Assert!!! Errors happened in Image Header BufferSize1 Check Failed!” | There is a BufferSize1 error in the offline file. | |
| “Assert!!! Errors happened in Image Header BufferSize Check Failed!” | There is a BufferSize error in the offline file. | |
| “TypeError: the 'package' argument is required to perform a relative import for” | There is a type error in the preprocessing file when executing the simulator command. | |
| “im, ratio, (dw, dh) = letterbox(im) SyntaxError: invalid syntax” | There is a syntax error in the preprocessing file when executing the simulator command. | |
| “struct.error: unpack requires a buffer of 3136 bytes” | There is an error due to an incomplete bin file while debugging with the Analysis Tool. | |
| “ValueError: max() arg is an empty sequence” | The input file format of the auto_dump_debug.sh script is incorrect. | |
| “KeyError: '100'” | An error occurred during the execution of the auto_dump_debug.sh script, where 100 is the incorrect tensor name in sigma_outtensor_dump_fixed.bin and sigma_outtensor_dump_float.bin. | |
| “UnicodeDecodeError: 'utf-8' codec can't decode byte 0xff in position 0: invalid start byte” | The txt file format is incorrect when executing the simulator. | |
| “ValueError: Not support soc_version: xxx” | The soc_version xxx is not in the supported chip list when executing the simulator. | |
| “ValueError: Cannot set tensor: Dimension mismatch. Got 320 but expected 640 for dimension 1 of input 0, name: images” | There is a parameter error in the preprocessing file while executing the simulator. | |
| “def image_preprocess(image_file, norm=True)SyntaxError: invalid syntax” | There is a syntax error in the preprocessing file while executing the simulator. | |
| “Assert!!! Errors happened in Concat output shape is invalid!” | There is an operator shape error in the offline file. | |
| “Assert!!! Errors happened in Image Header Batch mode check failed” | There is a batch mode error in the offline file. | |
| “RuntimeError: MI_IPU_CreateCHNWithUserMem failed: 54" | There is a mismatch between the current chip model and the soc_version during model conversion when running the RPC simulator. |